liver quiz prep with case studies
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
The abdominal aorta extends from
T 12 diaphragm to the fourth lumbar vertebrae where it bifurcates
What is the normal size of the aorta?
Below 3cm
Liver size and location
Right upper quadrant
Right and left hypochondrium and epigastrium
15 to 17 cm
Lobes of the liver are
Right lobe is the largest
Left lobe
Caudate lobe
The left lobe of the liver is divided into medial and lateral by
Left hepatic vein
A normal liver has smooth margins, and
Homogeneous texture
The liver should be_____ compared to kidney
Slightly hyperechoic or isoechoic
how bright or dark a structure appears on ultrasound
Echogenicity
Meaning: No sound waves reflected
Looks: Completely black
Usually fluid
Anechoic
Meaning: Reflects less sound than surrounding tissue
Looks: Darker than nearby structures
Hypoechoic
Meaning: Same echogenicity as adjacent tissue
Looks: Blends in — similar shade of gray
Isoechoic
Meaning: Reflects more sound than surrounding tissue
Looks: Bright or white
Hyperechoic
Hepatic veins drain away
From the liver into the IVC
The Caudate lobe is
Posterior in left lobe, position between anterior ligamentum venosum and IVC is posterior
This is the boundary of the right and left lobe, it adheres the liver to the interior wall
Falciform ligament
It also contains ligamentum Teres
Rounded terminal end Falciform ligament, closed shunt from in utero
Ligamentum Teres
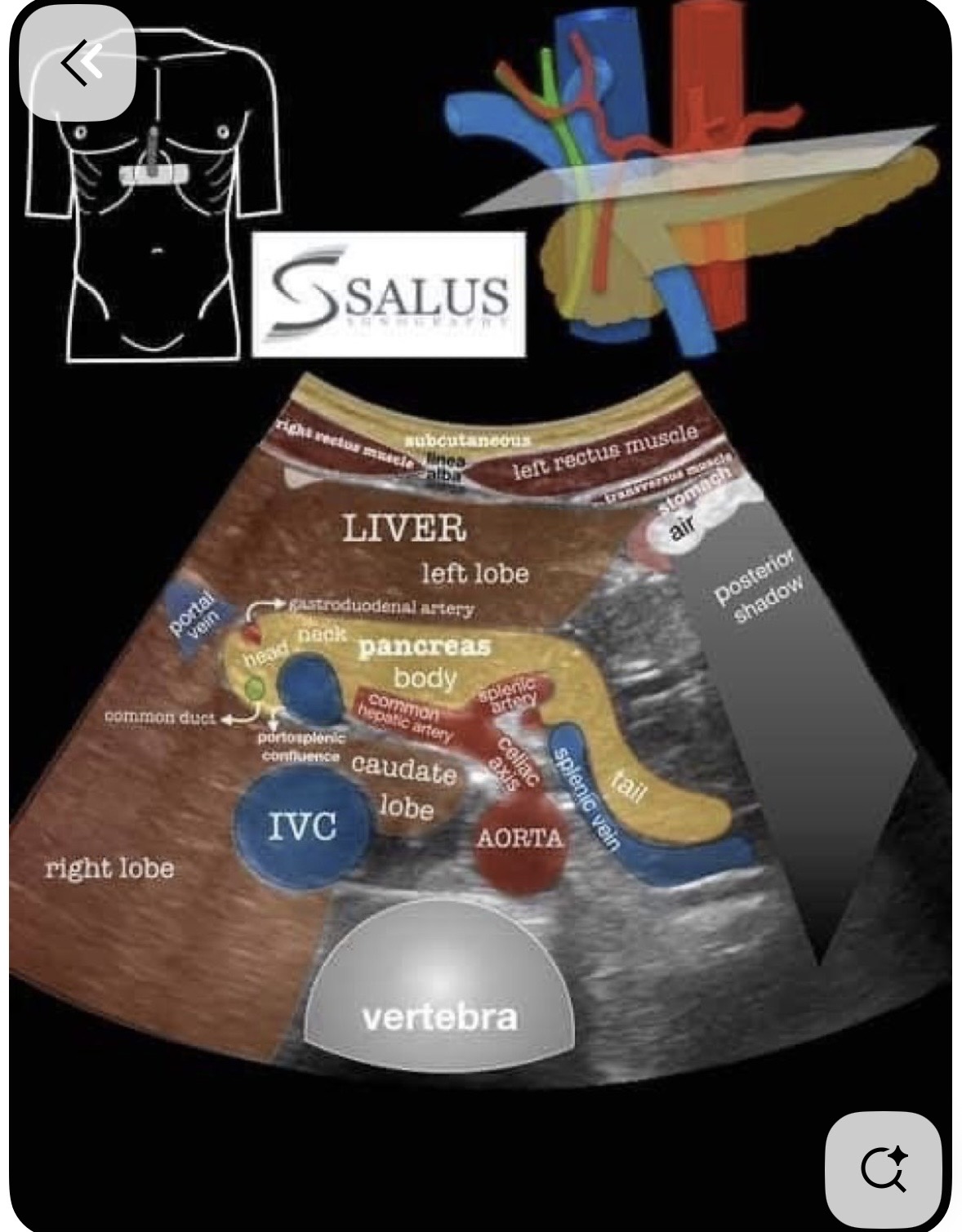
