ALL Exams for Final
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
T/F: In farm animals, high levels of P4 (progesterone) from a large follicle both prevents standing heat by having negative feedback on the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus
False
Explanation: High lvls of P4 come from CL which will have negative feedback on the production of GnRH, FSH, LH
T/F: melatonin helps regulate oxytocin release from posterior pituitary
False
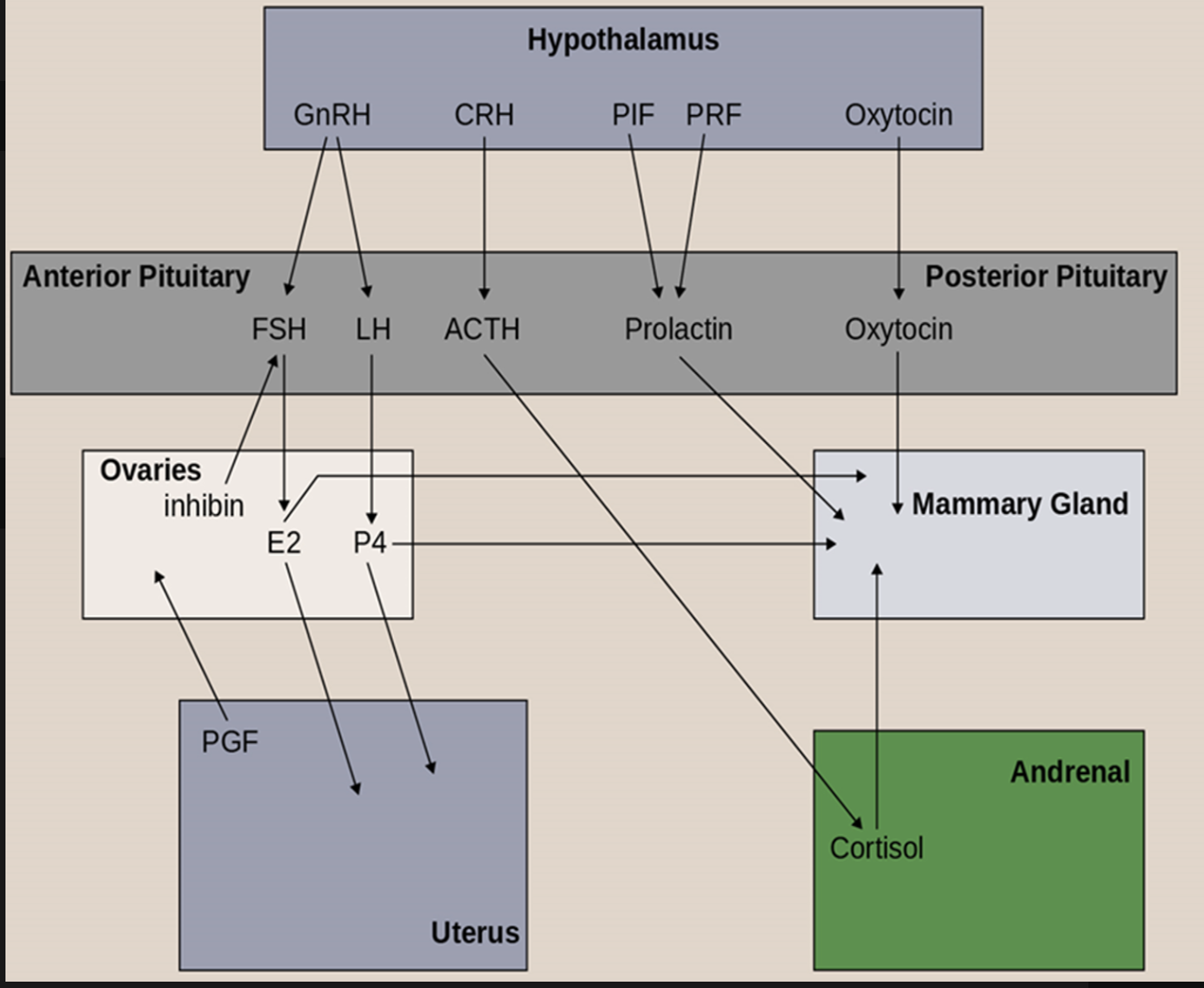
T/F: Portal vessel is the bloodstream pathway used to deliver hormones to the posterior pituitary
False
Explanation:
no portal vessel connecting the hypothalamus to posterior pituitary
hypothalamus to PP: series of nerve axons
portal vessel has a relationship with the hormones in the AP
T/F: There’s only one form of estrogens made in ovary
False
T/F: Implantation takes place in myometrium of uterus
False
Explanation: Implantation takes place in the ENDOmetrium of uterus
T/F: Posterior pituitary makes some of the hormones it releases
False
Explanation: Posterior pituitary makes NO hormones
Oxytocin is only stored and released in PP and made in the hypothalamus
T/F: Embryo transfer can be used to rapidly spread female genetics
True
T/F: anything that can bind to a receptor, including pesticides and heavy metals, will trigger a response from the cell
False
Explanation: Sometimes they don’t trigger a response but they just block the hormones from being produced
Lock and Key response
T/F: Receptor for steroid hormones is found inside the cell
True
T/F: Puberty in male is defined as maximum sperm output while in female, it is defined as first estrus
False
Explanation:
Puberty in males (sexual maturity) is defined as SUFFICIENT sperm to impregnate female and exhibits mature male mating behavior (libido)
maximum sperm output is reproductive maturity
Puberty in female (sexual maturity) is defined as the first estrus
Which hormone is responsible for stimulation of follicular development to induce multiple ovulations, super-ovulation?
