Final Exam
1/406
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
407 Terms
What is the primary function of myosin in the muscle contraction process?
motor protein that interacts with actin filaments during muscle contraction.
heads bind to actin and perform power strokes by using ATP, pulling actin filaments inward and causing the muscle to contract.
Describe the layers of a long bone and their functions.
Periosteum: Outer fibrous layer providing protection and a surface for tendon and ligament attachment.
Compact bone: Dense layer for strength and support.
Spongy bone: Contains red bone marrow for blood cell production.
Medullary cavity: Hollow chamber filled with yellow marrow for fat storage.
Which bones make up the appendicular skeleton?
Limbs (arms and legs),
pectoral girdle (clavicle and scapula),
and pelvic girdle (hip bones).
List the major bones of the arm, forearm, and hand.
Arm: Humerus
Forearm: Radius and ulna
Hand: Carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
What is the chemical composition of bone, and how does it contribute to its function?
Organic components: Collagen fibers for flexibility and tensile strength.
Inorganic components: Calcium phosphate and other minerals for hardness and support.
Where does the somatic nervous system exit the spinal cord, and what is the primary neurotransmitter used in the pathway?
Exits through the ventral roots of the spinal cord; the primary neurotransmitter is acetylcholine (ACh).
Afferent nerves (sensory nerves):
Carry sensory signals from the body to the central nervous system (CNS).
Efferent nerves (motor nerves):
Transmit motor signals from the CNS to muscles and glands
Identify the function of the postcentral gyrus in the parietal lobe.
It processes somatic sensory information such as touch, pressure, and pain.
What is the role of glial cells in the central nervous system?
Provide support, protection, and insulation for neurons, as well as maintain homeostasis
What structures are involved in controlling the autonomic nervous system, and where are they located?
Hypothalamus: Regulates autonomic functions from the brain.
Medulla oblongata: Manages vital functions like heart rate and respiration.
Spinal cord: Contains autonomic reflex centers.
What is the role of myelin in the conduction of nerve impulses?
Myelin insulates axons, increasing the speed of nerve impulse conduction through saltatory conduction.
Explain the process of muscle contraction, from action potential to the cross-bridge cycle.
Action potential triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Calcium binds to troponin, exposing actin binding sites.
Myosin heads form cross-bridges with actin and perform power strokes using ATP.
What is an EPSP, and how does it contribute to action potential generation?
An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a depolarization event that brings the membrane potential closer to the action potential threshold.
Compare and contrast skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissue in terms of structure and function.
Skeletal: Striated, voluntary, multi-nucleated, and attached to bones.
Cardiac: Striated, involuntary, and found in the heart.
Smooth: Non-striated, involuntary, and found in organs.
Describe the role of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane, triggering depolarization and initiating muscle contraction.
What are the main components of a synovial joint, and what is the function of each?
Articular cartilage: Reduces friction and absorbs shock.
Synovial fluid: Lubricates and nourishes the joint.
Joint capsule: Encases the joint, providing stability.
Ligaments: Connect bones and stabilize the joint.
What is the function of the meninges in protecting the brain and spinal cord?
The meninges are protective membranes that cushion the CNS, providing structural support and acting as a barrier against infections.
Identify the function of the thalamus and hypothalamus in the brain.
Thalamus: Relays sensory signals to the cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus: Regulates homeostasis, emotions, and the endocrine system.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds? Provide an example of each.
Ionic bond: Transfer of electrons (e.g., NaCl).
Covalent bond: Sharing of electrons (e.g., H2O).
What is the process of passive transport, and how does it differ from active transport?
Passive transport: Movement of molecules without energy input (e.g., diffusion).
Active transport: Requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
What is the function of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining cell homeostasis?
Pumps 3 sodium out and 2 potassium into the cell, maintaining electrochemical gradients essential for nerve impulses.
What are the components of an atom, and how do they contribute to its overall charge?
Protons: Positive charge
Neutrons: Neutral
Electrons: Negative charge; overall charge depends on the balance between protons and electrons.
how many AP are released in temporal summation?
single AP
how many AP are released in spatial summation?
multiple APs
excitatory indicates...
depolarization
inhibitory indicates...
repolarization
what causes depolarization?
an influx of Na+ when voltage-gated Na+ channels open in the cell membrane
What causes repolarization?
an influx of K- when voltage-gated K- channels open in the cell membrane
AP jumps from...
node to node
acetylcholine acts as a...
triggers the fight or flight response by stimulating the release of norepinephrine
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
relative action potential
a period of time during which you can
trigger an action potential, but it requires more depolarization than normal due to a refractory period
broca's area
controls language expression - an area, usually in the left frontal lobe, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
nerve plexus
network of interweaving anterior rami of spinal nerves
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor
Motor nerve that innervates four of the extrinsic eye muscles
Passes through the superior orbital fissure to enter the orbit.
