521 Atraumatic Knee
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
22.7% (28.9% in adolescent populations)
annual prevalence of anterior patellofemoral pain
SI joint, low back, hip
common regional areas that refer to the knee
true
true or false? for most people, activity will aggravate knee pain and rest will typically relieve it
morning stiffness for 30 minutes, pain worsens at end of the day, knee can throb when lying down at night
typical presentation of pain with knee arthritis
pain not alleviated with rest, feels hot and swollen without history of trauma, night pain, calf or thigh pain after surgery or after period of immobilization
red flags in a knee exam
Q-angle
degree of angle when measureing from midpatella to ASIS and tibial tubercle.
13, 18
normal q angle is ___ degrees for man and ___ degrees for a woman.
patellar tracking issues
if Q angle is larger than normal, what specific knee issue could we consider?
anterior knee pain
most common clinical symptom of atraumatic knee conditions
lumbar (SLR, CSLR, slump, kemp's, repeated movements), SI Joint (PSIS pain → SI test cluster), Hip (FADDIR + MtS breakouts)
What is included in the "screening" for the knee?
MtS breakouts as needed
What is included in the regional joint exam for the knee?
ASLR, PSLR, double knees to chest, prone rock
How to break out a dysfunctional Multi-Segmental Flexion
Lumbar locked T-spine rotation, prone on elbows lumbar extension/rotation, FABER, Thomas Test, Prone press up
How to break out a dysfunctional Multi-Segmental Extension
measure hip extension in prone
If the Thomas test is (-) in the regional joint exam, what is the next step?
Lumbar locked T-spine rotation, prone on elbows lumbar extension/rotation, Hip IR and ER seated and prone
How to break out a dysfunctional Multi-Segmental Rotation
false
True or False? If Multi-Segmental Rotation is not dysfunctional, then we do not need to look at tibial IR and ER in the local exam of the knee
DF, PF, Inversion, Eversion
How to break out a dysfunctional SLS
lift back toes off ground, clear base of the 5th met
criteria to look for when assessing DF in the regional screen in standing
20º ROM
criteria to look for when assessing DF in the regional screen in prone (if not passed in standing)
PF foot, 40º ROM, No rolling to outside of the foot
criteria to look for when assessing PF in the regional screen in standing
40º ROM
criteria to look for when assessing PF in the regional screen in prone
medial foot clears floor (bilaterally)
criteria to look for when assessing Invesion in the regional screen in sitting
lateral foot clears floor (bilaterally)
criteria to look for when assessing eversion in the regional screen in sitting
tandem stance against wall, bending knees down
how to we break out a dysfunctional squat pattern (CKC DF)?
40º ROM, No valgus collapse, no heel lifting
criteria to look for when assessing CKC DF in the regional screen in standing
30º
criteria to look for when assessing CKC DF in the regional screen in prone
eversion, inversion, hip flexion, hip IR, Hip ER
if not assessed previously, what else (other than CKC DF) needs to be assessed for a dysfunctional squat pattern?
tibiofemoral joint, patellofemoral joint, tibial IR, tibial ER
major things to assess in the local biomechanical assessment of the knee
patellofemoral pain syndrome
anterior knee pain of insidious onset where the pain is on or behind the patella
walking up/down stairs, prolonged sitting, squatting, running
common activities which cause pain with PFPS
inflammation of patellar fat pad
hoffa's disease
inflammatory degenerative process on the backside of the patella and trochlear groove; cartilage irritation
chondromalacia
multifactorial
true PFPS =
glute med, glute max
weakness in these muscles are common sources of PFPS
flexion, adduction, IR
if the glute med and max are weak, what position will the hip want to be in
patella doesn't sit flat at rest
patellar tilt
high riding patella
patella alta
patellar tilt test, Clarke's Sign/Patellar Grind, Lateral pull test, eccentric step down, movie goer's sign
special tests of PFPS
Clarks' Sign
what PFPS test is being performed?
