Grammar and Writing Concepts
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and definitions related to grammar and writing, focusing on register, metafunctions, and passive voice.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Register
A variety of a language used for a specific purpose or in a particular social situation, dependent on context.
Metafunctions
Concepts introduced by Halliday that represent three functions of language:
field = experiential metafunction:(what the text is about),
tenor = interpersonal: (the role relation between speaker and hearer)
mode (medium) = textual: (how the text is organized).
SPEAKING model (Hymes 1972)
16 components à discourse situation
• temporal and local setting
• participants and their relationship
• ends of the discourse
• mode
• social norms
• genre
Passive voice
A grammatical construction in which the subject of the sentence is acted upon rather than performing the action, often used for formality in written academic English.
Agents
The doers of an action in a sentence, as in the subject performing the verb.
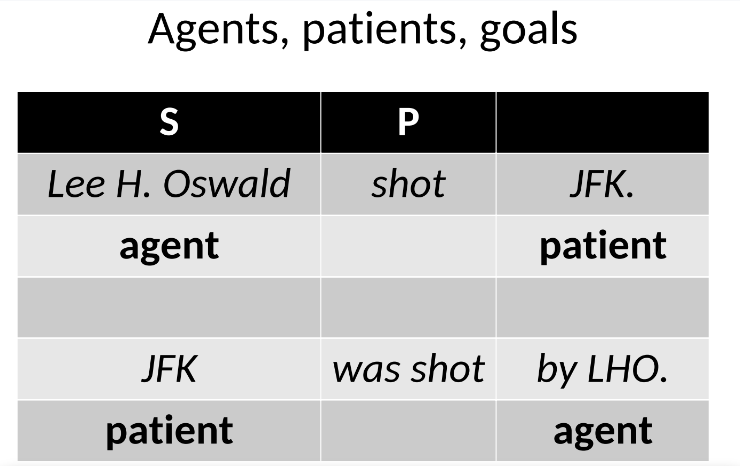
Patients
The receivers of the action in a sentence, often the subject in a passive construction.
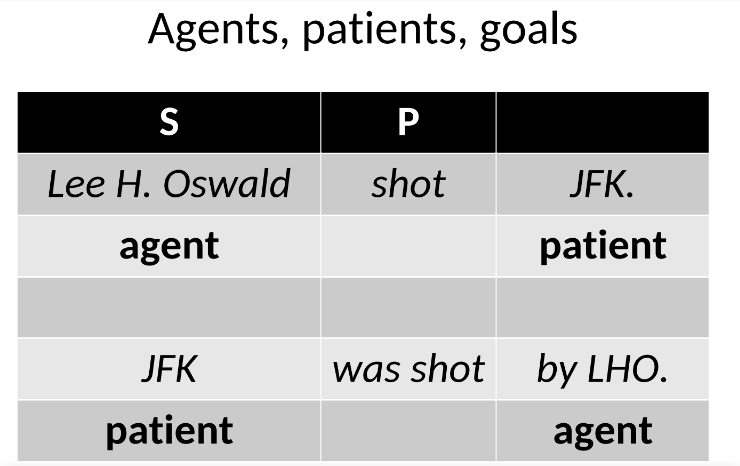
Goals
The entities toward which actions are directed in a sentence, particularly in active voice scenarios.
Patient deletion
A technique in passive constructions where the patient (receiver of the action) is omitted, focusing on the action itself.
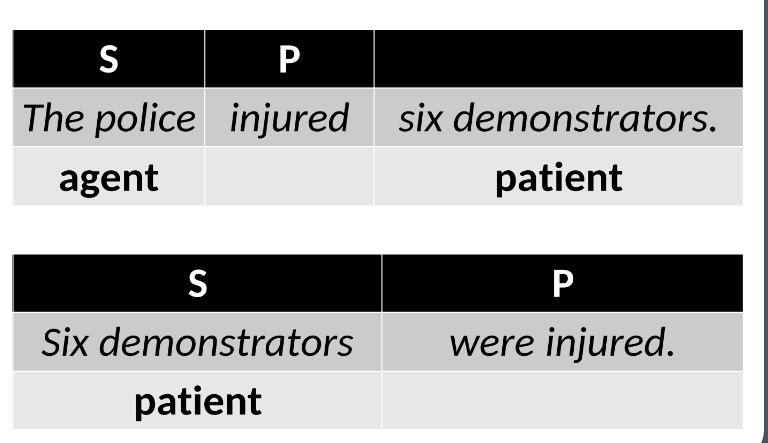
Agent deletion
A strategy often used in formal writing where the agent (doer of the action) is removed to emphasize the action or to avoid placing blame.
• when agent is unkown / unimportant/ obvious / the general public
Ideological passive
A passive construction that omits the actor to obscure responsibility or promote a particular narrative.
Several rioters got killed in yesterday's clashes.
Several rioters got killed in yesterday's clashes with the police.
Several rioters got killed in yesterday's clashes by the police .
The police killed severl rioters in yesterday's clashes.
Use the passive
• when focus is on issue and not on people involved
The research was carried out over a period of six months.
• to describe rules and procedures
Papers must be submitted through SafeAssignment on Blackboard.
Candidates will be interviewed in alphabetical order.
• to describe commercial, industrial, scientific processes
Minutes will be taken and submitted to the chair for approval.
All components are electronically tagged and transported to the production line.
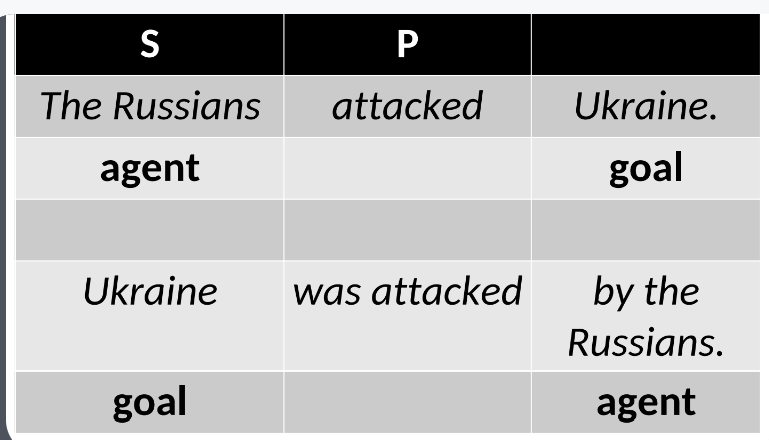
Event – Goal
A passive construction that highlights the result or goal of an event without explicitly naming the agent responsible for it.
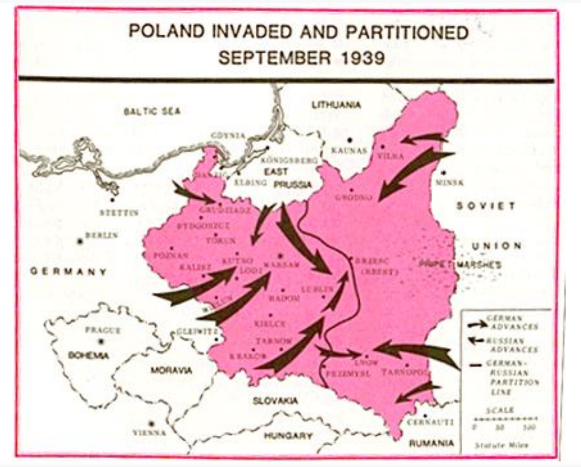
• Treaty of Non-aggression between
Germany and the Union of Soviet
Socialist Republics 1939
• Ribbentrop–Molotov Pact
• Nazi–Soviet Pact
• Hitler-Stalin Pact
• Fake news
Impersonal passive
A construction used in a sentence where the subject is unknown or irrelevant, focusing instead on the action or result, often used to create an objective tone.
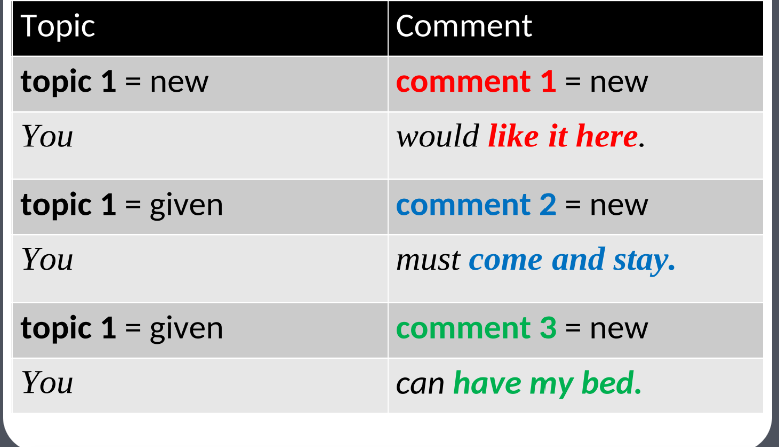
Informational structure
The organization of a sentence, where focus may be placed on either the topic or the comment, influencing the delivery and reception of information.
information structure
(Halliday 1984):
Topic <—> Comment
Theme <—> Rheme
Given <—> New
Action Comics
A genre in stylized comic books that features narratives driven by action-oriented stories.
Topic - comment
utterance can be split into two aspects
• theme/topic - the thing talked about
• rheme/comment - what is said about the theme

topic - comment structures:
Outside my window there is a big lawn. In the middle of the lawn there is a flower bed. This bed was planted by my late aunt Vespasia.

Alternative: topic - comment structures:
The story of Icarus is one of the most famous myths to have been preserved from ancient Greek times. Icarus and his craftsman father, Daedalus, were summoned to Crete to work for King Minos.
Content-based instruction
An approach to language teaching where learners acquire a language while studying subject matter in that language.
Academic English
A type of language use that is simple, passive, neutral, and objective, often used to convey scientific facts and stable states of affairs.
Simple form:
• Event uses
• State uses
–neutral
–objective
–stable states of affairs
–scientific facts