Chapter 3: Acids & Bases
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
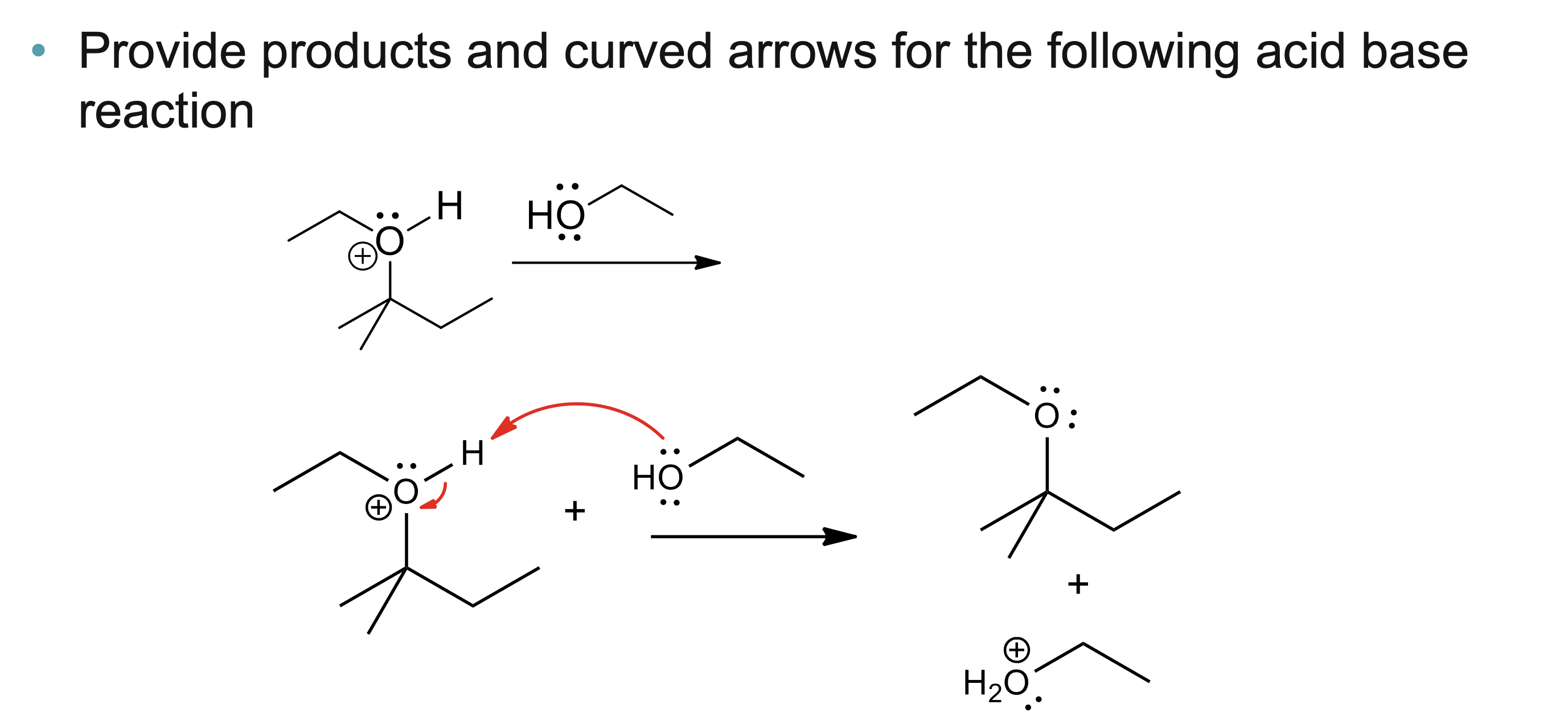
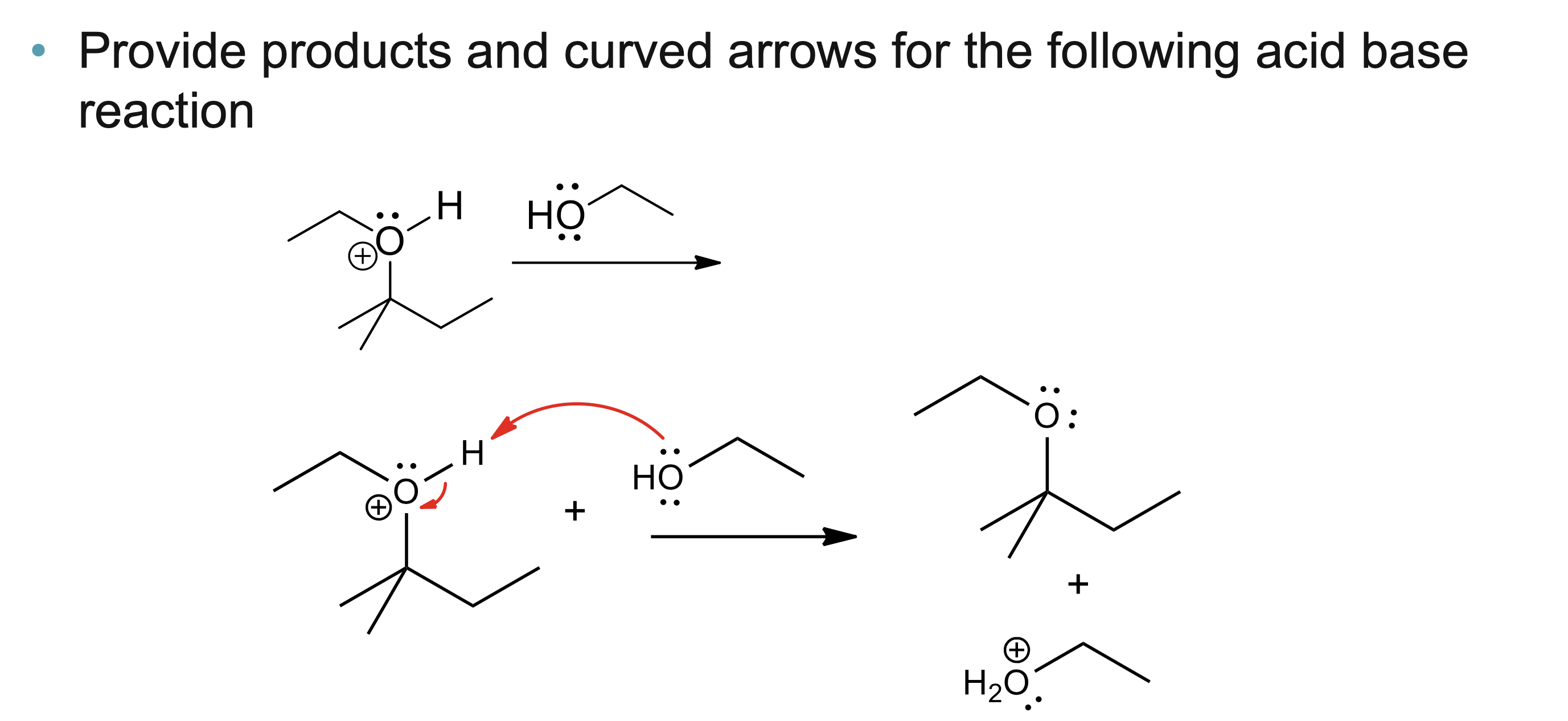
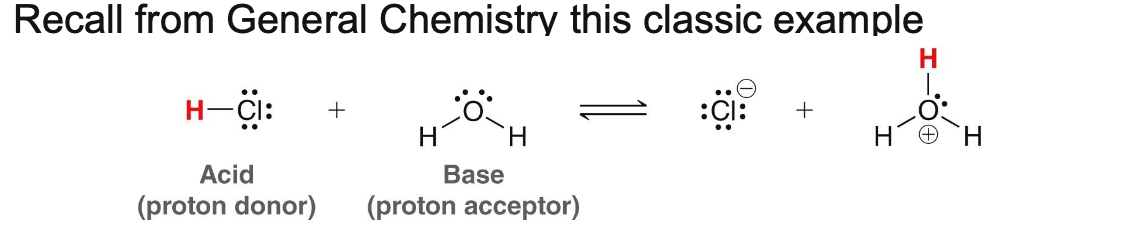
What is a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
A substance that donates a proton (H+)
What is a Bronsted-Lowry base?
A substance that accepts a proton
In a Bronsted-Lowry reaction, what always moves?
A proton (H+) moves from the acid to the base
What is a conjugate acid?
The species formed when a base gains a proton (H+)
What is the conjugate base?
The species formed when an acid loses a proton (H+)
How can you quickly identify the acid and base in a reaction?
Find the H⁺
Who loses H⁺ = acid
Who gains H⁺ = base
An example of acid and base
Label the acid, base, and the conjugates in the reaction below
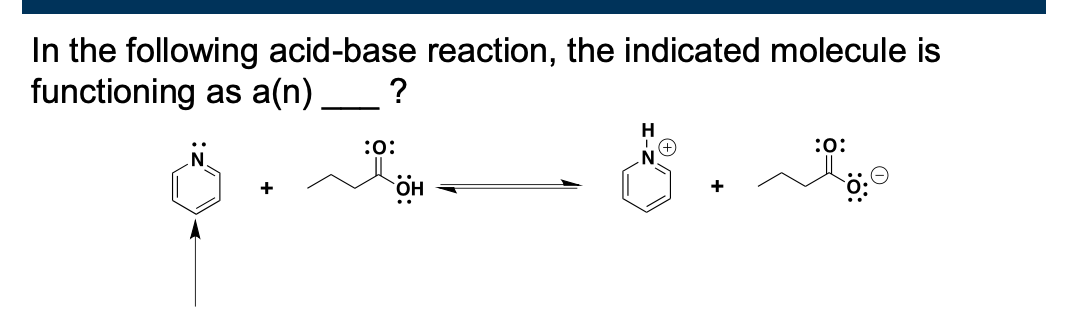
base
What do curved arrows represent in reaction mechanisms?
Curved arrows show the movement of electron pairs that result in bond breaking and bond forming during a chemical reaction
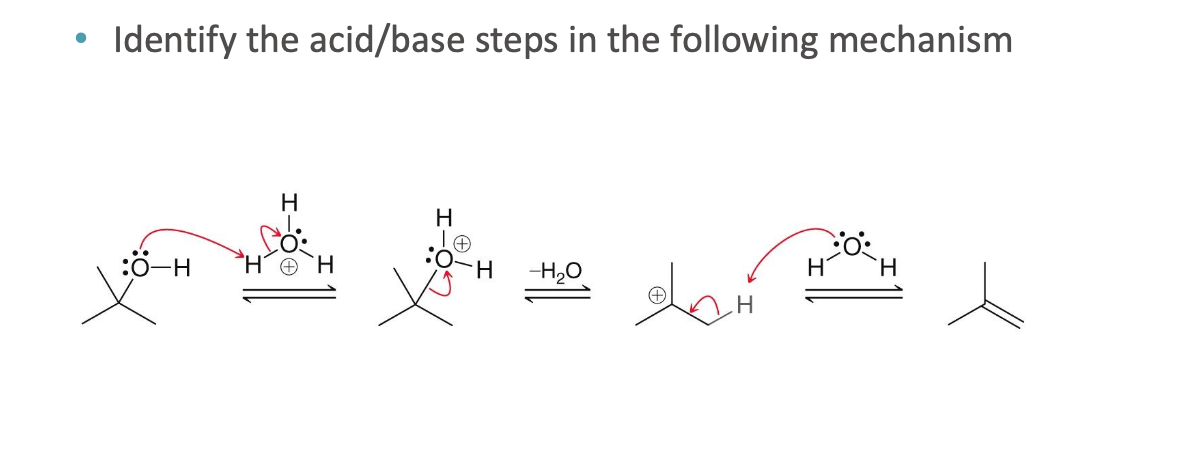
base, acid
How do strong acids differ from weak acids?
Strong acids fully dissociate in solution, while weak acids partially dissociate
What does pka measure?
measures acid strength
Lower pka= stronger acid
What is the relationship between Ka and pKa?
They are inversely related:
Large Ka → small pKa → strong acid
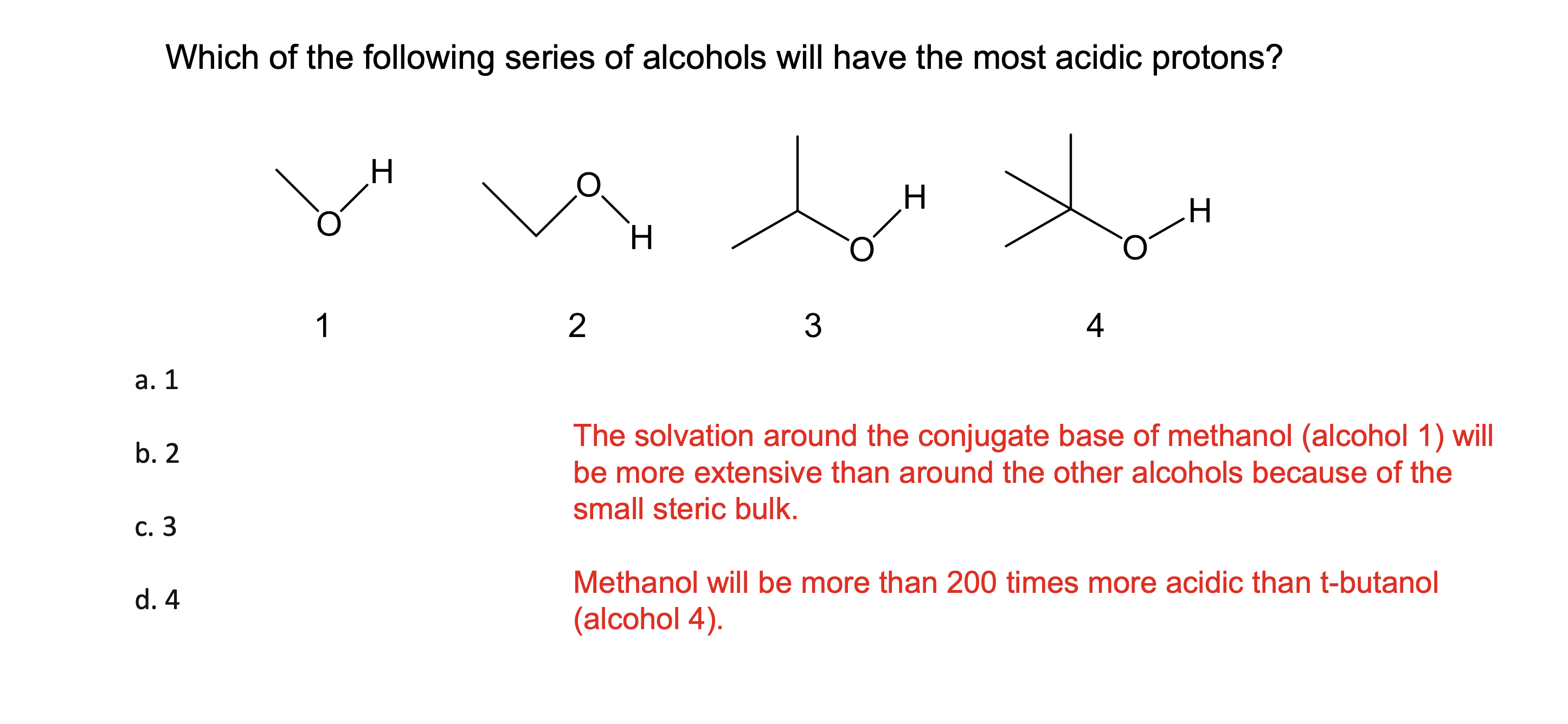
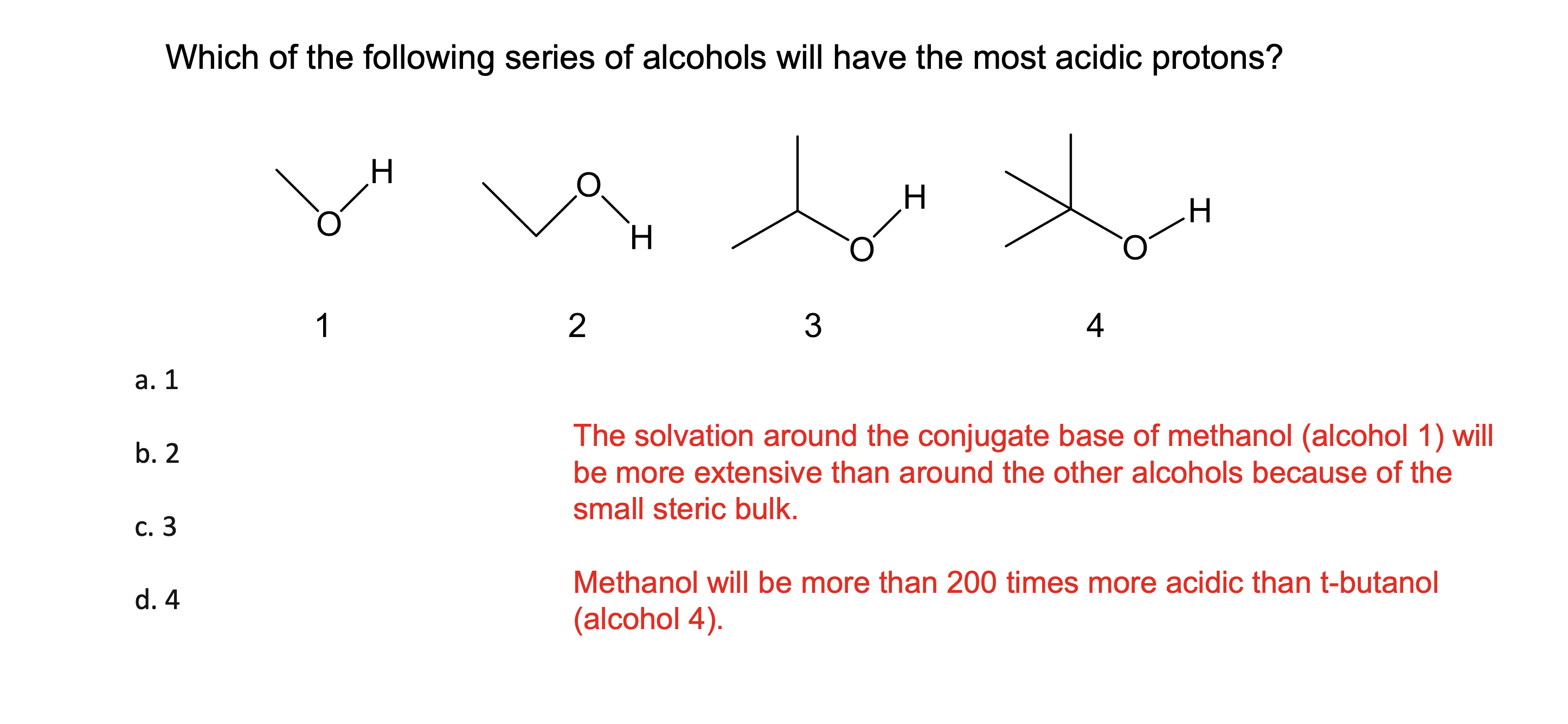
How much stronger is an acid with a pKa that is 1 unit lower?
