ch 21 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Overview
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
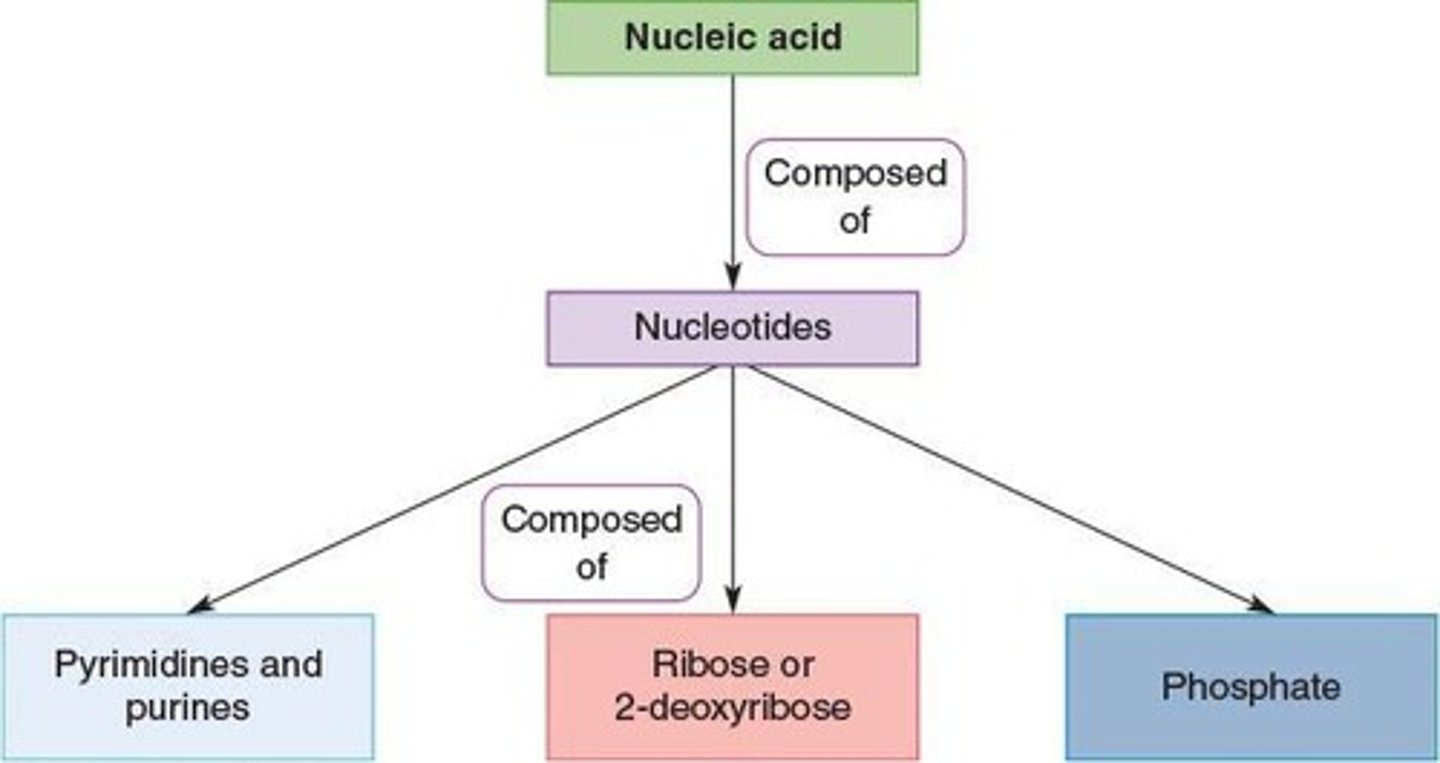
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules transferring genetic information between cells.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, primarily found in cytoplasm.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, mainly located in cell nuclei.
Nucleotide
Monomeric unit forming polymeric nucleic acids.
Pyrimidine
Single 6-membered ring with 2 nitrogen atoms.
