UNIT 1 ENVIRO EXAM
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
Accuracy
How close the data is to the true value
Precision
How close all the data is to each other
Repeatability
consistency of results when repeated under the same conditions
Reproduceability
other researchers can obtain the same results using the original data and methods
True value
the actual, ideal value of a quantity that would be obtained if the measurement were performed perfectly without any errors
Validity
how well an experiment or investigation actually measures what it is supposed to measure
E.g of personal errors
misreading scales, miscalculations, or using the wrong procedure
E.g of systematic errors
a miscalibrated scale consistently registers weights as higher than they actually are
E.g of random errors
what is uncertainty
not being sure of the answer
what are outliers
observation that lies an abnormal distance from other values
what are stakeholders
a person with an interest or concern in something
what is something biotic
something in the environment thats living
what is something abiotic
something in the environment that’s not living
examples of biotic factors
plants, fungi, bacteria, animals, herbivores, carnivores, decomposers
examples of abiotic factors
temperature, terrain, soil, water, sunlight, oxygen
what is a biome
a large geographical area defined by its distinct climate, vegetation, and animal life
what is an ecosystem
a community of living organisms in a particular area
what is a habitat
natural home or environment of an animal, plant or other organism
what is a community
group of living things that live in the same place or have a particular characteristic in common and how they interact
what is a population
all the inhabitants of a particular place
what is an open system
a system that has influences from outside of its self
