RE 1
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:47 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
1
New cards
Ch 17
sources of commercial debt and equity capital
2
New cards
2018 value of CRE in the US
$12.6T, 50% of the value of the stock of owner-occupied houses ($25.9T), 70% of the value of outstanding US treasury securities ($17.8T) and 30% of the value of corporate equities ($4.29T)
3
New cards
$12.6T market value of commercial real estate can be broken down into 4 groups
- $1.6T public equity capital
- $6.3T privately held equity
- $1T in publicly traded mortgage debt
- $3.7 T in privately held mortgage debt
- $6.3T privately held equity
- $1T in publicly traded mortgage debt
- $3.7 T in privately held mortgage debt
4
New cards
debt accounts for apprx 37% of market value of CRE...
low bc large organizations like pension funds typically purchase CRE with 100% equity
5
New cards
advantages of pooling equity; allows investors to...
- acquire more expensive properties than they could otherwise afford
- diversity their portfolios
- take advantage of economies of scale
- access debt at lower interest rates to achieve greater returns
- to pool their capital and allow someone else to manage it and take advantage of the skills of the sponsor/syndicator
- diversity their portfolios
- take advantage of economies of scale
- access debt at lower interest rates to achieve greater returns
- to pool their capital and allow someone else to manage it and take advantage of the skills of the sponsor/syndicator
6
New cards
disadvantages of pooling equity
- investors usually have to cede their right to manage and control the property to the active sponsor
- sponsor has to be compensated either with fees, a salary, or a disproportionately large share of equity cash flows
- sponsor has to be compensated either with fees, a salary, or a disproportionately large share of equity cash flows
7
New cards
two considerations that determine the choice of ownership for pooled equity investments
tax issues (avoid double taxation)
limited liability (want to avoid unlimited liability)
management control issues
ability to access additional equity capital
ability to reduce return volatility and share risk
ability of investors to dispose of their interests in org
ability to distribute cash flows to investors base on perfcentages
limited liability (want to avoid unlimited liability)
management control issues
ability to access additional equity capital
ability to reduce return volatility and share risk
ability of investors to dispose of their interests in org
ability to distribute cash flows to investors base on perfcentages
8
New cards
general partnership
simplest form of pooled ownership; most important benefit of a general partnership is that it features pass-through taxation
treated as conduits for tax purposes (taxable income and losses flow through to the individual partners who pay the tax)
treated as conduits for tax purposes (taxable income and losses flow through to the individual partners who pay the tax)
9
New cards
disadvantage of general partnership
have unlimited liability; liable for all debts of the partnership (personal assets are subject to the claims of partnership's creditors)
10
New cards
limited partnership
A partnership in which one party (the general partner) assumes unlimited liability in exchange for control of all material decision making. The limited partners enjoy liability that is limited to the extent of their equity contributions to the entity. All parties involved benefit from flow-through income and taxation; that is, the partnership is not taxed.
general partners can be entities rather than individuals
general partners can be entities rather than individuals
11
New cards
advantages and disadvantages of limited partnership
pro: allows the limited partners to cap their personal liability to an amount equal to their total equity investment in the partnership; pass-through tax treatment
con: in exchange for limited personal liability, the limited partners give up day-to-day control of the partnership and are prohibited from participating in management or policy making (principal-agent relationship)
con: in exchange for limited personal liability, the limited partners give up day-to-day control of the partnership and are prohibited from participating in management or policy making (principal-agent relationship)
12
New cards
C corporation
Corporate ownership structure that provides limited liability, but suffers from double taxation and does not enable losses to flow through to investors for current use.
advantage: shareholders enjoy limited liability
disadvantage: shareholders subject to double taxation
advantage: shareholders enjoy limited liability
disadvantage: shareholders subject to double taxation
13
New cards
subchapter S corporation
Corporate ownership structure that is a federal tax election made with the unanimous consent of the shareholders. An S corporation possesses the same limited liability benefits for its shareholders as do C corporations but it is not a separate taxable entity.
14
New cards
limited liability company (LLC)
A hybrid form of ownership that combines the corporate characteristics of limited liability with the tax characteristics of a partnership.
15
New cards
intermediaries
In real estate investment, third party specialists who use their expertise and knowledge to invest and manage funds on behalf of clients.
popular bc supply better expertise, improve liquidity, and allow the investor to diversity and share risk
popular bc supply better expertise, improve liquidity, and allow the investor to diversity and share risk
16
New cards
direct investment in CRE
most commonly used by large institutional investors and high-net-worth private investors
includes: pension funds, life insurance companies, etc.
includes: pension funds, life insurance companies, etc.