A) Prolactin
B) ACTH
C) CRH
D) FSH
E) LH
D) FSH
Explanation:
Prolactin: milk synthesis
ACTH (hypothalamus) → CRH (AP) → cortisol
LH causes ovulation
[1. What] is responsible for corpus luteum formation. Once functional, the CL will secrete [2. What]
A) FSH, Progesterone
B) FSH, Estrogen
C) LH, Estrogen
D) LH, Progesterone
E) None of the above
D) LH, Progesterone
Which of the following hormones is not considered a reproductive hormone, but can have positive effects on reproductive process by being synergistic w/ prolactin in female and increasing milk synthesis?
A) Placenta lactogen
B) PIF
C) PRF
D) Cortisol
E) All of the above
D) cortisol
Which hormone is called the hormone of pregnancy and supports blood supply to lining of uterus keeping it healthy?
A) Prolactin
B) PGF2 Alpha
C) PGF2
D) Progesterone
E) Cortisol
D) progesterone
Which hormone can be administered to animals for synchronization of estrus and ovulation- artificial insemination (AI), embryo transfer, in vitro fertilization (IVF), and other ART procedures?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Prolactin
D) Melatonin
E) Oxytocin
B) progesterone
Which of the following parts of the female repro tract can serve as site of sperm deposition (think across all species)?
A) Uterus
B) Cervix
C) Vagina
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
D) all of the above
Which of the following hormones is NOT synthesized in the anterior pituitary gland?
A) FSH
B) LH
C) Prolactin
D) ACTH
E) None of the above
E) None of the above
Explanation:
Hypothalamus makes CRH, GnRH, PIF, PRF, Oxytocin
AP makes FSH (gonadotropin), LH (gonadotropin), Prolactin, ACTH
PP stores oxytocin
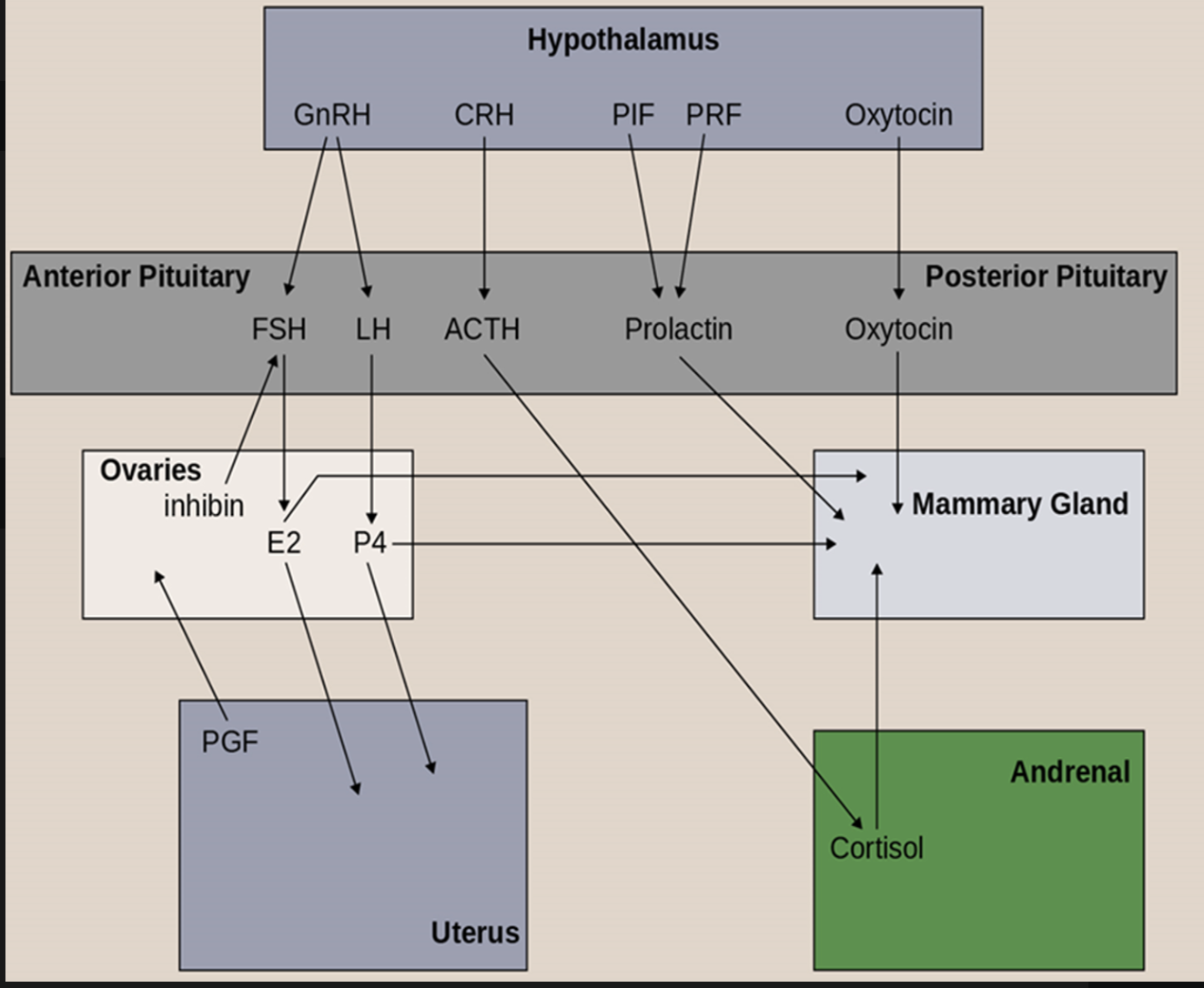
GnRH is synthesized in the [What] and stimulates the release of [What]
A) Posterior pituitary, oxytocin
B) Anterior pituitary, ACTH
C) Hypothalamus, LH
D) Hypothalamus, Prolactin
E) None of the above
C) Hypothalamus, LH
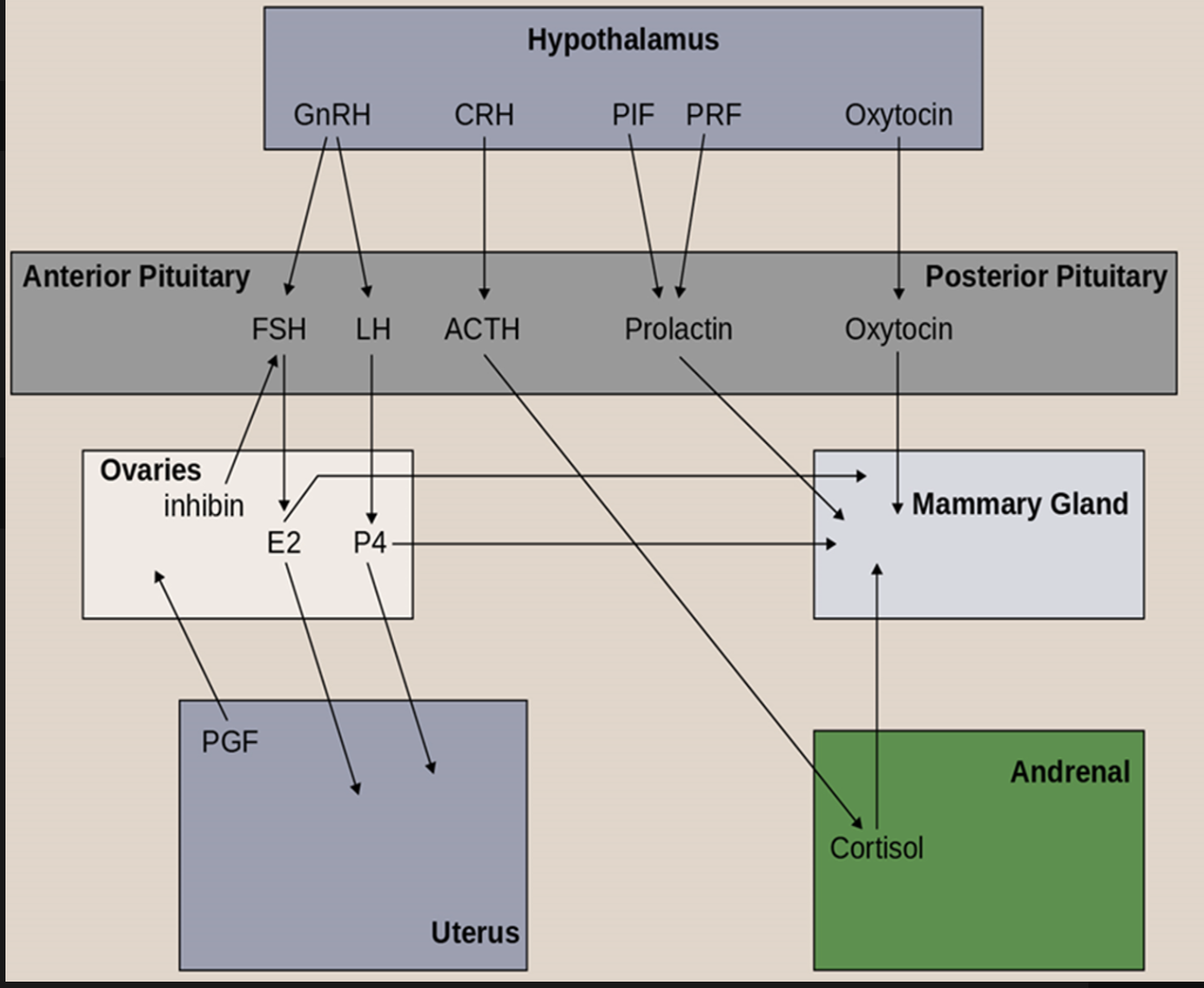
When estrogen levels are low, but present, GnRH is being secreted due to a
A) Positive Feedback Loop
B) Negative Feedback Loop
C) Direct Inhibition
D) Direct pathway
E) None of the above
A) positive feedback loop
Explanation:
Direct inhibition would be inhibin shutting off FSH
Negative Feedback Loop would be increasing concentrations of P4, T, or really high levels of E2 inhibiting release of GnRH to FSH and LH
[What] is synthesized in the [What] and is responsible for maintaining specific testosterone range
A) Inhibin, Testis
B) Inhibin, Anterior Pituitary
C) FSH, Posterior Pituitary
D) Estrogen, Ovary
E) None of the above
A) inhibin, testis
Which of the following would be caused by very high levels of estrogen
A) uterus would be relaxing
B) mucus would thin out
C) cervix would be opening
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
D) All of the above
Which of the following hormones are MADE and SECRETED by posterior pituitary
A) Oxytocin
B) LH
C) FSH
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
E) None of the above
*REMEMBER NO HORMONES ARE MADE BY THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY; OXYTOCIN IS ONLY RELEASED FROM PP