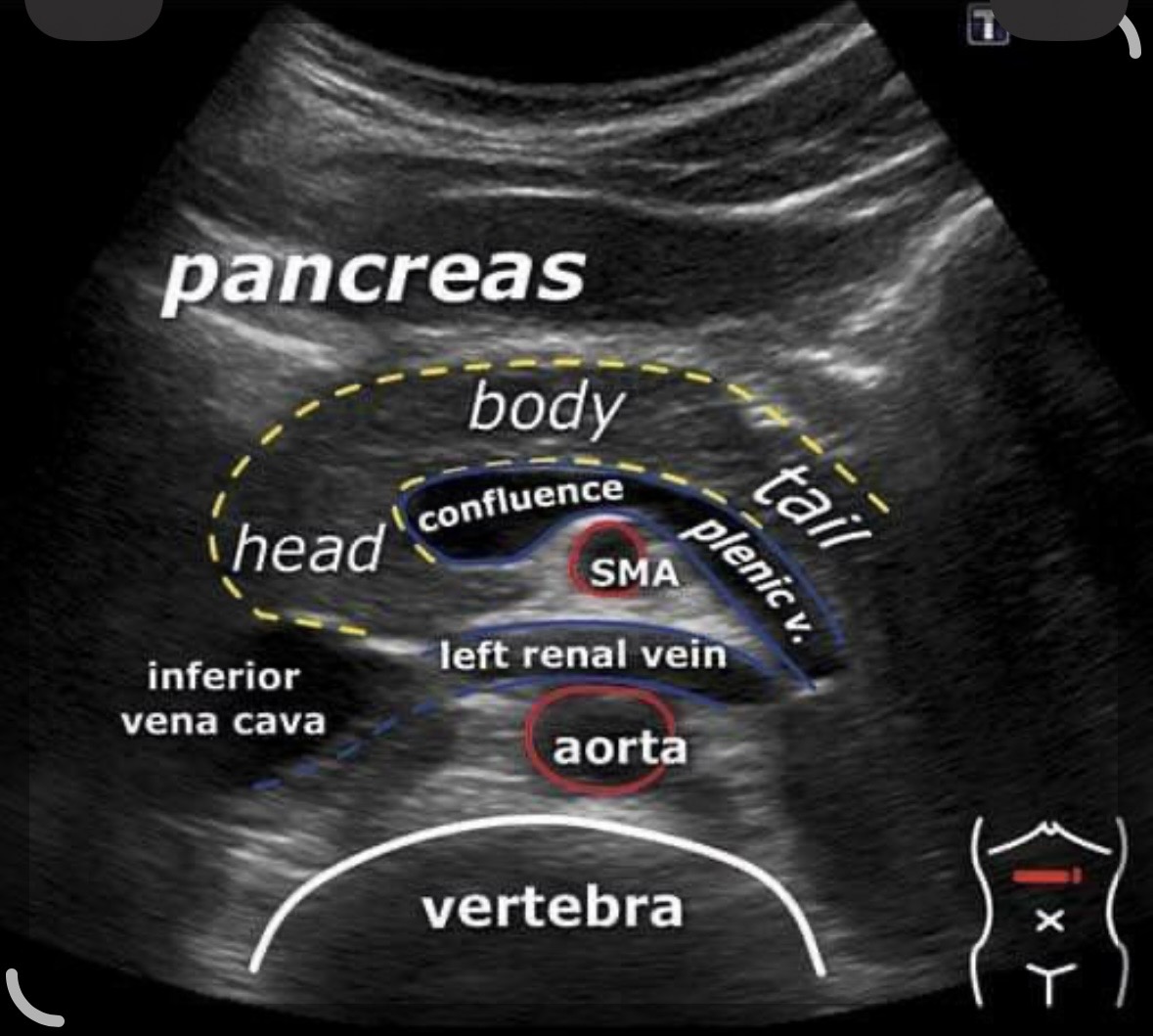
Anterior of aorta and runs parallel
Superior mesenteric artery SMA
Superior of SMA
Celiac trunk
The celiac trunk branches
Hepatic artery and splenic artery with a small left gastric branch
Hepatic is left on screen in trans
The common iliac arteries start bifurcation
Fourth lumbar vertebrae
Run lateral off IVC courses anterior the Aorta
left renal vein - nut cracker can get pinched under SMA
runs off of the aorta laterally and posterior to the IVC
Right renal artery
It’s also longer than the left
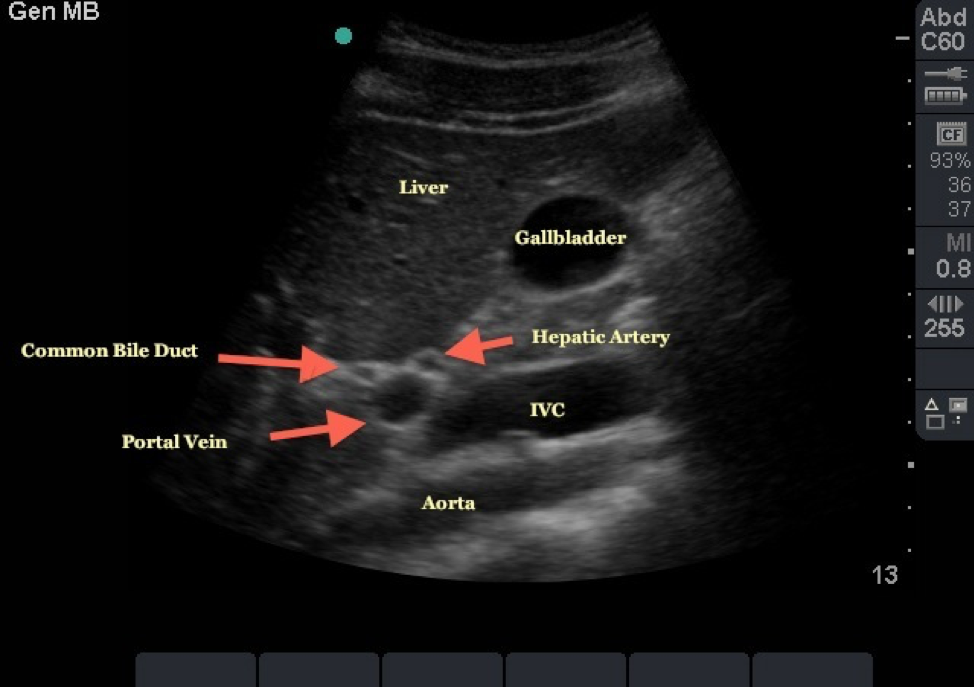
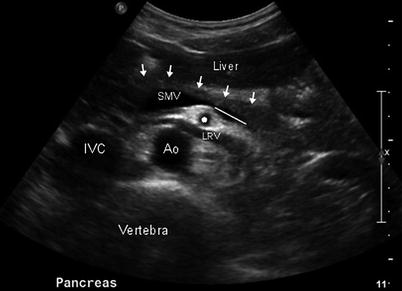
What plane is this
Transverse right lobe of liver
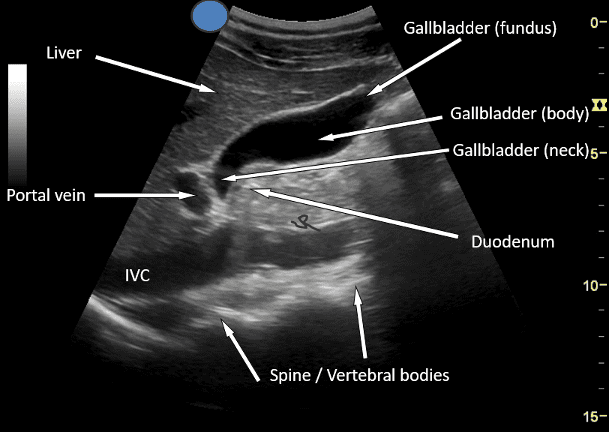
What plane is this?