It is 10x stronger
if it goes down by 2 its acidity goes up 100X
if it goes down by 3 it s acidity goes up 1000x
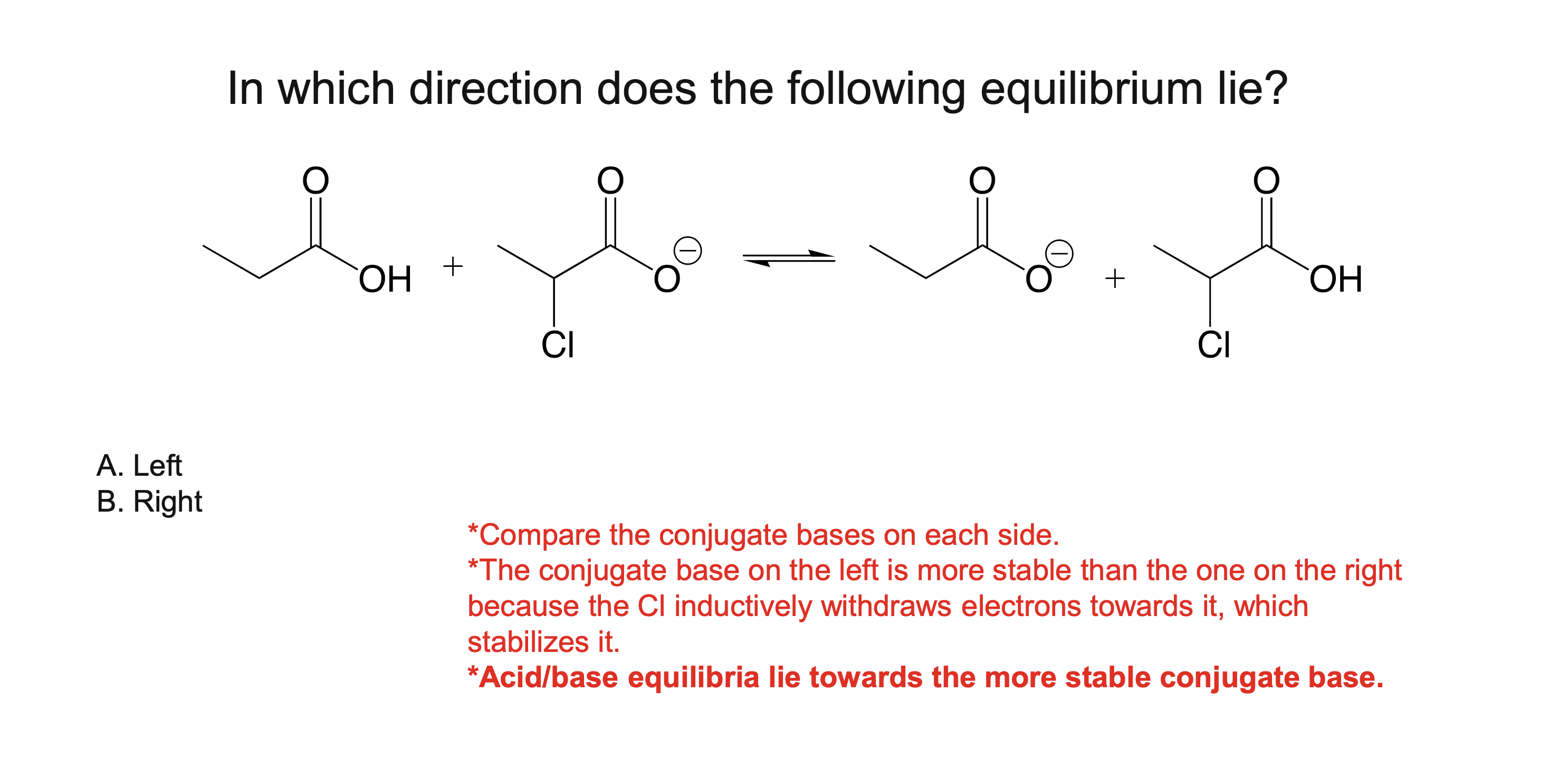
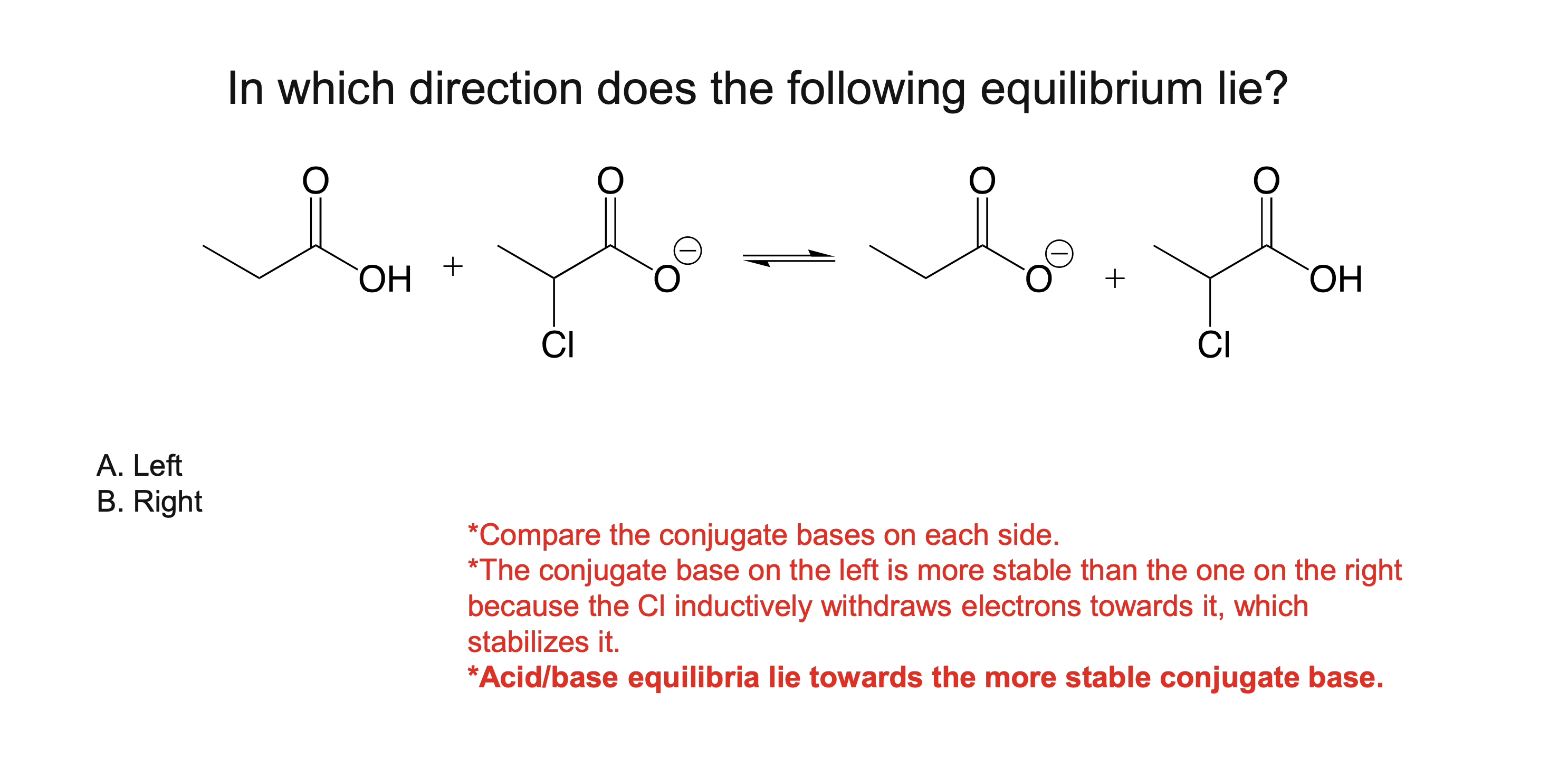
In an acid base reaction, which direction is favored?
Reactions favor formation of the weaker acid and more stable conjugate base
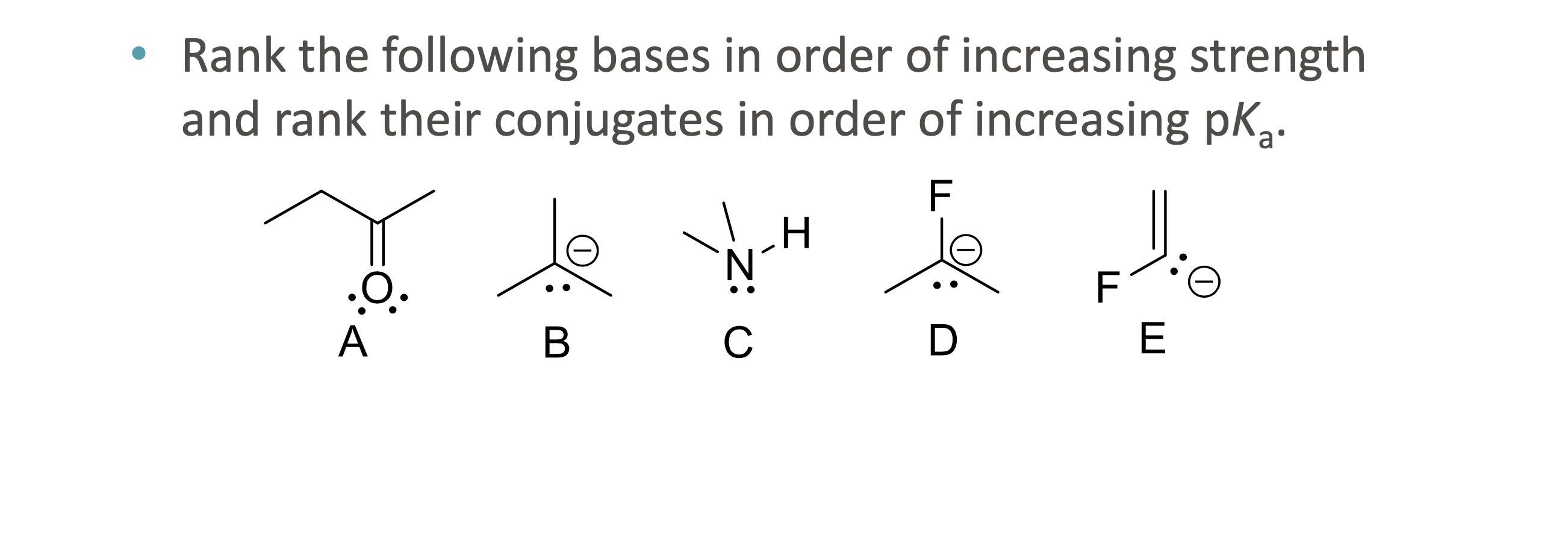
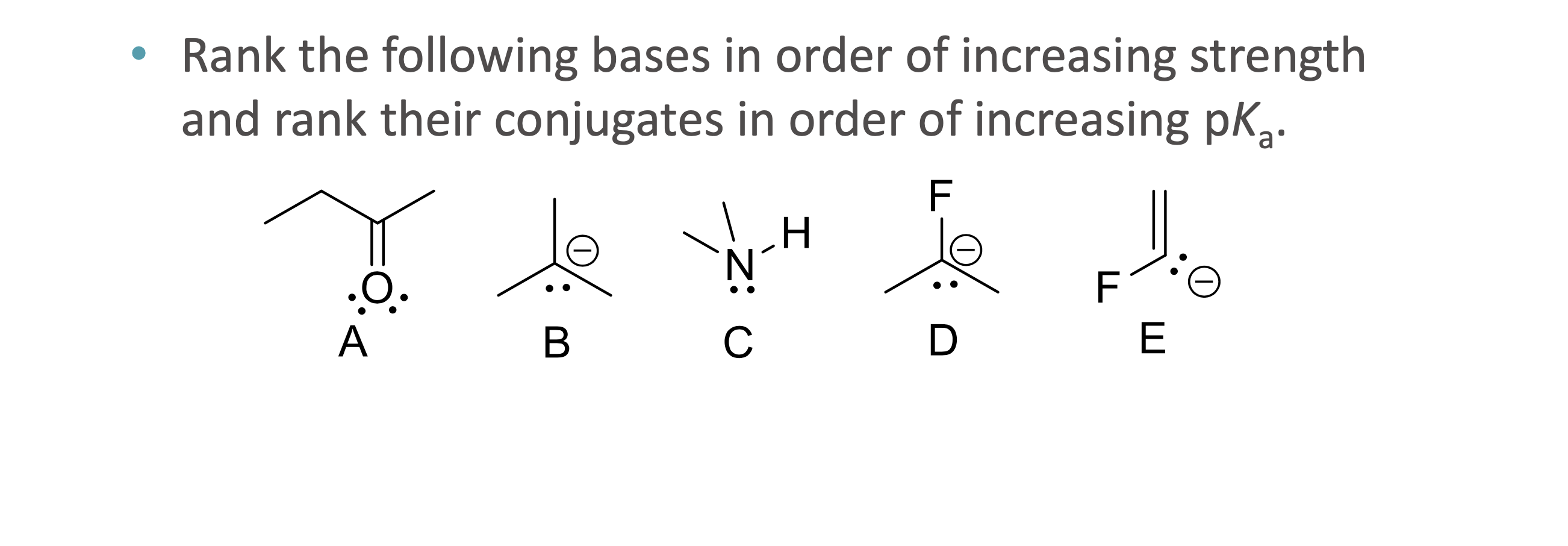