In long day breeding animals, decreased sunlight will [What] melatonin production, thus triggering animal to enter [What]
A) Increase, Estrous
B) Increase, Anestrus
C) Decrease, Anestrus
D) Decrease, Estrous
E) None of the above
A) Increase, Anestrus
Which of the following hormones is NOT needed to synthesize milk
A) Prolactin
B) PIF
C) PRF
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
B) PIF (Prolactin Inhibiting Factor)
Which type uterus would be characterized as a large uterine body w/ little to no horns
A) simplex
B) bicornuate
C) duplex
D) bipartite
E) None of the above
A) simplex
Which hormone is released from the anterior pituitary in response to extremely high levels of estrogen
A) Prolactin
B) FSH
C) LH
D) ACTH
E) None of the above
C) LH
A cow has a dominate follicle and no corpus luteum on her ovary, which of the steroid hormones is she making
A) Estrogen
B) Testosterone
C) Progesterone
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) Estrogen
Explanation: CL on the ovary produces P4
Which placental hormones directly control fetal growth
A) Protein B
B) Placental lactogen
C) PMSG
D) relaxin
E) none of the above
B) placental lactogen
Cilia are present on surface cells of the [What] to help move sperm up the female tract
A) Uterus
B) Cervix
C) Oviduct
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
D) All of the above
Once mammary tissues are in place, which hormone(s) from placenta help control milk production
A) Prolactin
B) Placental lactogen
C) Estrogen
D) Progesterone
E) None of the above
B) Placental lactogen
In the milk letdown pathway, which of the following does NOT occur
A) young animal suckling at mother’s teat, sets off nerves in the teat
B) nerve impulse sent up the spine to the thalamus in the brain
C) nerve impulse follows the path down the axon to the posterior pituitary and triggers the release of oxytocin into bloodstream
D) oxytocin travels to mammary and binds to glands, triggering contraction
E) None of the above
E) None of the above
Production and release of [What] is directly related to time light exposure time
A) Oxytocin
B) Androgen BP
C) Testosterone
D) Melatonin
E) PMSG
D) Melatonin
A follicle is about to ovulate
A) estrogen levels are high
B) FSH is under positive feedback effects of progesterone
C) Estrogen release is triggered by high levels of progesterone
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) estrogen levels are high
Which of the following endocrine glands makes relaxin
A) placenta
B) uterus
C) gonad
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
D) All of the above
To be a neurohormone, a hormone can
A) be made in the hypothalamus
B) travel thru the portal vessel
C) be made by nerve cells
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Using the classic definition of a hormone:
A) hormones are made by ductless glands
B) hormones must enter blood stream
C) hormones do not initiate chemical reactions
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Which of the following can be used to define puberty
A) sufficient sperm output in male to settle a female
B) sexual maturity
C) regular ovulations in female