Sagittal or long
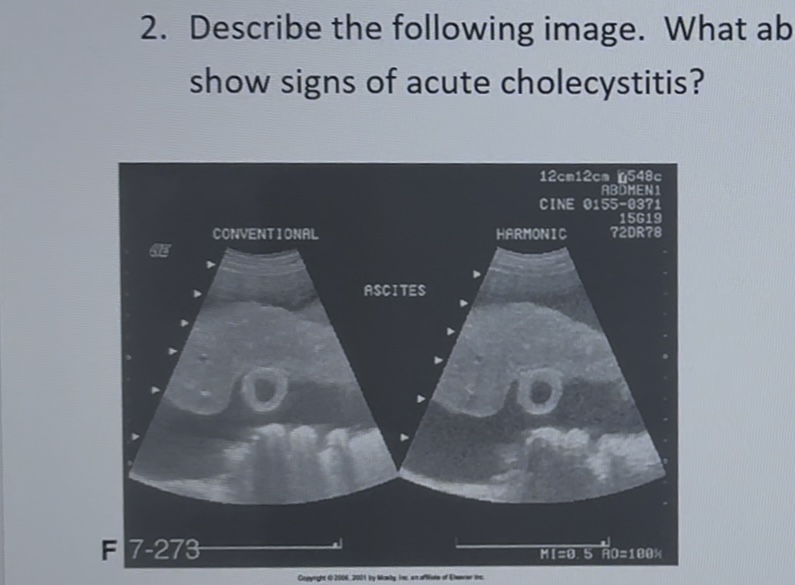
describe the image like you were going to chart
atrophy liver with coarse texture, consistent with cirrhosis. Ascites surrounding the liver, gallbladder wall is thickened. Thickened wall could be due to ascites or cholecystitis.
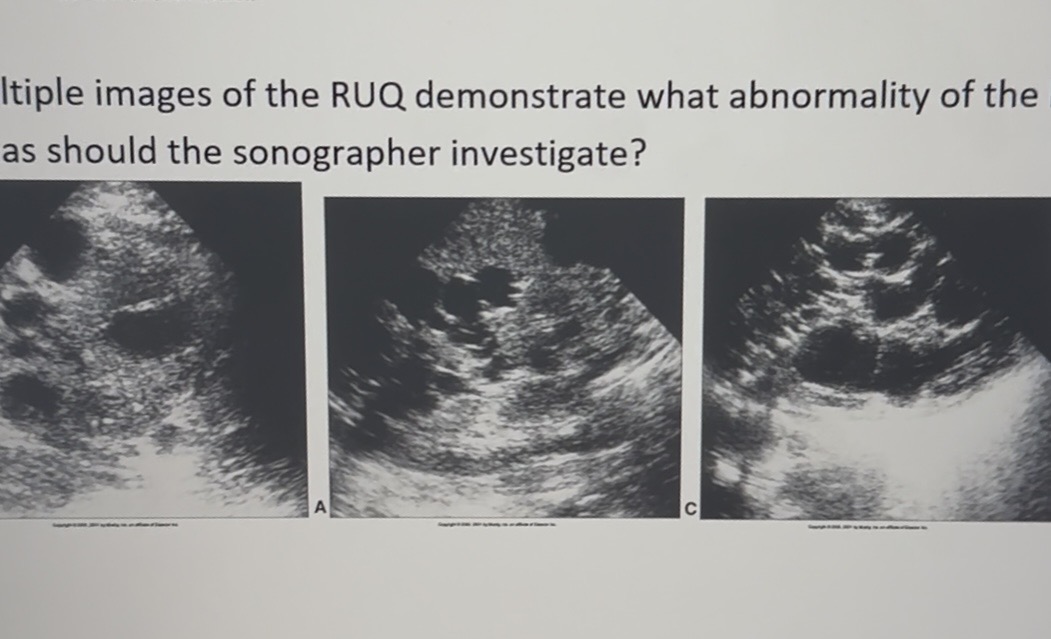
Chart this for ordering physician
Polycystic liver disease
Multiple cysts with posterior acoustic enhancement, consistent with polycystic liver disease.
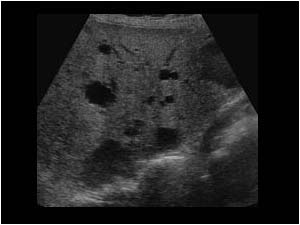
What is this pathology?