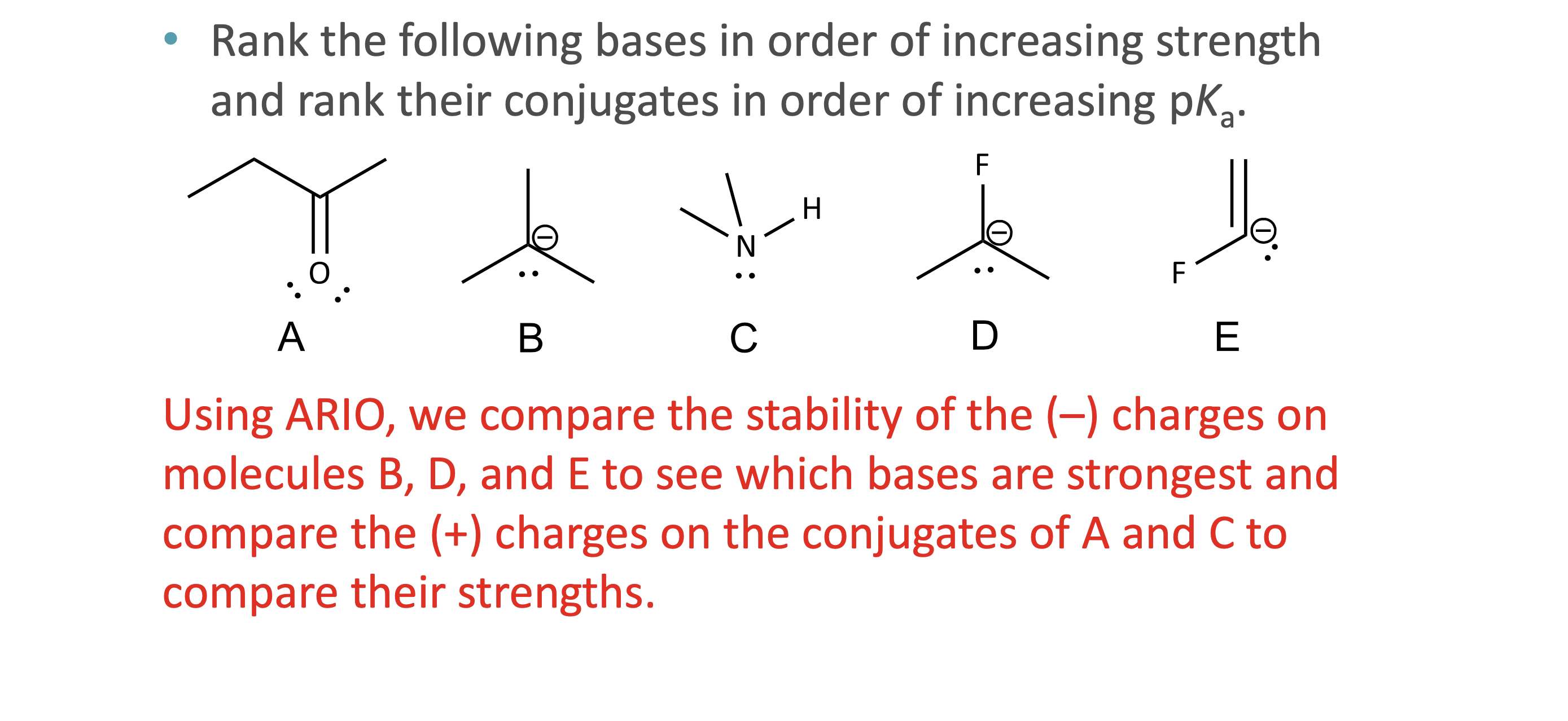
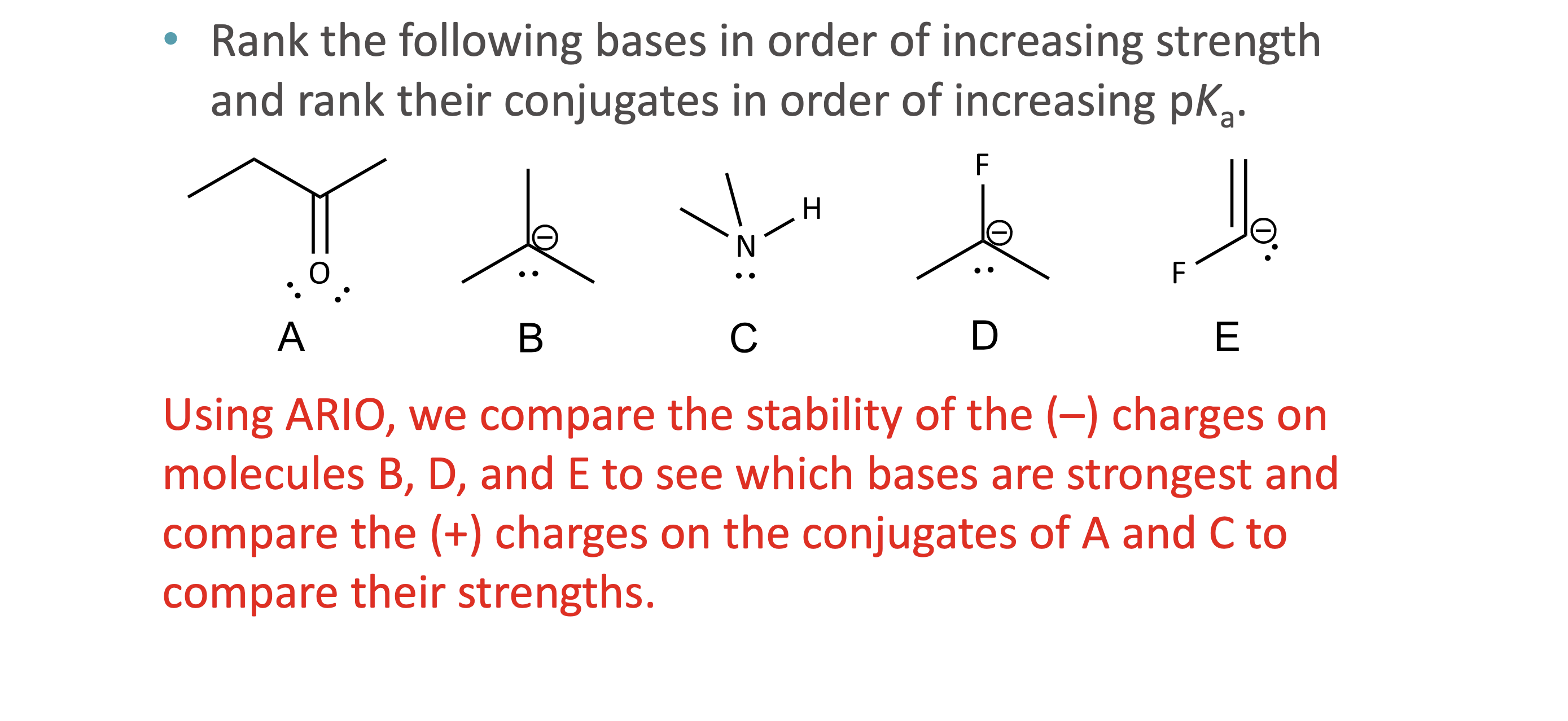
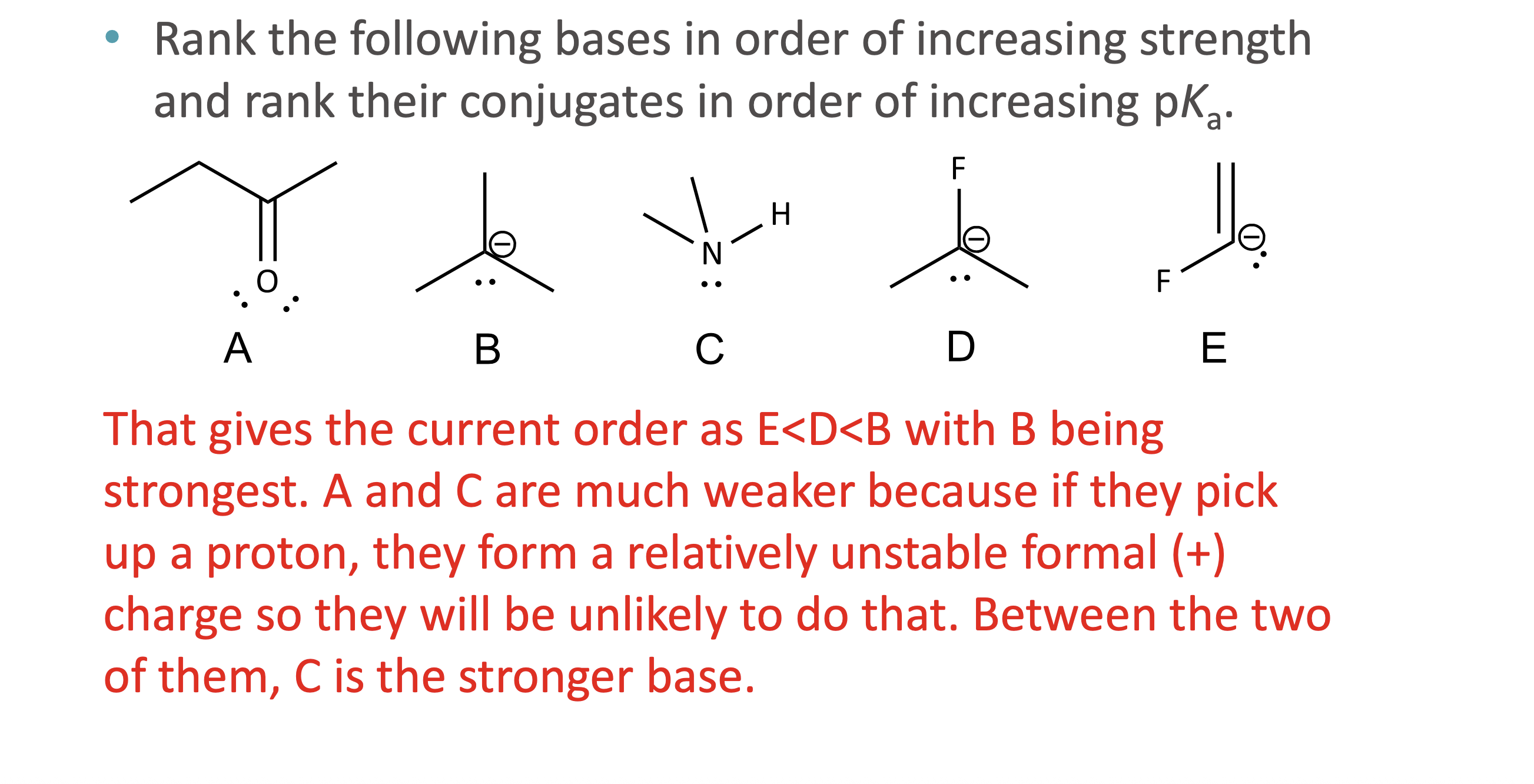
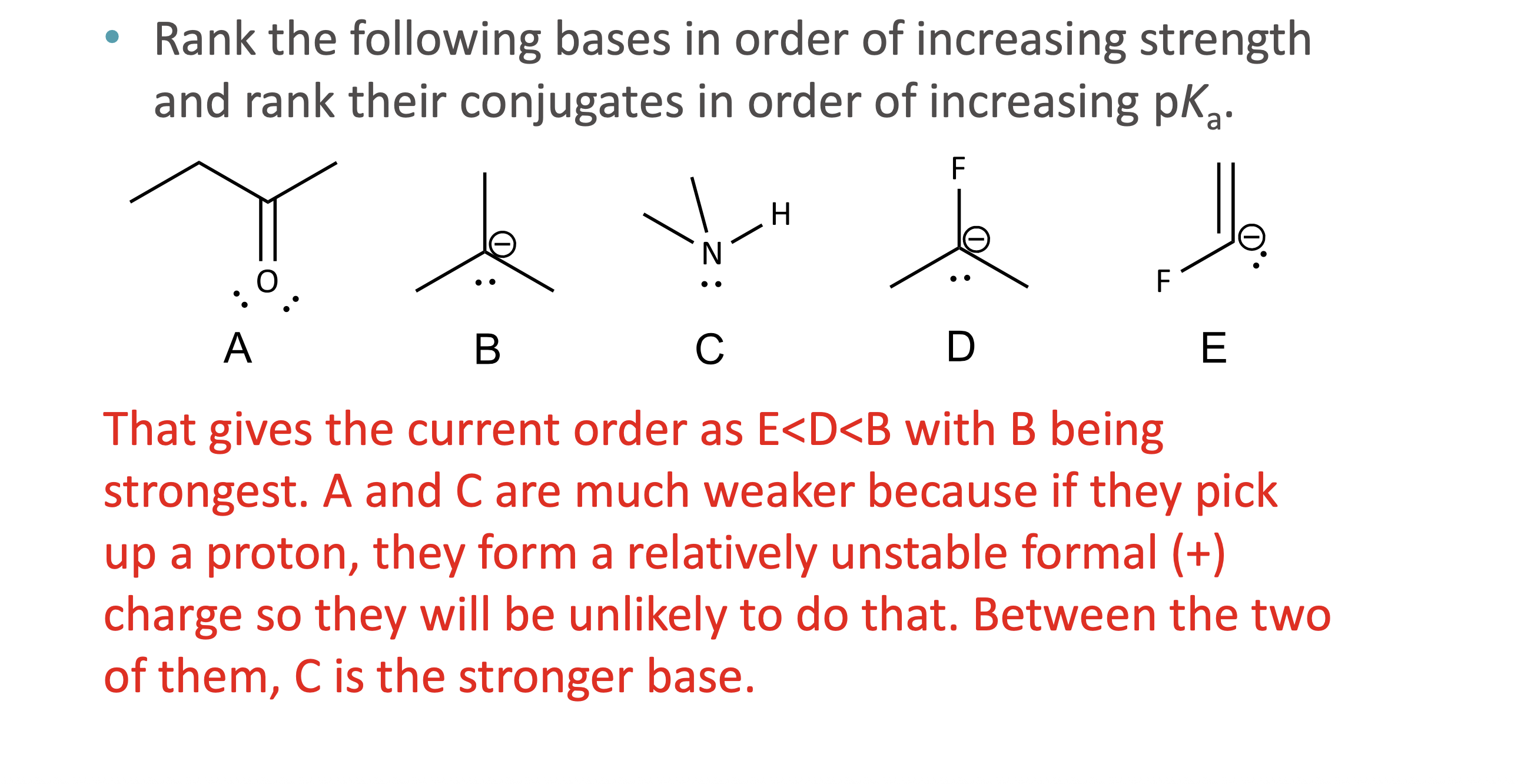
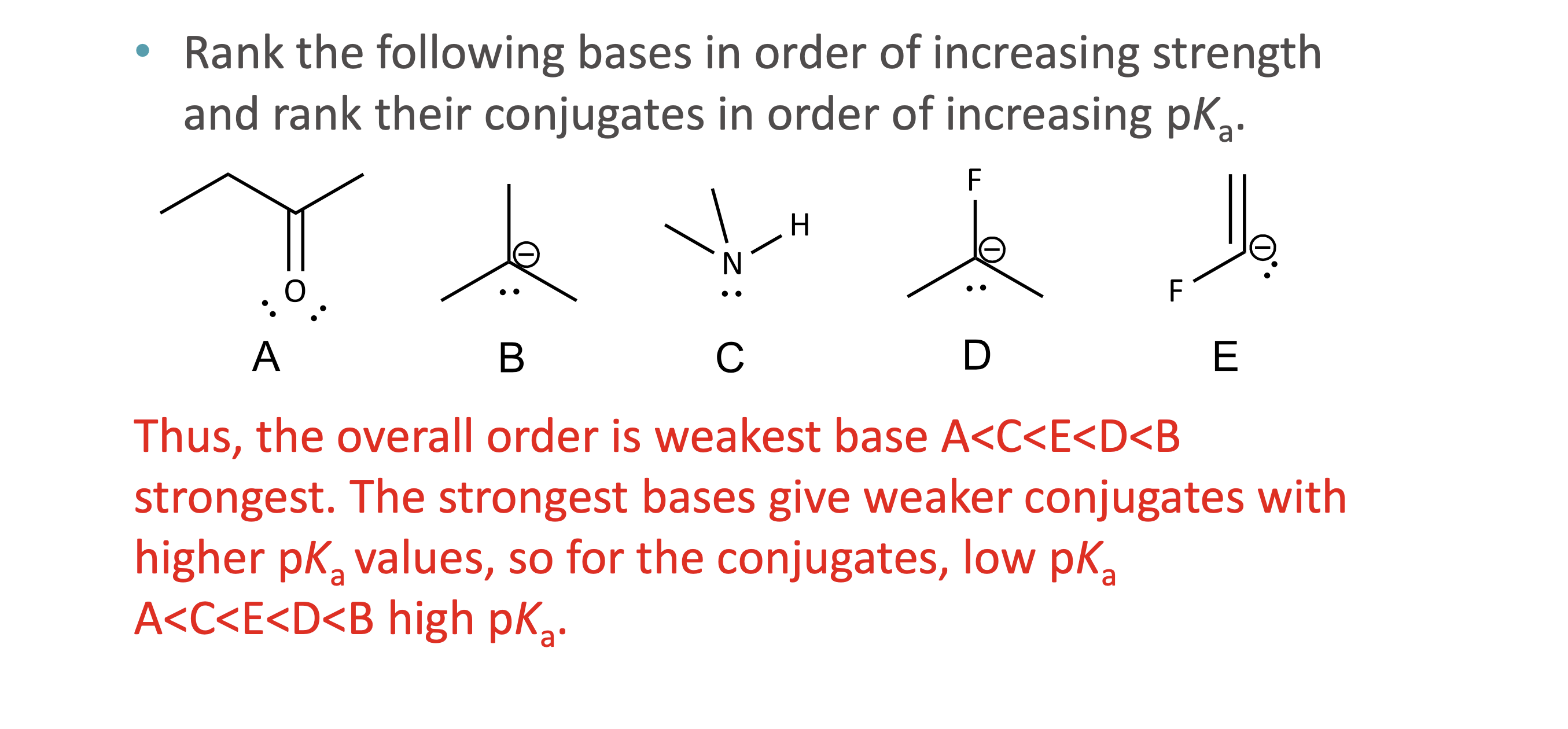
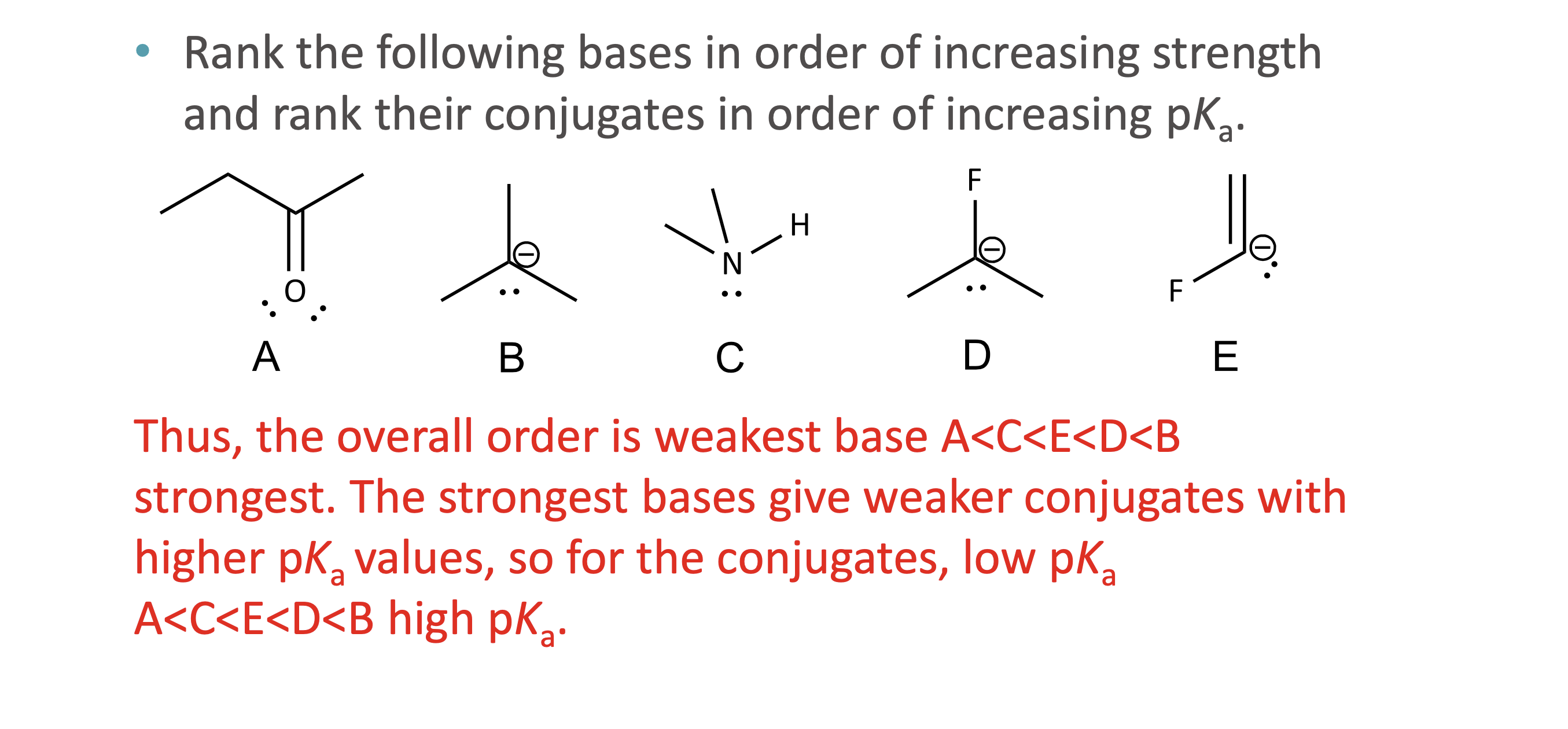
What is quantitative acid strength analysis?
Comparing pKa values to determine which acid or base is stronger
What is qualitative acid strength analysis?
