Lecture 5: Indexing and Storage
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is an index in a database?
A separate data structure that organizes data records on disk to speed up searches on certain fields.
Like a book index or library card catalog, it maps a search key to where the data is stored.
What does an index speed up?
Selections (queries) involving the search key fields.
Example: an index on mage speeds up queries filtering on mage.
What is a search key?
Any subset of a table’s attributes used to build an index.
Examples:
(mage)(mschool)(mschool, mage)
Do search key values have an order?
Yes. The order matters.
Example: Index on (mschool, mage) is different from index on (mage, mschool).
What is a data entry in an index?
Entry given when we look up k.
Each record in the index file.
If the search key is value k, the entry is written as k*
and contains info that lets you find 1 or more matching data records.
What is a clustered index?
An index where the physical order of index entries roughly matches the physical order of the data records on disk.
This means related records are stored close together.
Why does clustering matter?
Retrieval cost varies greatly:
Clustered index → fast sequential access (data stored near each other)
Unclustered index → slow (data scattered across disk pages)
Which caluse is designed to filter results of GROUP BY?
HAVING
What will the condition WHERE M.mage >= ALL (SELECT M2.mage FROM Members3 M2) return?
The member(s )with the highest age
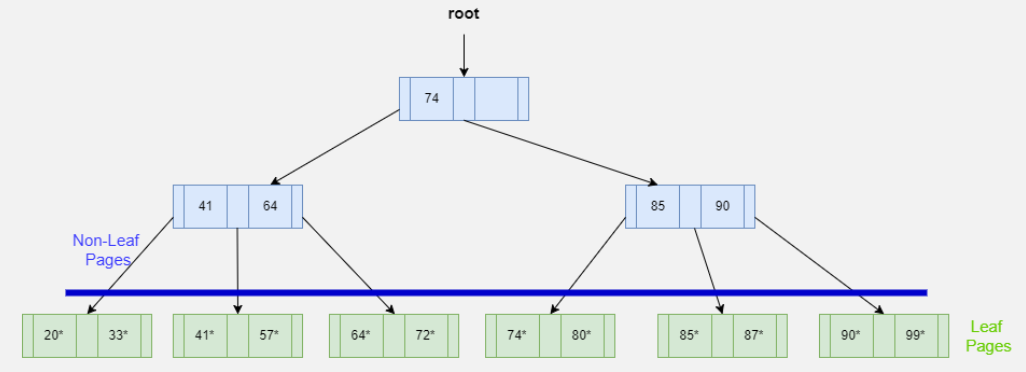
What are index nodes? What do they contain?
These are the upper levels of the index tree (ISAM or B+ tree).
What they contain:
Search key values (guideposts)
Pointers to child pages (other index nodes or leaf pages)
What they DO NOT contain:
Actual data entries (k*)
Records or RIDs
Overflow chains
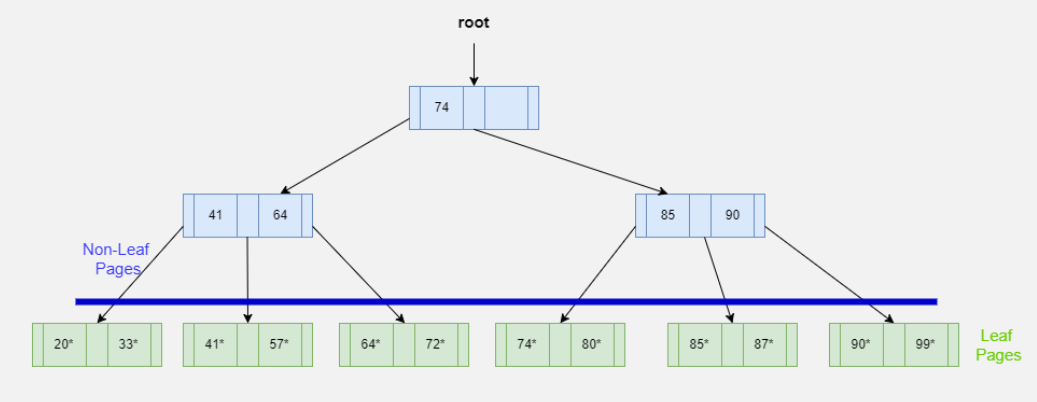
What are leaf pages? What do they contain?
Leaf pages are where the actual data entries live.
What they contain:
Data entries (k*)
Each k* contains I(k) → pointer(s) to real records
ISAM: What are overflow pages? What do they contain?
These are extra pages created when a leaf page runs out of space.
What they contain:
More data entries (k*) that didn’t fit in the leaf
Pointer to the next overflow page (linked list)
Purpose:
Handle insertions after the index was built.
(ISAM is static — leaf count is fixed, so new inserts go to overflow pages.)
NOTE: Overflow pages are not sorted → this slows down search.
ISAM: What happens to empty overflow pages?
Overflow pages are released if empty
ISAM: What happens to empty leaf pages?
Leaf pages aren’t released if empty
What does it mean that ISAM is a static index?
ISAM’s structure is fixed after creation:
Number of leaf pages is set at creation
Index nodes never change
Inserts/deletes affect only leaf pages
Overflow pages handle extra insertions
Cost of searching in ISAM
I/O cost: logF N where F = # entries/index page, N = # of leaf pages
What are 3 downsides of ISAM’s static structure?
Long overflow chains may form
Searching overflow chains can be slow
Values in index nodes may not match actual leaf values over time
What is the recommended way to reduce overflow chains in ISAM?
Create the index with 20% free space in each leaf page so future inserts fit before causing overflows.
OR
Rebuild/reallocate the index tree occasionally.
Why is ISAM good for concurrency?
Internal nodes never change → read-only → no locks needed
Only leaf pages change → only they require locking
Fewer locks → less waiting → faster performance