2.7 Forgetting and Other Memory Challenges
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
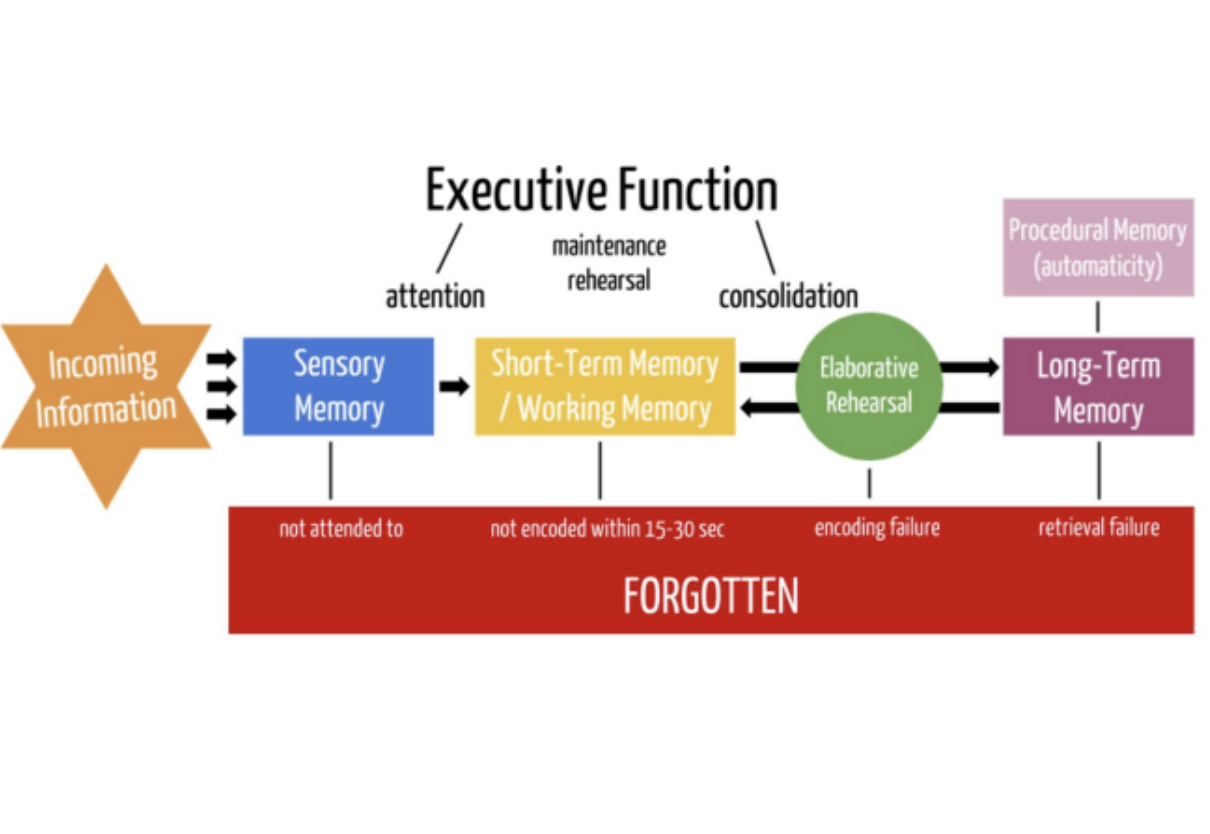
Forgetting can occur at any memory stage.
Anterograde amnesia
is the INABILITY to form new memories.
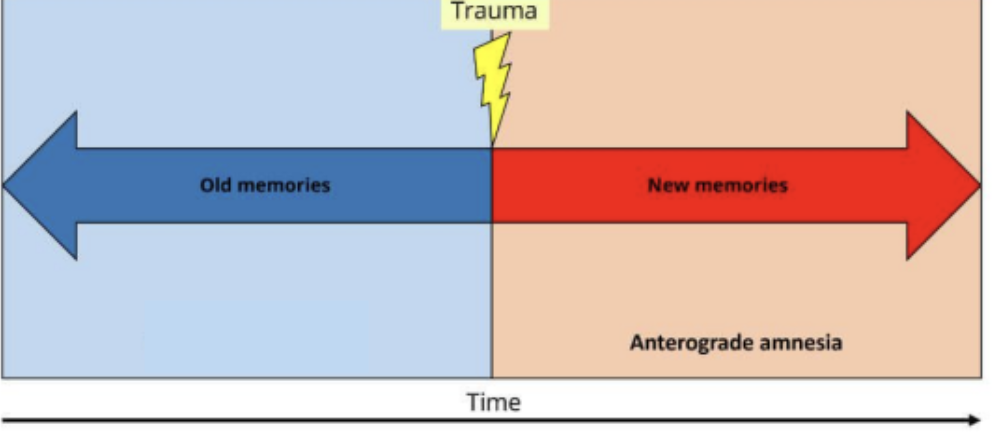
Retrograde amnesia
is the inability to retrieve old memories.