D) All of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Neck of a bull thickens as he grows this an example of
A) secondary sex characteristics
B) progestin effects
C) estrogen effects
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) secondary sex characteristics
PGF2 alpha and PGF2 have all the same functions EXCEPT which of the following
A) causes constriction of blood vessels
B) stimulates smooth muscle contraction for sperm transport
C) assists in ovum transport and ovulation
D) has luteolytic effects on CL
E) none of the above
D) has luteolytic effects on CL
What would be an individual animal’s primary purpose for reproduction
A) Production of food and fiber
B) spread of a single individuals’ genes
C) survival of the species
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
B) spread of a single individuals’ genes
Which is the proper sequence for steroid hormone production
A) progesterone, estrogen, testosterone
B) progesterone, estrogen, androgen
C) androgen, testosterone, cholesterol
D) estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
E) none of the above
E) none of the above
Explanation: cholesterol (27C) → progesterone (21C) → testosterone (19C) → estrogen (18C)
Which of the following hormones might represent a serious risk to a pregnant woman working with synchronizing cattle
A) PGF2 alpha
B) LH
C) estrogen
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) PGF2 alpha
In mid pregnancy, CRH levels drastically increase, but are non-affective due to
A) CRH BP
B) ACTH BP
C) Androgen
D) endogenous opioids
E) cortisol
A) CRH BP
[What] is a physiological pathway involving nerve to nerve or nerve to hormone interaction which creates a demand and then supplies a physiological product
A) Negative Feedback Loop
B) Positive Feedback Loop
C) Direct pathway
D) Direct inhibitor
E) Arc Reflex
E) Arc Reflex
In non-pregnant and early pregnant animals [what] levels would be high and in late pregnant to early postpartum animals [what] levels would be higher
A) CRH, ACTH
B) PIF, PRF
C) Prolactin, PIF
D) oxytocin, melatonin
E) placental lactogen, estrogen
B) PIF, PRF
Hormonal Feedback loops are a physiological process where a hormone is measured by the pathway that creates is thus being part of the mechanism that [what]
A) determines half life
B) acts on all cells in the body
C) makes more receptors
D) regulates its own production
E) All of the above
D) regulates its own production
Lutalyse and Estrumate are 2 commercially available compounds of what hormones
A) LH
B) FSH
C) GnRH
D) Progesterone
E) PGF2 alpha
E) PGF2 alpha
PMSG has [what] like effects in horse and helps to recruit secondary CL’s to increase progesterone production help maintain pregnancy, however in all other domestic species, it mimics effects of [what]
A) LH, FSH
B) progesterone, LH
C) FSH, progesterone
D) LH, estrogen
E) PGF2 alpha, FSH
A) LH, FSH
Placental lactogen has 2 important roles, it increases milk synthesis and [what]
A) is a growth regulator
B) stimulates ovulation
C) causes smooth muscle contraction
D) triggers oxytocin production
E) none of the above
A) is a growth regulator
Temperature of the testes