“a system that freely exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings”
what is a closed system
A system that doesn’t get anything coming into it
what is a semipermeable system
Only some things can come into the system
e.g. semipermeable membrane
what is an organism
a living thing
what is an autotroph
Produces it’s own food
e.g plants, algae, phytoplankton
what is photosynthesis
Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of glucose (sugar).
What is an heterotroph
Does not produce it’s own food
e.g animals, fungi, Detritivores
What is a food chain
illustrates the flow of energy in an ecosystem by showing who eats whom
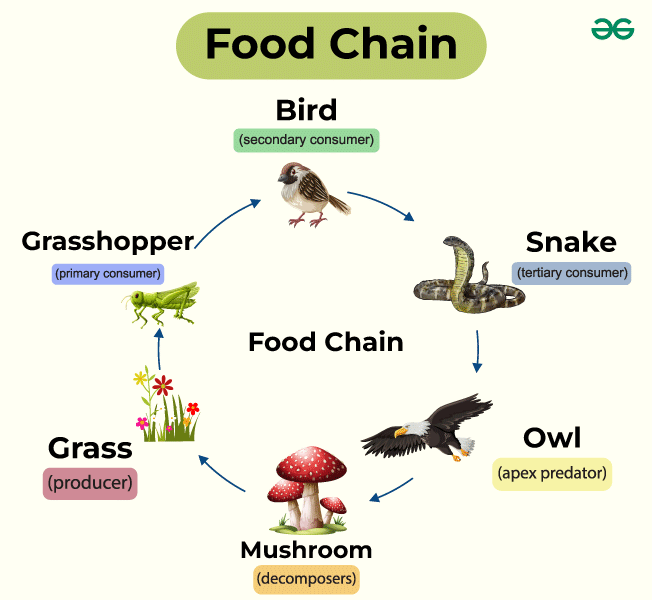
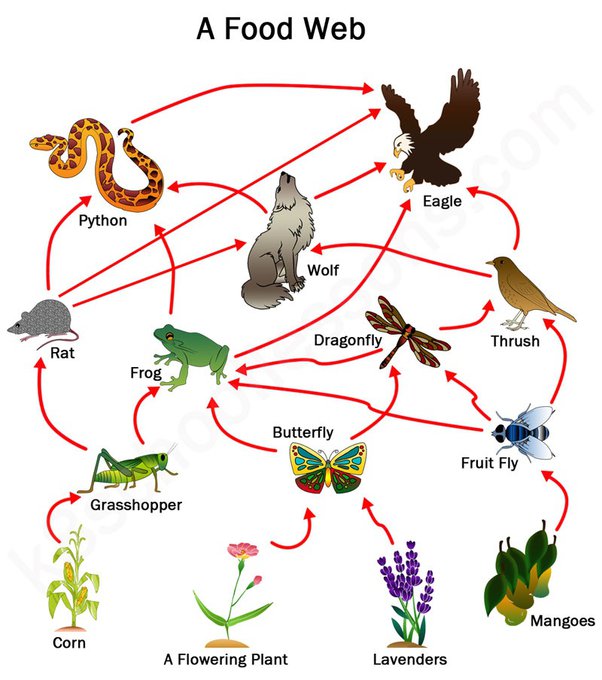
What is a food web
network of interconnected food chains, demonstrating the various paths that energy and nutrients can take through different species
What are the trophic levels
producers, primary consumers (herbivores)
secondary consumers (carnivores)
tertiary (third) consumers (carnivores)
What is a producer
organism that creates its own food
What is a consumer
something that doesn’t make it’s own food, eats producers
What is a primary consumer
an animal that eats producers, like plants or algae, and is the first level of consumer in a food chain
herbivores
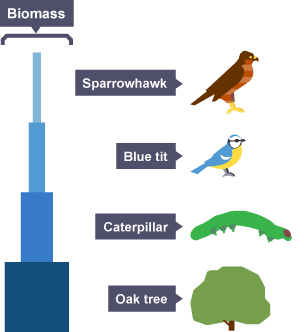
What is a biomass pyramid
illustrates the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level in a food chain or food web
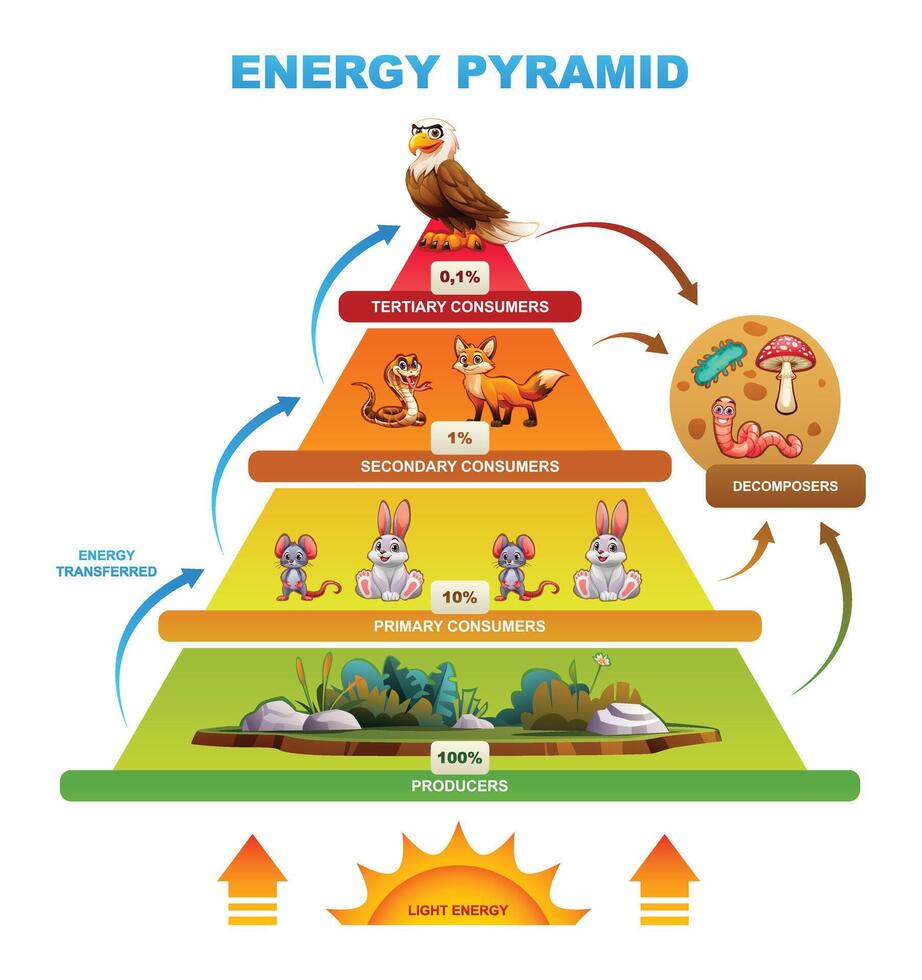
What is an energy pyramid
a diagram that represents the flow of energy from one trophic level to the next in an ecosystem
What is a numbers pyramid
represents the number of organisms at each trophic level within a food chain or ecosystem
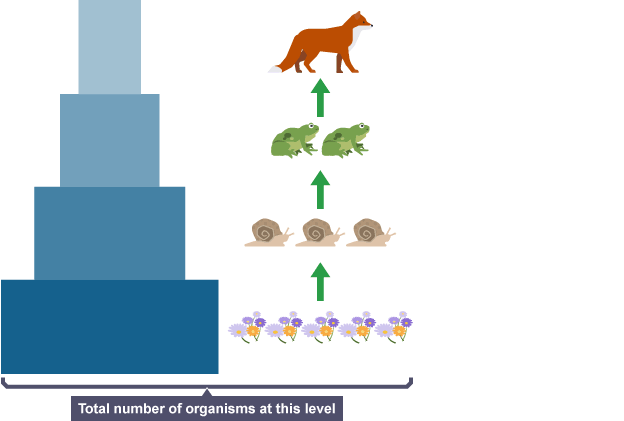
What is ecosystem productivity
rate at which biomass is generated in an ecosystem, essentially how quickly living things are producing organic matter