Polycystic liver disease
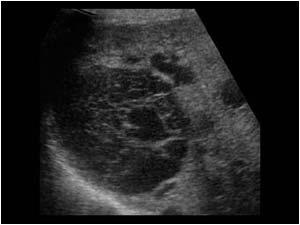
What is this pathology?
Polycystic liver disease
How do you fix attenuation
TGC or reduce frequency
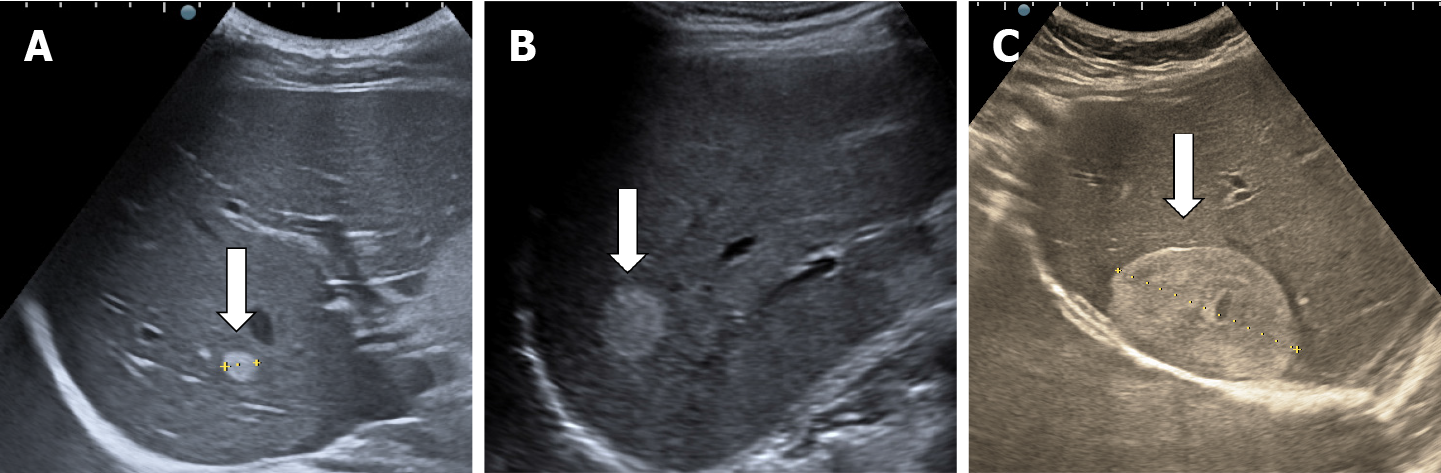
Chart this
Well defined echogenic mass seen in the right lobe. Probably Cavernous hemangioma.

Chart this
Will defined echogenic mass seen in the dome of the right lobe. Colored Doppler shows increased flow within the lesion. Possible Cavernous hemangioma.

Chart this
A patient with a history of cirrhosis shows evidence of hepatomegaly
Large heterogeneous mass in the right lobe of the liver. It extends from the dome of the liver almost filling the entire right lobe. With the history of cirrhosis, this is most likely hepatocellular carcinoma.
