simple machines
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what are input forces
the force applied
what are output forces
the force which is applied to the task
what is a mechanical advantage
machine takes a small input force and increases the magnitude (size) of the output force
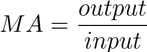
how do you calculate mechanical advantage?
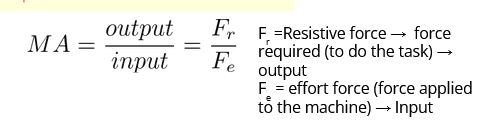
what is a lever
A lever is a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum
The bar may be straight or curves
In use, a lever has both an effort (applied) force and a load (resistive) force
what is a 1st class Lever
Resistance/load is closer to the fulcrum vice versa effort is further from the fulcrum
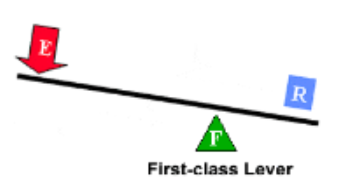
what does 1st flass lever do
multiplies EF and changes it’s direction
what are examples of first class lever
crowbars
scissors
pliers
tinsnips
seesaws
what is a second class lever
the fulurm is at the end of the bar.
resistance force/load is in the middle
effort forces at the opposite end of the fulcrum
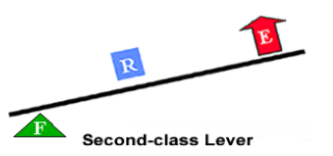
what does 2nd lever forces
effort moves more than resistance
multiplier Effort force but does not change direct
what are examples of 2nd class levers
nut crackers
wheel barrows
doors
bottle openers
what is a 3rd class levers?
fulcrum is at the far end
effort force in the moddle
resistance/load at the opposite far end

what are examples of 3rd class levers?
tweezers, hammers, shovels
what do third class levers do?
does not multiply force
resistance moves faster than effort
what is the equation for energy efficiency
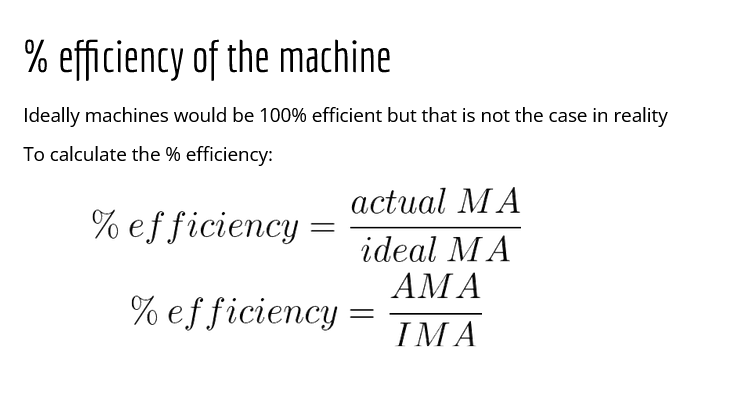
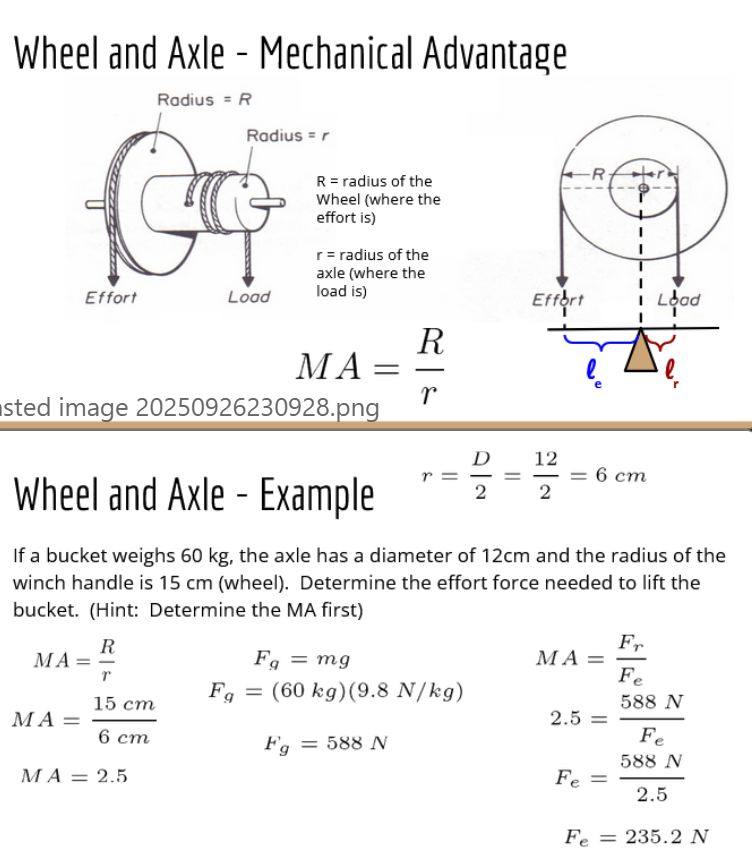
how do you calculate forces on wheel and pulies
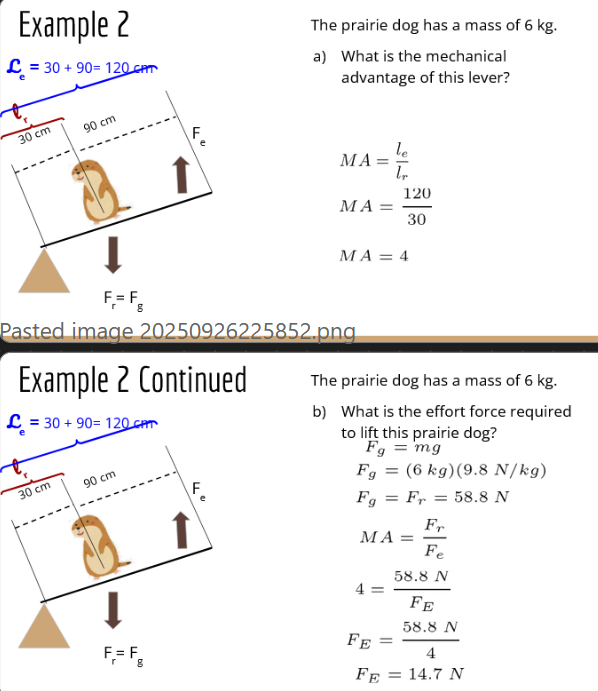
how do you calculate lever forces
How do you calculate forces of gears

what is a steering whel system in a car
rack and pinion
what system is used in jacks to lift cars
screw gear type1
what system is used to help a crankshaft itès a type of motio
slider crank