What are the different value systems
Anthropocentrism, biocentrism, ecocentrism and technocentrism
What is Anthropocentrism
viewpoint that places humans at the center of the universe
What is biocentrism
The value we give living things
What is ecocentrism
belief that gives inherit value to individual living things & ecosystems
What is technocentrism
world view that prioritizes technology & scientific advances
What’s the atmosphere
protective layer made of air, containing mainly nitrogen and oxygen, along with other gases like argon, carbon dioxide
What’s the hydrosphere
water on the surface of of earth
e.g oceans, rivers, lakes, rain
What’s the lithosphere
earths crust, landforms (rocks & soils)
continental crust
oceanic crust
soil structure
What’s the biosphere
living matter on earth, including all animal and plant life forms
What’s groundwater
all underground water
What’s an aquifer
body of rock/sediment that has groundwater
What is the recharging of aquifers
process by which an aquifer is replenished with water
happens through natural processes like rainfall seeping into the ground or from surface water sources like rivers and streams
What’s fresh brackish (saltwater)
mix of saltwater and freshwater
What’s river delta
landform created where a river flows into another body of water, like an ocean, lake, or another river, and deposits sediment
What’s desalination
process of removing salt and other impurities from saltwater to produce fresh water
What’s the asthenosphere
semi-molten layer in the upper mantle, is directly beneath the lithosphere
What’s the mantle
largest and thickest layer of the Earth, located between the crust and the outer core
What is continental crust
thicker, less dense crust that forms the landmasses of the Earth.
What’s oceanic crust
outermost layer beneath the oceans, thin, dense, and primarily composed of basalt and other mafic rocks.
