Gastrulation & trimina
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is gastrulation?
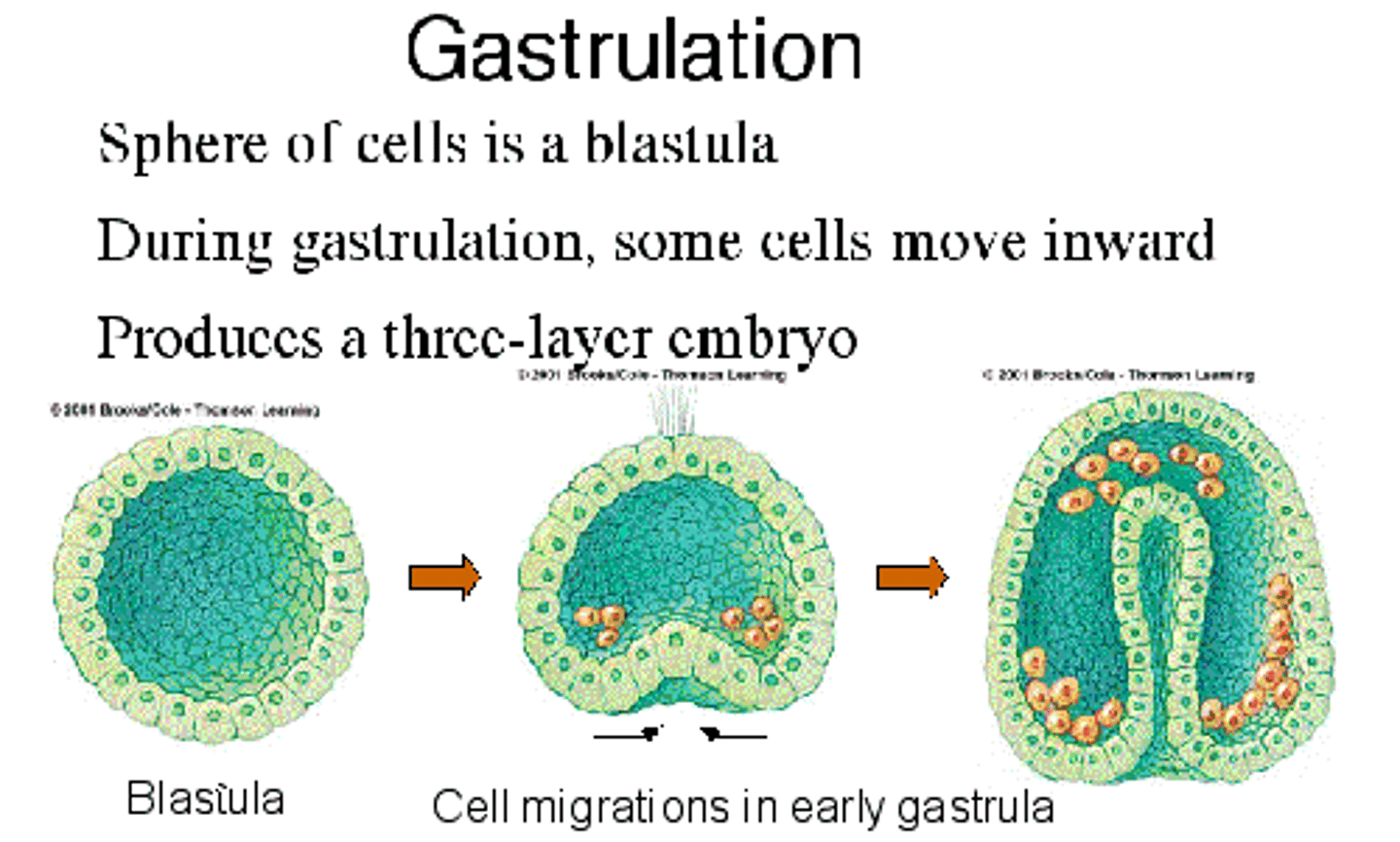
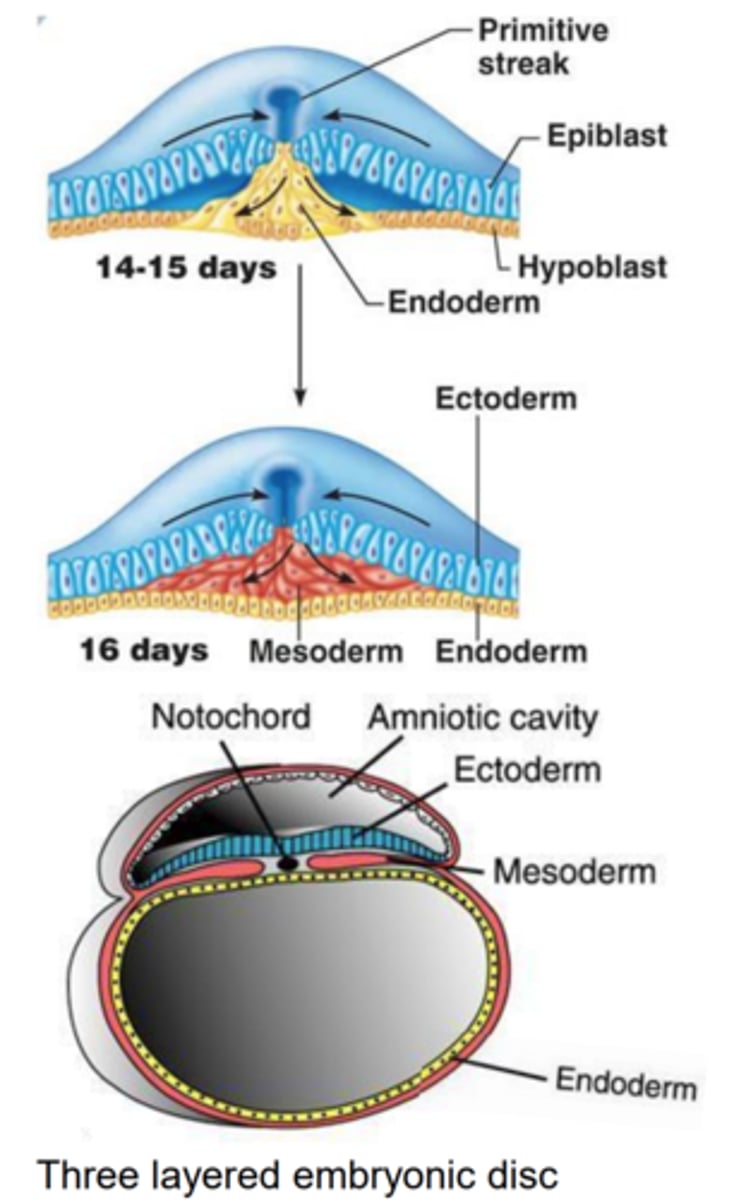