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
motor and sensory nerve for face, conducts sensory impulses from mouth, nose, eyes; motor fibers for muscles of mastication. Control of jaw movements
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial
Both - Moves face, tastes, salivates, Sensory information from taste buds on anterior 2/3 of tongue
Proprioceptive information from face and scalp
Motor information for facial expression and closing the eye
Autonomic information for crying and salivation
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
gagging; swallowing - sensory; taste
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Sensory from visceral organs (Heart, Lungs, Digestive system) and smooth muscle contraction.
simple reflex
Controlled at the spinal cord - connecting a two-neuron pathway from the receptor to motor
no interneuron
crossed extensor reflex/complex
when a withdrawal reflex is initiated in one lower limb, the crossed extensor reflex causes extension of opposite lower limb
needs interneuron
dorsal root ganglion (DRG)
associated with the dorsal horns; cell bodies of sensory neurons are located here
ventral root ganglion (spinal cord)
the location where preganglionic sympathetic neurons leave the spinal cord
They are motor neurons that give rise to the function of effector organs.
When the preganglionic sympathetic neurons reach the sympathetic chain ganglia, it was synapse with a post ganglionic neuron, who's axon will leave through the spinal nerve and travel to whichever organ it needs to supply. This is the route the majority of preganglionic sympathetic neurons take.
Exceptions
• Preganglionic sympathetic neurons may not synapse at the sympathetic chain ganglia. It it will go through either upward or downward through the trunk and synapse at a higher or lower level ganglion.
• Some may leave through the ventral root and travel through the chain ganglia without synapsing at them. They will synapse at a different ganglion (ex: celiac ganglion).
• Some may leave through the central root at synapse at the same level ganglia, but the postganglionic neurons will not leave through the central root. It will travel to a higher centre (upper cervical segments or the brain) for decision making (the brain controls autonomic reflexes).
Central Nervous System (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
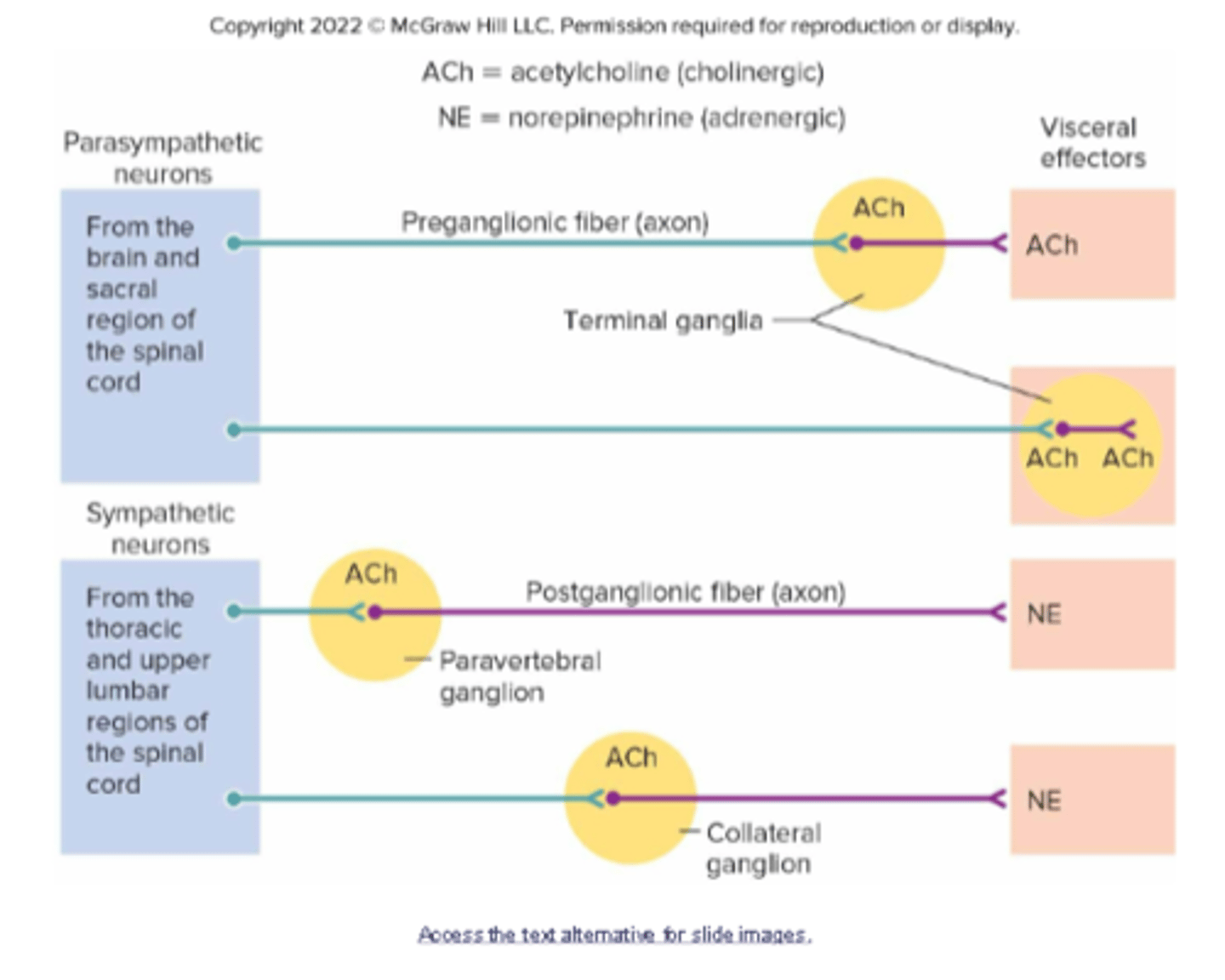
what is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system neurons?