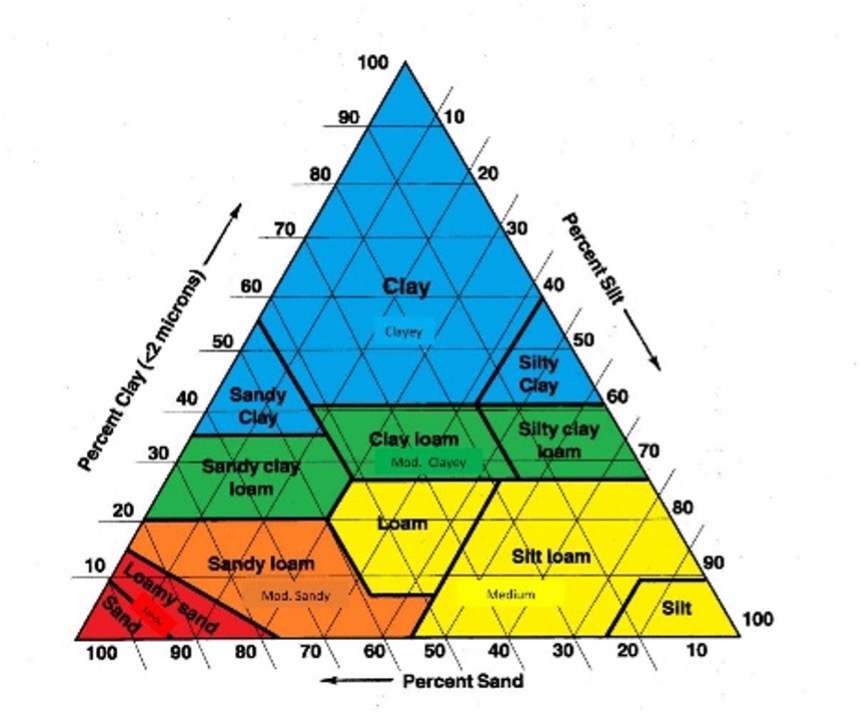
What are the different soil textures
clay, silt, sand , loam
What does porosity mean
he quality of being porous, or full of tiny holes
What’s pH
used to measure acidity and basicity
What’s loam
Loam is a “perfect” mix of clay, loam and sand
What’s sand
Sand are small granuals of rock
What’s silt
a sediment particle size that falls between sand and clay
What’s clay
Clay is a solid that is soft and moldable when wet and hardens when heated
example is australian soil
What’s the O horizon
the topmost layer of soil, composed primarily of organic matter like decomposed leaves and plant material