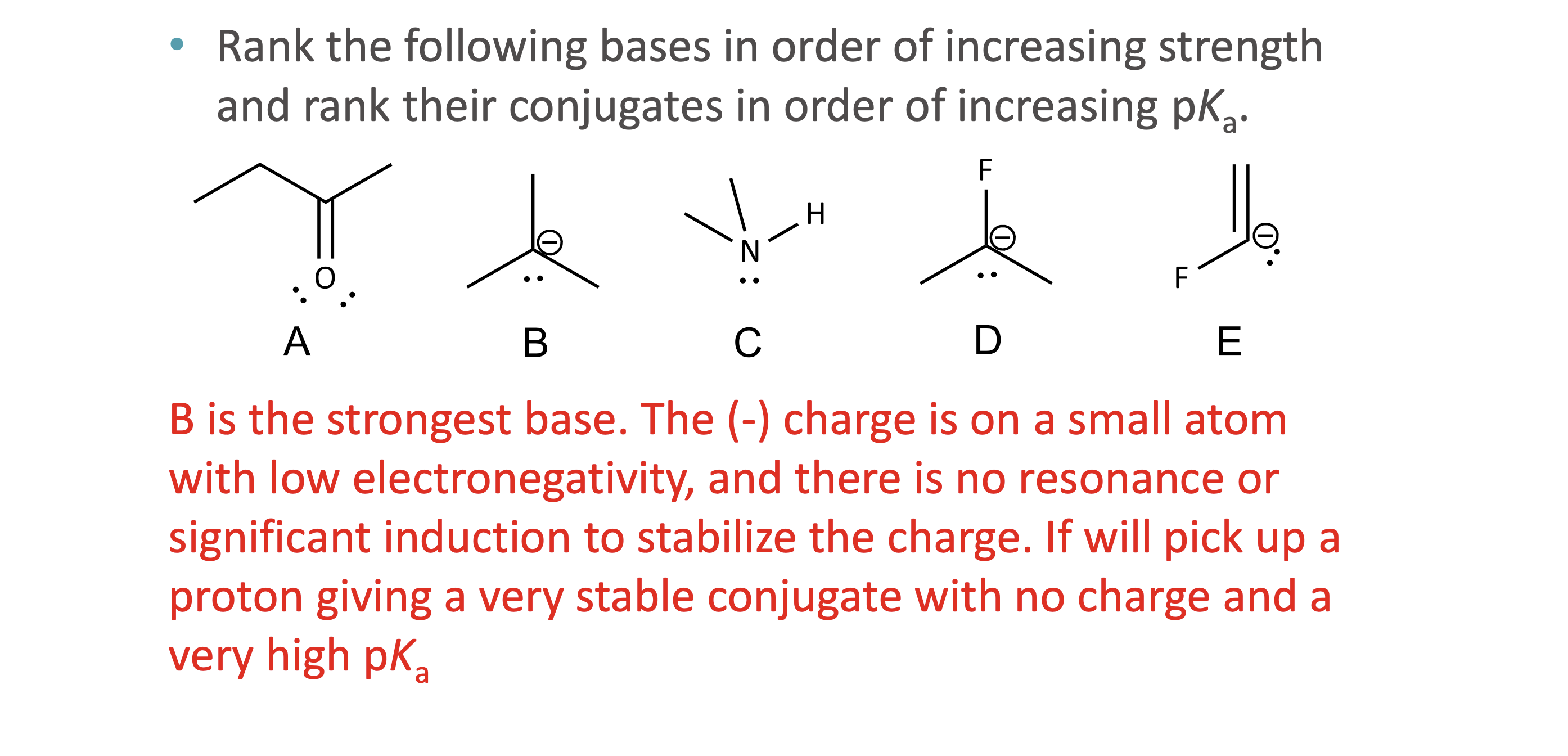
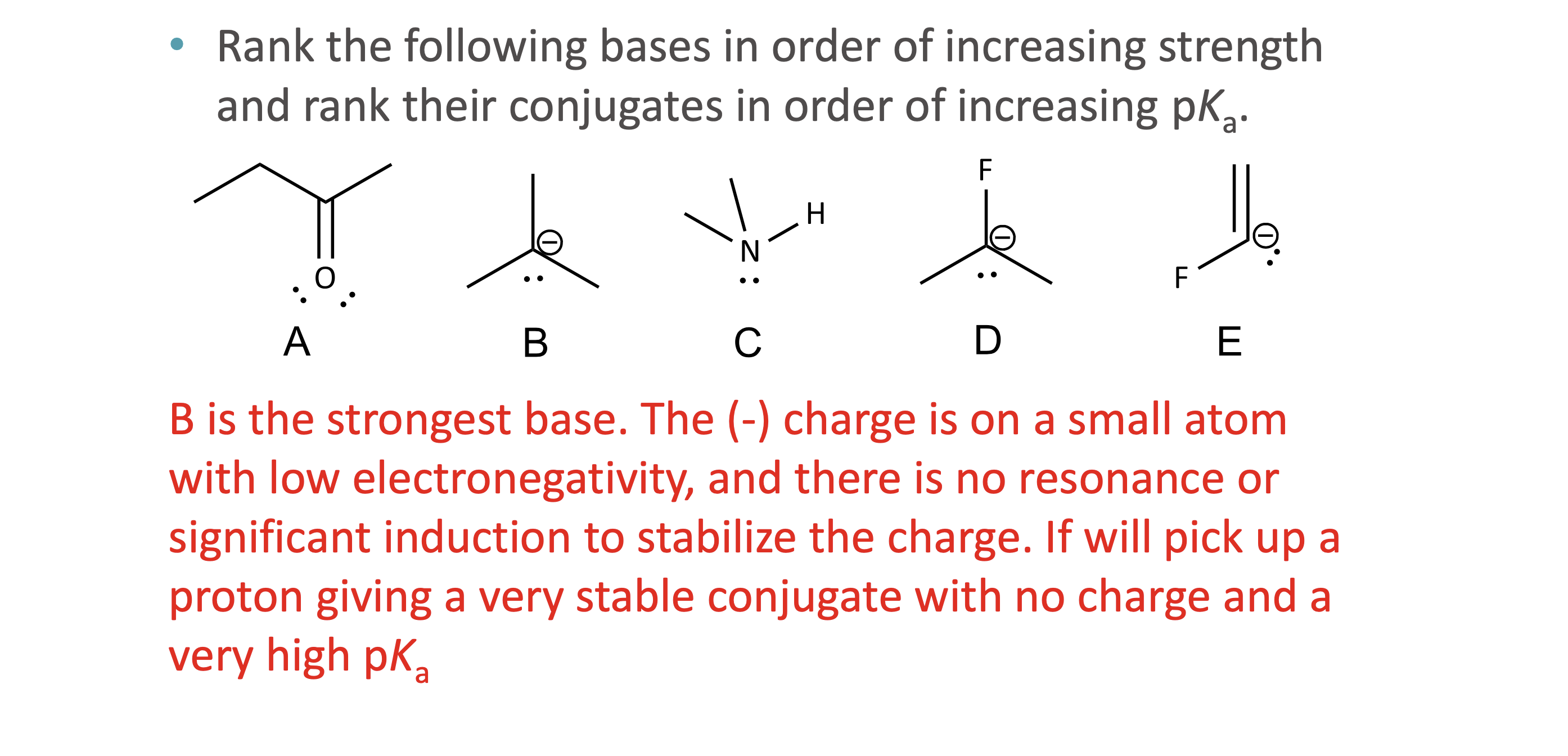
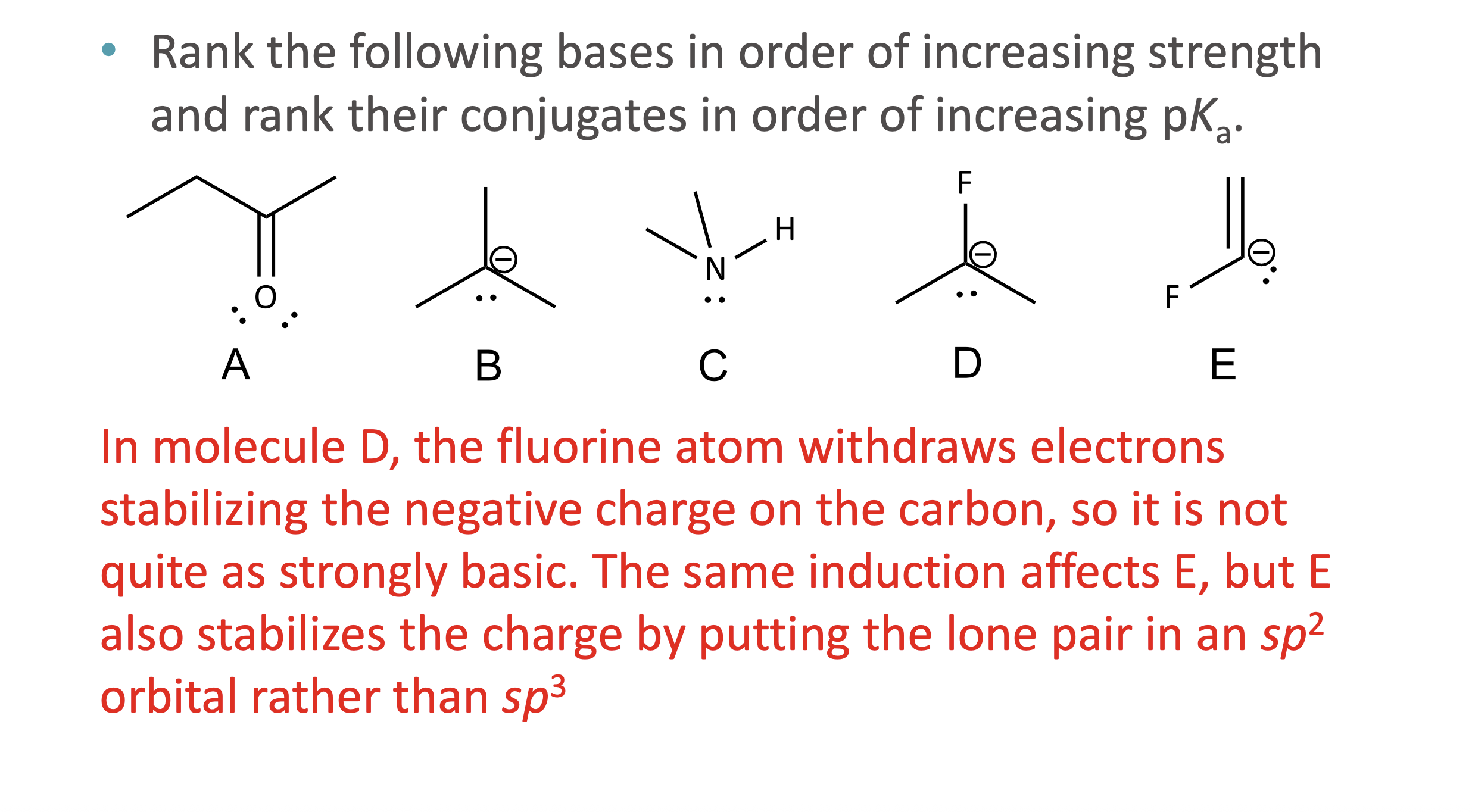
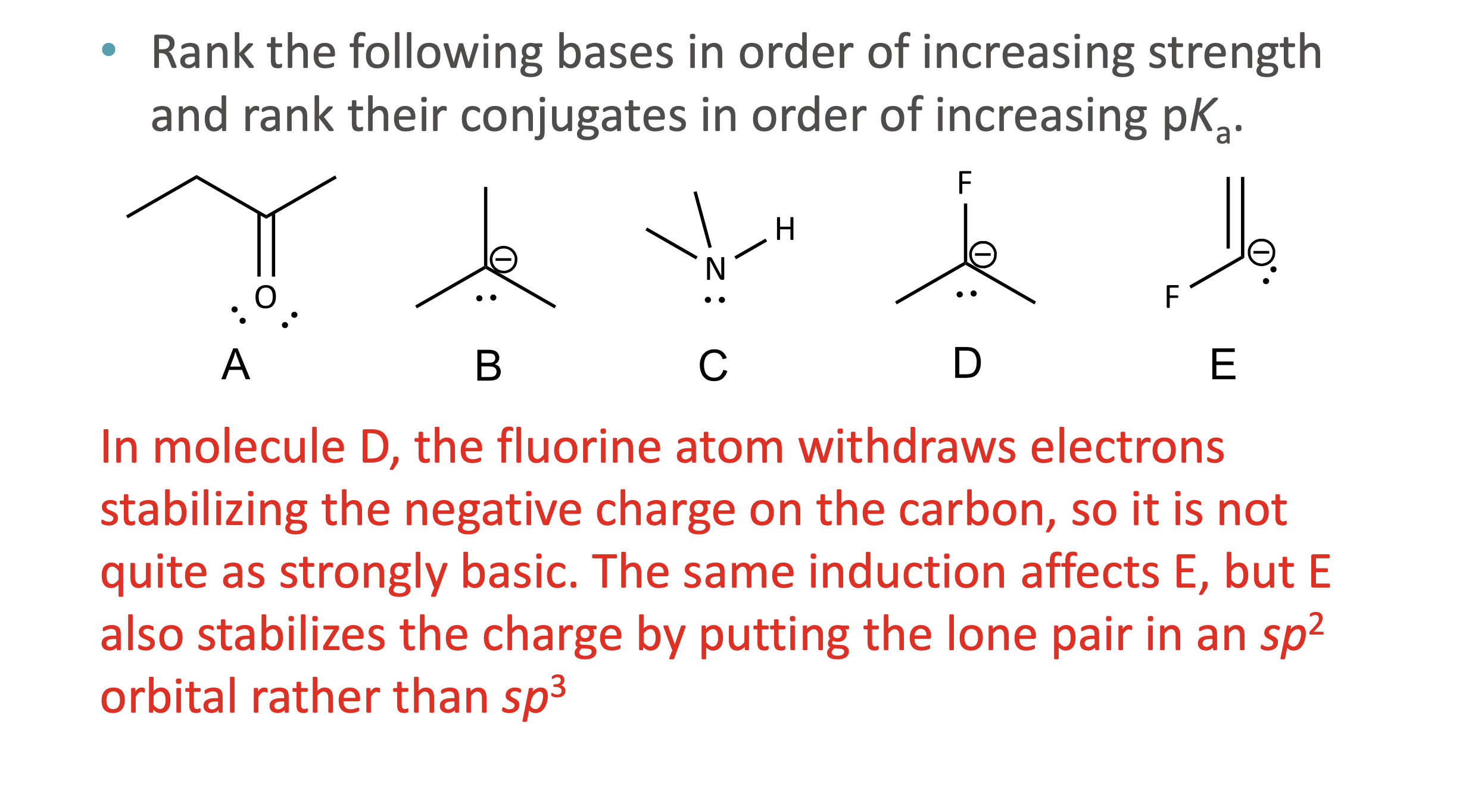
Comparing structural stability (resonance, induction, hybridization, atom size) when pKa values are unavailable
What makes a conjugate base more stable?
Resonance delocalization
Higher electronegativity
Larger atom size
Greater s-character (sp > sp² > sp³)
How is base strength related to conjugate acid pKa?
Stronger base ↔ conjugate acid has higher pKₐ.
Name the strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI
H₂SO₄, HNO₃, HClO₄
The conjugate base of a strong acid is
weak
The conjugate base of a weak acid is?
strong

e

ask Erick
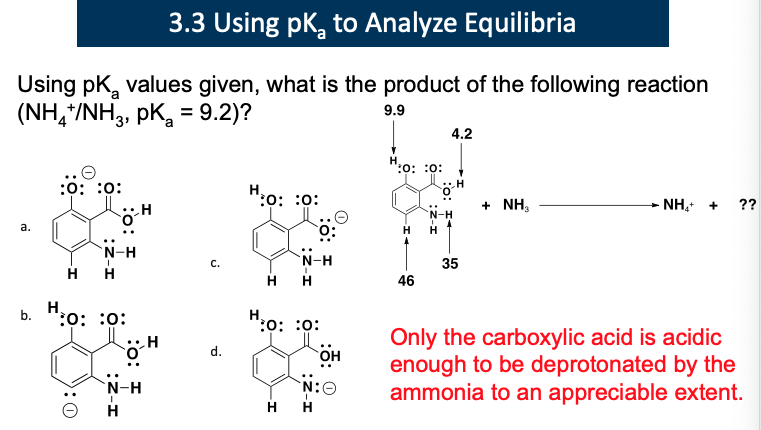
c
What determines the strength of an acid?
The stability of its conjugate base
More stable conjugate base → stronger acid
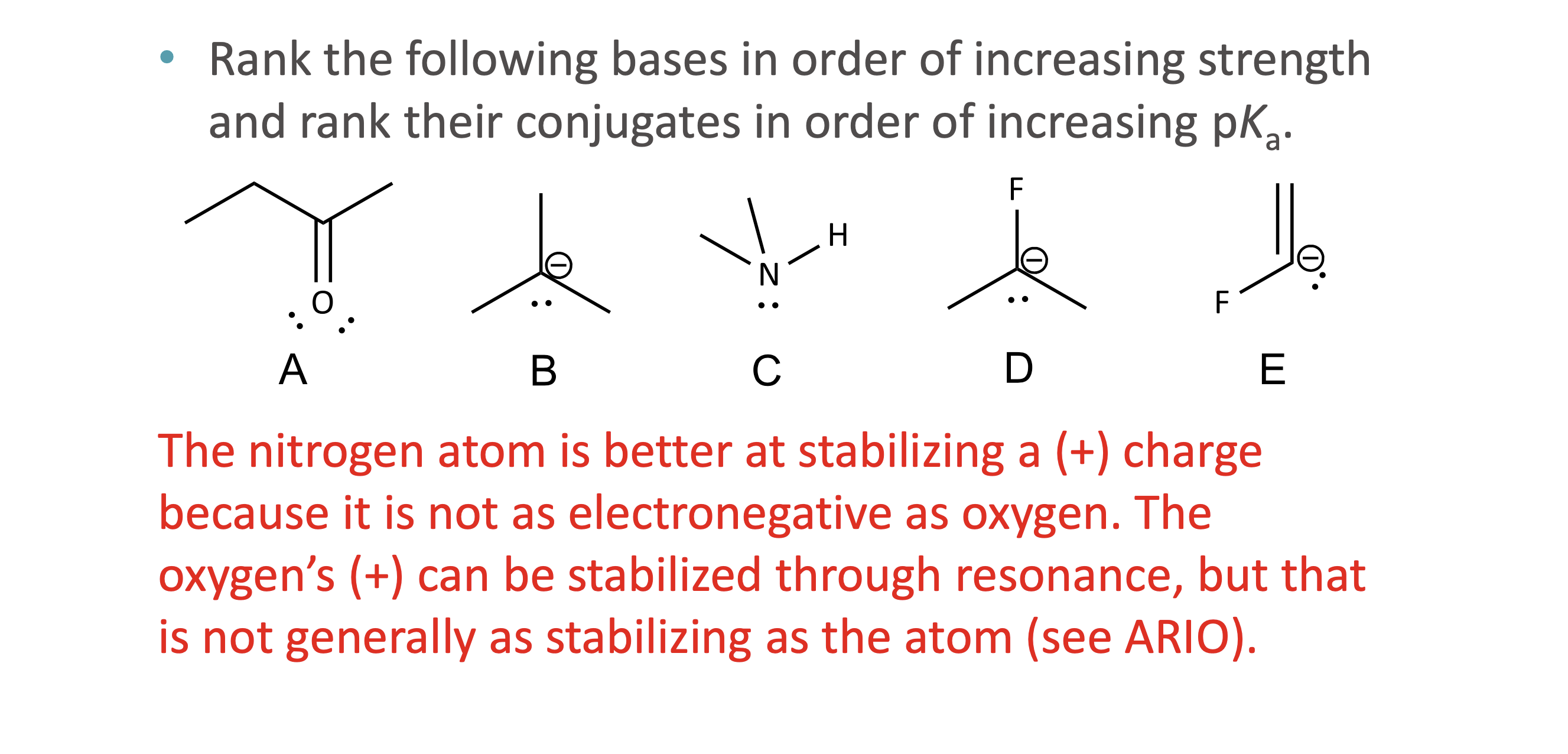
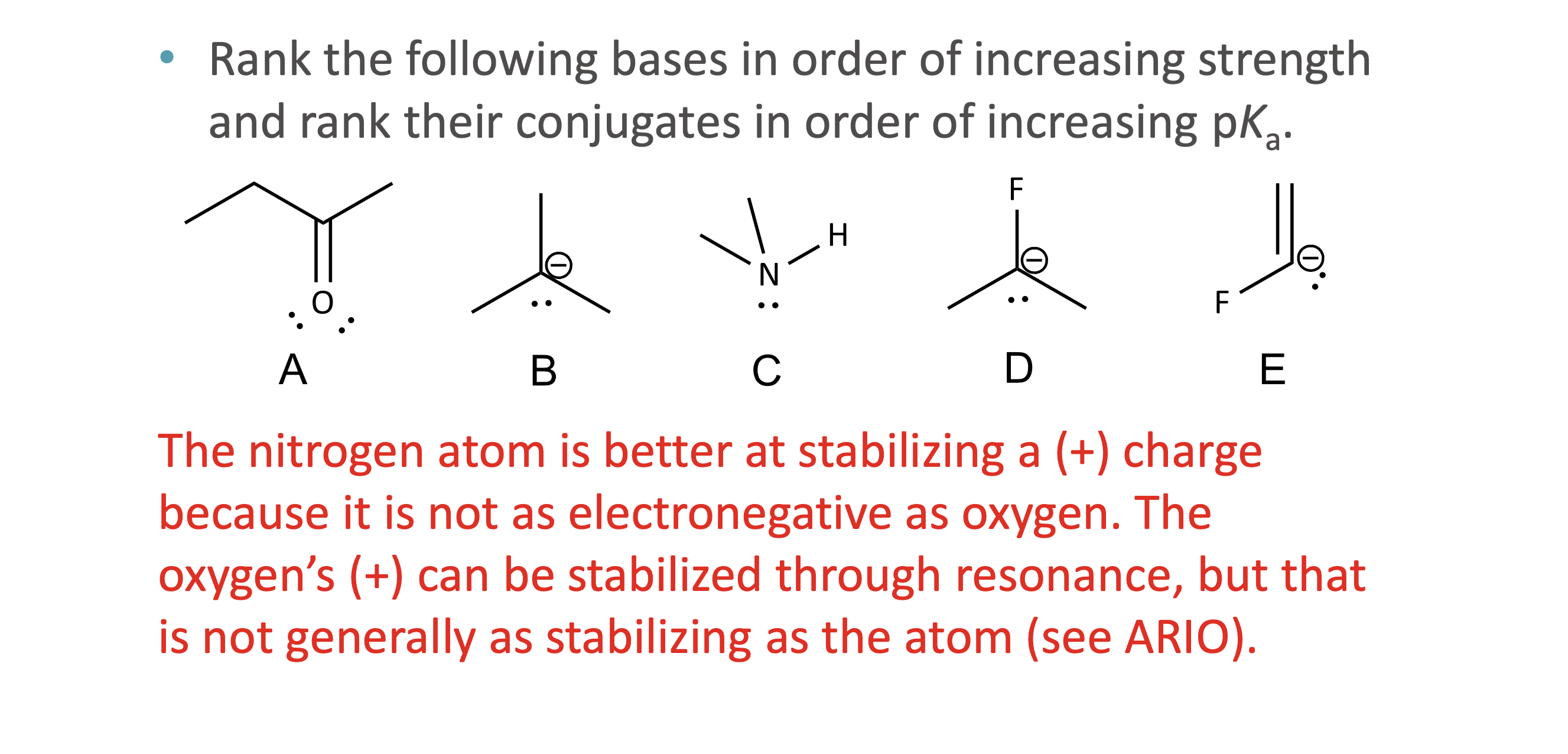
What does ARIO stand for in acidity analysis?