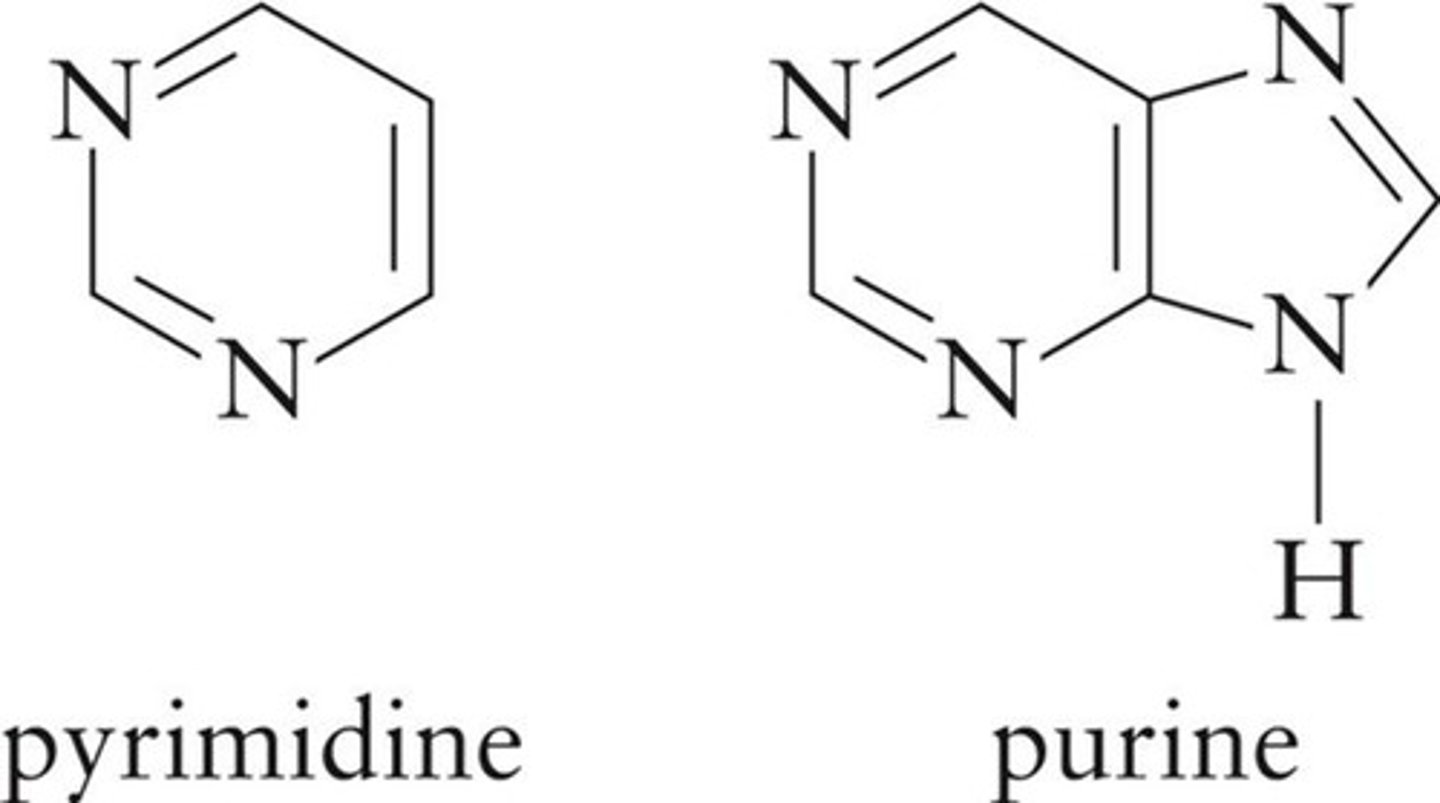
Purine
Fused ring system with 6 and 5-membered rings.
D-Ribose
Sugar in RNA, has a hydroxy group at 2'.
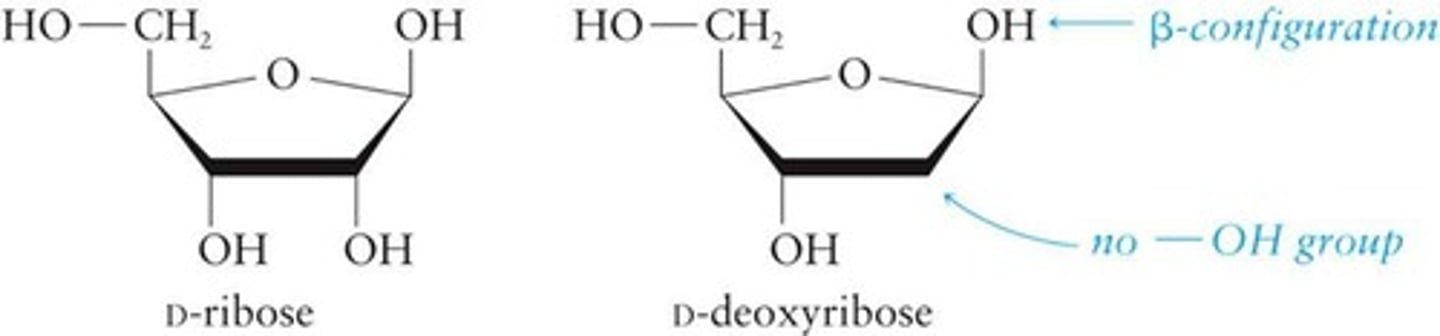
D-Deoxyribose
Sugar in DNA, lacks hydroxy group at 2'.