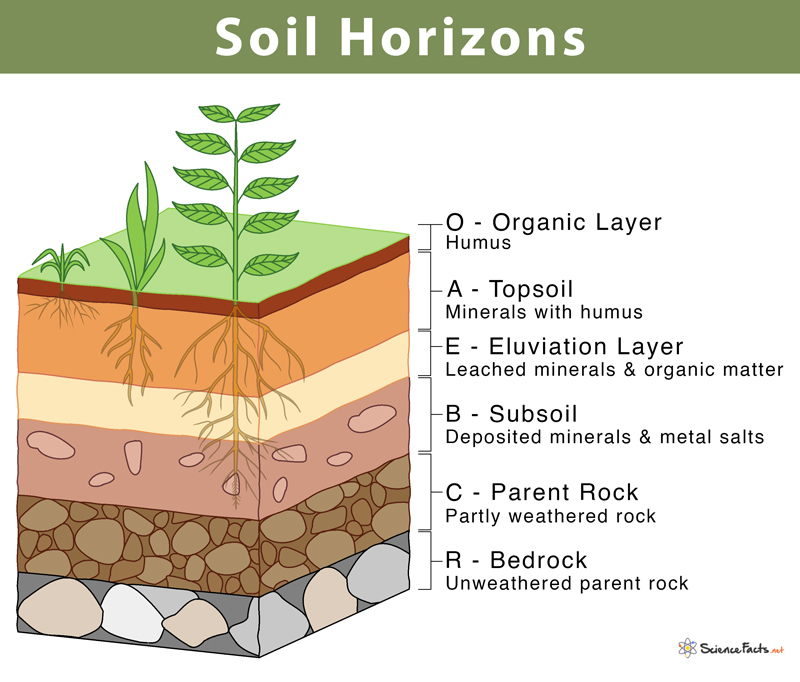
What’s the A horizon
topsoil, a mineral soil layer rich in organic matter and essential for plant growth
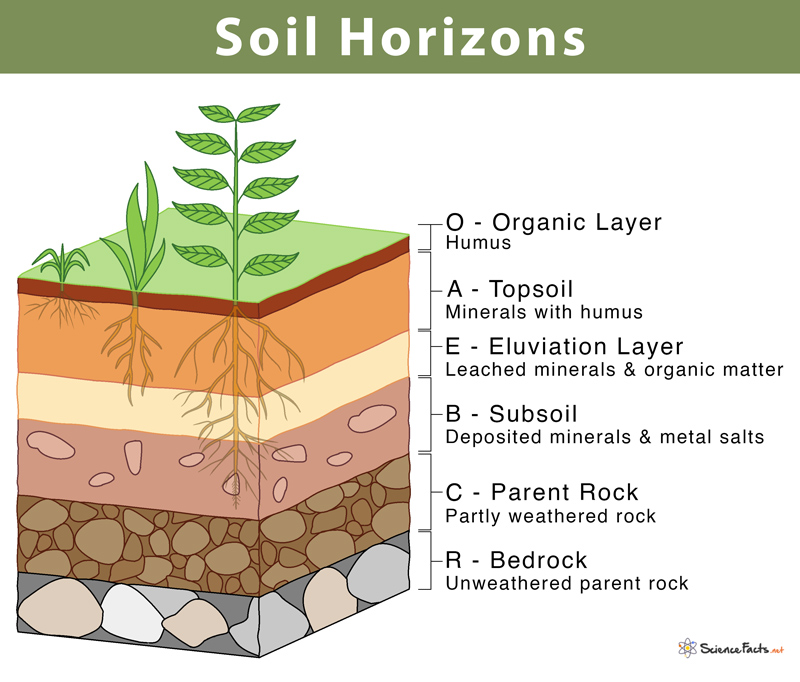
What the B horizon
accumulation of materials leached from the A horizon, particularly clay, iron, and aluminum oxides
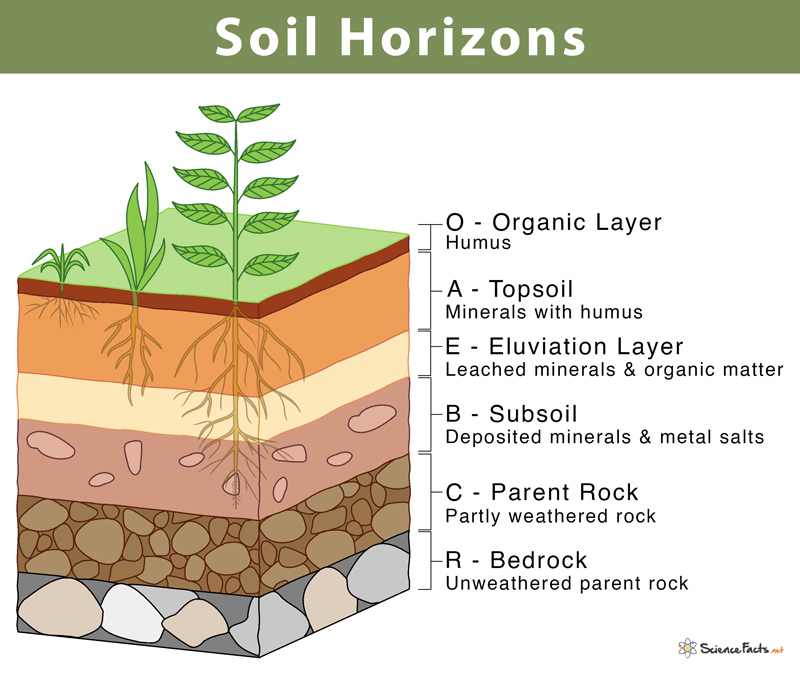
What’s the C horizon
primarily composed of unconsolidated parent material that has been little affected by soil-forming processes
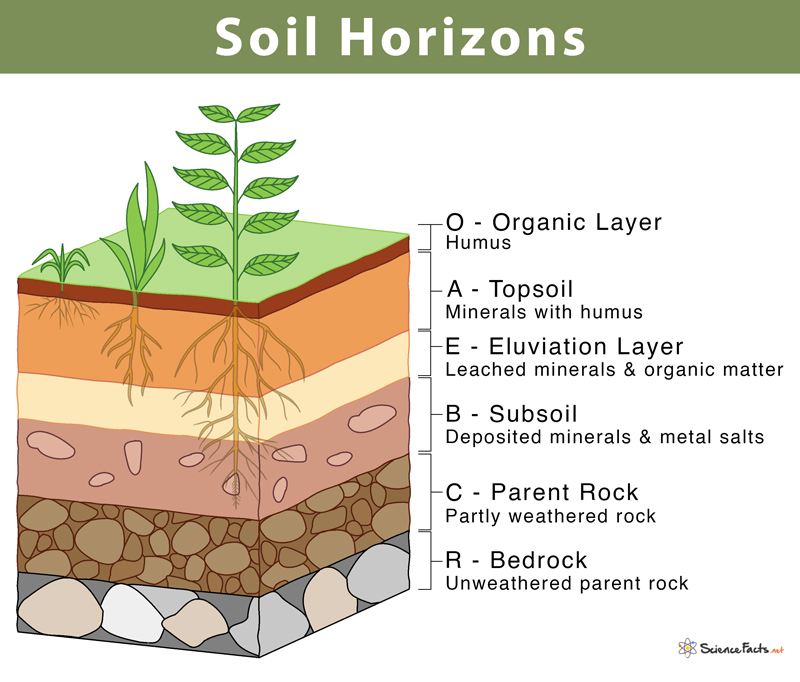
What’s parent rock
the original rock from which soil is formed
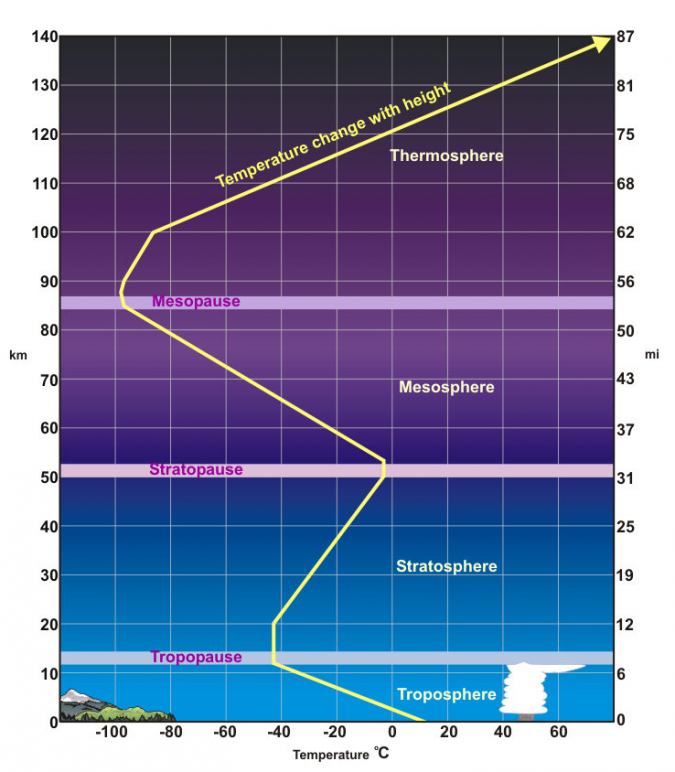
What’s the troposphere
the lowest layer of the Earth's atmosphere,
most weather occurs
contains about 80% of the atmosphere's total mass
What’s the mesosphere
decreasing temperatures with altitude
located above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere
What’s the thermosphere
high temperatures
feel incredibly cold to humans due to the low density of air
not enough gas molecules to transfer heat
very few atoms and molecules in this layer
What’s the exosphere
extremely low gas density
where particles are so far apart that they often behave like individual atoms and molecules
can even escape into space.