A) is controlled in part by blood temperature
B) is controlled in part by cremaster muscles
C) can be lowered by sweating
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Where would you expected to find highest concentration of sperm cells within male’s reproductive tract
A) testes
B) vas deferens
C) epididymis
D) it would be same in all of the above
E) none of the above
C) epididymis
Biochemically, sperm cells in the [what] are first to contain the enzymes necessary to fertilize an egg
A) epididymis
B) uterus
C) vas deferens
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) epididymis
Which of the following species can ovulate during postpartum estrus
A) caprine
B) ovine
C) equine
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
C) equine
explanation: foal heat occurs during 5-15 days after parturition
It takes approx [what] days from time a spermatogonia begins to divide until its resulting spermatozoa can be released from cauda epididymis
A) 45 days
B) 5 days
C) 15 days
D) 60 days
E) none of the above
D) 60 days
Under normal circumstances, which of the following parts of the male anatomy are paired
A) pelvic urethra
B) epididymis
C) penile urethra
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
B) epididymis
Which of the following cells has a haploid set of chromosomes
A) Spermatid
B) spermatogonia
C) primary spermatocyte
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) spermatid
Explanation:
spermatogonia are 2N
primary spermatocyte are 2N
T/F: cortex of the ovary contains blood and nerve supply and all forms of corpus luteum
false
T/F: granulosa cells are cells that surround the oocyte within the follicle
true
What dictates each phase of the estrous cycle
A) structures on the ovary
B) uterus
C) presence of the opposite sex
D) fetus
E) none of the above
A) structures on ovary
Period when ovary and hormones are quiescent (quiet) like they were before puberty
A) anestrus
B) diestrus
C) metestrus
D) no estrus
E) ovulation
A) anestrus
Metestrus can be identified when which structure is on the ovary
A) Corpus hemorrhagicum
B) Corpus luteum
C) graffian follicle
D) Corpus albicans
E) there is no structure at this time
A) corpus hemorrhagicum
Diestrus is described as
A) longest period of the estrous cycle in domestic species
B) characterized by rising or high levels of progesterone (GnRH, FSH, and LH are inhibited)
C) maternal recognition must occur in this phase if animal is pregnant, she must realize she is pregnant
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Estrous animals with a constant desire to mate and whose ovulation is triggered by act of mating is termed
A) polyestrous
B) monoestrous
C) seasonal estrus
D) continuous estrus
E) none of the above
D) continuous estrus
T/F: corpus hemorrhagicum is considered a functional structure
false
T/F: an animal must have a functional corpus luteum to respond to PGF2 alpha
true
Explanation: Large luteal cells (formerly granulosa) at day 5 gain receptors
Scar tissue that forms from corpus luteum regresses and once a cycle ends
A) corpus albicans
B) corpus hemorrhagicum
C) corpus luteum
A) corpus albicans