17
New cards
pension funds
Retirement savings accounts that now represent a major source of equity capital in commercial real estate markets.
$542B, less than 7% of CRE equity
$542B, less than 7% of CRE equity
18
New cards
life insurance companies
involves the payment of premiums by the insured in exchange for benefits to be paid upon the death of the insured
19
New cards
value of US CRE Equity
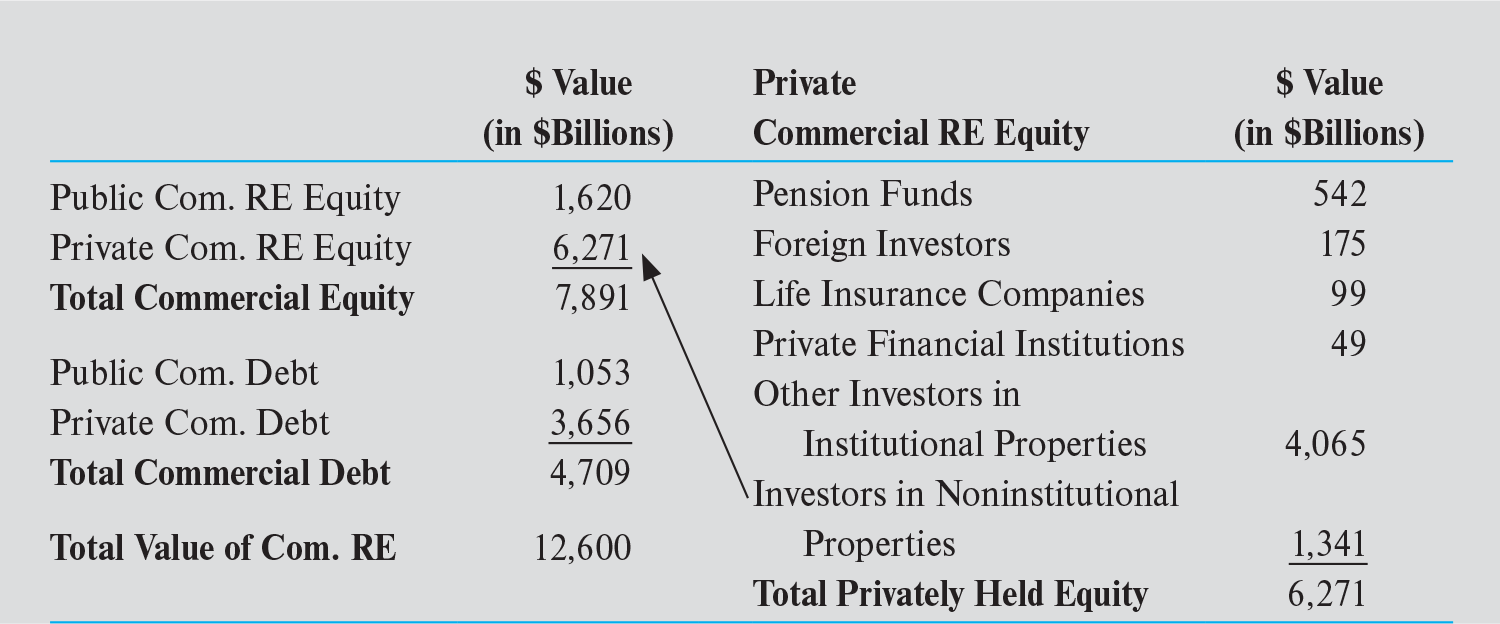
20
New cards
securitized investments
Investment instruments that pool investment assets, enabling investors to purchase a share in the pool of assets.
21
New cards
syndicate
A group of persons or legal entities who come together to carry out a particular investment activity.
can be formed by institutional or non institutional investors, typically organized as limited partnerships or LLCs
can be formed by institutional or non institutional investors, typically organized as limited partnerships or LLCs
22
New cards
pooled equity investment alternatives
- separate accounts
- commingled real estate funds (CREFs)
- closed-end real estate private equity funds
- full platform operating company
- commingled real estate funds (CREFs)
- closed-end real estate private equity funds
- full platform operating company
23
New cards
separate accounts
An investment manager acting on behalf of multiple clients holds each client’s assets in a separate account rather than as part of a commingled fund to permit customized investments for each client.
24
New cards
commingled real estate funds (CREFs)
A collection of investment capital from various pension funds that are pooled by an investment advisor/fund manager to purchase commercial real estate properties.
offered by major banks, life insurance companies, investment banks, etc.
allow for better diversification for a management fee
min about $1M-$10M
front-end fee for acquiring properties and back-end fee upon disposition (1.5%)
closed-end (finite life; offer no liquidity until the funds begin to sell properties at end of life) or open-end (infinite life; allows investors to redeem interests periodically)
offered by major banks, life insurance companies, investment banks, etc.
allow for better diversification for a management fee
min about $1M-$10M
front-end fee for acquiring properties and back-end fee upon disposition (1.5%)
closed-end (finite life; offer no liquidity until the funds begin to sell properties at end of life) or open-end (infinite life; allows investors to redeem interests periodically)
25
New cards
closed-end real estate private equity funds
These funds have a finite life, typically 7–10 years, with an option for the fund manager or sponsor to extend the life by an additional year or two. Because of this finite life, the fund manager is forced to eventually dispose of the assets and return the investors’ capital. These funds typically have meaningful side-by-side investment by the fund sponsor/manager, aligning the manager’s economic outcomes with those of the investors. The fee structures are also usually richer and more complex, allowing more features that further align interests.
limited partners earn a preferred return before general partner
carried interest/founder's equity: general partner receives a percentage of the rest of the profits
limited partners earn a preferred return before general partner
carried interest/founder's equity: general partner receives a percentage of the rest of the profits
26
New cards
core funds
least risky and offer the lowest returns (primarily invest in high-quality properties with strong leases in large metro areas)
27
New cards
value-added funds
have intermediate level of risk and offer an intermediate level of returno
28
New cards
opportunistic funds
highest risk and highest returns
29
New cards
full platform operating companies
This is an investment strategy that involves starting or acquiring and then operating a real estate company. The company may then acquire real estate investments, develop properties, and/or act as a general partner in a variety of investments funds. High net-worth families have been common investors in full-platform companies, while more conservative pension funds have gravitated toward safer, more passive forms of investment.
30
New cards
institutional investors vs non-institutional investors
institutional investors (78%) account for 4.93T of the 6.27T in real estate private CRE equity in 2018
non institutional investors (22%) account for 1.34T in private CRE equity; typically high net worth individuals and family offices
non institutional investors (22%) account for 1.34T in private CRE equity; typically high net worth individuals and family offices
31
New cards
Real estate investment trust (REITs)
A corporation or trust that uses the pooled capital of many investors to purchase and manage income property (equity REIT) and/or mortgage loans (mortgage REIT). special type of corp. and creature of the US tax code
design allows investors to enjoy the same limited liability as c corps but also enjoy pass-through taxation unlike c corps
design allows investors to enjoy the same limited liability as c corps but also enjoy pass-through taxation unlike c corps
32
New cards
equity REITs
real estate investment trusts that invest in and operate income-producing properties
33
New cards
mortgage REITs
REITs that purchase mortgage obligations and effectively become real estate lenders
34
New cards
sources of CRE Debt
78% of the 4.7T in outstanding mortgage debt is privately held by institutional and individual investors; commercial banks and saving associations hold 61%
remaining 22% is publicly traded as commercial mortgage-backed securities or REIT unsecured debt; dominated by commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBs)
remaining 22% is publicly traded as commercial mortgage-backed securities or REIT unsecured debt; dominated by commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBs)
35
New cards
development and construction lending
development and construction of commercial properties achieved by short-term development and construction loans; risky bc likelihood that the project will not be successfully completed on time and on budget
commercial banks typically lend (also savings institutions, credit agencies, and private equity lenders)
commercial banks typically lend (also savings institutions, credit agencies, and private equity lenders)
36
New cards
How much of a person's financial portfolio should be in real estate?
10% to 15%
37
New cards
Private Commercial Real Estate Investment Markets
- local LLCs
- private equity commercial real estate funds
- private REITs (about 750 in existence)
- public commercial real estate markets
- private equity commercial real estate funds
- private REITs (about 750 in existence)
- public commercial real estate markets
38
New cards
National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts (NAREIT)
has website and good info about publicly traded REITs
39
New cards
real estate investment trust (REITs)
a company that owns, develops, operates, manages, or finances income-producing properties; corporations that have a special tax designation that allows them to forego the potential double-taxation of dividends
40
New cards
equity REITs
own and manage real estate properties and derive most of their revenues from rent (164 publicly traded, 96% of the market cap of publicly traded REITs)
41
New cards
mortgage REITs
hold or trade mortgages and mortgage-backed securities; most revenue derived from interest payments (44 publicly traded, 4% market cap)
42
New cards
key benefit of REITs
qualified reits can deduct dividends paid from corporate taxable income; avoid taxation of corporate income if it distributes all of its taxable income as dividends
43
New cards
five or fewer rule
the entity can have no more than half its shares held by five or fewer individuals
44
New cards
REIT entities must pay dividends equal to at least...
90% of its taxable income every year (not cash flow)
45
New cards
REIT entities must be in the real estate business
75% of its assets have to be invested in real estate, government securities, or cash, and 75% of its gross income must come from real estate
46
New cards
REIT trends
1960s, 1990s became popular (increase from $13B to $438B in 2006), 2007-2008 housing collapse decreased market cap by 50%, now growing again
47
New cards
umbrella partnership REITs (UPREITs)
an organizational structure in which a publicly traded REIT owns a fractional interest in an operating partnership that owns all or part of individual property partnerships
more than 80% reits structured like this
more than 80% reits structured like this
48
New cards
One way to invest in commercial real estate is to buy a commercial property, hold the title to it, and exercise complete control over it. This is an example of...
direct investment in private commercial real estate equity (bc investor owns the underlying property, not the debt)
49
New cards
Double taxation is a negative characteristic of which entity type?
C Corporation
50
New cards
syndicate
a group of individuals or legal entities that come together to carry out a particular activity
51
New cards
Tenancy in Common (TIC
form of direct ownership in which multiple investors have undivided ownership interests in the property, evidenced by a separate deed
52
New cards
which of the following holds the largest share of private CRE debt in the US?
banks and savings associations (hold 61% of all private CRE debt, and 47% of overall cre debt)
53
New cards
what percentage of real estate private equity in the us is held by investors in institutional-quality properties?
78%, res held by investors in non-institutional properties
54
New cards
What percentage of debt that finances private commercial real estate is privately held?
78% of the $4.7T in outstanding mortgage debt is privately held by institutional and individual investors, and the remaining 22% is publicly traded as commercial mortgage-backed securities or REIT unsecured debt
55
New cards
Which was the fastest-growing source of long-term commercial mortgage funds until their market collapsed in 2008?
commercial mortgage-backed securities
56
New cards
in the US, the largest and most common holders of cre are
LLCs
57
New cards
Which pooled ownership structure is most commonly used by private funds that attempt to attract capital from high-net worth individuals and institutional investors?
limited partnerships
58
New cards
Price-FFO Multiple
(Price/share) / (FFO/share)
59
New cards
Net Asset Value in relation to REIT's
if REIT price < price/share NAV = discount
if REIT price > price/share NAV = premium
if REIT price > price/share NAV = premium
60
New cards
For a REIT to maintain its special tax status under US tax law, what is the min. amount of investors and how much of its taxable income must be distributed in the form of dividends?
at least 100 investors; 90%
61
New cards
the FTSE NAREIT ALL REIT index
a market capitalization-weighted index that includes all tax-qualified REITs that are listed on the NY stock exchange, NASDAQ, and the American Stock Exchange. It is an index for public, listed REITs
62
New cards
What was the significance of the development of the UPREIT in the early 1990s?
it is now easier to convert private ownership of real estate to reits (IRS no longer treats as a normal sale, so the owners do not accrue tax liability like capital gains and depreciation recapture tax, which are disincentives)
63
New cards
REIT status is a voluntary election under the
internal revenue code
64
New cards
according to the "five or fewer" rule...
a qualified REIT can have no more than half of its shares held by five or fewer individuals
65
New cards
two kinds of reits
equity reits (invest in and operate commercial properties)
mortgage reits (buy mortgage obligations and are effectively real estate lenders)
majority of all reits are equity reits
mortgage reits (buy mortgage obligations and are effectively real estate lenders)
majority of all reits are equity reits
66
New cards
advantages of investing in REITs
- higher-than-average expected returns
- strong corporate governance
- possibility for diversification
- increased liquidity
- strong corporate governance
- possibility for diversification
- increased liquidity
67
New cards
one major downside of investing in public non-listed REITs is that...
they typically have high fees associated with them (10%-15%)
68
New cards
Over the past 20 years, returns on the REIT index fund have been ____ than those of other index funds. Investing in REITs helps diversify a person's portfolio because they are _____ correlated with other investments (such as stocks and bonds)
greater (annualized returns of more than 12%); not highly (useful for portfolio diversification)
69
New cards
Funds From Operations (FFO)
adds depreciation and other amortization expenses to net income
= NI + Depr + amortization of leasing expenses + amortization of improvements made to tenants' space - gains from infrequent and unusual events
= NI + Depr + amortization of leasing expenses + amortization of improvements made to tenants' space - gains from infrequent and unusual events
70
New cards
Conditions that REITs must satisfy to maintain special tax status
- must be at least 100 investors
- no five investors can own more than half of the shares
- 75% or more of the REIT's assets must consist of real estate assets, cash, or government-backed securities
- REIT has to distribute at least 90% of its taxable income as dividends to shareholders
- no five investors can own more than half of the shares
- 75% or more of the REIT's assets must consist of real estate assets, cash, or government-backed securities
- REIT has to distribute at least 90% of its taxable income as dividends to shareholders
71
New cards
What is true about investment value?