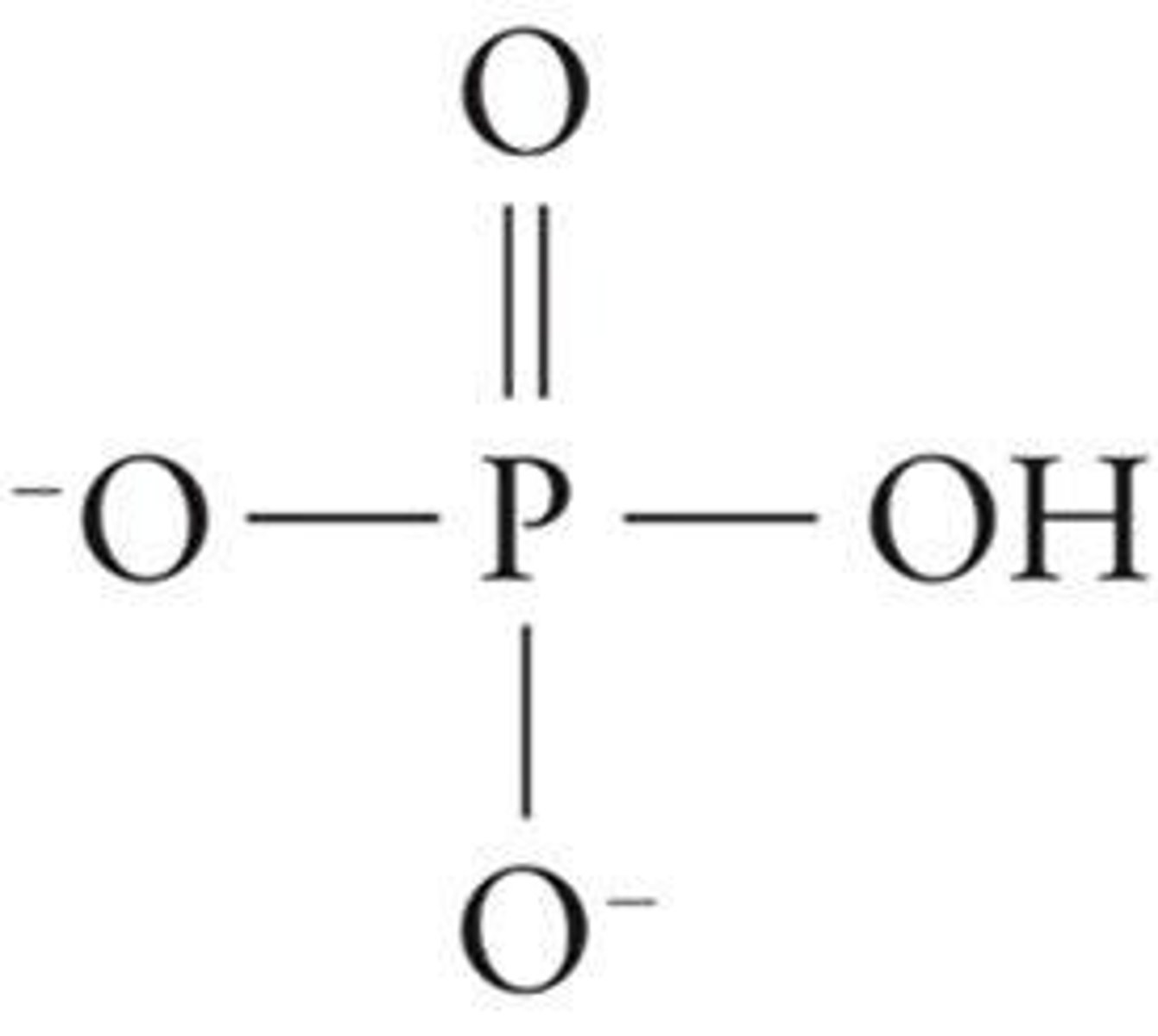
Phosphate Group
Derived from phosphoric acid, carries 2- charge.
Phosphodiester Bond
Links nucleotides via 5' to 3' carbon connections.