Atom, Resonance, Induction, Orbital
When should ARIO be used instead of pka values?
When pKa values are not given or not easily known
What does A (Atom) mean in ARIO?
The type of atom holding the negative charge
More electronegative or larger atoms stabilize charge better
When do you use electronegatively in acidity comparisons?
When the negative charge is on different atoms in the conjugate bases
What does R (Resonance) mean in ARIO?
The ability to delocalize negative charge through resonance structures
Why does resonance increase acidity?
Resonance spreads out negative charge, stabilizing the conjugate base
What does I (Induction) mean in ARIO?
Stabilization of charge through electron-withdrawing effects of nearby electronegative atoms via sigma bonds
How is induction different from electronegativity?
Electronegativity applies when the atom holds the charge
Induction applies when nearby atoms influence the charge
What does O (Orbital) mean in ARIO?
The hybridization of the atom holding the charge
More s- character = more stable negative charge
Rank the stability for negative charge
sp> sp2>sp5
Which ARIO factor usually has the greatest effect
Resonance
What is the correct order to apply ARIO?
Atom → Resonance → Induction → Orbital
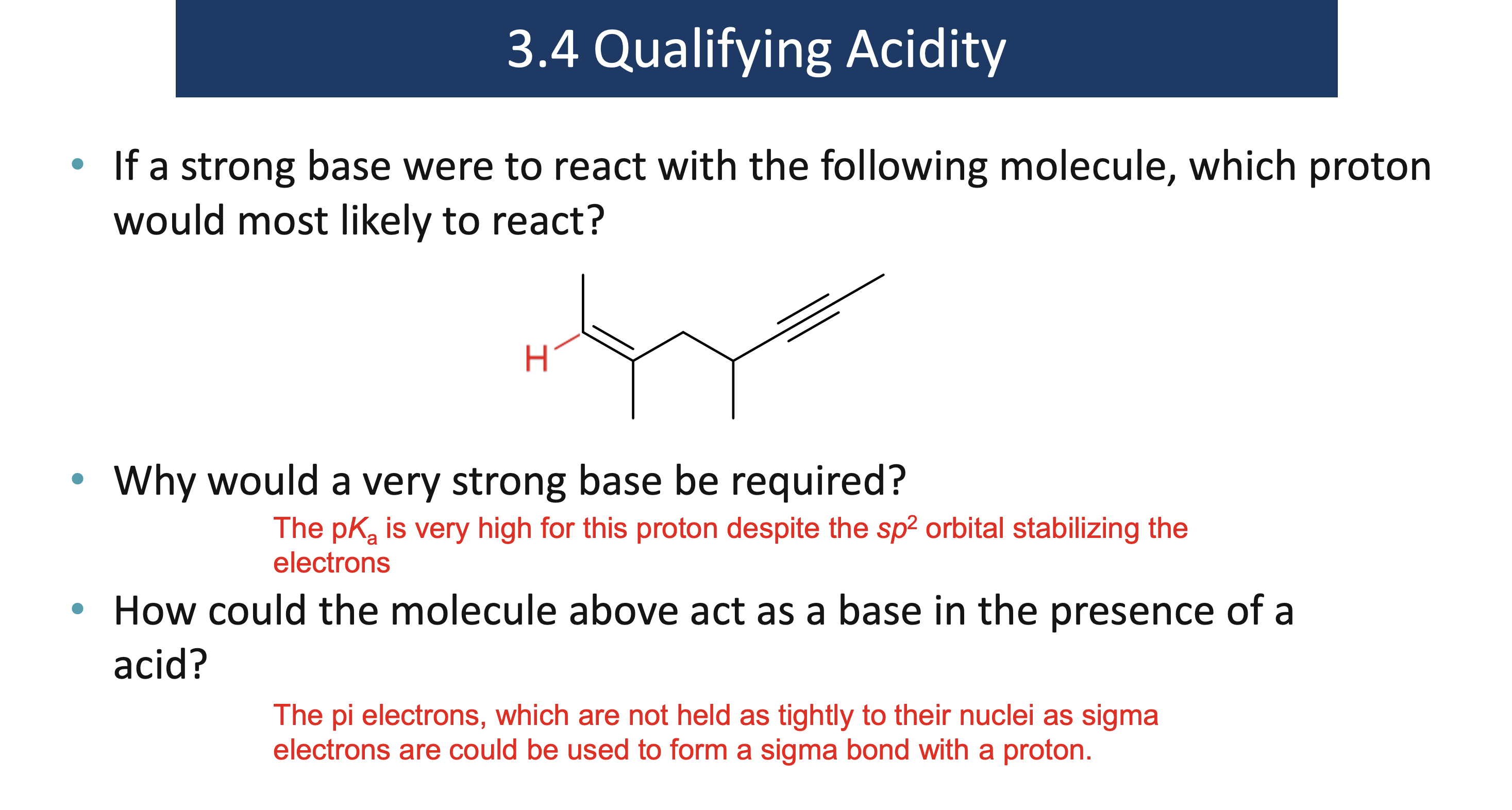
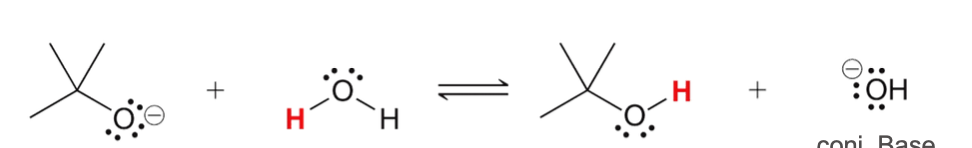
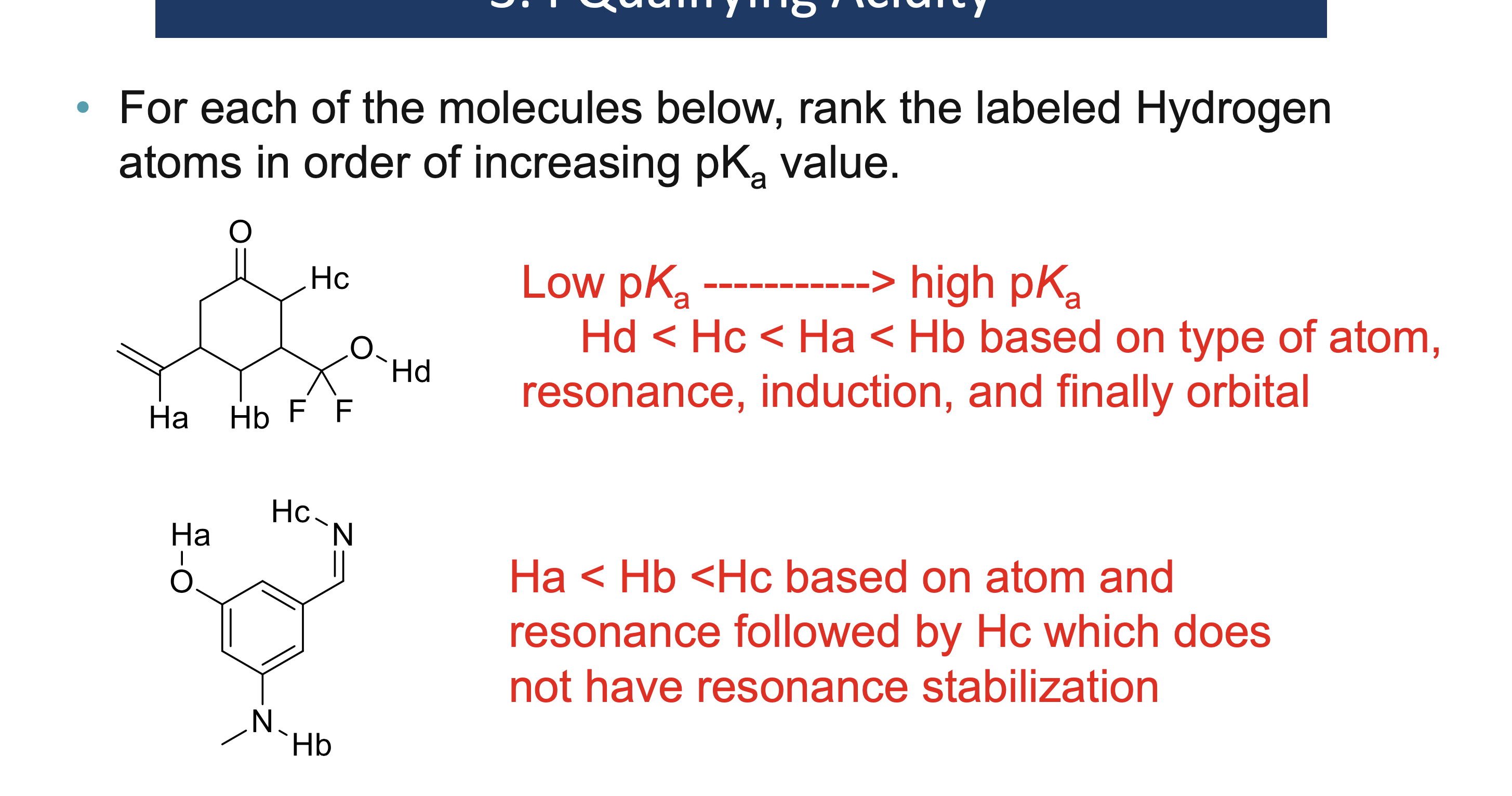
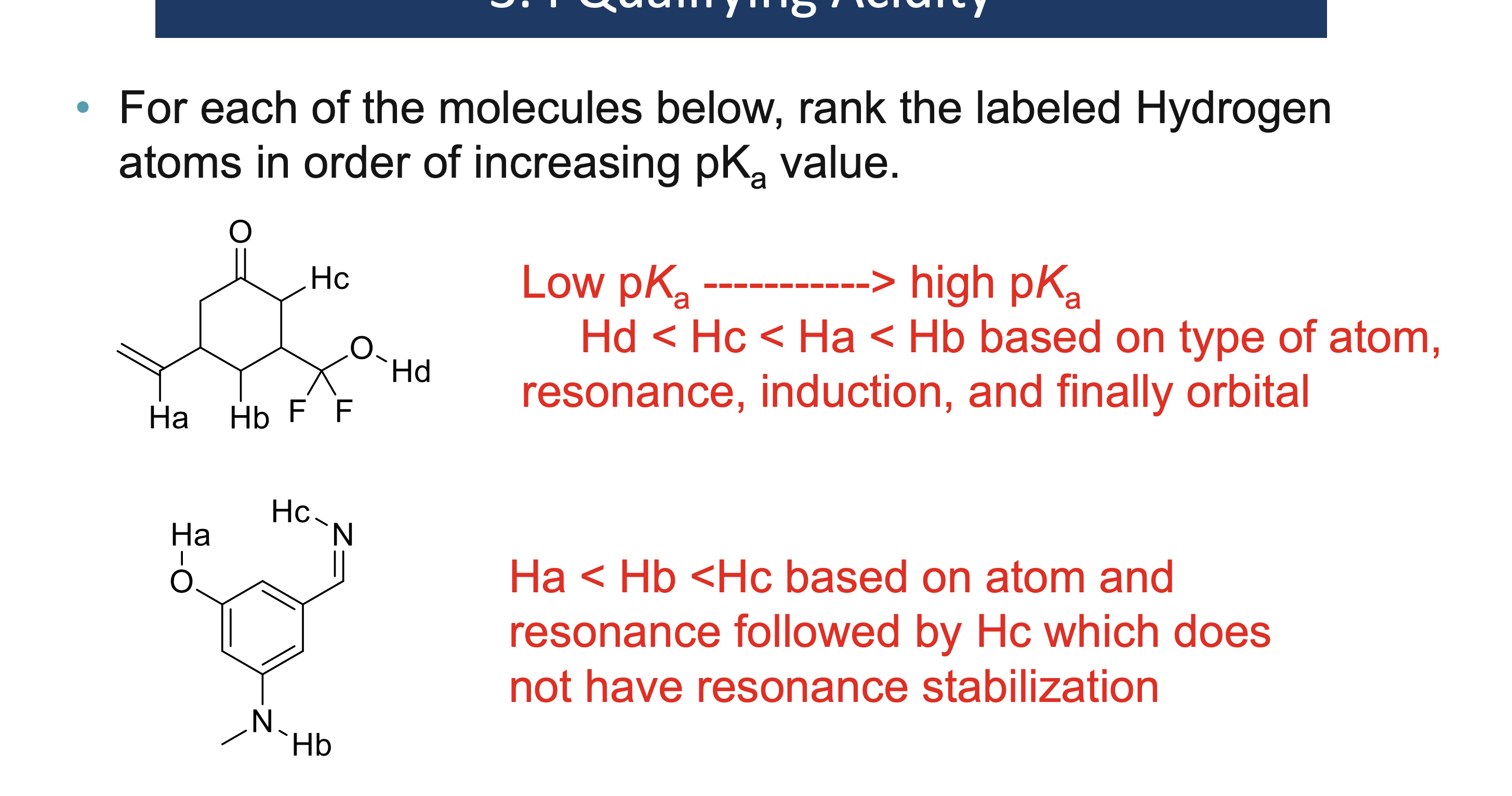