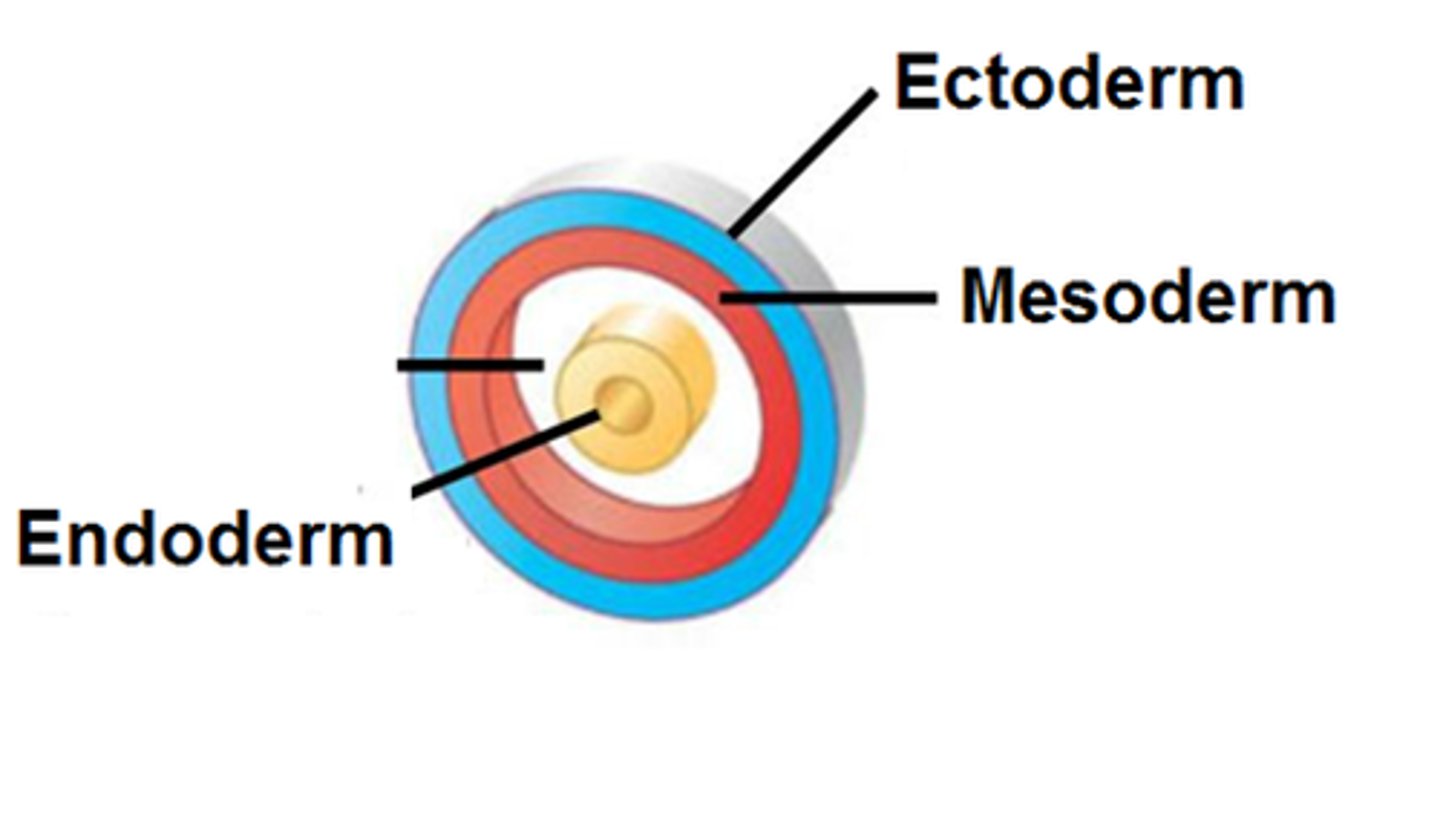
Gastrulation is the process that transforms the simple bilaminar disc into a *trilaminar disc* with