Parasympathetic:
-long preganglionic fiber (axon)
-no chain ganglion
-short post ganglionic fiber (axon)
-ACh
Sympathetic:
-short preganglionic fiber (axon)
-has chain ganglion
-long post ganglionic fiber (axon)
-NE
frontal lobes function
control skilled voluntary movements of limbs and trunk
coordinate muscles involved in speech
control voluntary movements of eyes and eyelids
concentration, problem-solving, and planning
parietal lobe function
somatic sensory processing
Sensory areas provide sensations of temperature, touch, pressure, and pain involving the skin.
Association areas function in understanding speech and in using words to express thoughts and feelings
Temporal lobe function
Sensory areas are responsible for hearing
Association areas interpret sensory experiences and remember visual scenes, music, and other complex sensory patterns
occipital lobe function
visual processing
cerebrum function
Largest part of the brain; two hemispheres connected bythe corpus callosum
thinking, personality, sensations, movements, memory
Basal nuclei (basal ganglia) function
Masses of gray matter deep within the cerebral hemispheres
influence complex automatic movements, affects short-term memory
diencephalon function
includes masses of gray matter (thalamus and hypothalamus)
strengthen then distributes sensory information to the appropriate brain center
Brainstem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, responsible for automatic survival functions.
Contains pons, midbrain, and medulla oblongata
Pons function
Management of sleep, arousal, and facial expressions. (4)
Relays impulses between the medulla oblongata and cerebrum; helps regulate rate and depth of breathing
Midbrain function
Contains masses of gray matter and bundles of nerve fibers that join the spinal cord to higher regions of the brain
Contains reflex centers that move the eyes and head; maintains posture
medulla oblongata function
Conducts ascending and descending impulses between the brain and spinal cord;
contains cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory control centers and various nonvital reflex control centers
Cerebellum function
includes two lateral hemispheres connected by the vermis
process and store information, coordinates voluntary movements (posture, balance, speech)
Sensory neuron
Dendrite, cell body, and axon of a sensory neuron
Conducts an impulse from the receptor into the brain or spinal cord
Interneuron
Dendrite, cell body, and axon of a neuron within the brain or spinal cord
Serves as processing center; conducts an impulse from the sensory neuron to its synapse with a motor neuron
Motorneuron
Dendrite, cell body, and axon of a motor neuron
Conducts an impulse from the brain or spinal cord out to the synapse with an effector
grey matter in brain
consists of unmyelinated cell bodies and dendrites
white matter of brain
myelinated axons
A meniscus can be found in which joint?
Knee
While cupping your hands to hold water, in order to limit the amount leaking through your fingers you would need to perform which action?
Adduction of the fingers.
The cranium is composed of a series of bones
Fused together at sutures.
The bone extending down the distal lateral portion of the leg
Is the Fibula
What bone is referred to as the nasal septum?
Vomer
What major bones does the squamosal suture join?
Temporal and Parietal bones.
All ribs articulate with the sternum.
False
The elbow joint is made by the articulation of
The Olecranon Process of the Ulna joining the Olecranon Fossa of the Humerus.
A coxal bone includes the
Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis.
A long bone is covered externally with a sheath called the_________, whereas the marrow cavity is lined with the_________.
periosteum; endosteum
The major bone forming cells are
Osteoblasts
The glenoid cavity and acetabulum are both
Sockets where condyles of large bones articulate.
The common name of the clavicle is the
Collar bone.
Which of the following is part of the facial bones?
