Chapter 1: Marketing and Marketing management
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is marketing?
activity to satisfy consumer needs
Right product, place, price and time (what is right for consumer)
Marketing Management approach
Customer orientation
customer and/or consumer is key and center
Managerial process
Analysis
Planning
Strategy
Implementation
Control
more recently
increasing importance of the role of institutions
Role of government
Role of marketing institutions: auctions, cooperatives
Today’s “affluent society”
quality > quantity
need for variation
New products, differentiation, innovation
Sustainability
The core concepts of marketing
Needs, wants and demand
Products
Value, cost and satisfaction
Exchange, transactions and relationships
Markets
Marketing and marketeers
Need
State of feeling of deprivation (shortage)
Want
desire for specific satisfier
Demand
want backed up by spending power and willingness to pay
Product
offers satisfaction to a need or a want
Physical product or service
Value
estimate of the capacity to satisfy a need
Exchange
one way to obtain a product
two parties
things of value for both parties
communication and delivery
freedom to accept or reject
belief in appropriateness to deal
Market
group of people sharing same need/want
Willing and able to engage in exchange
Aim: satisfy the need or want
Marketeer
party seeking exchange more actively
Counterpart = prospect
Marketing concept vs Selling concept
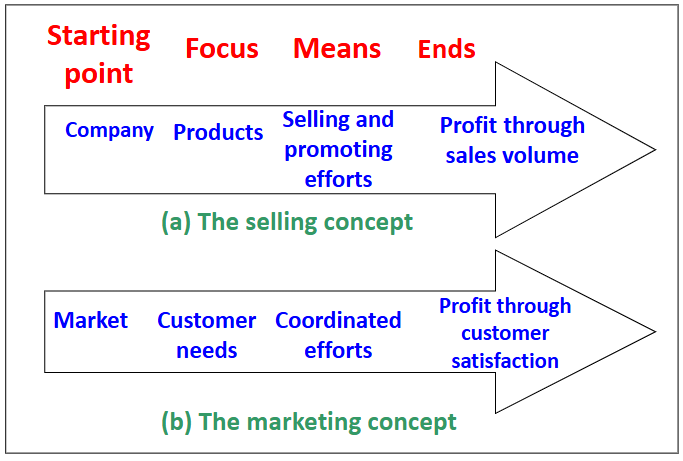
Possible company orientations towards markets
| Production orientation | Product orientation | Selling orientation | Market orientation |
Major attention point | Product availability (low cost, high production) | Product quality (good products) | Selling and promotion efforts | Needs and wants of target market → to deliver satisfaction |
The marketing concept
Market orientation (consumers’ needs, food companies) < - > (production orientation: produce more, farming businesses)
Customer focus
Coordinated effort
Profit oriented
4 pillars of the marketing concept
Market
As starting point, but a focus is needed
Choose your target market
Customer focus
Define need from customer viewpoint
Realise customer retention
Through providing customer satisfaction
Maximise the opportunity to complain
Coordinated effort
Involving all marketing functions
Together with other company departments
Profitability
Make profit to stay in business
By satisfying needs/wants/customers better than competitors do
==> combine 4 P’s towards optimal results:
Product
Price
Promotion/ Communication
Place of distribution
Driving forces to adopt the marketing concept
Sales decline
Slow market growth
Changing buying patterns
Increasing competition
food vs non-food expenditures
at home vs out of home consumption
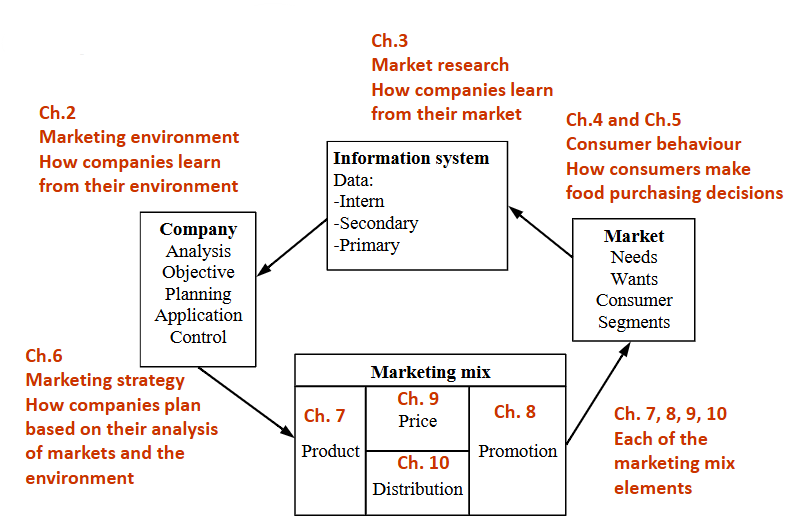
Marketing model in this course