What’s tropopause
boundary between the Earth's troposphere and stratosphere, acting as a transition layer
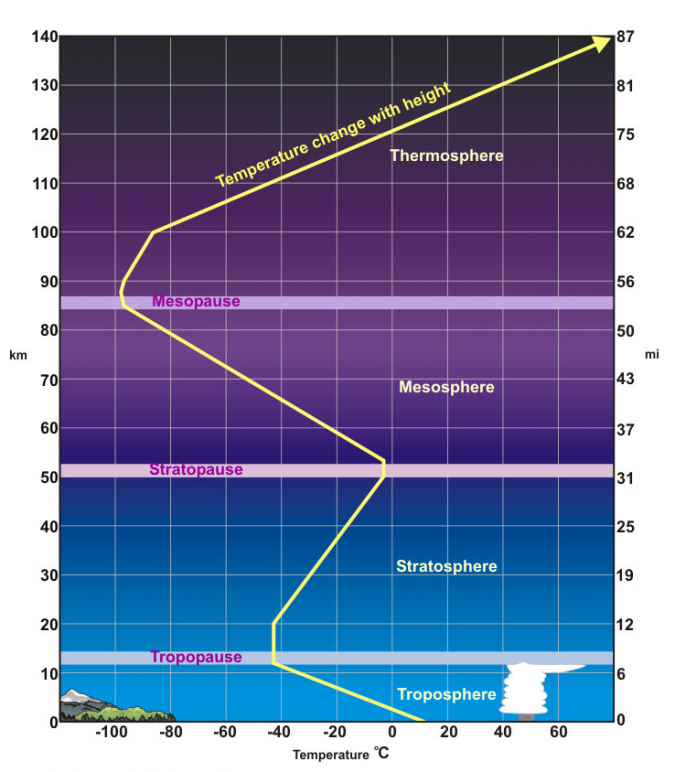
What’s stratopause
point where temperatures stop increasing with altitude, as is typical in the stratosphere, and start decreasing with altitude, as in the mesosphere.
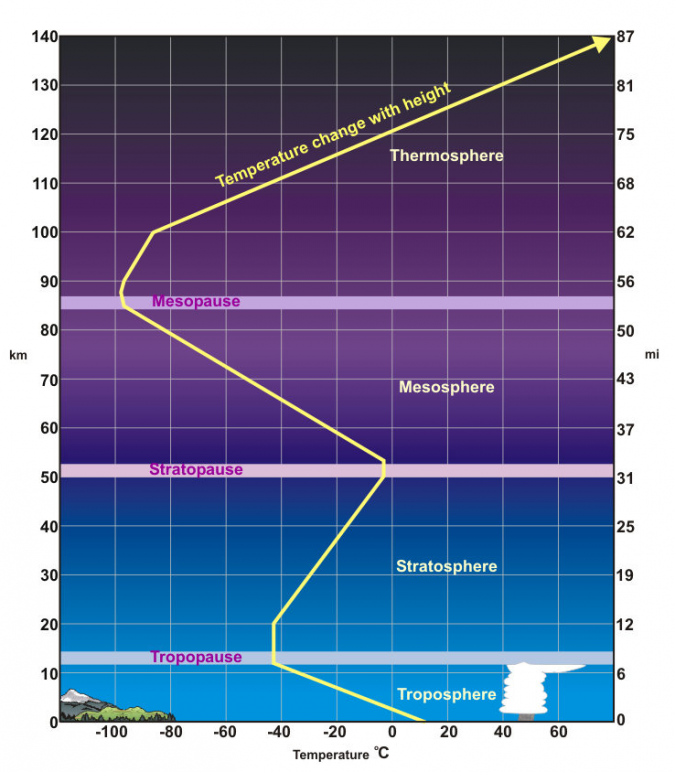
What is mesopause
temperature stops decreasing with increasing height and begins to increase.