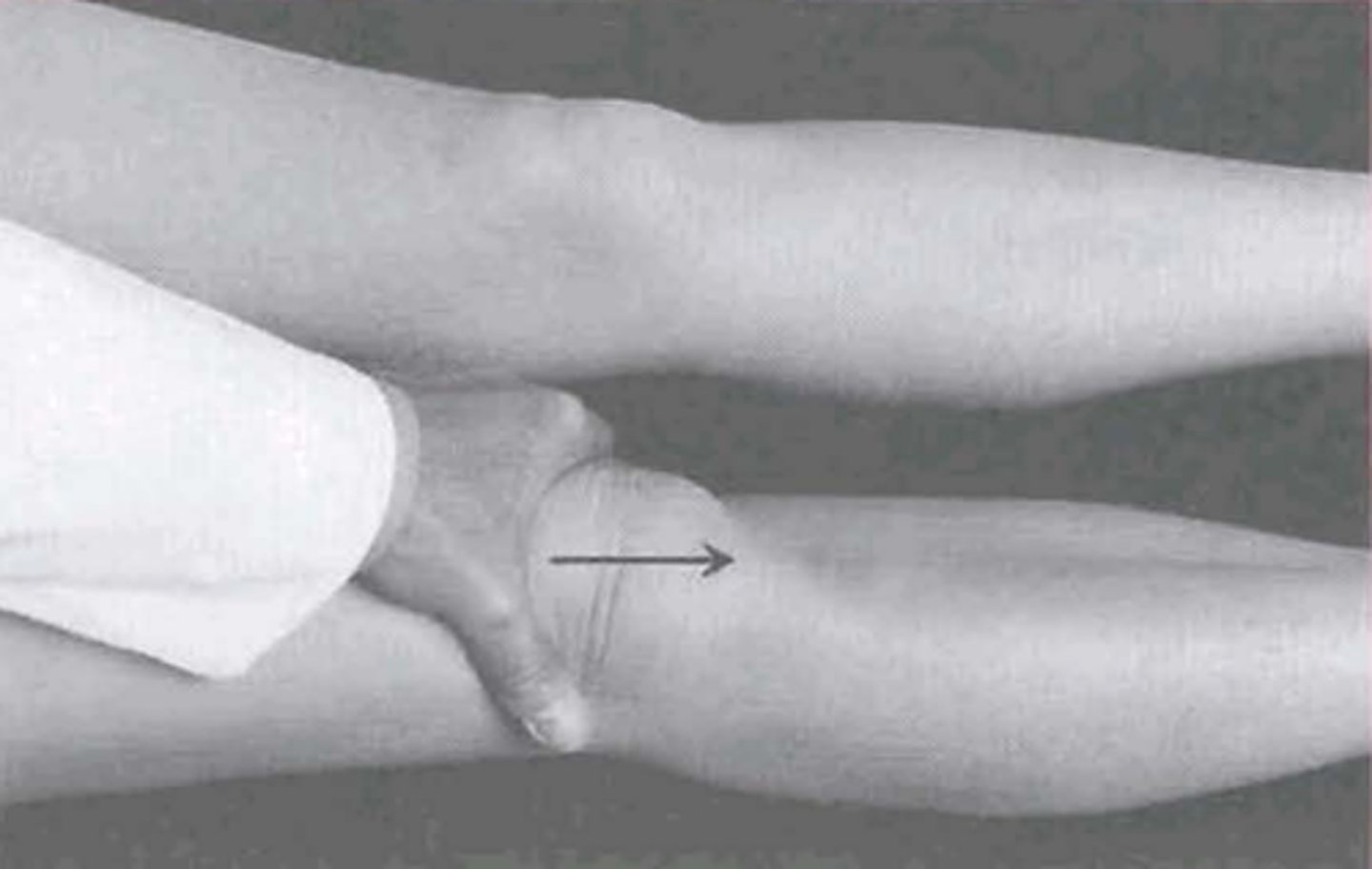
patellar tilt test
what PFPS test is being performed?
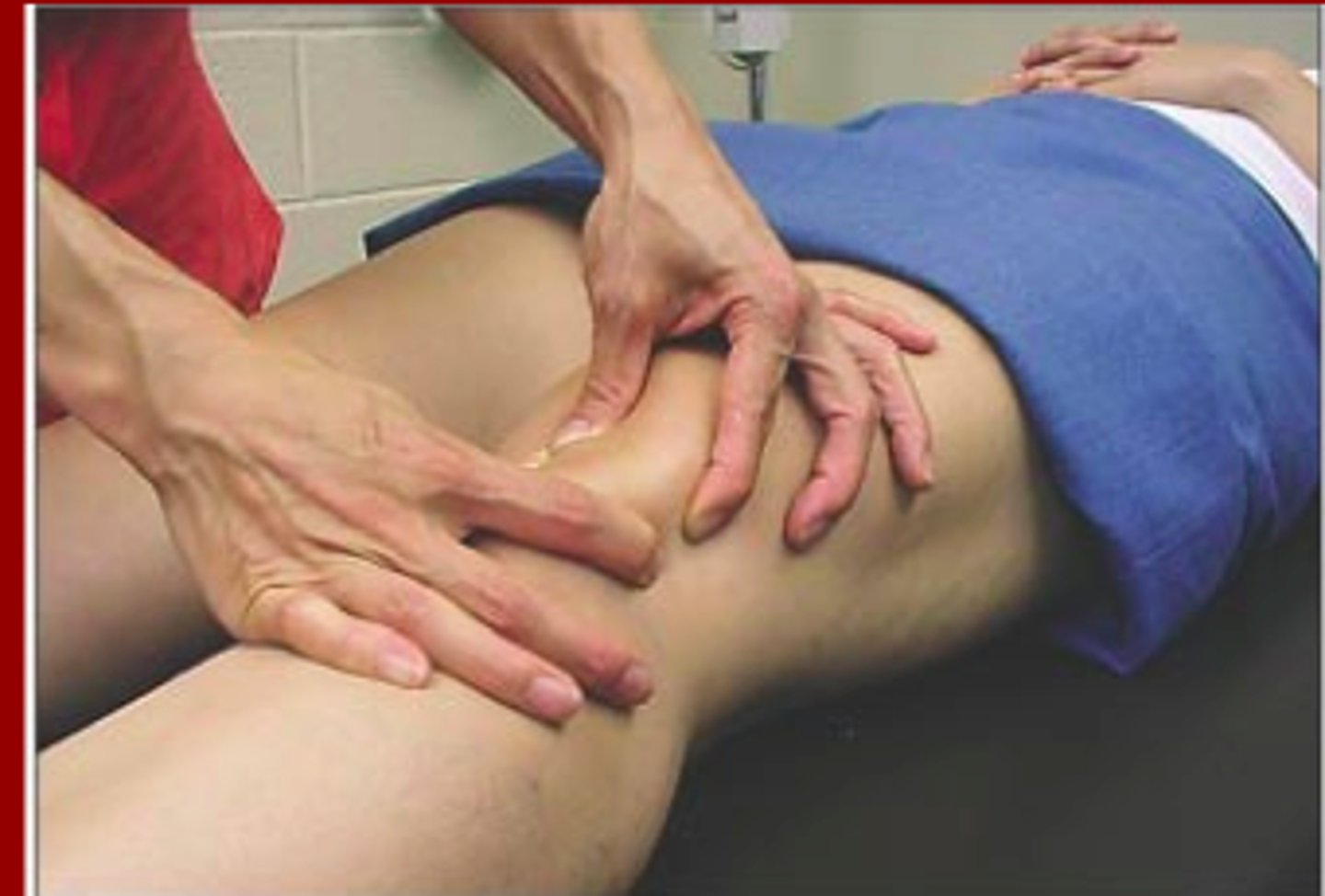
No (+ for reproduction of pain)
during the eccentric step down, the patient goes into valgus collapse. Is this a positive test?
ruling in
are the PFPS tests typically used for ruling in or ruling out?
pain with squatting?
pain with stair climbing?
pain with kneeling?
pain with resisted knee extension?
what questions could you ask that have diagnostic utility for ruling OUT PFPS?
clear patellar and regional mobility, pain control, McConnell taping, motor control, core stability, quad strengthening, hip abductors, hip extensors
txment for PFPS
1. muscle performance deficits
2. Movement coordination deficits
3. Mobility impairments
4. Overuse/Overload without other impairments
PFP Classification System to Guide Treatment
patellar tendinopathy
acute degeneration of the patellar tendon from overuse, misuse or underuse
jumper's knee
other name for patellar tendinopathy
location of pain
difference between patellar and quad tendinopathy
pain with palpation, pain with stretch, pain with resistance
special tests for patellar tendinopathy
clear local and regional mobility, eccentric quads, soft tissue mobilization, Quad/Hamstring stretching, pain control, compression strap, core stability
txment for patellar tendinopathy
Osgood Schlatter
partial avulsion of the tibial tuberosity in pubescent males and females involved in running, jumping, and landing
gradually increasing pain and swelling below involved knee, pinpoint tenderness, limited and painful knee flexion, painful resisted knee extension
symptoms of Osgood Schlatters
Sinding Larsen-Johansson
Traction injury at patellar tendon insertion on patella
clear local and regional mobility, activity modification, quadriceps soft tissue mobilizations/stretching, knee pads, self-limiting
txment for Osgood Schlatter/Sinding Larsen-Johansson
ITB Syndrome
overuse injury typically caused by a tight iliotibial band. aggravated by excessive or abnormal rotational movements of the femur and tibia while running or walking.
painful popping (especially with hill running), lateral knee pain, pain at insertion of IT band
symptoms of ITB syndrome
Ober
special tests for ITB syndrome
Thessaly's, Appley's, Joint line palpation, McMurray's
special tests for degenerative meniscus lesions
insidious onset if pain/stiffness (30 min in morning), pain with EB, buckling, locking, giving way, difficulty with stairs/walking/rising from seat
Patient presentation of OA at the knee
varus/valgus knee, joint effusion, diffuse joint line tenderness, capsular pattern of loss
Exam findings of OA
greater loss of flexion that extension
capsular pattern of loss for knee
age >50, daily knee stiffness <30 minutes, crepitus, bony tenderness, bony enlargement, no palpable warmth
Criteria to diagnose OA at the knee
4
# of criteria need to rule in OA
3
# of criteria need to rule out OA
narrow joint space, bone sclerosis, periarticular cysts, osteophytes
what will imaging reveal in knee OA?
corticosteroids (4/year), improve hip mobility, hip strengthening, pain relieving mobs, foot orthotics, non-WB aerobic exercise
txment for knee OA