encoding failure
when information never makes it into long-term memory because it wasn't adequately processed or attended to in the first place, making it impossible to recall later
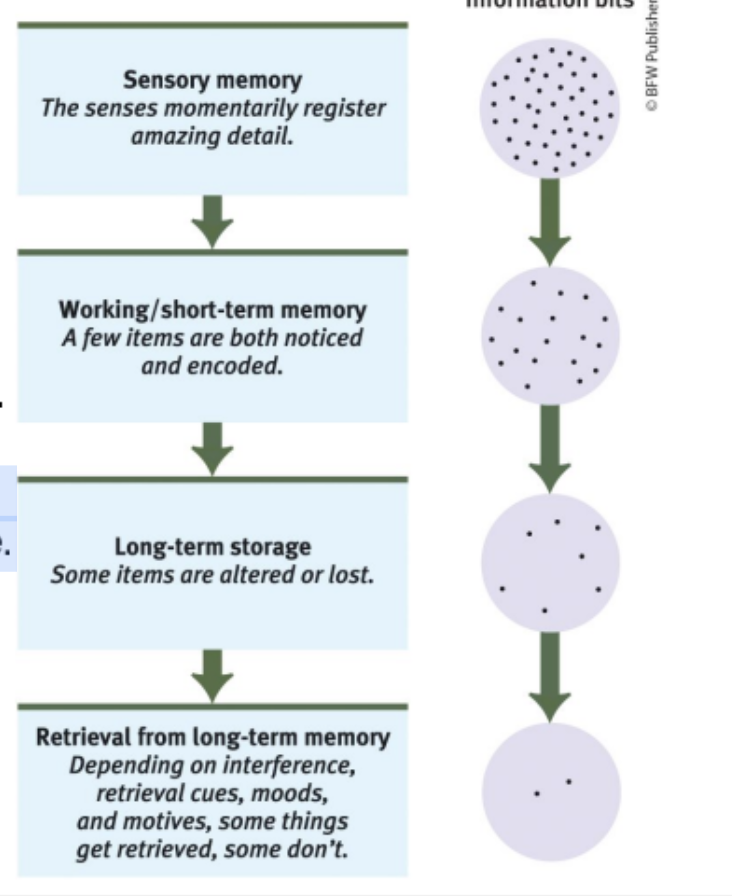
Storage Decay
Even after encoding info to your LTM, you can forget it if you don’t retrieve the info after a long period of time.
Ebbinghaus
forgetting curve study confirms that the course of forgetting is initially rapid, then levels
off with time.
Retrieval Failure
Sometimes we worked hard to encode and store info. into our LTM but we just can’t seem to retrieve it when we need it.
Tip of the tongue phenomenon
often occurs when we can only retrieve bits of the information at a time.
Proactive (forward acting) interference
PAST learning gets in the way of recalling new learning.
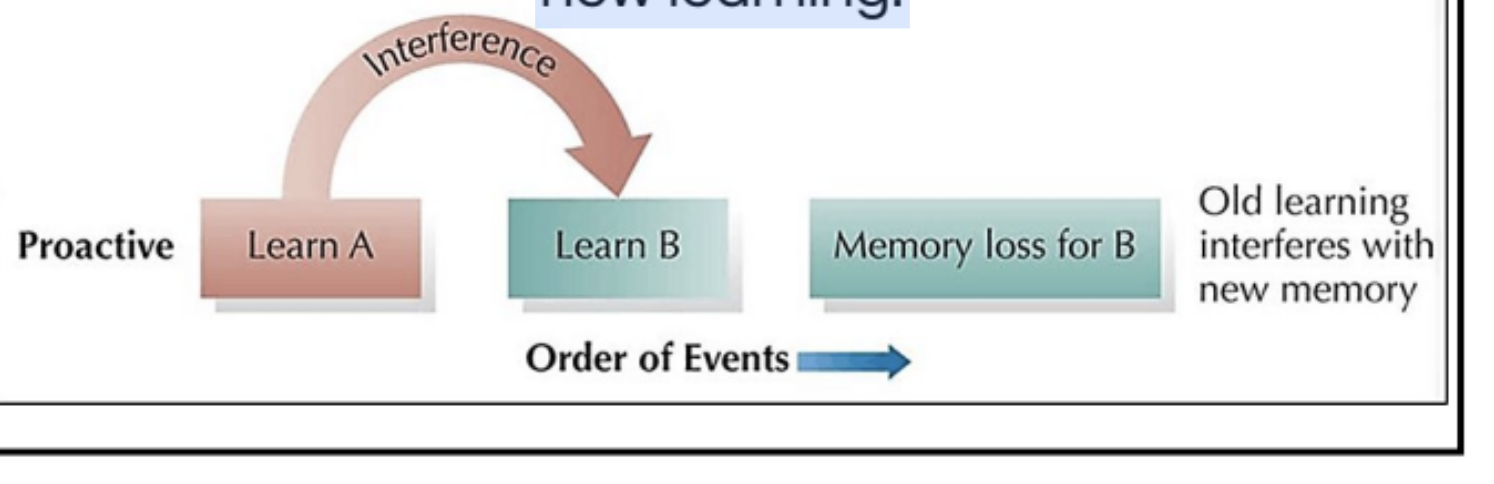
Retroactive interference
occurs when NEW learning gets in the way of recalling old learning.
Sigmund Freud
explained that sometimes painful or unacceptable memories are repress, not retrievable because they are shut out from our consciousness in order to reduce anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories.
REconsolidation
is a process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again.
Misinformation effect
occurs when a memory has been corrupted by misleading information. When exposed to misleading information, we tend to misremember.
Imagination effect (also called imagination inflation
occurs when imagining or seeing a suggested event makes people more likely to believe it actually happened, even when it didn’t.
Source amnesia
means you remember something feels familiar but you don’t remember how, when or where it came from.