During a non-pregnant cycles, CL regresses due to
A) release of PGF2 alpha from uterus
B) death of large luteal cells
C) lack of a continuing LH like stimulus to small cell luteal cells
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Explanation: lowering P4 → stop small LH P4 production → endometrial lining releases PGF2 alpha → large cell receptors take in PGF2 alpha → die
In horse, melatonin
A) production is lowered by long periods of daylight
B) causes stimulation of GnRH
C) is present in large amounts when animals are in cycles
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
a) production is lowered by long periods of day light
Explanation: more daylight → decreased melatonin and less daylight → increase melatonin (melatonin is the sleepy hormone)
In sheep, melatonin
A) production is blocked by long periods of daylight
B) causes stimulation of GnRH
C) is present in large amounts when animals are in cycle
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) All of the above
Explanation: sheep are cycling w/ increased melatonin
Which of the following can be used to define spring
A) always occurs from March through June
B) a period of increasing daily light
C) occurs at same time in the Northern and Southern hemispheres
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
B) a period of increasing daily light
In general, during nonbreeding season, males are
A) more affected by melatonin than females
B) still retain enough sperm to result in pregnancy
C) reproductive systems are less effected by heat than female
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
B) still retain enough sperm to result in pregnancy
In monoestrous animals, what is the long periods called that separates each cycle
A) diestrus
B) true polyestrous
C) seasonal polyestrous
D) induced ovulation
E) anestrus
E) anestrus
During a silent heat
A) animal will ovulate
B) animal will not stand to be mate
C) is seen in animals after a long anestrus
D) can be caused by heat stress
E) all of the above
E) all of the above
Reproduction is a series of physiological and psychological events that must be properly
A) thought out
B) executed
C) timed
D) seen
E) none of the above
C) timed
A point where male has mated too many times and is producing too few sperm to allow for a reasonable chance for pregnancy is called
A) Maximum reproduction
B) reproductive maturity
C) sexual maturity
D) Breeding exhaustion
E) none of the above
D) breeding exhaustion
Granulosa cells while under the influence of [what], the enzyme aromatase remove the last carbon and causes formation of organic ring in the estrogen molecule
A) FSH
B) LH
C) GnRH
D) PGF2 alpha
E) none of the above
A) FSH
Most mammals can ovulate over almost the entire ovarian surface; horses ovulate at only one specific point termed the
A) Ampulla
B) infundibulum
C) Ovulation Fossa
D) Theca
E) fimbriae
C) Ovulation Fossa
Reproductive Maturity in Male occurs when
A) he is showing signs of aggression
B) he demonstrates desires to mate
C) has mature gametes
D) he demonstrates high libido
E) has maximum sperm production
E) has maximum sperm production
Which can influence onset of puberty