What’s the ozone layer
absorbs most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation
the reason it’s thinning is because of the chlorofluorocarbons carbons
made up of O3 (three oxygen atoms)
What is weather
short term changes in the atmosphere
state of the atmosphere at a particular time
temperature changes
What is climate
long term changes in the atmosphere
What’s the inversion layer
normal temperature profile is reversed
meaning temperature increases with height instead of decreasing
This creates a stable situation where warm air sits above cooler air
trapping pollutants and preventing the air from mixing effectively
What’s the Coriolis effect
circulating air is deflected toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left in the Southern Hemisphere
What’s El Nino
the weather pattern where hot air is pushed towards south america through trade winds across the pacific ocean
What’s El Nina
Where hot winds are pushed from western south America towards the western pacific ocean
What are the biogeochemical cycles?
The water or hydrological cycle, the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and phosphorus cycle.
What’s evaporation
the process where a liquid changes into a gas (or vapor)
What’s respiration
the action of taking oxygen and turning it into carbon dioxde
essential for producing energy at a cellular level.
What’s condensation
process where a substance, often water
changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state, typically due to cooling
What’s a carbon sink
natural or artificial system
absorbs and stores more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases
What’s combustion
chemical process where a substance reacts rapidly with an oxidant, usually oxygen, releasing heat and light
example: when fuel reacts to of oxidant and releases heat and light (a flame)
What are living things
organisms that breathe
What is coal
combustible rock
primarily composed of carbon
formed from the remains of plants that died millions of years ago
What is oil and gas
naturally occurring
combustible hydrocarbons formed from the remains of prehistoric organisms
such as: giant ferns and trees
What is limestone
sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcium carbonate
formed by the accumulation and lithification of shell fragments, coral remains
What is nitrogen fixation
process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into reactive forms like ammonia (NH3) or ammonium (NH4+) that plants and other organisms can use
animals use nitrogen as sources of nitrogen for building organic molecules like proteins and nucleic acids
What is denitrification
naturally occurring process where bacteria convert nitrate in soil into nitrogen gases
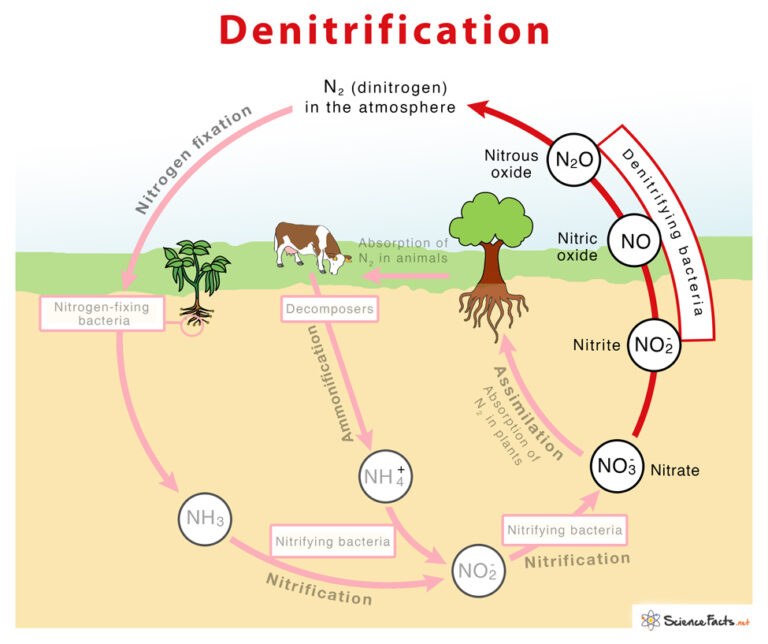
What is ammonia
naturally occurring compound
essential for many biological processes and a key component in the nitrogen cycle.
significant industrial chemical
used in fertilizers, plastics
What is urea
Urea is the waste from the blood before it’s diluted with water in the kidneys
waste product formed by the body during protein breakdown
What are proteins
Made by ribosomes
made up of amino acids, which are linked together in long chains
What is lightening
powerful electrical discharge that occurs in the atmosphere, primarily during thunderstorm
What are legumes
ecological importance due to their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants