Ecology L8 Community & Species Diversity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Define Community Structure
Attributes of a community
# of species
Kinds of species
Distributions
Interactions
Define Taxonomic Affinity
Organisms grouped by classifications
Define Guild
Group of organisms that use the same resources
Define Functional Group
Species functioning similarly but not necessarily using the same resources
What is lognormal distribution?
Continuous probability of a random variable whose logarithm is normally disturbed. Each new individual in a sample can add a new species but eventually further accumulation of individuals results in few to no new species
Define Species Composition
Identity of the species present in a community
Define Species Diversity
Measure that combines the number of species and their relative abundances compared with one another
Define Species Richness
Number of species in an area
Define Species Evenness
Relative abundance of species in an area
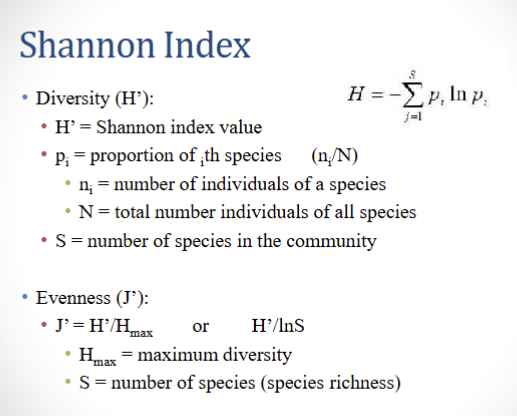
Shannon Index
Focuses on richness
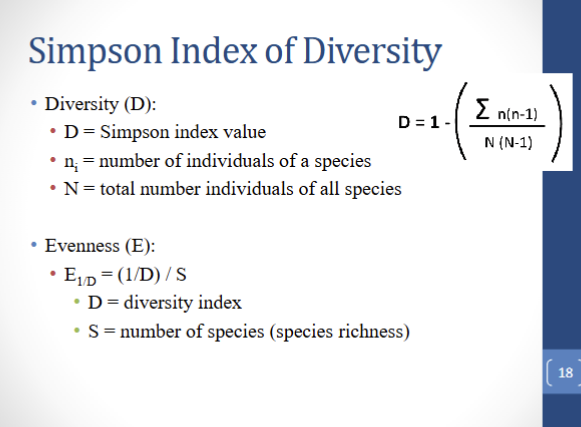
Simpson Index
Focuses on abundance
What factors influence environmental complexity?
Nutrient distribution & quantity
Predator distribution
Topography
Moisture distribution & quantity
Competition
Which factors of environmental complexity also influence species diversity?
Nutrient distribution and competition influence
Define Direct Interactions
Occur between two species and include trophic and non-trophic interactions

Define Indirect Interactions
Occur when the relationship between two species is mediated by a third or more species
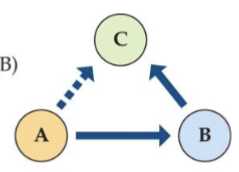
Define Trophic Cascade
A change in the rate of consumption at one trophic level that results in a series of changes in species abundance or composition at lower trophic levels
Define Trophic Facilitation
An interaction in which a consumer is indirectly facilitated by a positive interaction between its prey or food plant and another species
Define Competitive Networks
Competitive interactions among multiple species in which every species has a negative effect on every other species
Define Disturbance
Relatively discrete event that causes an abrupt change and alters resource availability, substrate availability, or physical environment
How does disturbance affect species diversity?
Creates gaps in communities and has variosus impacts on both spatial and temporal scales; impacts may not always be negative
Define Disturbance Regime
characteristics of the disturbances occurring in that ecosystem
What are the four things used to describe Disturbance Regime?
Intensity
Size
Frequency
Timing
What are the 7 types of disturbances?
Wind
Water
Animals
Earthquakes & volcanoes
Disease
Human activity
Fire
How can wind impact a community?
Through windthrow - blow down of a branch, part of a tree, whole tree, or group of trees
Important in tropical forests to open up space for new communities to grow
May result in soil erosion
How can water disturbance impact a community?
Through drought - an extended period of months or years of a deficiency in water supply
How can animal disturbances impact a community?
Associated with herbivory; large herds and insect swarms
How can earthquakes/volcanoes impact a community?
May be massive in size, associated with landslides/mudflows/avalanches/lava flows, and can lead to primary succession
How can disease impact a community?
Through various intensities of fungi, bacteria, and viruses
How can human activity affect a community?
Can be accidental or intentional
Domestic animals
Logging
Farming/ranching
Recreation activities
How can fire disturbances impact a community?
Major source in many communities due to its great potential for destruction
What does fire require?
Fuel, proper climate conditions, and an ignition source