- it includes the impact of the cash flow from the ultimate sale of the property
- it is calculated via the application of a discount rate to future cash flows
- it is a function of estimated cash flows from operations
- based on the value that a PARTICULAR investor places on the property
- it is calculated via the application of a discount rate to future cash flows
- it is a function of estimated cash flows from operations
- based on the value that a PARTICULAR investor places on the property
72
New cards
market value considers...
most probable selling price under "normal" sale conditions, so it is based on the expectations of the average (typical) investor
73
New cards
Effective Gross Income Multiplier
EGIM = (Acquisition Price/ EGI)
74
New cards
going-in cap rate
RO = NOI/Acquisition Price
75
New cards
Net operating income is a ____ cash flow and before-tax cash flow is a ____ cash flow
noi is unlevered bc it does not account for the use of financial leverage (does not deduct debt service, mortgage pmt.)
BTCF is levered bc it deducts debt service
BTCF is levered bc it deducts debt service
76
New cards
Financial risk ratios
measures the ability of the property to produce income that meets its operating and financial obligations
77
New cards
minimum acceptable debt yield ratio and debt coverage ratio
DYR = at least 10%
DCR = at least 1.2
DCR = at least 1.2
78
New cards
Equity dividend rate (EDR)
represents the residual cash flow return to equity investment, after subtracting the debt service from NOI.
aka "cash-on-cash" return (used for smaller investments)
aka "cash-on-cash" return (used for smaller investments)
79
New cards
Before-tax cash flows are considered...
levered cash flows because they subtract the mortgage payment from NOI
80
New cards
Before-Tax Equity Revision
BTER = Net Sale Proceeds - RMB
81
New cards
The use of leverage increases both the project's NPV and its IRR when...
the unlevered IRR > effective borrowing cost
82
New cards
The use of leverage will increase the levered IRR as long as the unlevered IRR is...
unlevered IRR > effective borrowing cost of the mortgage (income taxes reduce the going-in IRR)
83
New cards
The NPV of a project ____ as the investor's required rate of return increases, which makes it ____ likely the investor will take the project
decreases (bc PV of future cash flows gets smaller); less
84
New cards
What is captured by the calculation of effective rent?
The effective rent (equivalent level rent) is the fixed monthly payment that has the same present value as the actual lease payments after concessions and operating expenses. Takes the time value of money into account (NOT interlease risk, re-leasing costs, or need for flexibility)
85
New cards
Expansion option
obligates the property owner to provide space for the tenant to expand the size of their leased space
86
New cards
right of first refusal
allows the tenant to lease adjacent space if it becomes available
87
New cards
gross lease
the owner pays for all of the operating expenses, including property taxes
88
New cards
Graduated rent clause (escalation clause)
step-ups; authorizes pre-specified increases in the rental rate over the course of the lease
89
New cards
allows a mortgage lender to terminate a tenant's lease when the property owner defaults
90
New cards
rent for commercial properties is typically quoted in terms of...
dollars per square foot per year
91
New cards
concession
a lease clause that reduces the cost of the lease to the tenant and thus provides an incentive to lease space from the owner
(ex: offering free rent for x months)
(ex: offering free rent for x months)
92
New cards
triple net lease
tenant responsible for paying all operating expenses
93
New cards
what is a key downside of long-term leases?
loss of flexibility
94
New cards
tenant improvement allowance
the landlord agrees to pay a certain amount to rebuild out or refurbish space so that it is adequate for the tenant's use
95
New cards
Double taxation of the income produced by the underlying properties is most likely to occur if the commercial properties are held in the form of a
C Corporation
96
New cards
With regard to double taxation, distribution, and the treatment of the losses, general partnership are most like
limited partnerships
97
New cards
Special allocations of income or loss are available if the form of ownership is a
LLC
98
New cards
Small to medium sized real estate syndicates that develop or acquire property in a local market are most typically organized as
LLCs
99
New cards
Which of the following forms of ownership involve both limited and unlimited liability?
limited partnerships
100
New cards
General partnerships
not a taxable entity