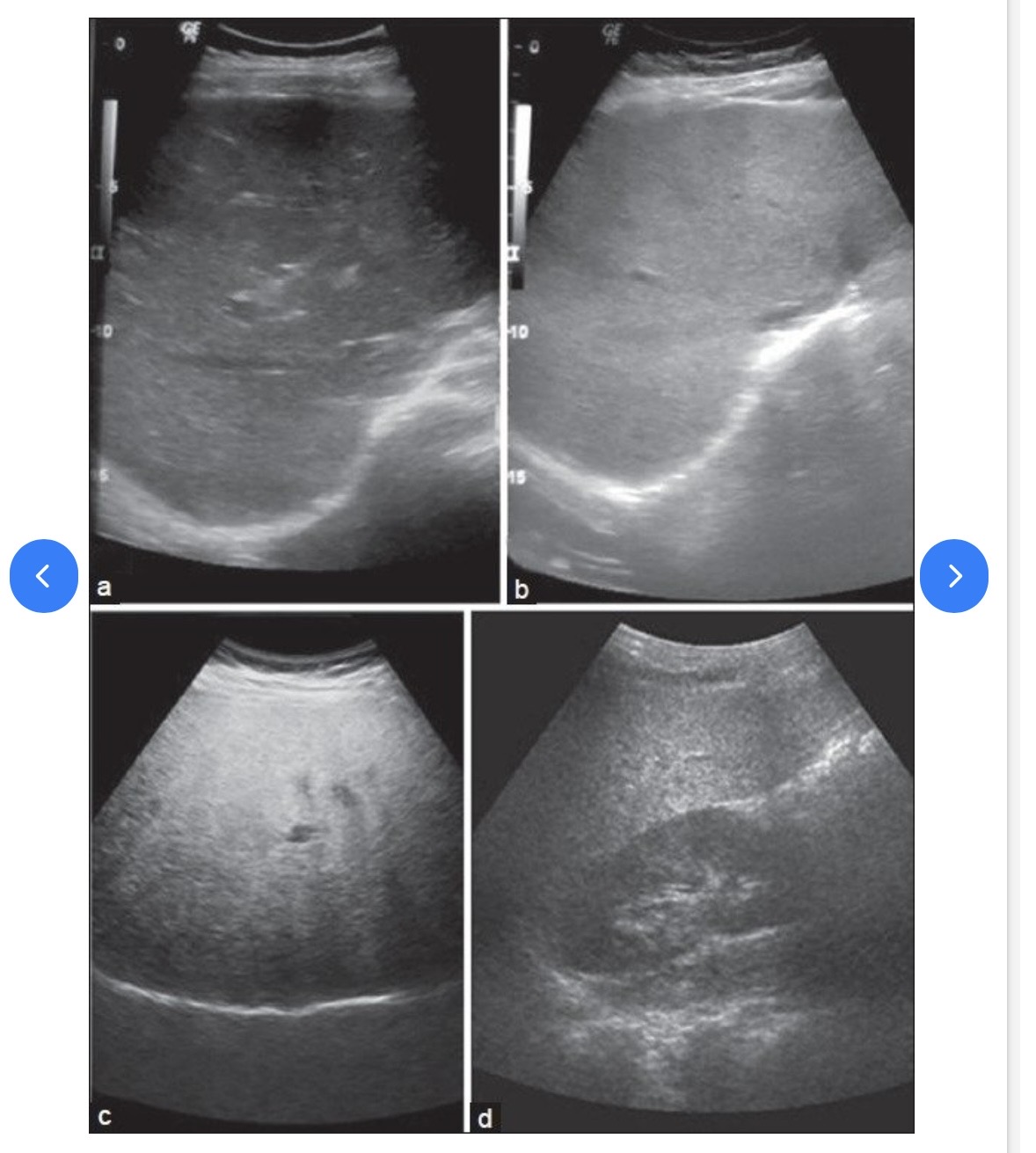
Grades of fatty liver on visual analysis. Ultrasound image shows (a) Normal liver echogenicity (b) Grade 1 fatty liver with increased liver echogenicity (c) Grade 2 fatty liver with the echogenic liver obscuring the echogenic walls of the portal venous branches (d) Grade 3 fatty liver in which the diaphragmatic outline is obscured
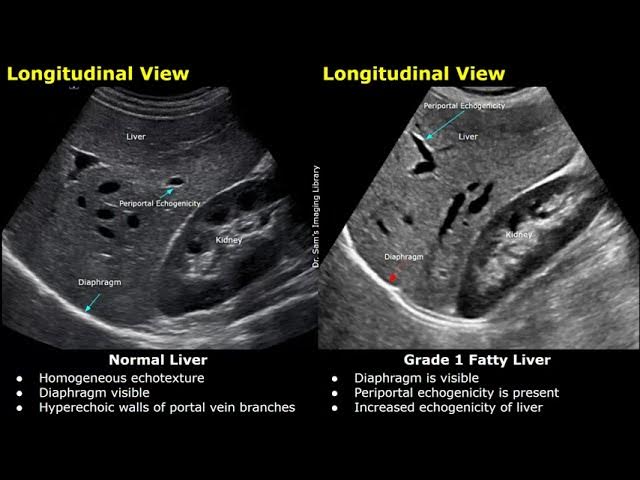
Fatty liver should be charted as echogenic liver. Difficult to penetrate. Consistent with Fatty liver.

62 year woman with a history of RUQ pain is seen for abdominal ultrasound. The patient also reveals a history of breast cancer and confirms weight loss.