Maxillary bone
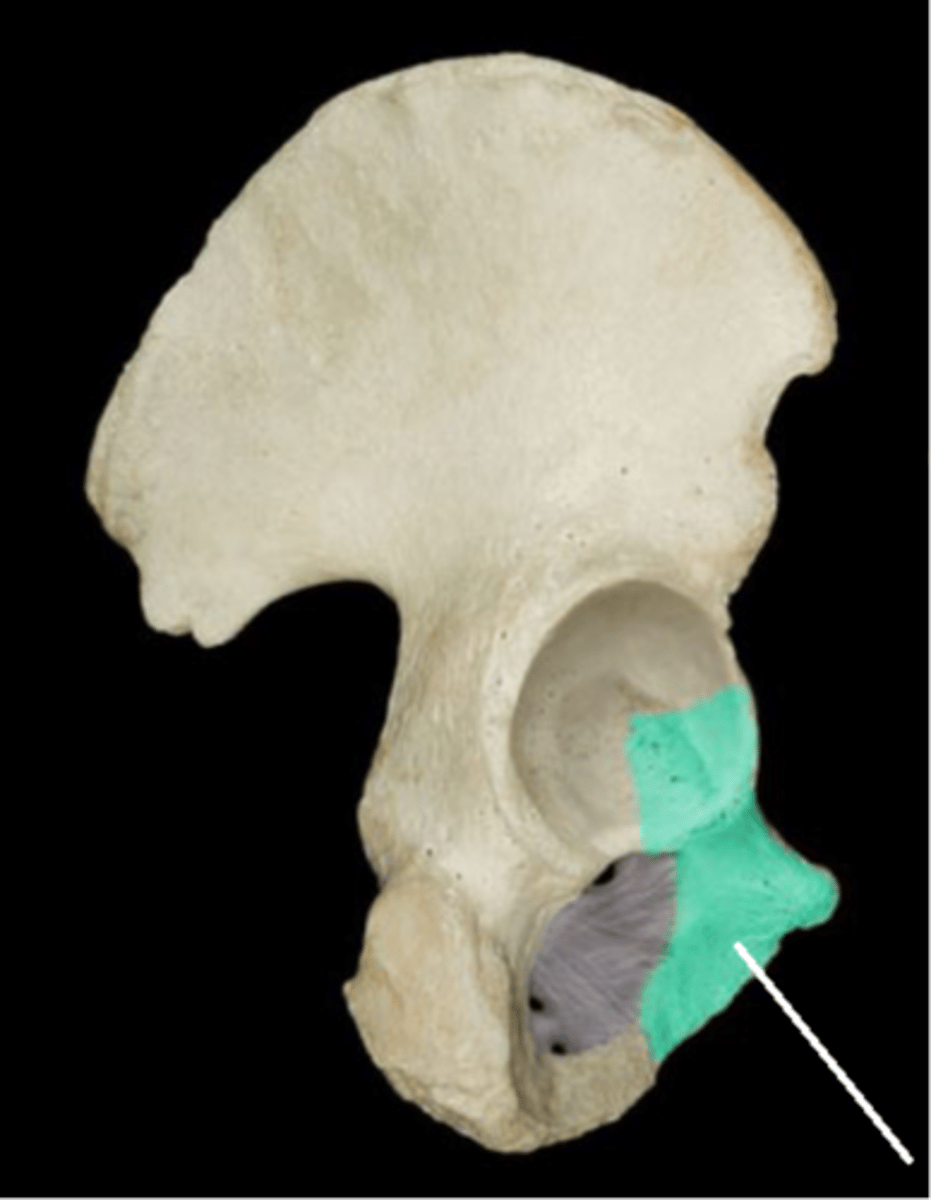
Which region of the hip bone is designated in green with a leader line in this picture?
Ischium
What vitamin helps absorb Calcium?
Vitamin D
What is the main mineral that bones store?
Calcium
How many ribs do humans have?
24
The joint between the diaphyses of the radius and ulna is a_________.
syndesmosis
A rounded knob that articulates with another bone is called a(n)_________.
condyle
When_________ become enclosed in lacunae, they become cells called_________.
osteocytes; osteoclasts
How many tarsals are there?
7
Which of the following is found in the palm of your hand?
Metatarsal
The external acoustic meatus is
Part of the Temporal bone and is the ear canal/tube.
When you are sitting, your body weight rests on which of the following?
Ischial tuberosity
Which of the following do costal cartilages connect?
The ribs with the sternum
What hormone gets released when blood Calcium levels are low? What is the impact?
Parathyroid hormone, bones release Calcium.
The diaphysis and epiphysis are portions of a
Long bone.
The scapula contains
The acromion and coracoid processes.
The microscopic bony chamber that houses mature bone cells are called
Lacunae
The cells responsible for removing excess bone tissue after the fracture repair process are
Osteoclasts
Both the foramen magnum and the obturator foramen are
Large holes in bones
The distal end of the Ulna is
The Trochlear Notch.
Cervical vertebrae can be distinguished from other types of vertebrae by the presence of
Transverse foramina