MAAE 2300 Fluid Mechanics Final Exam
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
Describe the atomic arrangement of a solid
Atoms are arranged in a lattice with a constant molecular spacing
Describe the intermolecular forces in solids
Large cohesive forces
Describe relative motion in solids
No relative motion other than vibrations
What is a distinguishing feature between a solid and liquid
Solids can resist shear stresses
Describe the intermolecular structures of fluids
Constant average spacing
Compare the intermolecular forces between solids and liquids
For solids they are far stronger than liquids
Why are liquids considered incompressible
average intermolecular spacing is constant
Describe the intermolecular forces and spacing in a gas
Molecules can freely travel because the intermolecular forces are weak
Why does a gas completely fill the space which it exists in?
Typically, gravitational forces are negligible compared to buoyancy forces.
What is the continuum?
The volume for which the number of atoms inside is nearly constant with time, so, the density can be considered constant.
What is the continuum volume for fluid density?
10^-9mm³
Why is the continuum important?
So we can apply differential calculus over this volume when it is considered to be small enough
Why do we need dimensions and units?
To ascribe quantitative properties to the physical condition of a fluid
What is a dimension?
The measure by which a physical variable is expressed quantitatively.
Denoted with curly brackets. {L}
What is a unit?
A particular way of attaching a number to the quantitative dimension with meaningful reference.
Denoted by square brackets [m]
What are the five primary dimensions in fluid mechanics?
Mass, length, time, temperature, and electerical current.
{M}, {L}, {T}, {Ω}, { I }
What are the dimensions for force {F}
{ MLT^-2 }
What are the four International Units?
[kg]
[m]
[s]
[K[
What are the four british gravitational units
[ft]
[s]
[degrees R]
[lbf]
What are three mistakes to avoid when applying math to a physical system?
Never mix BG and SI units in a calculation
Never mix prefixes when adding or subtracting
Never use dimensionally inconsistent equations
What does the principle of dimensional homogeneity state?
All added terms must have the same dimensions
Why did air canada flight 143 boeing 767-233 go down in 1983
Conversion between SI and BG units was wrong for the fuel, and there was only half what they thought. Air Canadas first plane to use metric measurements
Why did mars climate orbiter go down in 1999
System from lockheed martin communicated units in US customary whren NASA expected them in SI
What are two types of fluid properties and what do they stand for?
Extensive is related to the total mass of a system. Intensive is independent of the mass of a system
What is the limitation of an intensive property?
Applies to any mass within the continuum
What are the 7 intensive fluid properties?
Pressure and Stress
Density
Specific Weight
Specific Gravity
Bulk Modulus
Temperature
Viscosity
What is pressure?
P = dF/dA. The average pressure is F/A
For fluids, is density more sensitive to temperature or pressure?
temperature
What is the bulk modulus
The change in pressure ro reduce a volume.
E_v = -dp/(dV/V)
Compare E_v for gasses and liquids
Liquids have a high Ev, gases have a low Ev
Convert degrees Rankine to degrees Fahrenheit
degrees Kelvin to degrees Celsius
degrees Fahrenheit to degrees celsius

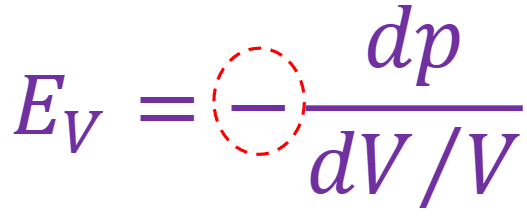
What is the purpose of the negative in the formula for Ev?
This is because dV is negative
What quality does Ev measure?
Resistance to compression.
What quality does viscosity measure?

What causes viscosity?
Momentum exchange between fluid molecules in the fast layer and slow layer. High momentum in the upper layers absorbed by the lower layers.
What does newtons law of viscosity state?
That the shear stress applied to a layer is directly proportional to the shear strain rate of that layer with respect to reference at the wall.
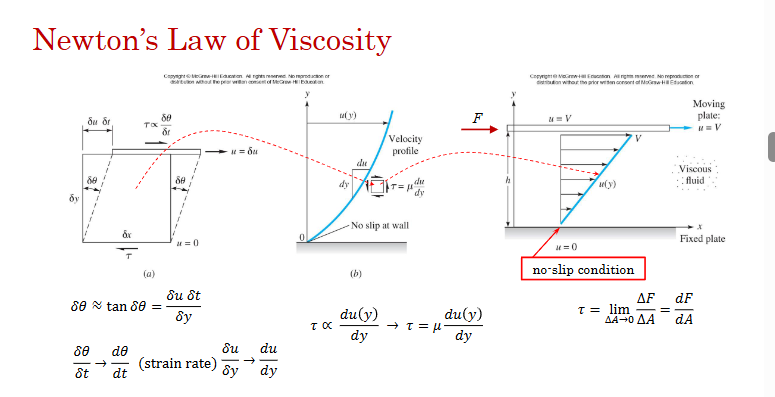
What is μ
The absolute or dynamic viscosity that measures resistance to fluid movement.
What is true for a newtonian fluid
Always the same viscosity
How is viscosity quantified for non-newtonian fluids?
A function of the strain rate
What are two key non-newtonian fluids?
Dilatant and Pseudoplastic
Compare dilatant and pseudoplastic fluids
For a dilatant fluid the viscosity increases with the strain rate. This is why you should not move quickly in quicksand
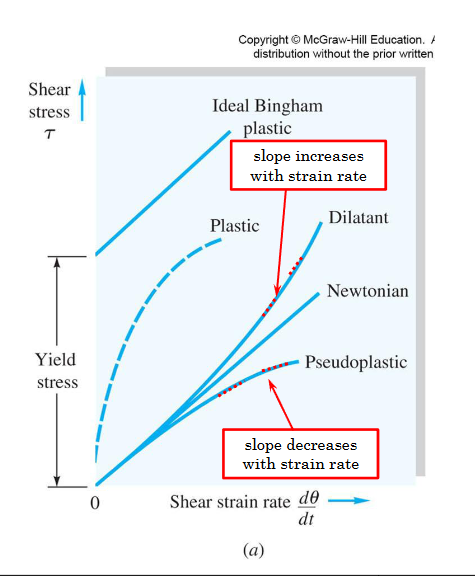
How do you use apparent viscosity in calculations?

How does viscosity change with pressure?
Increases with pressure slightly
How does viscosity change with temperature
What are the two equations used to fit viscosity variation with temperature
Andrade’s equation and Sutherland equation where B and C are constants

WHat do we call viscosity per density?
Kinematic viscosity
WHat is considered an ideal fluid?
One that is inviscid and incompressible
What is an inviscid fluid?
One that has zero viscosity, meaning, it will not form a boundary layer
What is the force that attracts molecules in a liquid
cohesion
What is the force that attracts molecules between a liquid and container
adhesion
Why do liquids prefer to be spherical?
Minimize surface area to volume ratio
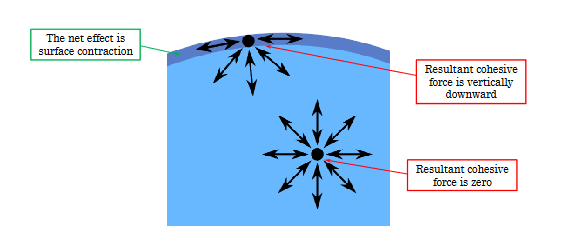
What is the definition of surface tension? What does it depend on?

What are two other names for surface tension?
free - surface energy; work per increase in the surface area of the liquid
How can free energy be interpreted from surface tension?
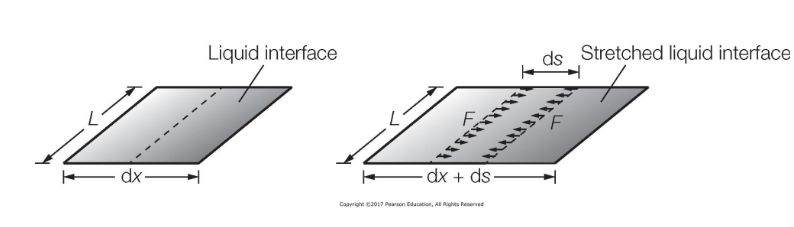
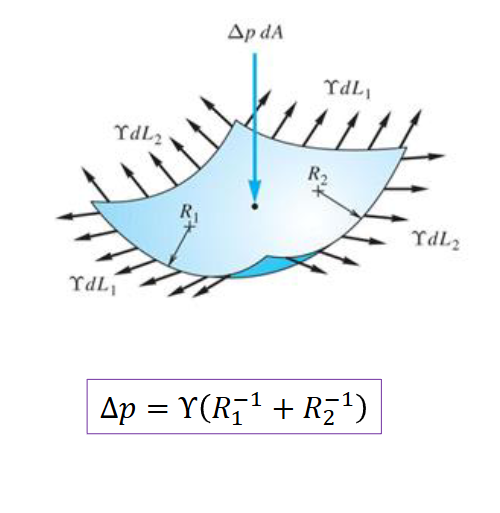
Derive the formula for pressure inside of a droplet and a bubble.
droplet is 2Γ/R, bubble is 4Γ/R
What is the general pressure inside of a fluid shape?
How do we distinguish between a concave and convex meniscus?
Whether the forces of adhesion are less or greater than the forces of cohesion
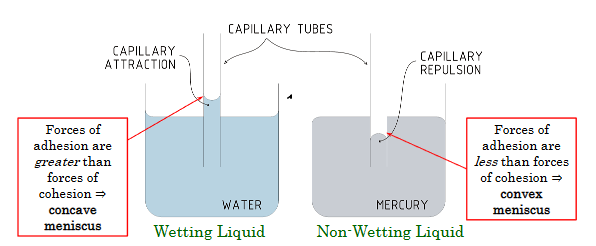
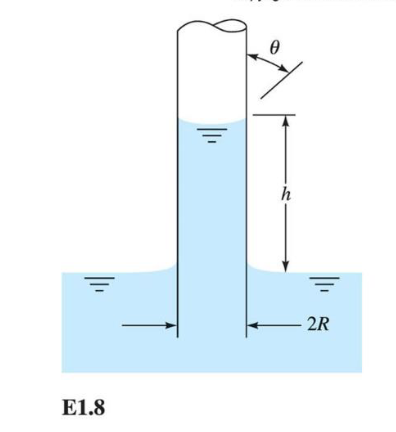
Find an expression for the change in height for a meniscus exposed to the atmosphere.
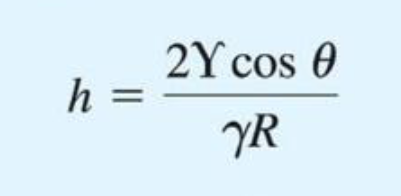
What is the hydrostatic condition?
px=py=px=p.
This states that for a point, all the pressure is the same, and is therefore a scalar value.
Why does a body in contact with a fluid experience a force?
Pressure
What can we say about another point in a fluid when the pressure changes at a different point?
Use pascals law.
A pressure change somewhere in a confined fluid will be experienced everywhere by that fluid.
What is the formula for static pressure variation
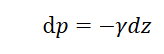

Is this true for all fluids?
No, only if we assume the fluid is incompressible
What is vacuum pressure?
Assumes the atmosphere is larger for a positive value

What is gage pressure

What is the pressure head
the height of a column of liquid that produces
the (gage) pressure 𝑝gage:
This is the gage pressure at the bottom of the column
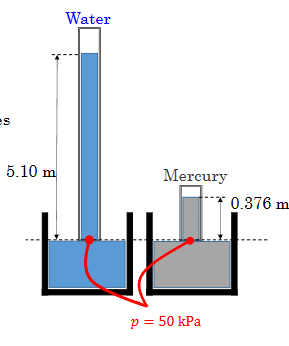
What is the equation for standard atmospheric pressure
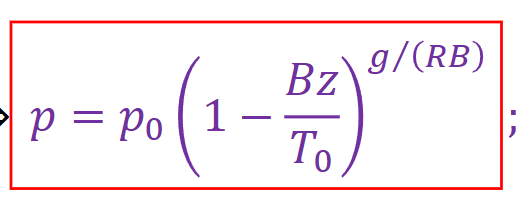
For a hydraulic jack, would we have a larger column diameter at the applied force, or the supported force?
Supported force
What is the force due to pressure on a general plane surface in a liquid?
Just the pressure at the centre of gravity (or the centroid for a non homogenous body) times the total submerged area.
Is the force on a hydrostatic surface dependant on the shape of the plate?
No, so long as the centroid does not change in height when the shape changes
What does ycp measure?
The distance below the centroid along the surface of the plate
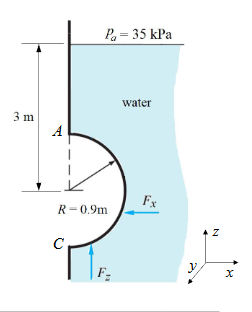
How do we find the resultant force and its line of action for a curved surface?
Just consider x and y separately.

What does the centroid for the vertical component of a curved surface correspond to?
Just the centroid of the plane projection
How to find the vertical force magnitude for this geometry?
It is just the specific gravity of water for the empty volume.
What is an important consideration to make for manometer analysis?
We can only draw isobars across the same fluid
WHat is a key consideration for resultant forces on submerged walls?
There is both a horizontal and vertical component
What principle must be used when determining the buoyancy of an object?
Archimedes law of buoyance
State Archimedes law of buoyancy
A body immersed in a fluid experiences a vertical buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces

How much water is in the bucket
A volume with weight of 2kg
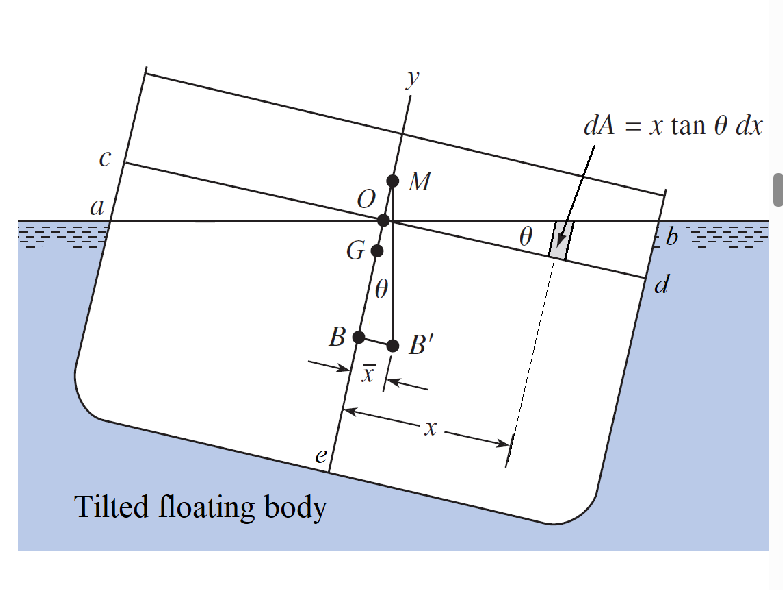
How does this diagram relate to buoyancy and stability?
M must be above G when an object is rotated by a small angle for it to be stable
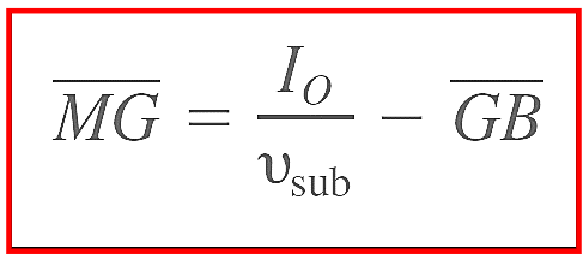
What is each term in this equation
The distance between the metacentre and the gravitational centre is equal to the distance between the metacentre and the buoyancy centre minus the distance between the gravitational centre and the buoyancy centre
What is always assumed for a floating object when assessing its stability?
M and G must both be above B
What is the condition for stability?

how is Io interpreted for a stability analysis of a floating body?
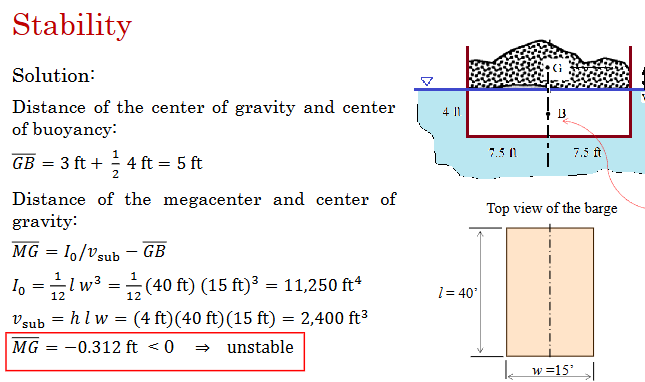
How do we find the centre of buoyancy?
This is always the centroid of the submerged volume.
What is considered a rigid body fluid?
A fluid with no relative motion between layers
What is the general equation that relate pressure to acceleration of a fluid?

Why is g positive in the general pressure from an accelerating fluid
Because g points downward, and pressure increases going downward. Its about relativity. When you sit down, you are “accelerated“ upwards
How is the free surface found for an accelerating object?
Apply the conservation of volume, and consider that the free surface is above a lid.
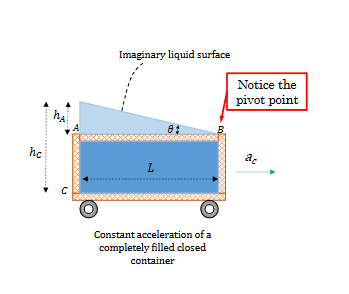
How do we find the free surface for a spinning rigid fluid?
Consider z=0 at the vertex of the polynomial. Apply conservation of volume to find Z, such that, the still water level is midway between z=0 and z(R).

How do we find the gradient line of a rotating rigid body fluid?
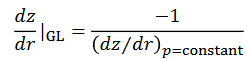
How is bernoulli’s equation derived
Force analysis on a differential fluid element moving along a streamline
What are two key assumptions made when deriving bernoulli’s equation
The streamline does not, itself, move.
The flow is incompressible (which implies temperature does not change!)
What are the three terms in bernoulli’s energy equation
Understand that this is energy per unit mass
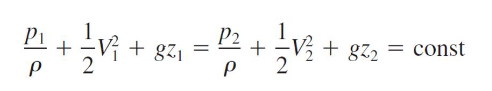
What is the head form of bernoulli’s equation
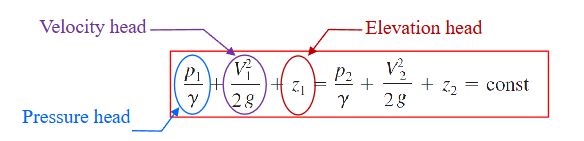
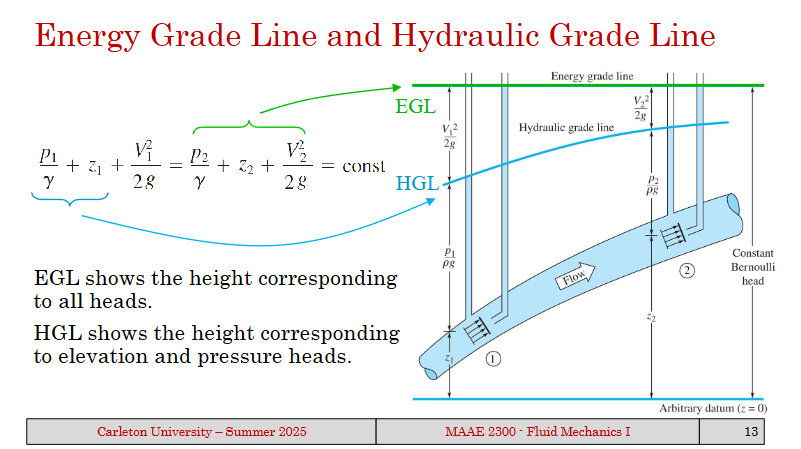
What are the two heads given special names in the bernoulli head equation?
The energy grade line and the hydraulic grade line
What are the six assumptions for benoullis’s equation
Steady flow
Frictionless flow (inviscid)
No shaft work
Incompressible flow
No heat transfer
Flow along a streamline
What are 6 systems five in the lecture that violate bernoulli’s equation?

What is the total pressure from all bernoulli terms called?
Stagnation pressure