Explain this
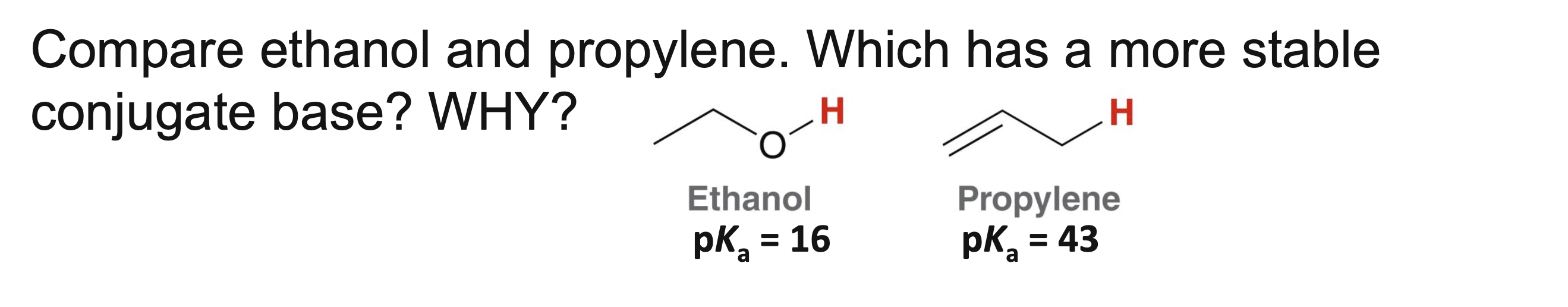
Ethanol has the more conjugate base because the negative charge resides on oxygen rather than carbon


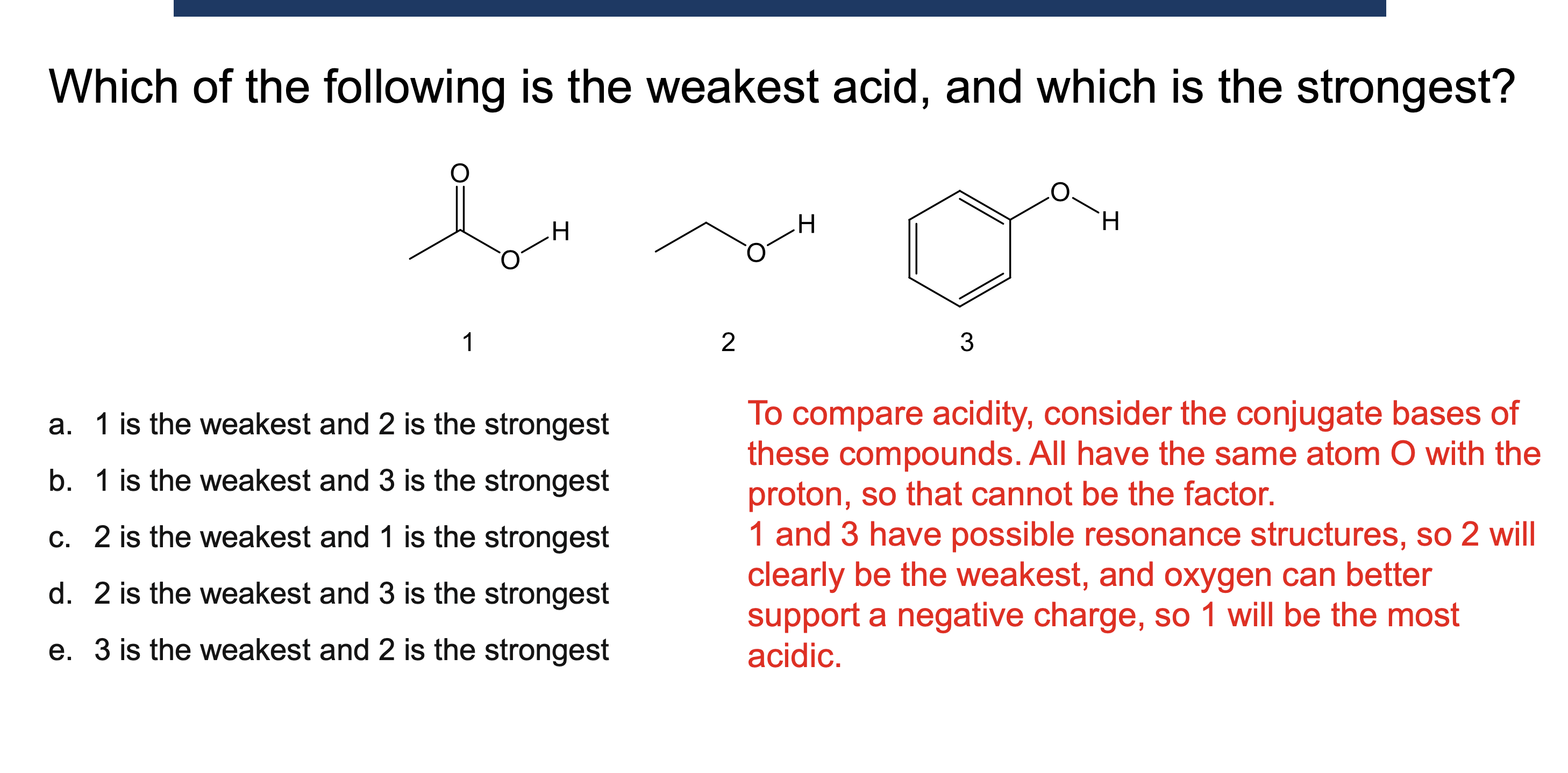
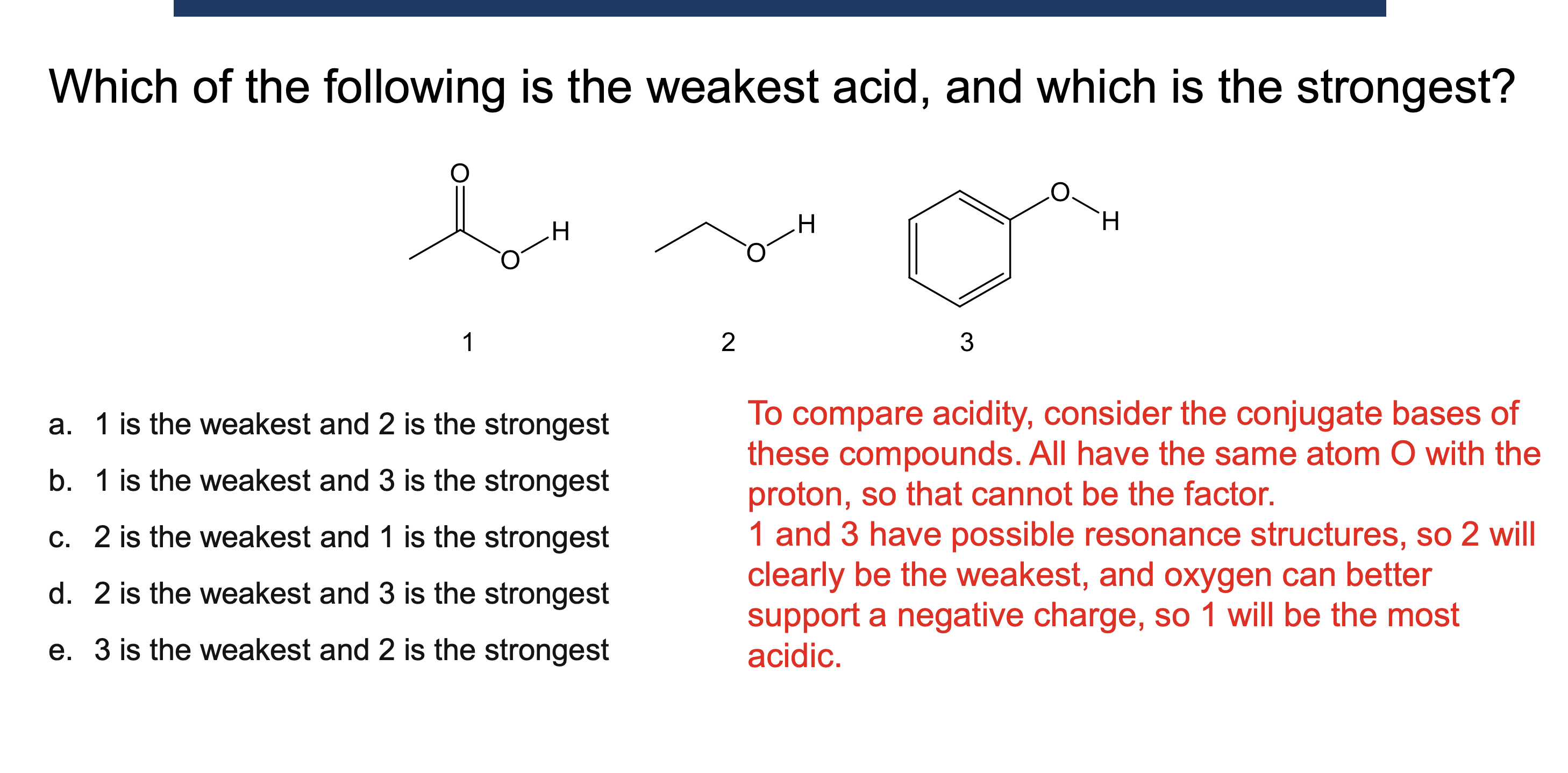
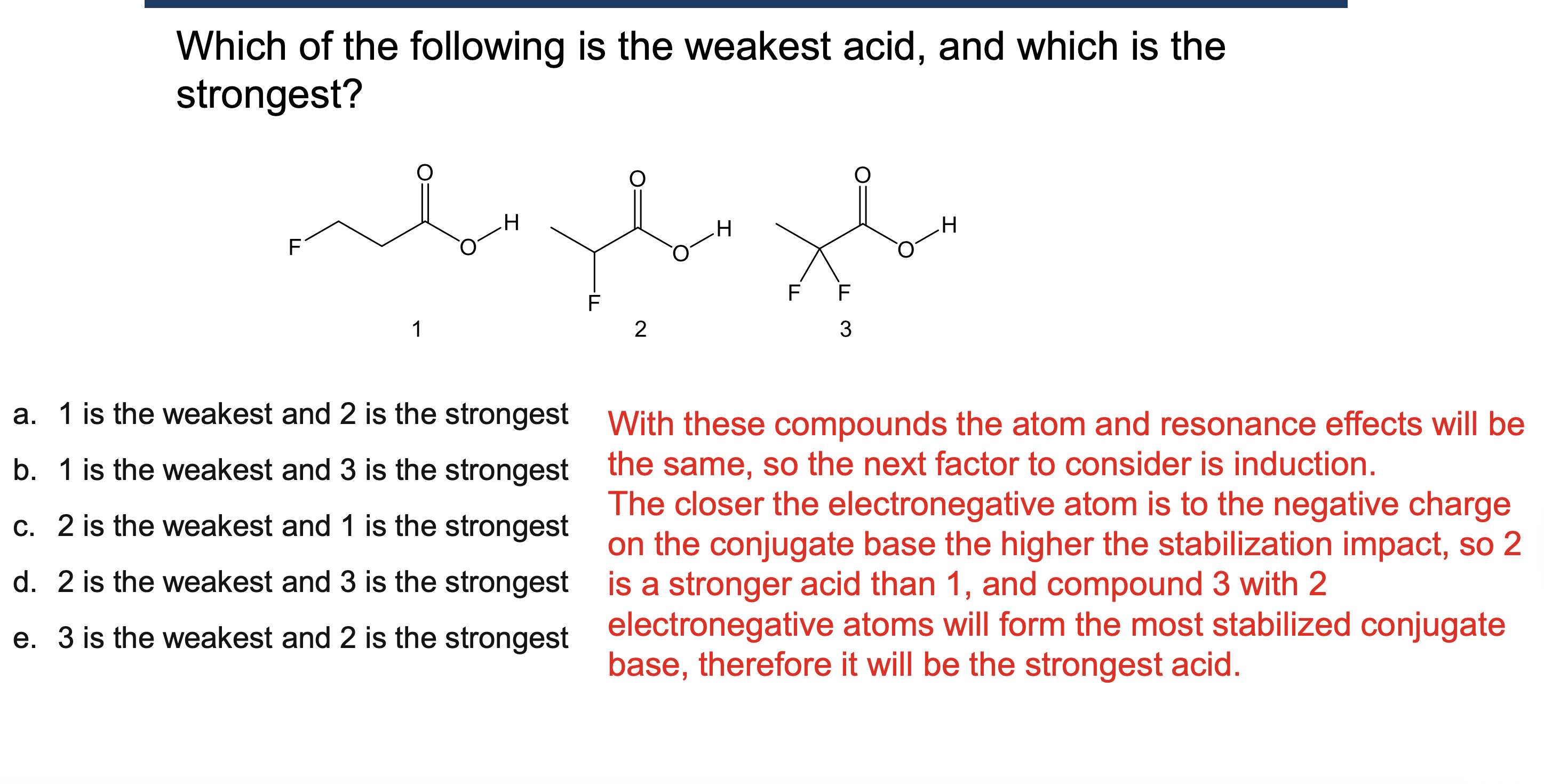
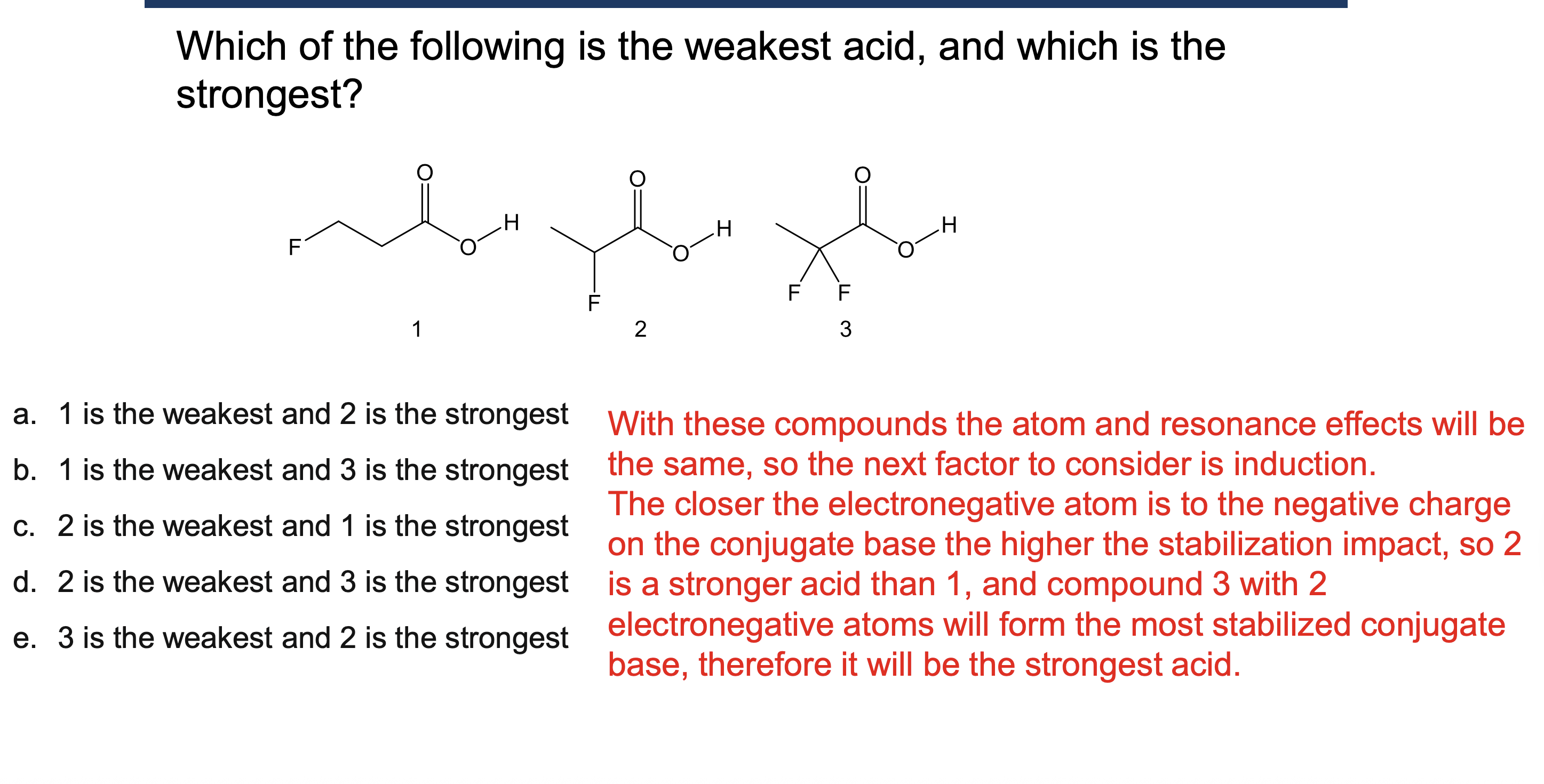
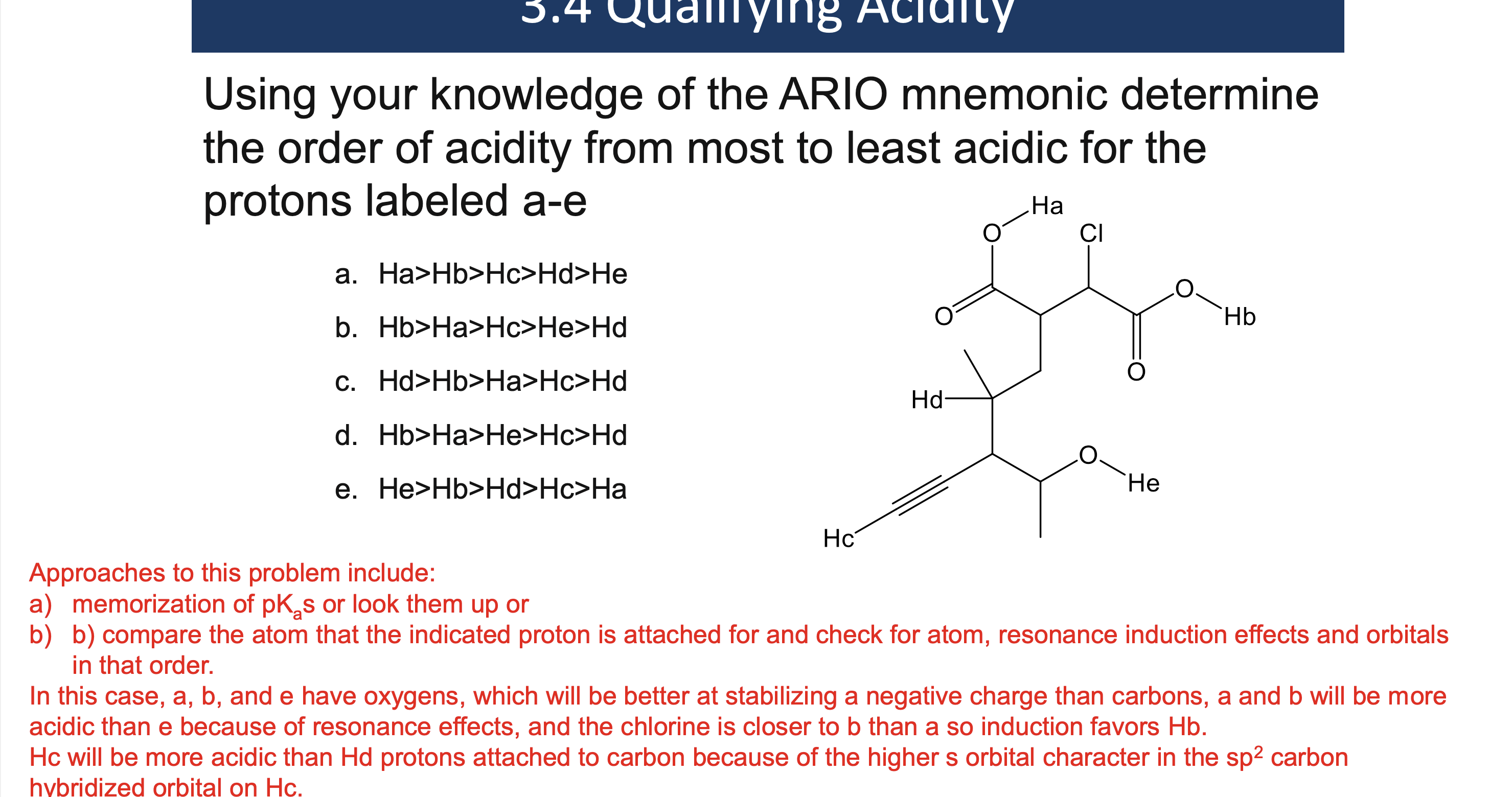
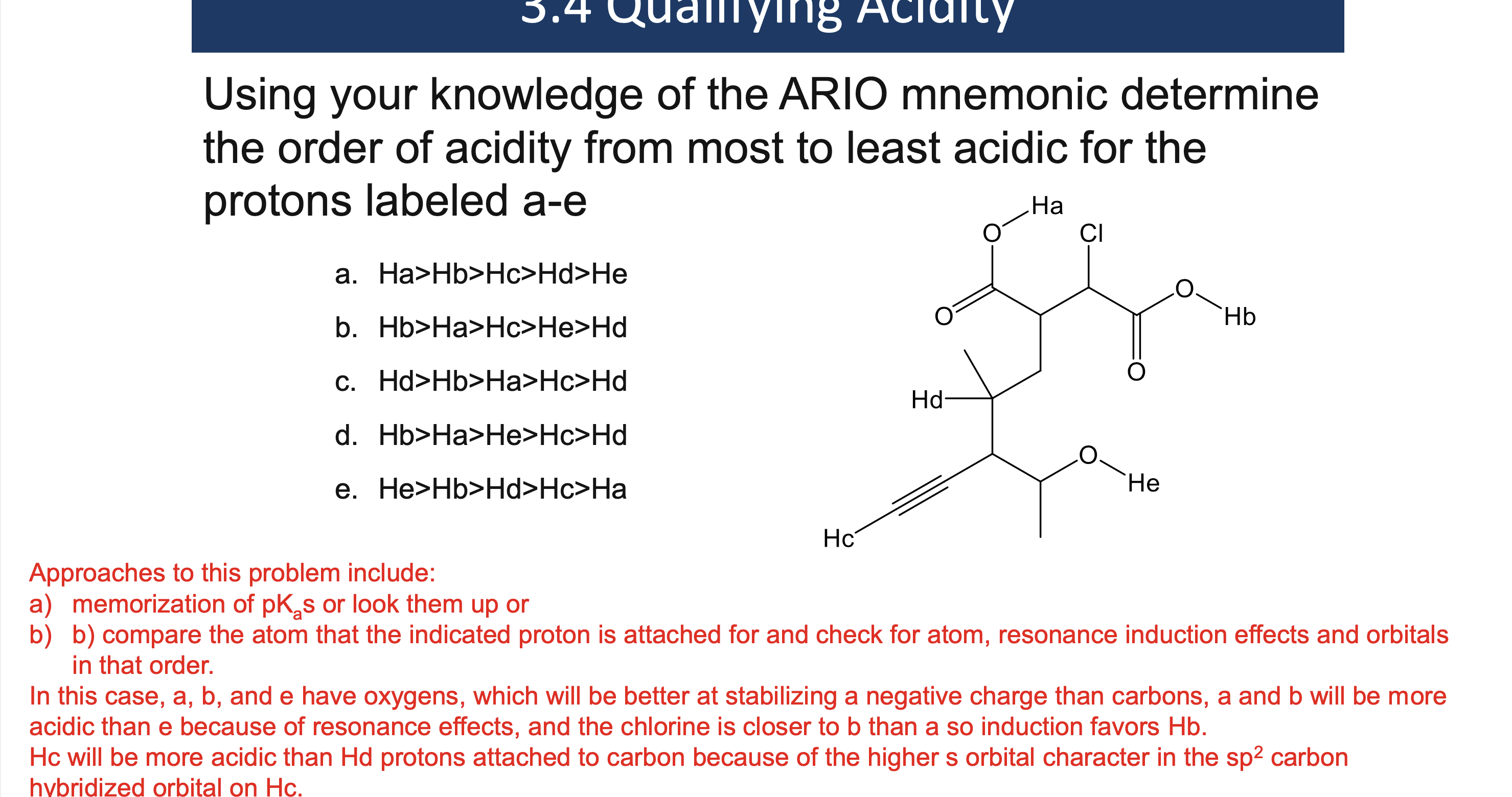
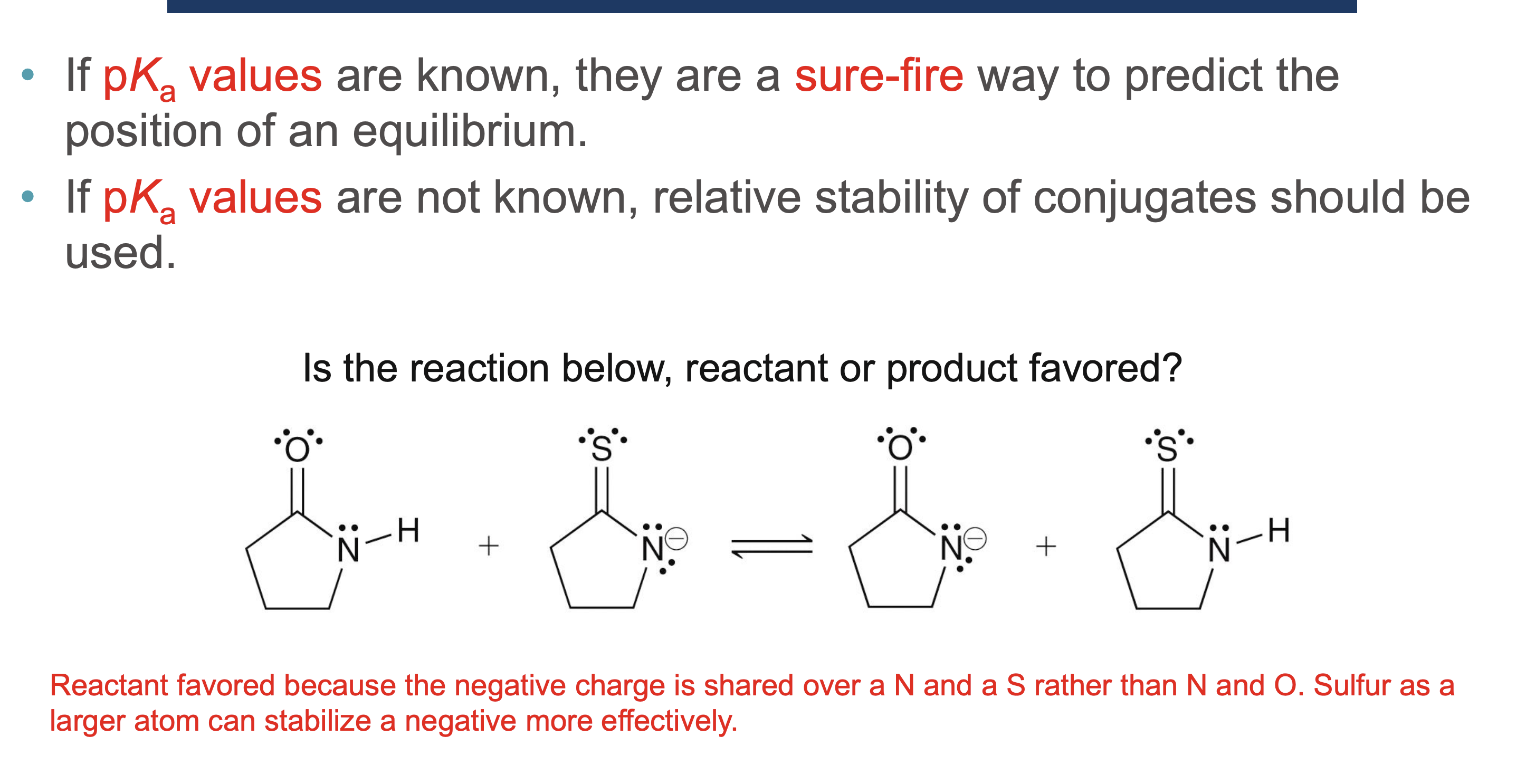
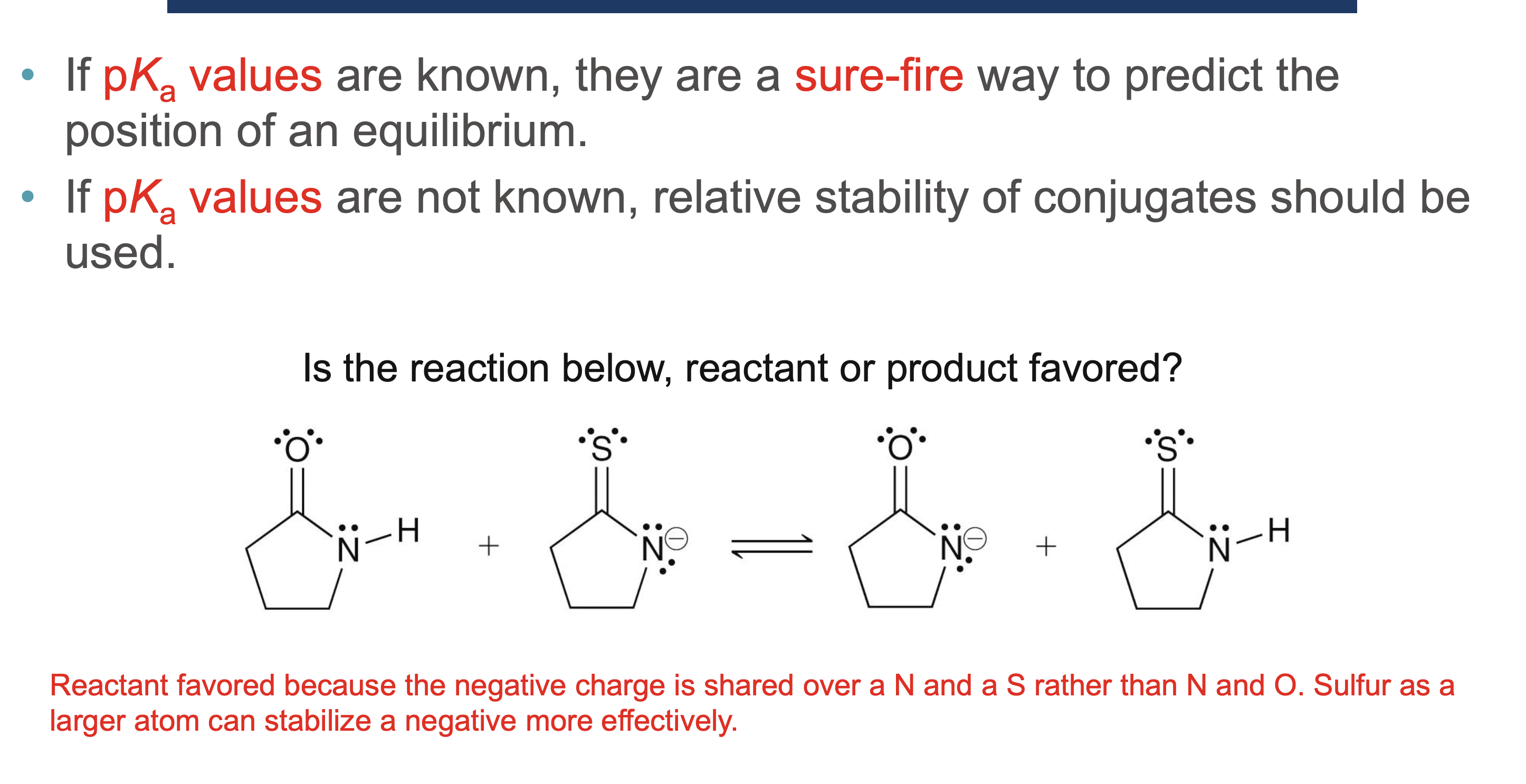




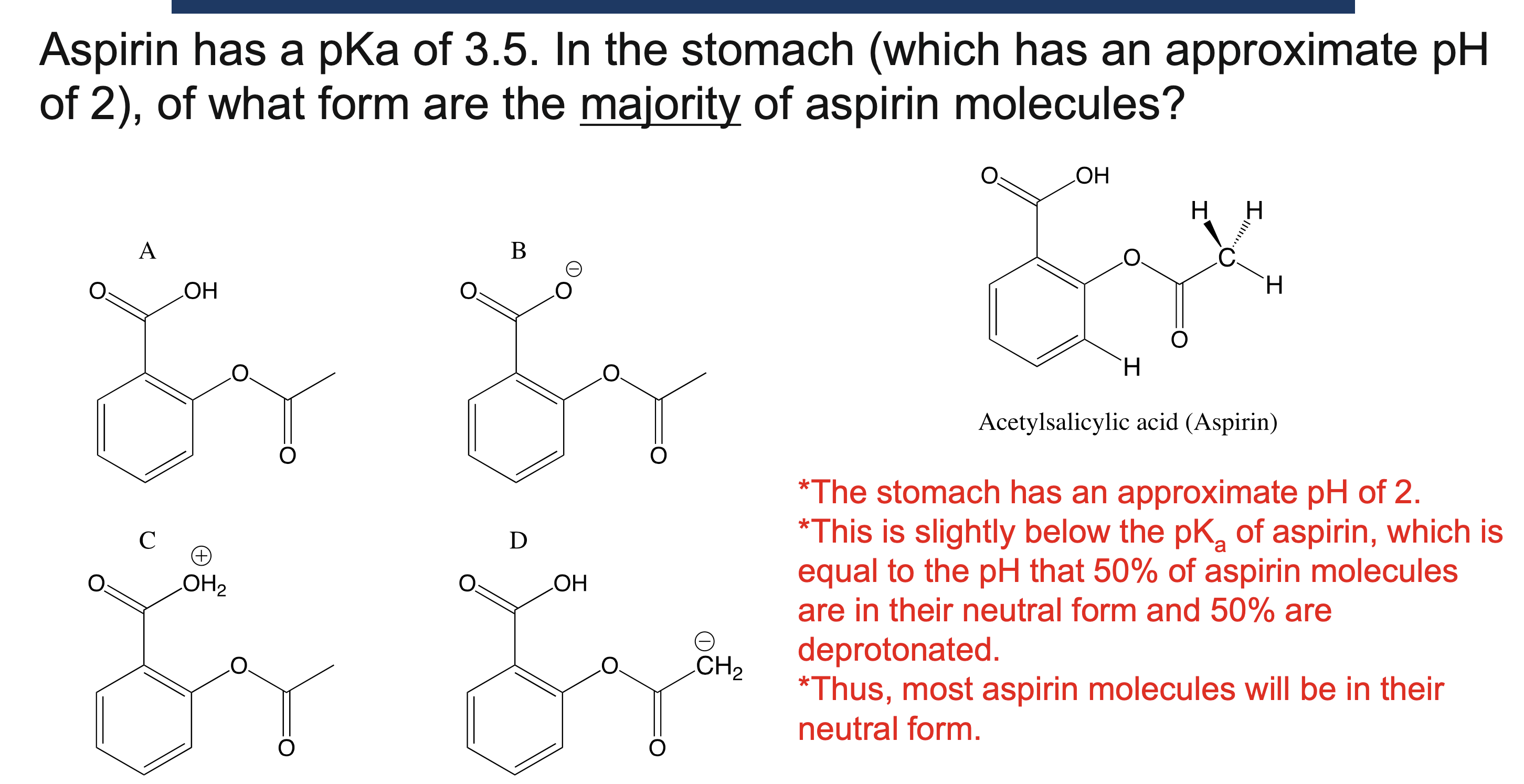
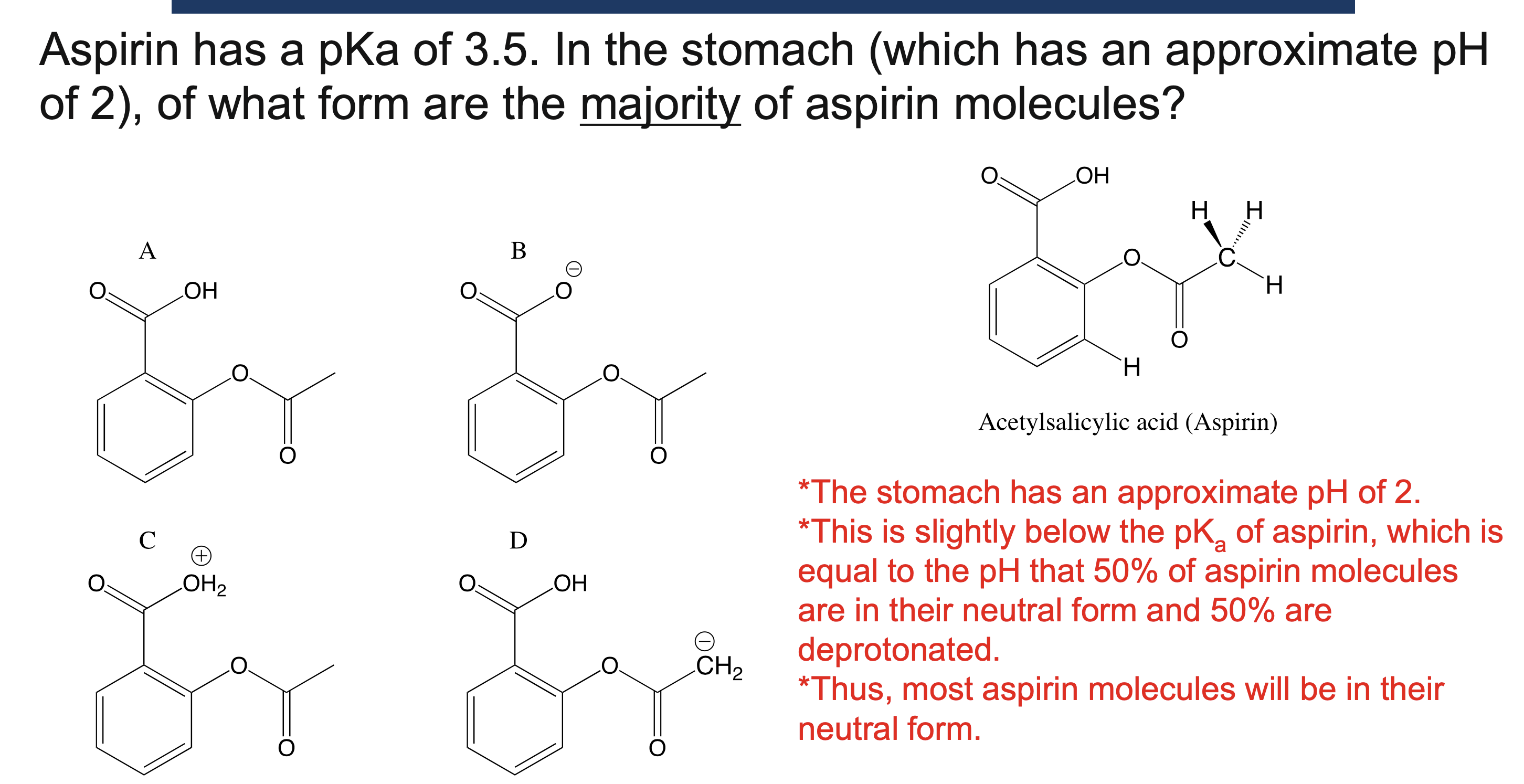
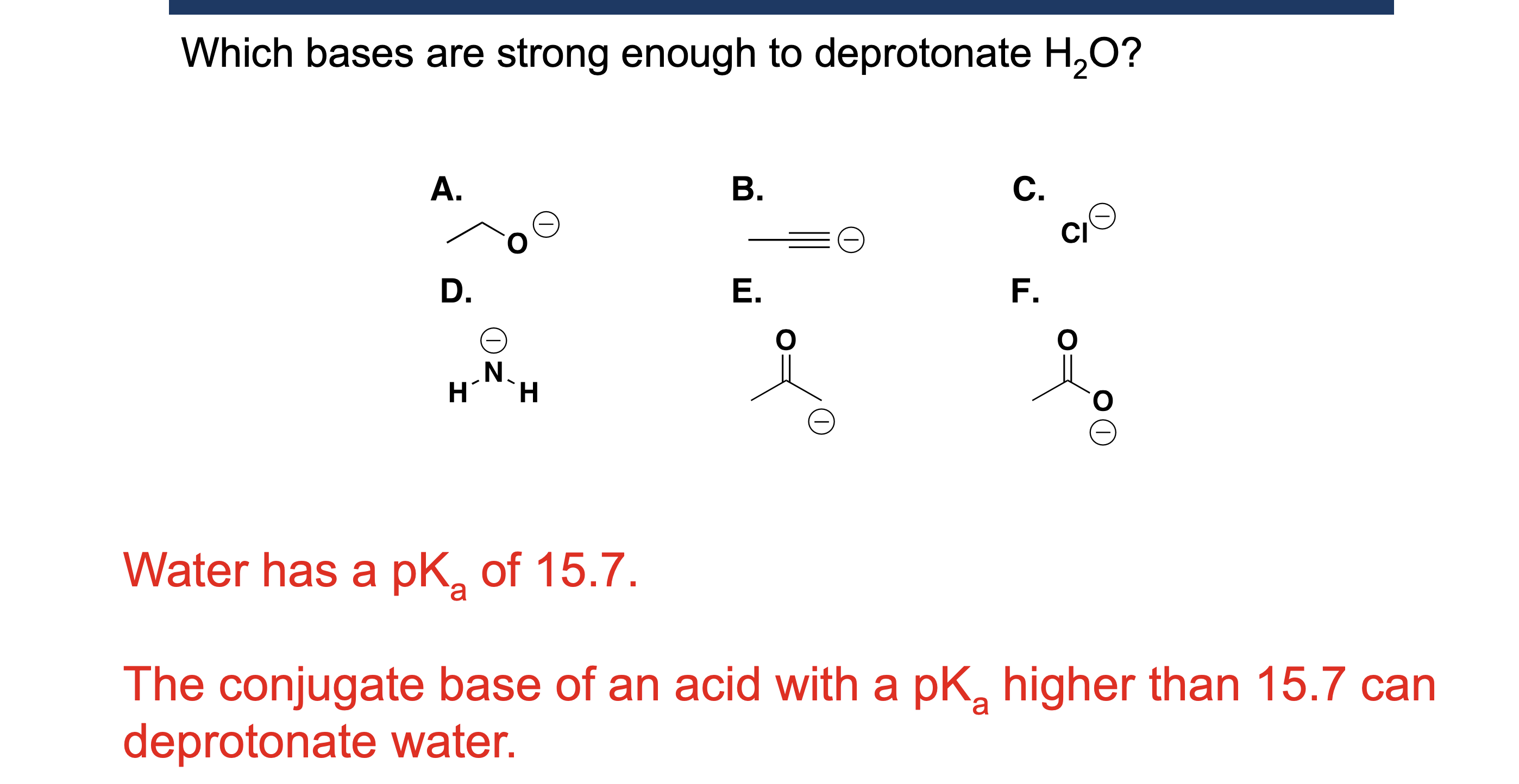
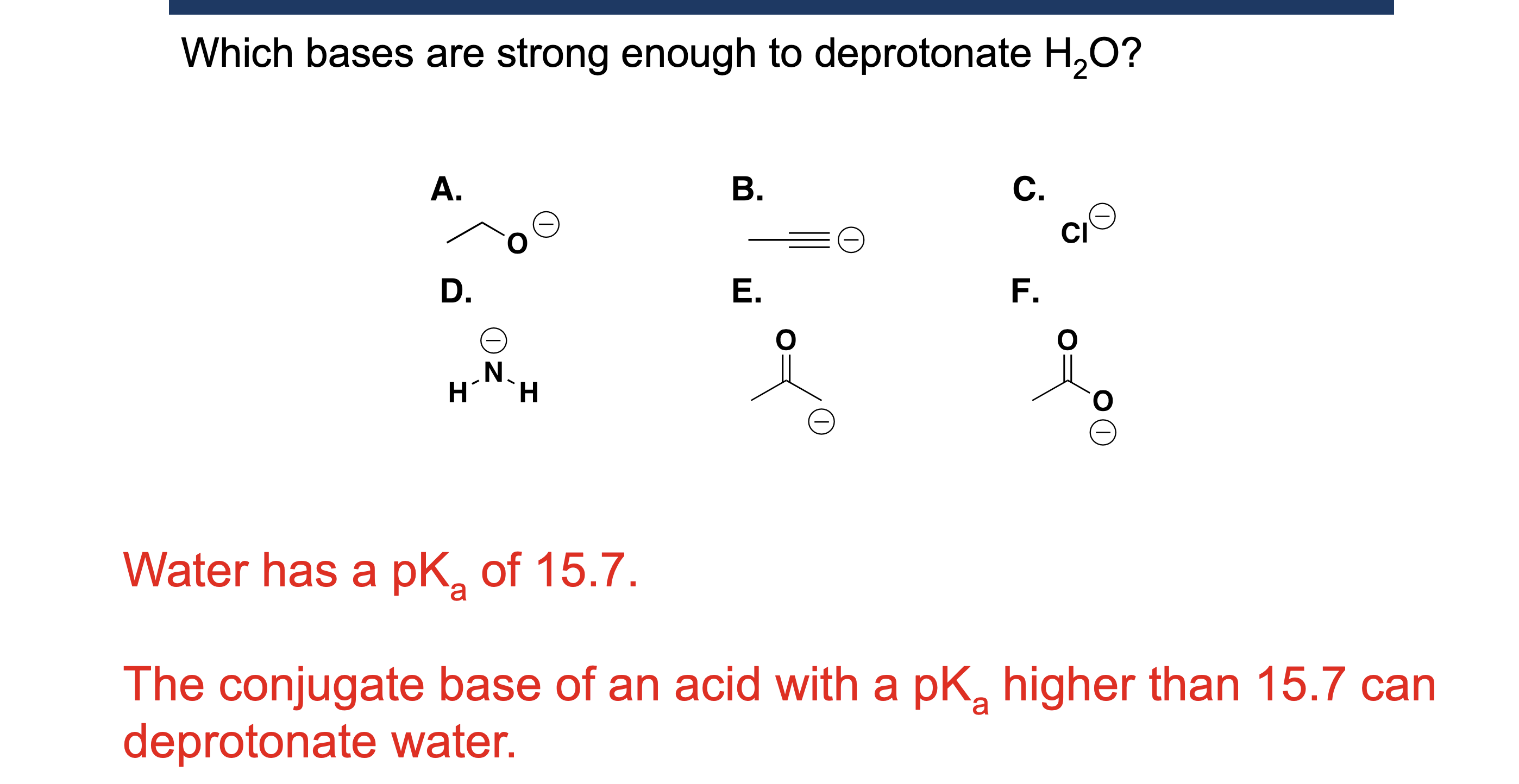
Why must a solvent not react in an acid/base reaction?