A) Genetics
B) Weight
C) Nutrition
D) Season
E) All of the above
E) all of the above
An animal is going into anestrus, she just finished the [what] phase of her estrous cycle
A) proestrus
B) estrus
C) metestrus
D) diestrus
E) none of the above
D) diestrus
Which species ovulates during metestrus
A) horse
B) pig
C) cow
D) sheep
E) none of the above
C) cow
T/F: 9% of all follicles will be ovulated
False
Explanation: only 0.5% will be ovulated and can become an embryo
T/F: Highest levels of progesterone during estrous cycle are associated with corpus luteum
true
T/F: hormone independent phase of follicle development only occurs during birth
false
Explanation: activation of primordial follicles happens in waves throughout the cycle even if they do become atretic
T/F: photoperiod varies most at the equator
false
Explanation: it would be 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of nighttime mostly
T/F: long nights lead to increased melatonin production in both horses and sheep
true
T/F: Moving seasonal polyestrous animals, during anestrus, across equator will lead to start of estrous cycles
true
Which part of a mature sperm cell contains the mitochondria
A) tail
B) midpiece
C) acrosome
D) head
E) none of the above
B) midpiece
Accessory glands provide the semen with
A) buffers
B) fluids
C) an energy source
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Serves as a common pathway for urine and semen
A) urethra
B) vas deferens
C) epididymis
D) All of the above
E) none of the above
A) urethra
Which is the term to describe the process for making a spermatogonium into a spermatocyte
A) spermiogenesis
B) spermatogenesis
C) spermatocytogenesis
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
C) spermatocytogenesis
Is the term to describe the metamorphosis of a spermatocyte to a spermatozoa
A) Spermiogenesis
B) spermatogenesis
C) spermatocytogenesis
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) spermiogenesis
In the sperm, the enzymes necessary to penetrate the egg are found specifically in the
A) tail
B) midpiece
C) acrosome
D) head
E) none of the above
C) acrosome
Complete final maturation of sperm takes place in the
A) testis
B) epididymis
C) female tract
D) All of the above
E) none of the above
C) female tract
Is the term to describe the complete process for transforming a spermatogonium into a spermatozoa
A) spermiogenesis
B) spermatogenesis
C) spermatocytogenesis
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
B) spermatogenesis
T/F: like females, males have the most mature spermatozoa they will ever have before birth
false
T/F: In theory, one dividing spermatogonium will result in formation of 32 mature sperm cells
False
Explanation: makes 64 sperm cells
T/F: Sperm tail is important for moving sperm from site of deposition to site of fertilization
false
Explanation: This is due to contractions in the female tract but the sperm tail is important for penetrating the egg
T/F: on average, scrotal sac is a few degrees warmer than rest of the male body
false
T/F: highest levels of progesterone during the Estrous cycle are associated with corpus luteum
true