Describe an Underground Fire
Below the surface. Most destructive, but very infrequent

Describe a Surface Fire
In contact with the ground. Less hot than other fires, but quicker moving. Fed by lightweight fuels. Can lead to crown fires via consumption of ladder fuels

Describe a Crown Fire
Can travel faster and burn with more intensity, and is capable of creating its own weather due to two different temperatures. Highly destructive
What are the four behavior determinants of a fire?
Ignition Pattern
Fuel
Weather
Topography
How does ignition pattern determine fire behavior?
Area and definition
How does fuel determine a fire’s behavior?
Physical properties
Quantity
Arrangement composition
Moisture content
How does weather determine a fire’s behavior?
Temperature
Humidity
Wind
Atmosphere Structure
Season
How does topography determine a fire’s behavior?
Land configuration, slope
Why is fire essential to ecosystems?
Removal of competitors and fuel
Recycles nutrients
Opens serotinous cones
Enhances wildlife habitats
What are some adaptions to surviving fire-prone ecosystems?
Thick bark, rapid growth, early maturity, evanescent branches, growth and germination stimulated by fire
Define Succession
Directional change in plant & animal communities following a disturbance or creation of a new substrate
Define Primary Succession
Colonization of ground that wasn’t previously vegetated
Define Secondary Succession
Colonization of ground previously occupied by a living organism
Which vegetation dynamics do succession responses depend on?
Pioneer Stage → Intermediate Stage → Climax Stage
Define Climax Community
Community whose populations remain stable until disrupted by disturbance
Define Stability
Persistence of a community or ecosystem; lack of or absence of change
Why is there controversy over the terms climax community and stability?
Populations may appear stable, but individuals or species aren’t. It depends on scale, measurements, and organisms of study.
What are some community changes that occur during succession?
Increases species diversity, and can increase or decrease species composition
What are some ecosystem changes that occur during succession?
Increase in biomass
Increase primary production
Increase respirationn
Increase nutrient retention
Alterations of diversity and composition, such as soil characteristics
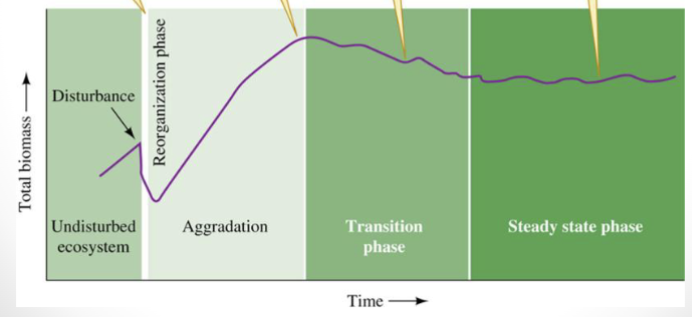
What is the ecosystem recovery model?
Disturbing a forest will induce a series of distinct recovery phases
Disturbance → Ecosystem reorganizes → Biomas increases → Biomass declines during transition → Biomass steadies into a state phase
What are the three mechanisms driving succession?
Facilitation
Tolerance
Inhibition
Define Facilitation
Pioneer species alter the environment and make it more suitable for the establishment of later successional species
Define Tolerance
Later successional species are able to tolerate the conditions created by earlier species
Define Inhibition
Early colonizers prevent the establishment of later species, slowing succession