Describe the image
Multiple target lesions throughout the liver, consistent with metastatic liver disease
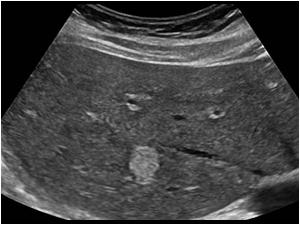
52-year-old woman is referred to ultrasound to rule out gallstones. During the exam, a hyperechoic mass was seen in the right lobe measuring 3.7× 2.5cm. What are possible diagnoses?
Hypoechoic mass seen in the right lobe of the liver measuring 3.7×2.5 cm. Adenoma, hemangioma, focal nodular hyperplasia, metastatic disease, hepatocellular carcinoma for possible diagnosis.
Hemangioma was confirmed with CT
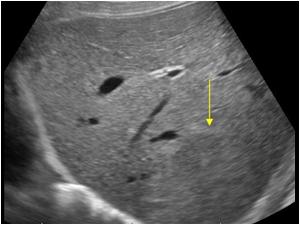
27-year-old woman is seen for an ultrasound of the liver after a C-section. The OB reported a hard liver mass at the time of surgery. The ultrasound shows an isoechoic mass of the liver that is relatively homogeneous. The patient states that she was taking oral contraceptive for seven years before the pregnancy, what’s most likely the diagnosis
Focal nodular hyperplasia
69-year-old woman is seen for ultrasound of gallbladder because RUQ pain. The patient states that she’s been having back pain and underwent treatment for colon cancer four years ago. The ultrasound reveals a target lesion in the left lobe of the liver and possibly two subtle lesions in the right lobe of the liver. The gallbladder appears normal what is the most likely diagnosis?
Metastatic disease
31-year-old woman is seen for an ultrasound. The patient is moderately obese and has vague peptic discomfort. She has no history of cancer, nausea or vomiting. The ultrasound is ordered to roll out biliary disease. Ultrasound reveals a hyper echoic liver that is difficult to penetrate vasculature is poor damaged. What is most likely the diagnosis
Fatty liver
27-year-old man undergoes RUQ ultrasound in the ER. The patient has right upper quadrant pain in a history of drug abuse ultrasound reveals hyper echoic liver with no distinct masses seen what is the best diagnosis
Acute hepatitis
64 year-old man undergoes an ultrasound to rule out of liver mass, He has RUQ pain, elevated liver, enzymes, and long history of alcohol abuse the ultrasound shows a diffusely heterogeneous liver. What is the best diagnosis?
Hepatocellular carcinoma
55-year-old man undergoes an ultrasound rule out of mass. The patient has increasing abdominal girth, vague discomfort and anorexia. AST and ALT levels are elevated. No distinct masses are noted but the liver is hyperechoic and free fluid is noted within the abdominal cavity. The border of the liver shows nodular irregularities. What is the best diagnosis?
Cirrhosis
21-year-old man undergoes a RUQ ultrasound in the ER. AST and ALT levels are elevated. The liver appears normal in echo texture without masses noted. The right posterior lobe extends inferiorly beyond the lower pole of the right kidney. What’s the best diagnosis?
Acute hepatitis
A 24-year-old woman is seen for a renal ultrasound because of a recently diagnosed congenital uterine anomaly. The renal ultrasound is unremarkable. Incidentally noted is a 1.5 cm echogenic mass in the right lower of the liver. This most likely represents what?
Hemangioma
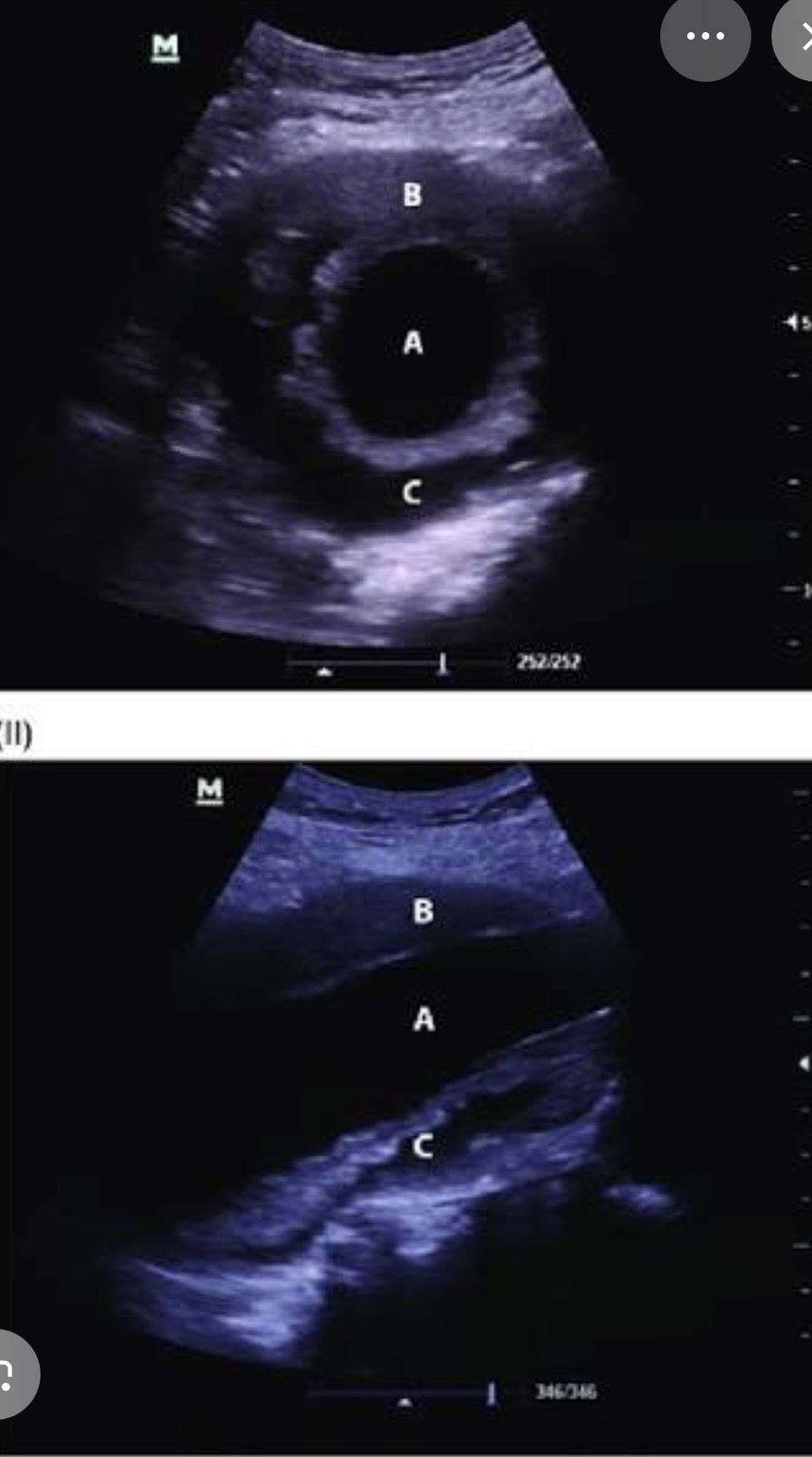
69-year-old man seen for RUQ ultrasound for persistent pain. The ultrasound reveals cholelithiasis (gallstones) with free fluid around the GB consistent with cholelithiasis. Incidentally noted are findings in the aorta the aorta measured 6.6 cm in AP diameter. What is the likely diagnosis?
AAA with thrombus patient is at risk for rupture
58-year-old man is seen for ultrasound of the aorta because of a pulsatile mass over the area of the umbilical on physical examination. The distal aorta measured 5.58 cm superior to iliac arteries. The proximal right and left iliac arteries measured 2 cm. What’s the likely diagnosis?
AAA measuring 5.8 cm with extension into iliac arteries
82-year-old man arrives in the ER via ambulance from a nursing care facility. The patient was unconscious and clinical exam reveals hypotension and abdominal pulsatile mass. A portable ultrasound exam is requested immediately and reveals a dilated aorta that measures 8.5 cm the findings and clinical examination Suggest what ?
AAA that has ruptured

79-year-old woman is seen for ultrasound exam of the aorta after several episodes of fainting. She has a history of poorly controlled hypertension and aneurysm as well as back pain. The ultrasound findings confirm a dilated aorta that measures 7 cm in AP diameter a linear echo is also identified within the aorta and color. Doppler confirms flow on both sides of the flap. What is most likely the diagnosis?
Aortic dissection
67-year-old man with vague abdominal pain is seen by his physician. Radiograph is ordered and is unremarkable except calcifications noted along the aorta. An ultrasound of the aorta reveals a distal, aortic diameter of 4 cm. This would be consistent with which of the following.?
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
40-year-old man with a history of Marfan syndrome is seen with intense chest pain in the emergency room. Which of the following diagnoses should be primary consideration?
Aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, aortic rupture, aortic, thrombus, or heart attack
Aortic dissection