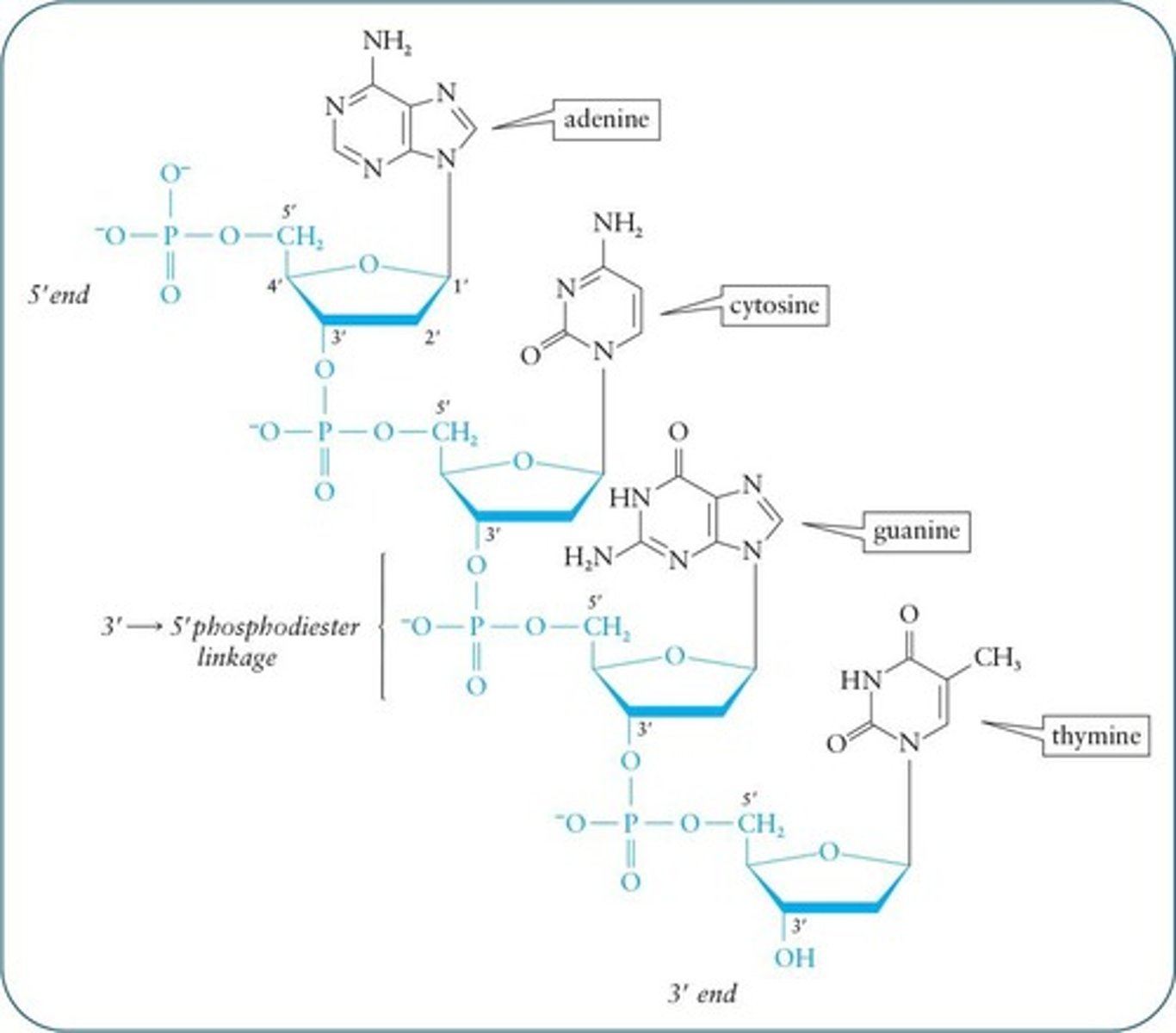
Nucleic Acid Backbone
Sugar-phosphate chain common to all nucleic acids.

Primary Structure of DNA
Order of bases in a DNA sequence.
Hydrogen Bonds
Hold complementary base pairs together in DNA.
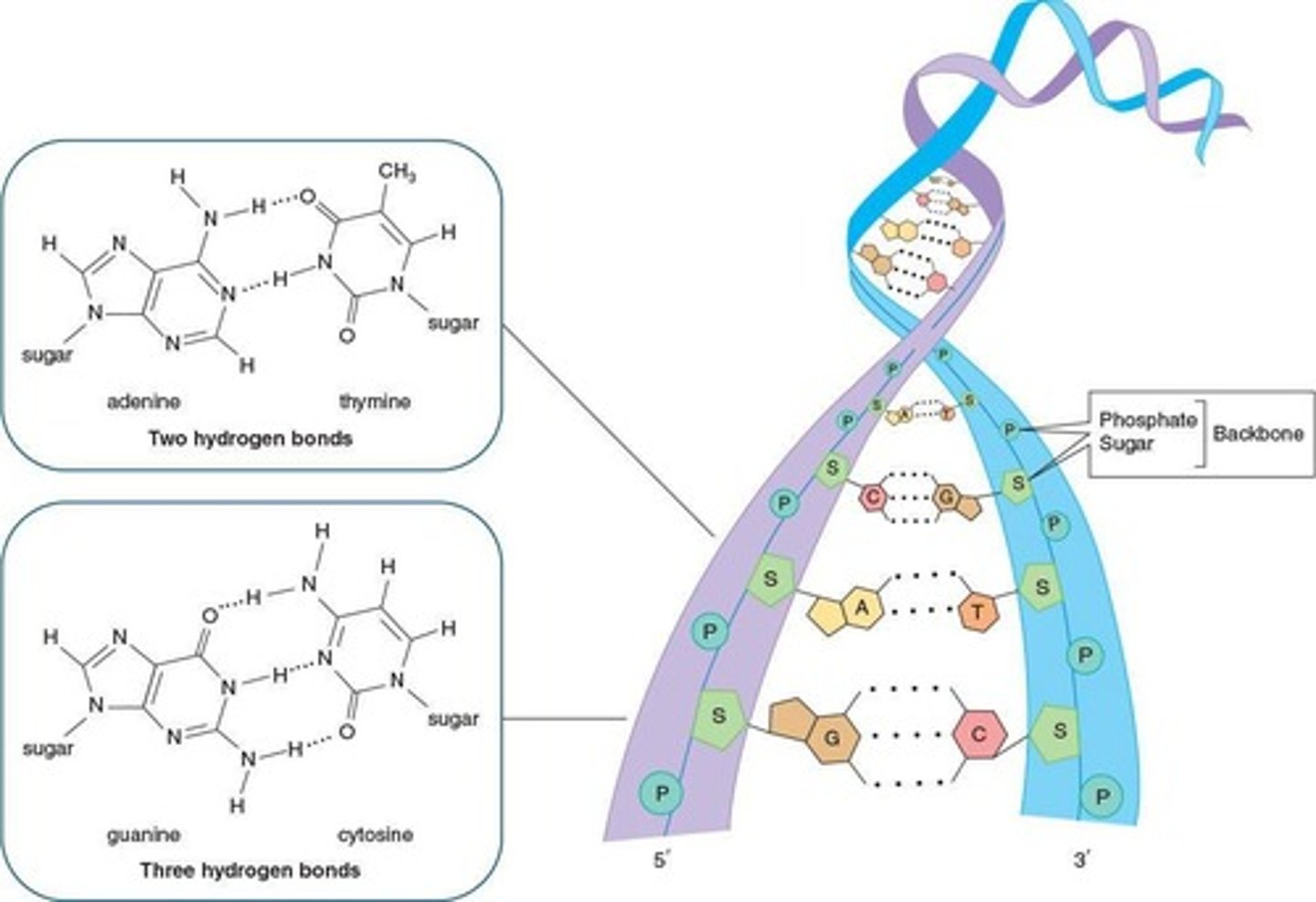
Adenine-Thymine Pairing
Connected by 2 hydrogen bonds in DNA.
Guanine-Cytosine Pairing
Connected by 3 hydrogen bonds in DNA.
Complementary Strands
DNA strands that pair via specific base pairing.
Base Sequence
Order of nucleotides in a DNA strand.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Chromosome
Tightly packed DNA and protein bundle for cell division.
Histones
Small, basic proteins that package DNA.
Gene
Segment of DNA directing specific protein synthesis.
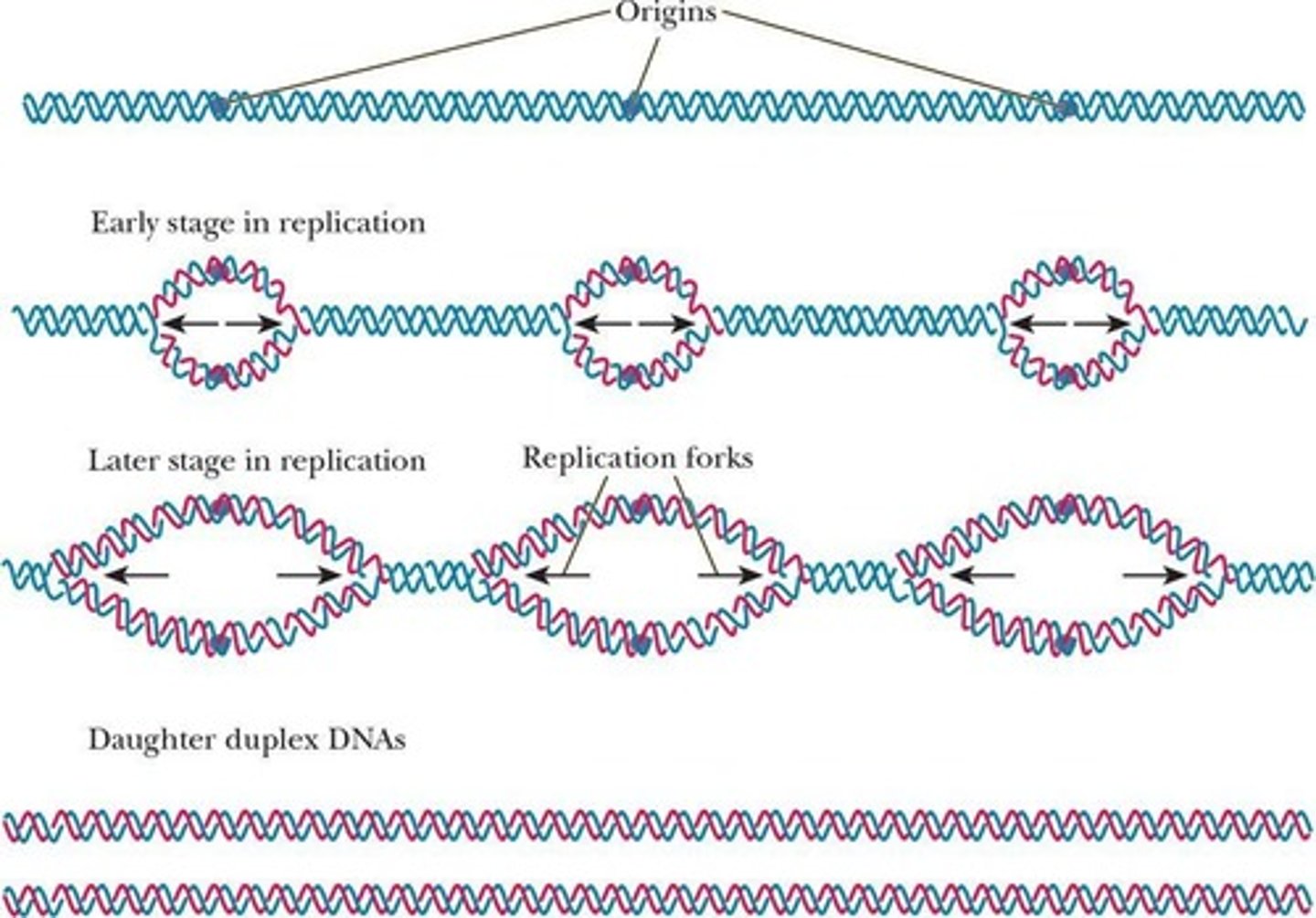
DNA Replication
Process producing an exact copy of DNA molecule.
