Pregnancy PK + Developmental Toxicology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Changes in the Cardiovascular System + Blood in PREGNANCY
Do the following increase or decrease?
plasma volume
cardiac output
stroke volume
heart rate
ALL INCREASE
**you are now pumping blood for TWO people so you need more of it and to push more of it out
what happens to the serum albumin concentration and serum colloid osmotic pressure during pregnancy?
DECREASE
Do coagulation factors and fibrinogen increase or decrease in pregnancy?
INCREASE
what happens to the inferior vena cava (brings deoxygenated blood into the heart) in pregnant individuals?
vena cava is compressed by the uterus
what happens to renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate in pregnancy?
both INCREASE
During pregnancy, changes are made to which enzymes in the liver? Are they increased or decreased?
oxidative liver enzymes such as CYP450
some increased some decreased
what increases in the lungs due in pregnant women?
minute ventilation (total inhaled and exhaled in one minute)
tidal volume (inhaled and exhaled in normal breath)
Physiological Changes in Stomach and Intestines:
nausea and vomiting
_______ gastric emptying
prolonged _________ _________ _________ _________
gastrointestinal _________
delayed gastric emptying
small bowel transit time (longer time in the small intestine)
reflux
do pregnant women have more or less hemoglobin?
less hemoglobin
which CYP450/ liver enzymes increase in activity during pregnancy?
CYP 2A6 and 2D6
CYP 2C9 and 3A4
UGT 1A4
6s got their own thing goin
2C9 isnt with 2C19 this time but w/ 3A4
and UGT 1A4 is loner
would you see higher or lower of the following substrates in pregnant individuals and why?
CYP1A2- caffeine, clozapine theophylline, olanzapine, (CCOT)— all end with eine
CYP2C19- proguanil
INCREASED levels of substrates because
CYP1A2 and 2C19 are DECREASED so the substrates wont be metabloized
which substrates would you see an increase in pregnant woman and why ?
caffeine, clozapine, olanzapine, theophylline (decreased CYP1A2)
proguanil (decreased CYP2C19)
would you expect higher or lower levels of the following substrates in pregnant women?
CYP2A6 - nicotine
CYP2D6 - fluoxetine, citalopram, metoprolol, dextromethorphan (md fc—6 is too young to be a doctor)
CYP2C9- phenytoin and glyburide (interesting name like 2C19)
CYP3A4- midazolam, indinavir, nifenidine (min- usually max)
UGT1A2 - lamotrigine
decreased substrates because the CYP activity of the following are increased in pregnant woman
further along in gestation levels of CYP1A2 increase/decrease
causing an increase/decrease in caffeine, clozapine, olanzapine, theophylline
CYP1A2 activity decrease
substrates increase
would there be a higher or lower AUC (concentration/time graph) for midazolam in post partum women or in pregnant women?
greater midazolam AUC in postpartum women bc/ it is metabolized by CYP3A4 which is enhanced during pregnancy
Increased digoxin clearance in pregnant women is due to which two enhanced transporters?
pregnancy clearance: 73± 22 (51-95mL/min) greater than 51
postpartum clearance: 37 ± 14 (23-51)
OATP (takes from blood into proximal tubule cell)
P-gp (takes from proximal tubule cell into filtrate)
Increased Amoxicillin clearance in pregnant women is due to which an increase in the ______ trasnporter and decrease in _______ and _______ transporters
2nd Trimester: 280± 105 (175- 385)
3rd Trimester: 259 ± 54 (205-313)
Postpartum: 167± 47 (120-214)
increased OAT (bring amoxicillin into the proximal tubule)
decreased hPEPT1 and hPEPT2 (allow for reabsorption of amoxicillin)
Increased Metformin clearance in pregnant women is due to an incrrease in which two transporters?
T2: 480 ± 190 (290-670)
T3: 419 ± 78 (341-497)
Post Partum: 313± 98 (215-411)
OCT2 and MATE1
Will there always be more drugs in the mother’s blood than in the milk?
