Occipital Lobe
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Cornea
80% of the eye’s focusing power. Differences in shape cause astigmatisms
Pupil
Expands and contracts like a camera lens
Lens
20% of the eye’s focusing power. The Ciliary muscles change its shape to be flatter or curved depending on the focused object
Retina
Contains photoreceptive cells, the fovea and a blind spot
Fovea
Part of the retina with the highest visual acuity
Optic Nerve
Part of the peripheral nervous system, signals from the eye leave to the CNS
Upper Retina Processes Which half of an image?
The lower half of the image
The lower retina processes which part of an image?
The upper half of an image
Photoreceptors
Type of neuron receptive to light
Two kinds of photoreceptors:
Rods and Cones
What kind of photo receptors are primarily found in the peripheral visual field
Rods
Rods are most active in what level of light?
Lower levels of light
Rods can process what type(s) of wavelengths of light?
Monochromatic
Do rods have high or low visual acuity?
Low visual acuity
Acuity
Precision of perceiving detail
How sensitive are rods?
Highly sensitive
There are approximately how many rods in the eye?
~120 million
Cones are primarily found where?
In the fovea/central vision
Cones are primarily active in what level of light?
Higher levels of light
What wavelengths of light do Cones process?
Color vision: Blue, Green, Red
S-Cones Process What kind of light?
Blue light (short-wavelength light)
M-Cones process what wavelength of light?
Green light (medium wavelength)
L-Cones process what wavelength of light?
Red light (long wavelength)
The visual acuity of cones is?
High
How sensitive are cones?
Low sensitivity — Accurate but need illumination to detect changes
How many cones are in the eye?
~6 million
The blind spot in the eye contains
No receptors
The fovea contains
A majority of the cones in the eye
The eye’s blind spot is approximately where?
~15 degrees laterally of the fovea on the nasal retinal side
The axons from the retinal ganglion cells form?
The optic nerve
The optic nerve is formed by
The axons from rentinal ganglion cells
Horizontal cells
Allow communication between rods and cones and bipolar cells
When light hits the retina its processed last by:
Retinal ganglion cells
Bipolar Cells
Receive signals from rods and cones and transmits the signals to retinal ganglion cells
Horizontal Cells
Connects photoreceptors and bipolar cells laterally
Amacrine cells
Connect bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells laterally
How many fibers make up the optic nerve
1 million
Retinal circuitry
Converges a large among of visual inputs into more condensed outputs
The input to output ratio of Cones
1:1
The input to output ratio of Rods
8:1
Cone-fed circuits are
Low convergence circuits
Rod-fed circuits are
High convergence
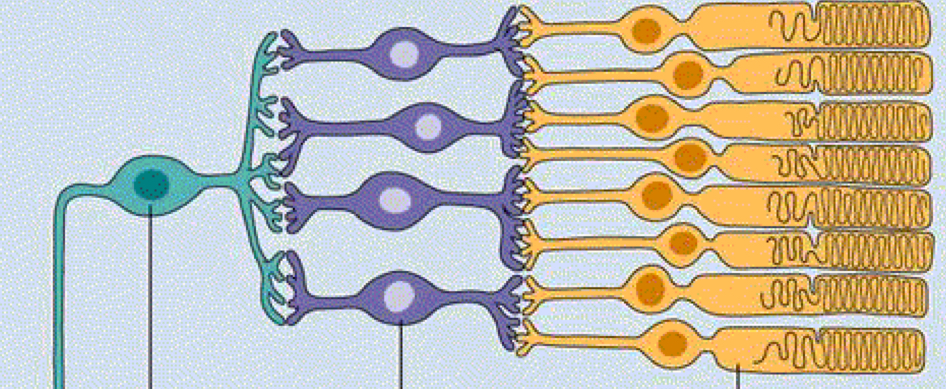
Channels of info broadcasting to the optic nerve
M- and P-Channels
The left half of each retina goes
To the left hemisphere
The right half of each retina goes
To the right hemisphere
Temporal retina sees
The nasal visual field
The nasal retina sees
The temporal visual field
Magnocellular layers of the LGN
Get inputs from rods, process luminance, motion, depth. Is faster
Parvocellular Layers of the LGN
Input from cones, processes colour, high acuity vision. Is slower
Koniocellular interlaminar layers
Gets input from rods and codes, processes blue light, motion, and has a role in the circadian rhythm
Layers 1-2 in the LGN
Magnocellular
Layers 1-6 in the LGN
Parvocellular
Interlaminar layers
Koniocellular
How many Koniocellular layers are in the LGN
6
Meyers Loop
Optic radiations carrying information about the upper visual field to the primary visual cortex
Dorsal Optic Radiations
Carry information about the lower visual field from the LGN to the primary visual cortex
Superior Retinal Quadrants see
the inferior visual field
Inferior reitinal quadrants see
the superior visual field
Superior calcarine sulcus
Processes the inferior (lower) visual field
Inferior calcarine sulcus
Processes the superior (upper) visual field
Parietal-occipital sulcus
Is the boundary between the occipital and parietal lobes
The first cortical region that receives input from the retina
V1; the primary visual cortex
Layer 4C Alpha in the V1
Magnocellular (V1)
Layer 4C Beta in the V1
Parvocellular (V1)
Layer 3 in the V1
Konicellular (V1)
V3 Dorsal
Uses visual information to control actions
V3 Ventral
Uses visual information for perception
Lateral Occipital (LO)
Processes outline and contours of objects
V4 and V8
Uses visual information for color
Damage to V4 and V8
Results in cortical colour blindness
LIP
Has a role in eye movements and attention
V7
Important for visuomotor transformations
Extrastriatal Body Area (EBA)
Processes bodies, body language, fine tuning movements
Middle Temporal Cortex (MT)
Responsible for motion perception
Damage to MT
Results in problems perceiving movement
FFA (generally)
Responsible for faces
Parahippocampal Place Area (PPA)
Specialized for places, spatial memories and cognitive maps
V1 is topographically organized
Meaning, damage to a specific part of V1 results in blindness in a specific portion of the visual field
Hemianopia
Homogenous loss of vision
Monocular blindness
Loss of vision in one eye
Bilateral Hemianopia
Loss of vision in the temporal fields
Nasal hemianopia
Loss of vision in the nasal field of one eye
Homonymous Hemianopia
Loss of the temporal visual field in one eye and the loss of the nasal field in the other
Quadrantanopia (lower)
Loss of vision in the left or right inferior quadrant of both eyes
Quadrantanopia (upper)
Loss of the superior quadrant of the left or right visual field
Damage to the optic nerve in one eye
Results in monocular blindness
Damage to the optic chiasm
Results in bitemporal hemianopia
Damage to an uncrossed fiber coming from one eye
Results in nasal hemianopia
Damage to the optic tract
Results in homonymous hemianopia
Damage to the upper (superior) V1 radiations
Results in Quadrantanopia (lower)
Damage to the lower (inferior) V1 optic radiations
Results in quadrantanopia (upper)
Damage to upper and lower V1 radiations
Results in homonymous hemianopia
Damage to the V1 in the right hemisphere
Results in hemianopia with macular sparing
Dorsal Processing stream
Guides action
Ventral processing stream
Perception and recognition
Visual Form Agnosia
Without knowledge of visual form, cant recognize objects visually
Visual Form Agnosia = ____ Stream damage
Ventral
Optic Ataxia
Impaired at visually guided actions
Optic ataxia = ____ Stream Damage
Dorsal