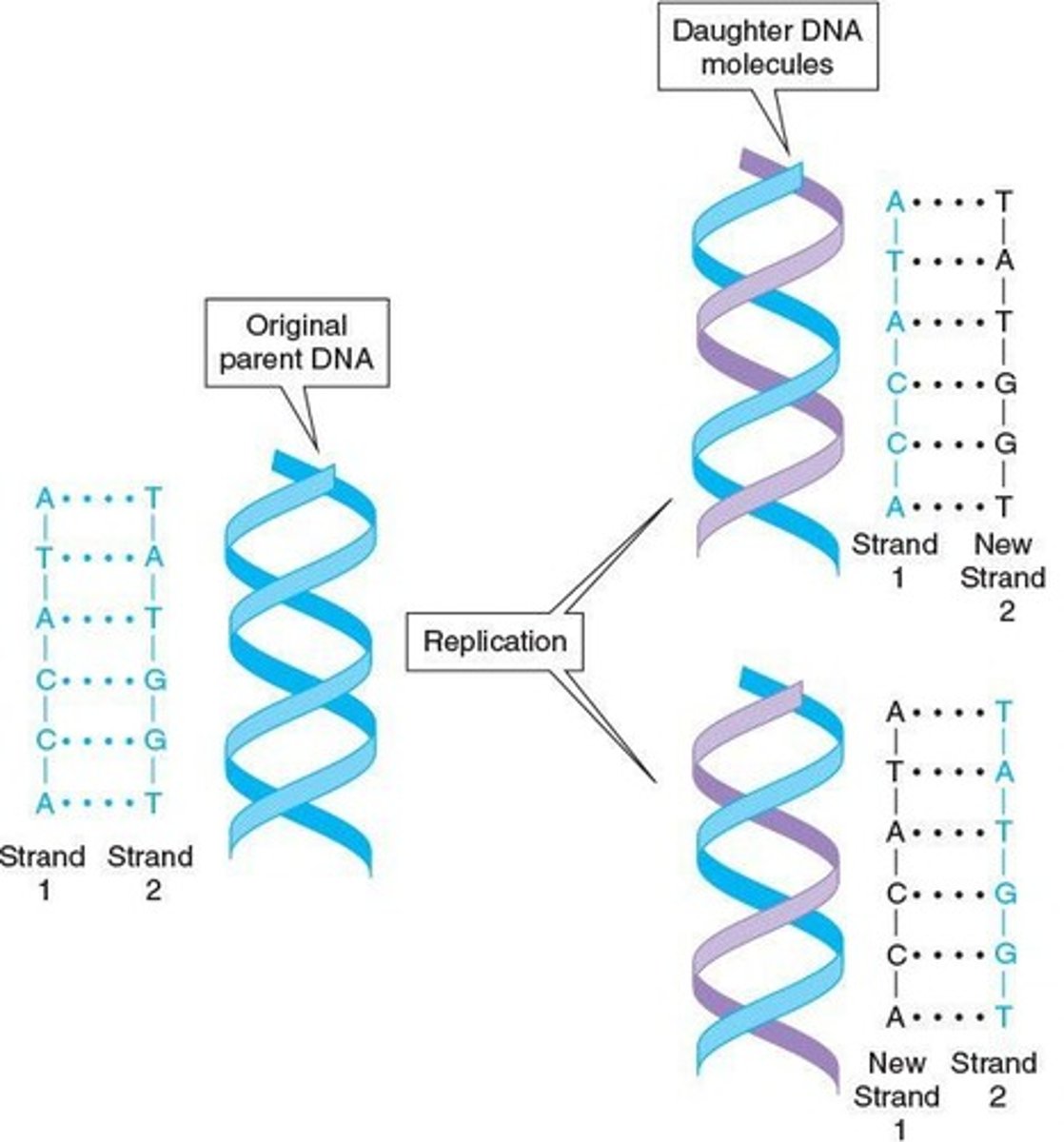
Template Strand
Original DNA strand serving as a guide for replication.
Semiconservative Replication
New DNA has one parent and one daughter strand.
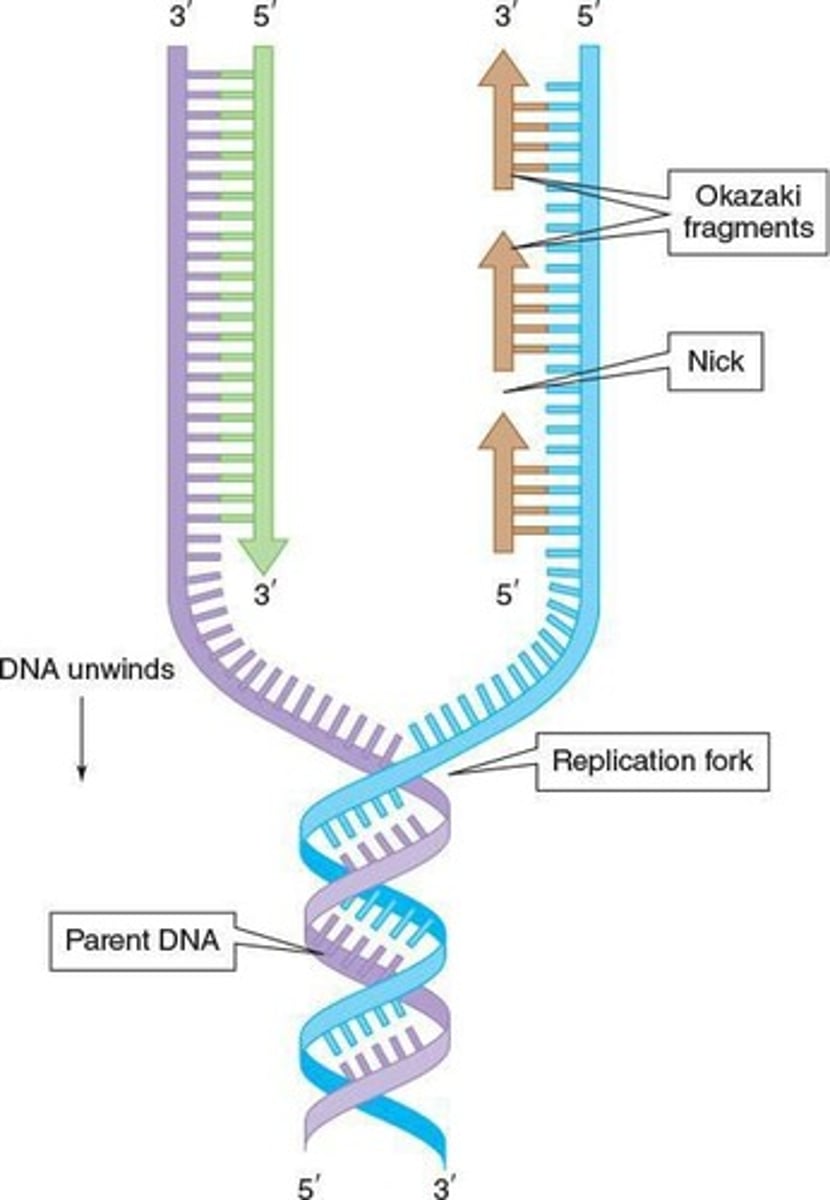
Replication Fork
Point where double helix unwinds during replication.
Helicase
Enzyme catalyzing unwinding of the double helix.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme linking nucleotides to form daughter strands.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA linked during synthesis.
Chromosomal Structure
Chromosomes contain one DNA molecule coiled tightly.
Okazaki fragments
DNA segments synthesized away from replication fork.
DNA ligase
Enzyme that closes nicks in DNA strands.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Technique amplifying DNA through thermal cycling.
Amplification factor
Theoretical increase of DNA copies, up to 1 billion.
Heat denaturation
Process of separating DNA strands at 94°C-96°C.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Main component of ribosomes, 80-85% of cellular RNA.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Delivers amino acids for protein synthesis.
Anticodon
tRNA region that binds to mRNA during translation.
Nicks
Gaps between segments in daughter DNA strands.
Single-stranded RNA
RNA structure lacking complementary base pairing.
Ribose
Sugar in RNA, replacing deoxyribose in DNA.
Uracil (U)
RNA base that substitutes thymine (T) in DNA.
Phosphodiester bonds
Link nucleotides in RNA via 3'→5' connections.
Cytoplasm
Location of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells.
Ester bond
Link between tRNA and amino acid at 3' end.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs.
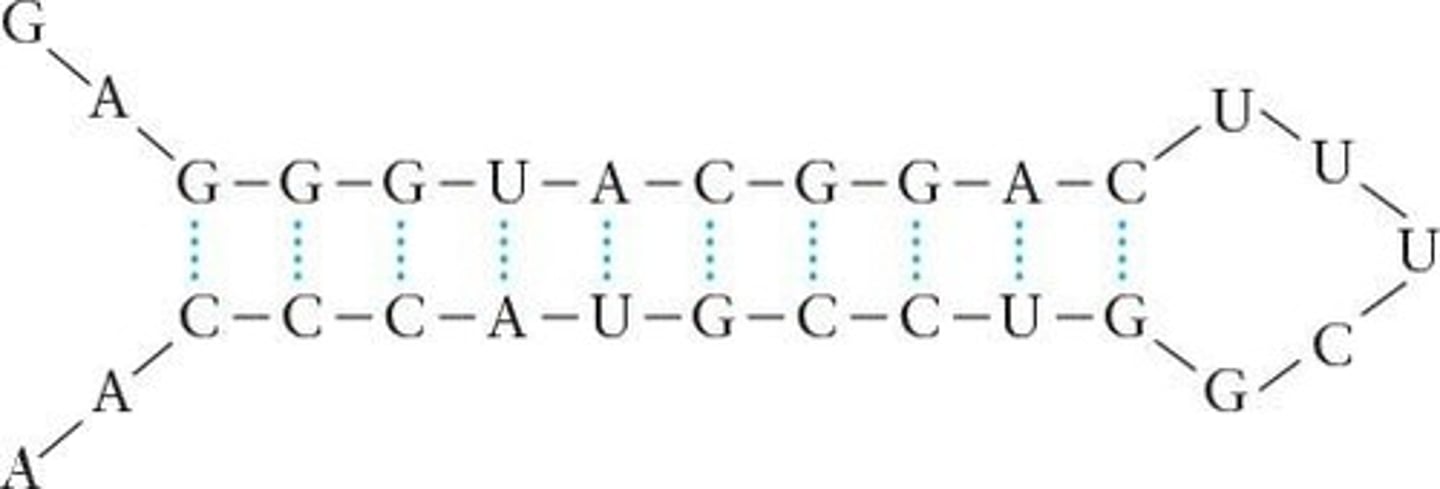
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
80% of RNA in cells, 3 subtypes, 1700 nucleotides.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
15% of RNA in cells, 46 subtypes, 73-93 nucleotides.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
5% of RNA in cells, many subtypes, 75-3000 nucleotides.
Introns
Non-coding segments of DNA, do not code proteins.
Exons
Coding segments of DNA that produce proteins.
Heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
Pre-mRNA that includes introns and exons.
Genetic code
mRNA template for assembling amino acids.
Precise code
Specific codon represents only one amino acid.
Chain initiation
Start of protein synthesis coded by AUG.
Chain termination
End of protein synthesis coded by UAA, UAG, UGA.
Total codons
64 codons in the genetic code.
mRNA codons
64 codons correspond to 20 amino acids.
Translation process
Exact translation from mRNA to tRNA.
A site
Location on ribosome for incoming tRNA.
Translocation
Ribosome movement during protein synthesis.
Termination factor
Binds to stop codon, ending synthesis.
Mutation
Change in DNA base sequence.
Sickle-cell disease
Genetic disorder caused by mutation.
Muscular dystrophy
Genetic disorder causing muscle degeneration.
Restriction enzyme
Enzyme cleaving specific DNA sequences.