NO there CAN be more drug in the milk than mothers blood
the milk:blood ratio can be greater than 1 for some drugs
which drugs should be avoided due to increased exposure to prenatal and postnatal babies through milk? (you will find more of these drugs in the milk than mothers blood)
aspirin
opioids (morphine, codeine, oxycodone)
amphetamines
lithium
marijuana
anticancer drugs
what is early milk from the first few days referred to as?
colostrum
what gives colostrum (early milk) its yellow color?
immunoglobins that are paracellularly transferred between cells into the milk to build babies immunity
Which types of drugs will make it into the milk?
high/low concentrations in maternal plasma
low molecular weight less than _______
high/low protein binding
pass easily into the _______ (due to high _________)
Drugs with high/low pka will get trapped in the milk due to the milk’s high/low pH
high
800
low (able to leave blood into milk)
brain lipophilicity
high pka stuck in low pH milk
is the milk basic or acidic?
which type of drugs would get entrapped in the milk due to their pka?
milk is acidic (low pH)
basic drugs (high pka) would get trapped in milk bc/ they are charged in acidic environments
which cells separate maternal blood with milk?
lactocytes (epithelia) in alveoli
which efflux transporter is used to take drugs out of lactocytes and into the milk ?
BCRP
is the pH of the mothers blood or milk lower?
pH or milk is lower (7) than mothers plasma (7.4)
_____ _______ is secreted from the lactocytes into the milk
drugs that are ______ can be secreted within them
milk fat
lipophilic
does BCRP on the apical side of mammary tissue increase neonatal exposure to drugs?
YES because it allows drugs to efflux out of lactocytes and into the milk
breast milk atenolol peak concentrations are _____ and _____ that maternal plasma peak
Does atenolol reach toxic concentration levels in infants?
higher later
NO due to the babies own ADME processes not all of the drug in the breastmilk is transported to its target of action
BELOW 10 ng/mL
is mammary clearance of atenolol INTO breastmilk greater 2-4 weeks postpartum or 3+ months postpartum?
greater mammary clearance = greater amount in milk 2-4 weeks postpartum compared to 3 months
the longer that atenolol is in the body after pregnancy, the less that makes it into the milk
how long is human gestation (period in womb)?
after how many weeks is a baby considered to be full term?
40 weeks
38 weeks
are babies more or less likely to be susceptible to teratogens during the first 2 weeks of gestation?
LESS likely (they have just merely been implanted, blood supply is not connected yet to be able to transfer drugs from mom to baby)
what happens during the first two weeks of pregnancy?
dividing zygote
implantation
bilaminar embryo
which weeks are considered to be the embryonic phase?
which organs are developed at this stage of pregnancy?
3-8 weeks = embryonic phase
CNS and heart
eyes
arms and legs
teeth
palate
external genetalia
if a child is born with a morphologic abnormality, it is most likely that it had happened during which stage of gestation?
embryonic (3-8 weeks)
if a child is born with a physiological or minor morphological defect, it most likely occurred during which stage of gestation?
9-38 weeks
When would you experience physiological defects (loss or gain of function) vs morphological defects (physical defect) in gestation?
morphological - 3-8 weeks
physiological - 9-38 weeks
toxicity that disrupts specific developmental programming (organogenesis)
teratogens
what can be considered a teratogen
drugs, chemicals, AND hormones that cause toxicity impacting development
TRUE/FALSE: effects of all teratogens are evidently visible
FALSE
not all teratogens are visible
lithium (mood stabilizer) is a teratogen
what effect does it have on the fetus?
cardiac defects
which teratogen leads to
hypoplastic nasal bridge AND chrondodysplasia (1st trimester)
CNS malformations (2nd trimester)
risk of bleeding (3rd trimester)
warfarin
which teratogen leads to
craniofacial
limb
growth deficiencies
phenytoin
which teratogen leads to
neural tube defects
cardiac and limb malformations
valproic acid/ valproate
which teratogen leads to
neuraltube defects
fingernail hypoplasia
carbamazepine
which teratogen leads to
cardiac defects
masculinization
sex hormones
which teratogen leads to
high risk of craniofacial
cardiac
CNS anomalies
retinoic acids (Accutane)
which teratogen leads to
phocomelia
thalidomide
which teratogen leads to
renal damage
ACE inhibitors (prils)
what are the two teratogenic effects you may see if taking warfarin during your first trimester?
hypoplastic nasal bridge
chondrodysplasia - stippling in the sacral and tarsal bones
______ _______ is a neural tube defect that is observed in pregnant woman taking _________ drugs such as ________ and ________ _______
what causes the defect?
spina bifida
antiepileptic
carbamazepine + valproic acid
caused by disruption to folate homeostasis
what defect results if folate homeostasis is disrupted?
spina bifida (neural tube defect)
which drug was used to prevent miscarriages in pregnant women from 1947-1971 (ineffective)?
did this drug increase progesterone or estrogen?
diethylstilbesterol
increased estrogen, even though now progesterone is known to prevent pre-term labor and the onset of parturition
was diethylstilbesterol pharmacologically appropriate?
NO the drug was made of estrogen and was meant to prevent pre-term labor but PROEGESTERONE is the pharmacologically appropriate drug to use to prevent miscarriage
what did the increased levels of estrogen from taking diethylstilbesterol during pregnancy lead to?
what age did you start seeing these effects in the children ?
clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina (40x more likely to develop than the average woman) and
increased risk of testicular cancer and infertility in males
SEEN IN 20s
were the effects of diethyltstilbessterol transgenerational?
YES
after 4 months of gestation __________ enters the fetal circulation and chelates the __________ leading to
discoloration of infant teeth (yellow-gray brown)
enamel hypoplasia
tetracycline
calcium
streptomycin: risk of __________ in the fetus by affecting 8th ______ nerve (rare toxicity)
ototoxicity (ear)
cranial
which two antibiotics are teratogenic? what do they lead to?
tetracycline- discoloration of teeth/ enamel hypoplasia
streptomycin - ototoxicity
THALIDOMIDE
Drugs can act as teratogens at specific stages of development:
was thalidomide a prescription or OTC drug?
what was thalidomide used for?
was it approved by the US?
OTC
morning sickness
NO it was approved in Germany and throughout Europe
THALIDOMIDE:
disrupts LIMB formation in the “_____ ________” stage of pregnancy
10,000 cases of ________ (only 50% survived)
______ _______ development occurs between the ___th and ____th week of embryonic life
other toxicities such as deformed _______, _____ , _______ ______, ________, and ______ defects
Which FDA individual was responsible for preventing the approval of thalidomide in the US?
vulnerable widow phocomelia (extremely short limbs)
limb bud 4th and 7th
eyes, heart, urinary tract, vision, and hearing
Frances Oldham Kelsey
what is the pH of the stomach of babies
in utero (in womb) and newborn
1-2 days old
1 week - 2 years (toddler)
2+ years
7
1-3
7
1-2 (final pH into adulthood)
what is achlorhydria which is seen in infants and toddlers (up to 2 years)?
decreased HCl production in the stomach
stomach is at pH 7 at these stages compared to 1-2 for adults
do infants and toddlers absorb weakly basic drugs or weakly acidic drugs better?
weakly basic because the pH of their stomach is basic (7) which keeps basic drugs unionized and able to make it to the blood and acidic drugs ionized unable to leave the stomach and go into the blood stream
would infants/toddlers absorb more penicillin or phenobarbital into their blood stream?
penicillin bc/ it is weakly basic and will remain unionized and able to cross to blood in pH 7 in stomach
phenobarbital which is weakly acidic will be charged in basic stomach pH and remain trapped in stomach
do weakly basic (acid-labile) drugs such as penicillin have an increased or decreased nonionized/ionized ratio in infants and toddlers?
what about weakly acidic drugs?
weakly basic = increased nonionized/ionized
weakly acidic = decreased nonionized/ionized
which enzymes are only present prenatally (before birth) and dramatically decrease (virtually 0 activity) in adulthood?
CYP 3A7 (turns into 3A4 in adults)
FMO1
SULT1A3
which enzymes are active postnatally (not present before birth)?
CYP 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, 3A4
FMO3
most UGT
which enzymes are present and active both before birth and after (constant expression) ?
CYP 3A5
SULT 1A1
TPMT
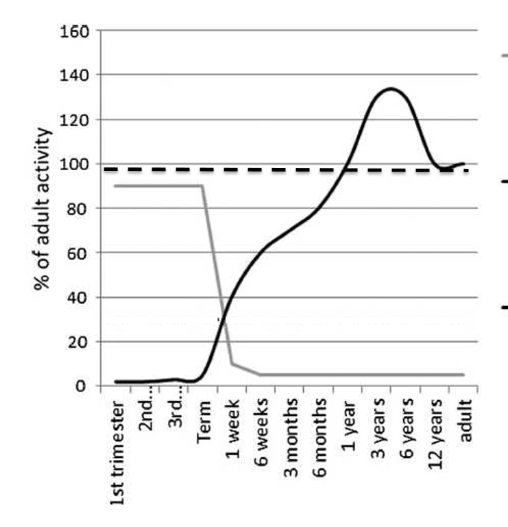
CYP3A7, FMO1, SULT 1A3
CYP 3A5, SULT 1A1, TPMT
CYP 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, 3A4, FMO3, most UGTs
Which lines represent each?
grey (only prenatal)
dashed (constant)
black solid (only postnatal)
which CYP enzymes are present in the fetus (but low activity) ?
CYP 3A4, 1A1, 3A5
which CYP enzymes appear after birth?
_______(weeks to 3 months)
_________ and __________ (days)
_________/______
______________
CYP3A4
CYP2D6 and 2C9
CYP2C18/ 19
CYP2E1
which enzyme(s) appear after 3-6 months?
CYP1A2
the human FETAL LIVER is a ________ tissue meaning it can create blood cells
hematopoietic
_______, __________, and ________ exceed adult capacity by 6-12 months of life
1A2, 2C99, and 3A4
_______ switches to ______ postnatally
________ metabolizes endogenous substrates in eutero
CYP3A7 to 3A4
3A7
______is relatively constant throughout gestation and postnatally
CYP3A5
the metabolism of _______ DECREASES as you age because of the decrease in which enzyme?
the metabolism of ______ INCREASES as you age because of the gradual increase in which enzyme?
metabolism of testosterone by 3A7 decreases as you age
metabolism of dehydroepiandrosterone by 3A4 increases as you age
how would levels of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone fluctuate as one ages?
higher testosterone as you age (less metabolism by 3A7)
lower dehydroepiandrosterone as you age (higher metabolism by 3A4)
Explain how a 3 week baby would metabolize DM?
DM —> DX (using 2D6) —> Glucoronidation (UGT)
How would a 6 month baby metabolize DM?
DM —> DX (using CYP 2D6) —> 3HM (using CYP 3A4) —> glucoronidation (UGT)
OR DM —> DMM (using CYP 3A4) —> 3HM ( using 2D6)
* since baby is older than 2 months they can use 3A4 for metabolism
What are two ways to get 3HM from Dethromethorphan?
Will you see 3HM in a 1 month old?
DM—> DX (2D6) —> 3HM (3A4)
DM —> DMM (3A4) —> 3HM (2D6)
NO to get to 3HM you need both 3A4 and 2D6 only get 3A4 when you are 2 months
CYP 1A2 converts __________ (bronchodilator for neonates) into __________ after 35-40 weeks
Theophyline to 1-3 dimethyluric acid
A 23 week baby (post conceptual — counting weeks since mothers last period)is on theophylline to treat their apnea, upon taking a urine sample will we see more theophyline or 1-3 dimethyluric acid?
Theophyline. Only at 35 weeks can the baby begin to metabolize theophyline to dimethyluric acid using CYP 1A2
What are the main modes of metabolism of chloramphenicol?
Glucoronidation (90%) and renal excretion (<10%)
What is cholarmphenicol used for?
Which organelle can it be toxic to?
Build up of chloramphenicol can lead to which syndrome?
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis ( bacteriostatic)
Mitochondria
Grey baby syndrome
What causes grey baby syndrome?
Symptoms include:
Build up of chloramphenicol due to lack of Glucoronidation (deficient UGT) and renal excretion