Because if the solvent reacts, it interferes with the intended acid/base chemistry.
Why is water a special case as a solvent in acid/base reactions?
Because water can act as both an acid and a base.
What is the leveling effect of water?
Water “levels” strong acids to H₃O⁺ and strong bases to OH⁻, making them appear equally strong.
Why can acids stronger than H₃O⁺ not be used in water?
Because water immediately converts them into H₃O⁺.
Why can bases stronger than OH⁻ not be used in water?
Because water immediately converts them into OH⁻.
When should water NOT be used as a solvent?
When studying or using very strong acids or bases, due to the leveling effect.
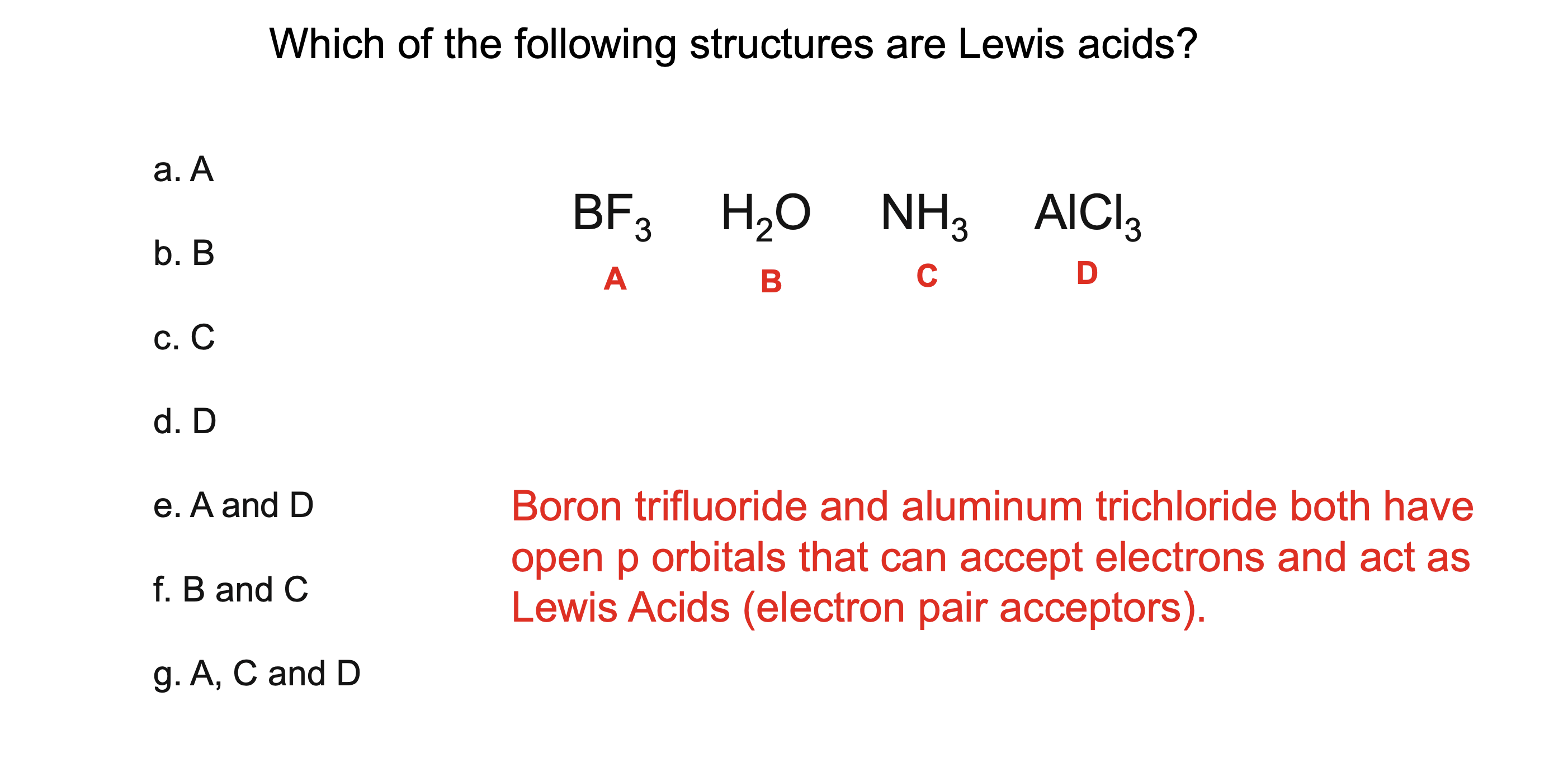
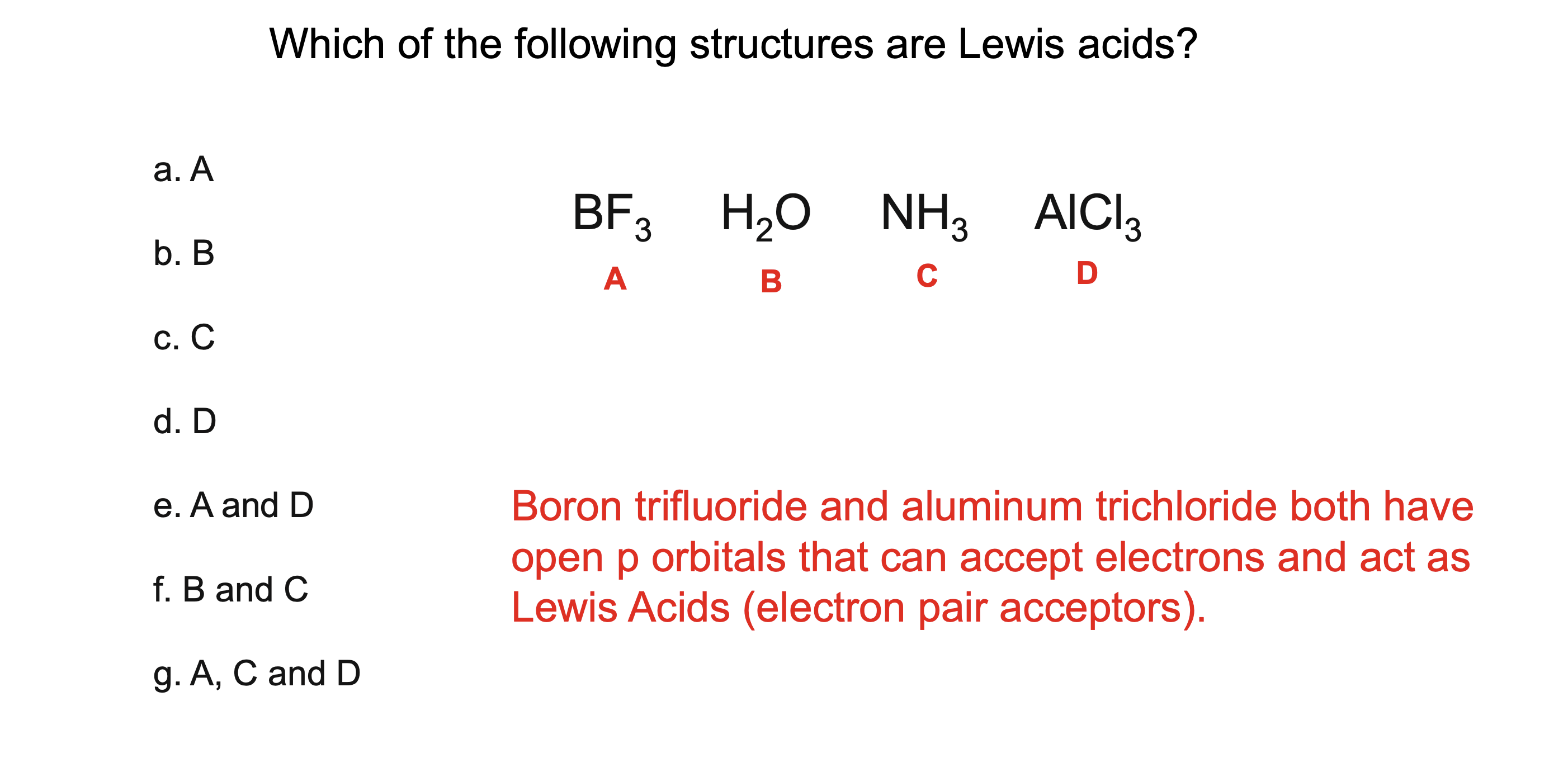
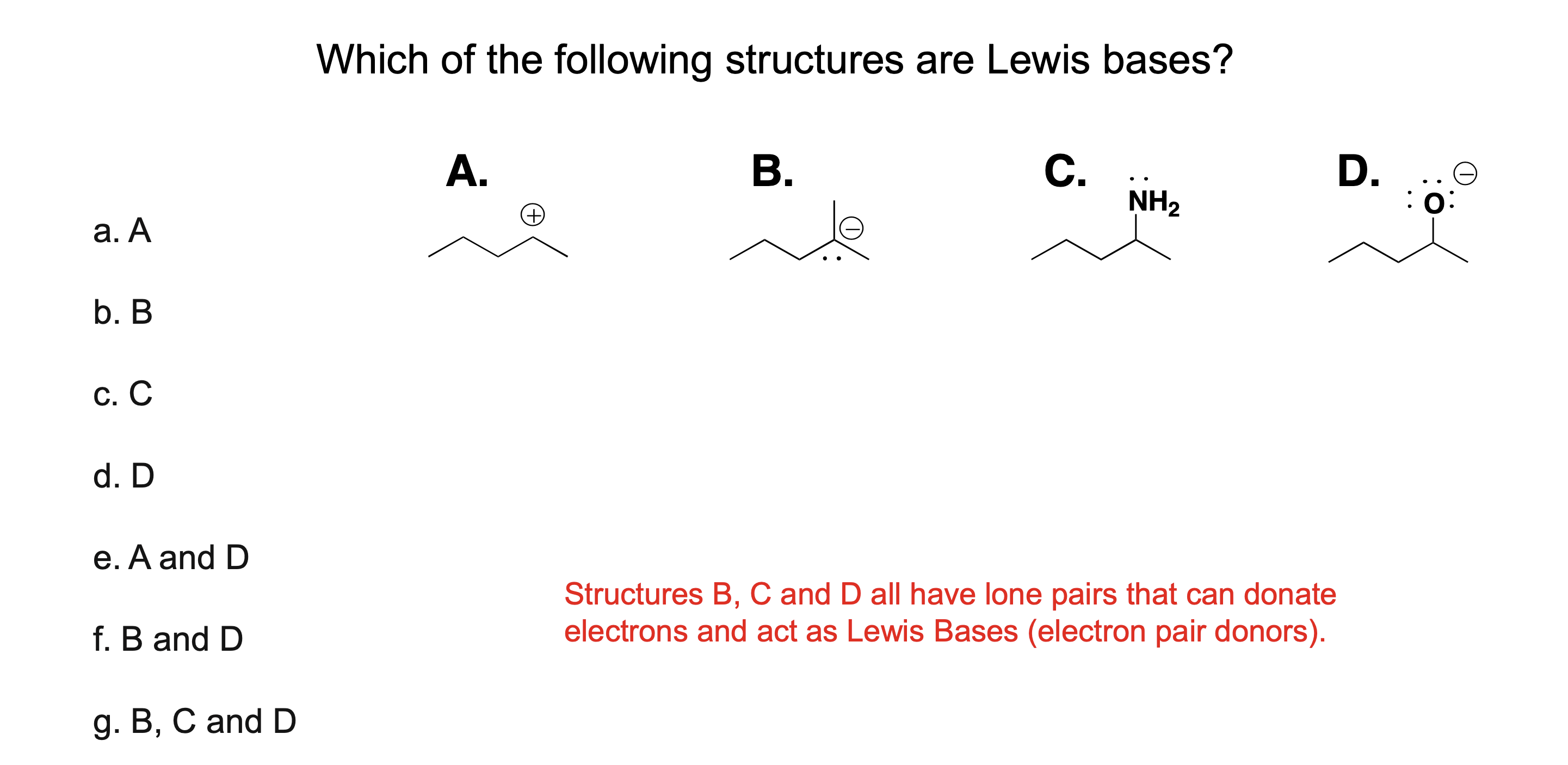
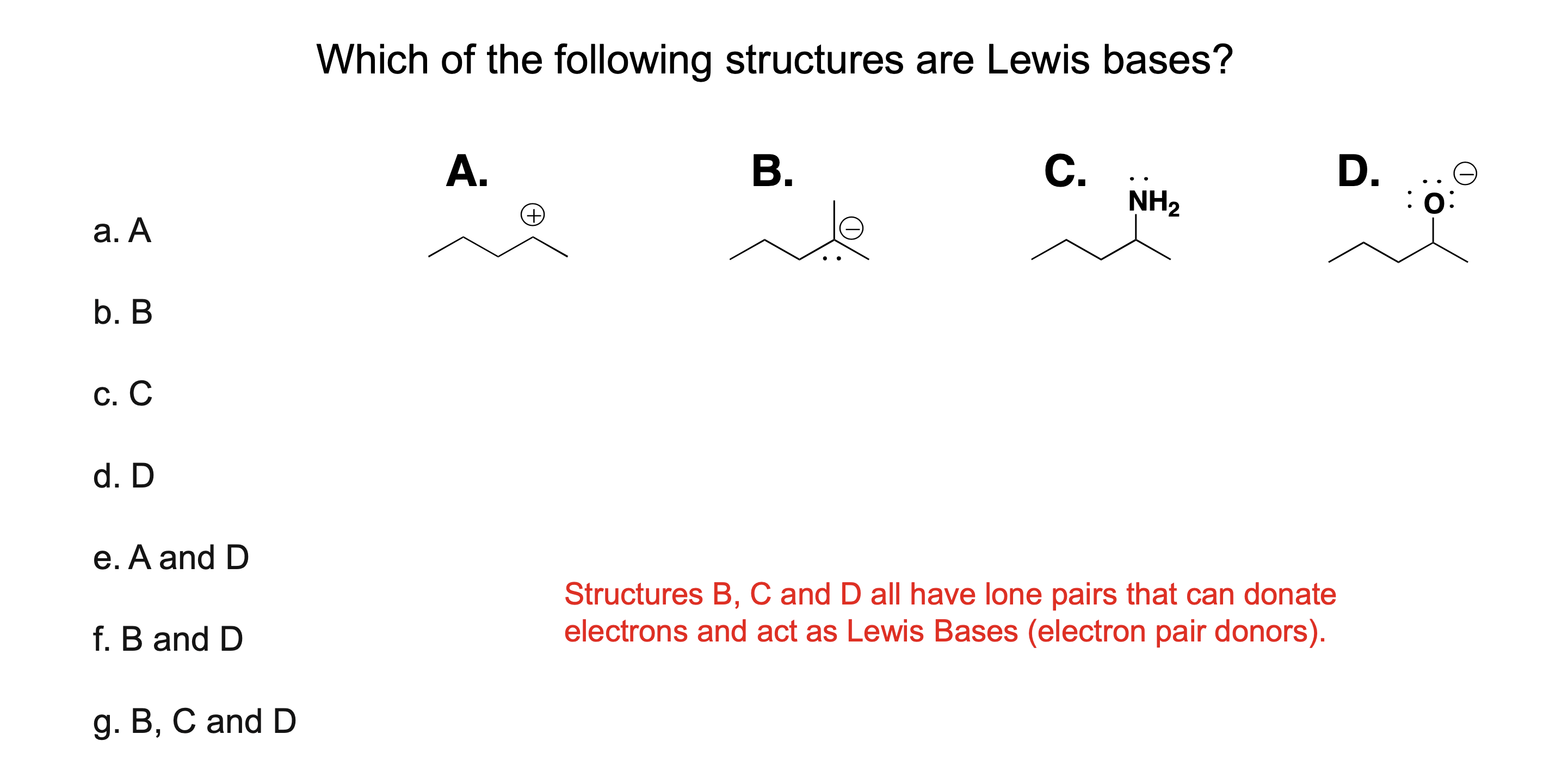
What is a Lewis acid?
A substance that accepts a pair of electrons
What is a Lewis base?
A substance that donates a pair of electrons
What do Lewis acids and bases share when they react?
They share an electron pair
Are all Brønsted–Lowry acids also Lewis acids?
Yes.
Are all Brønsted–Lowry bases also Lewis bases?
Yes.
Why is the Lewis definition broader than Brønsted–Lowry?
Because it includes reactions without proton transfer, only electron sharing.