three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. It sets up the body's basic plan.
When does gastrulation occur?
It starts in *week 3* of development. This is why we say "3 weeks → 3 layers." 📅 Mnemonic: "3 makes me."
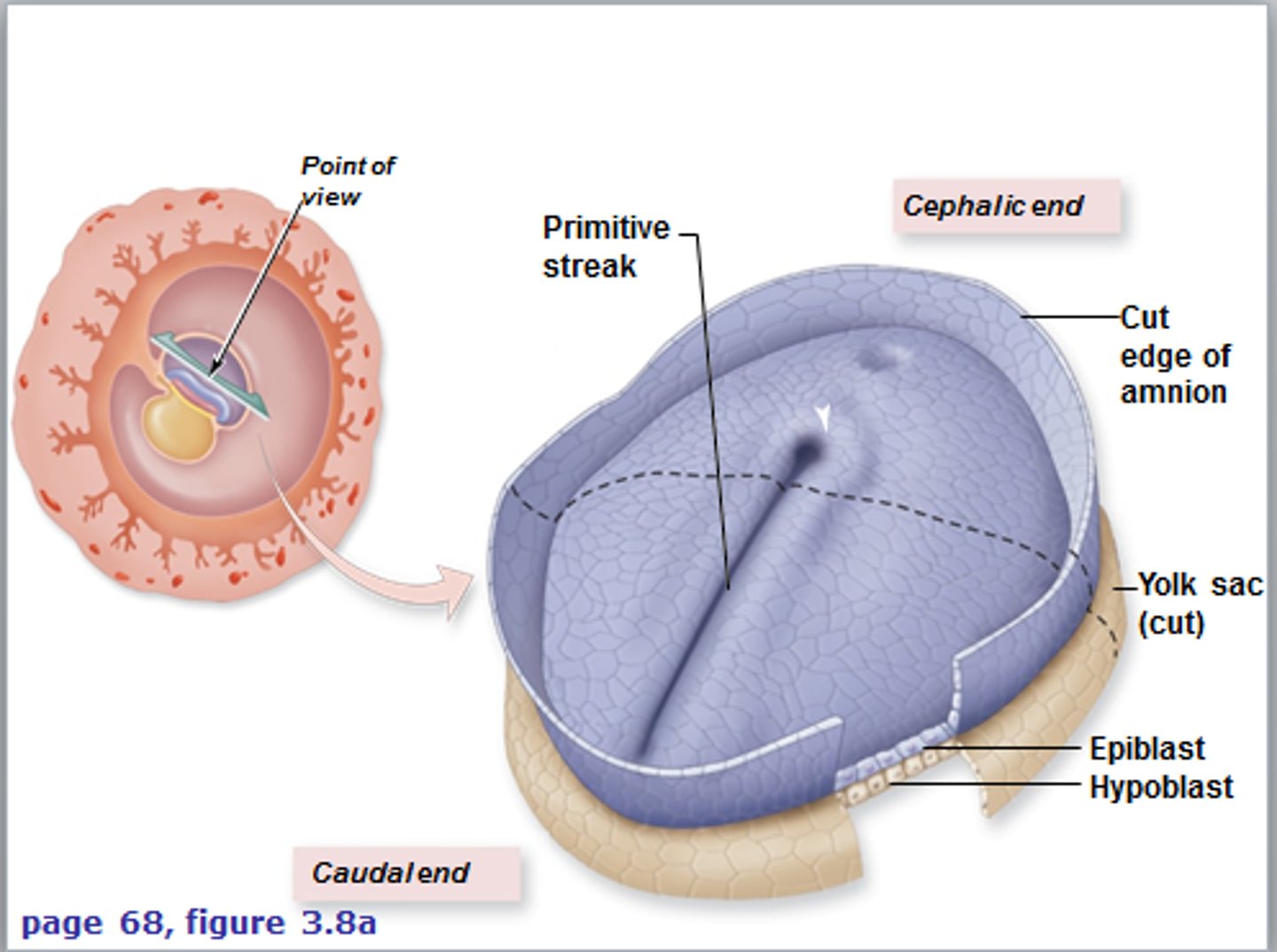
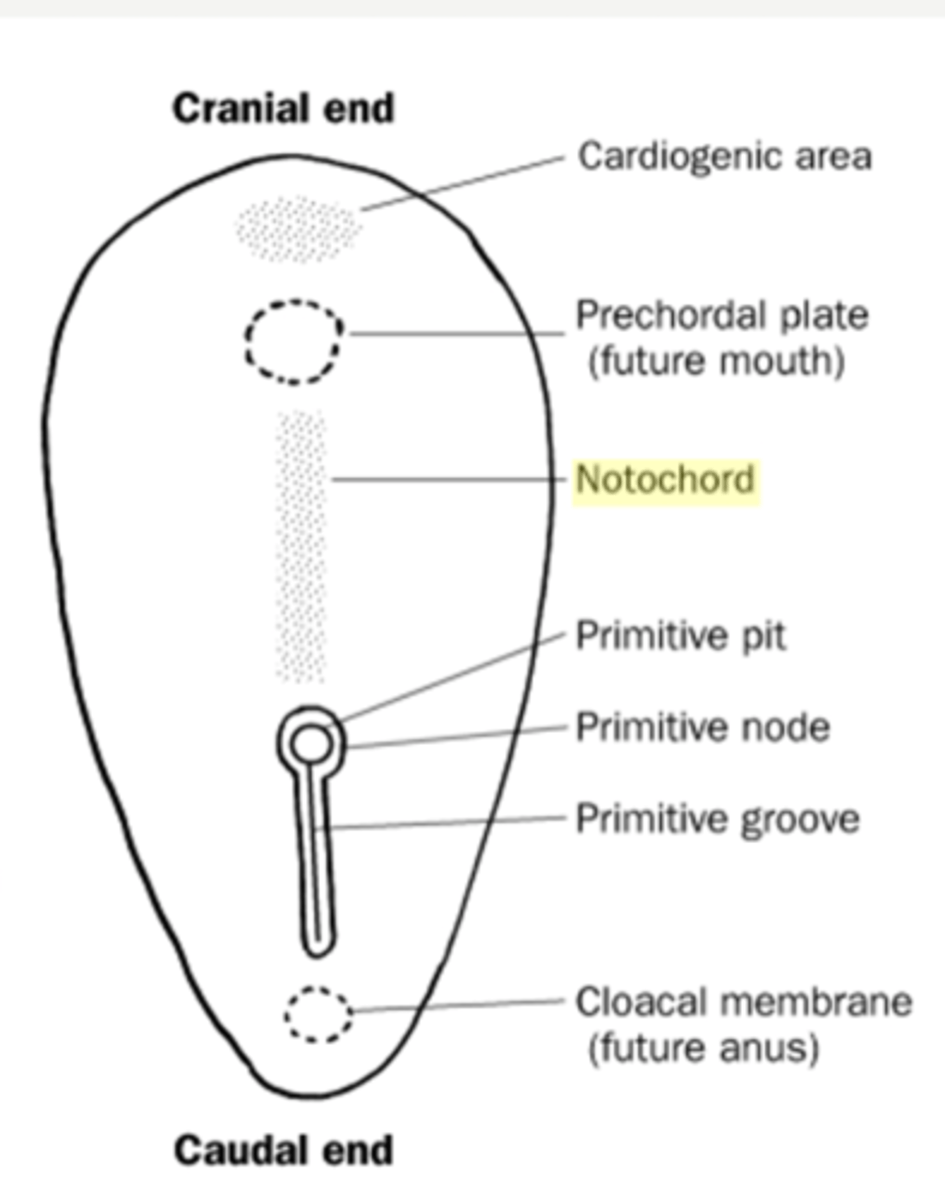
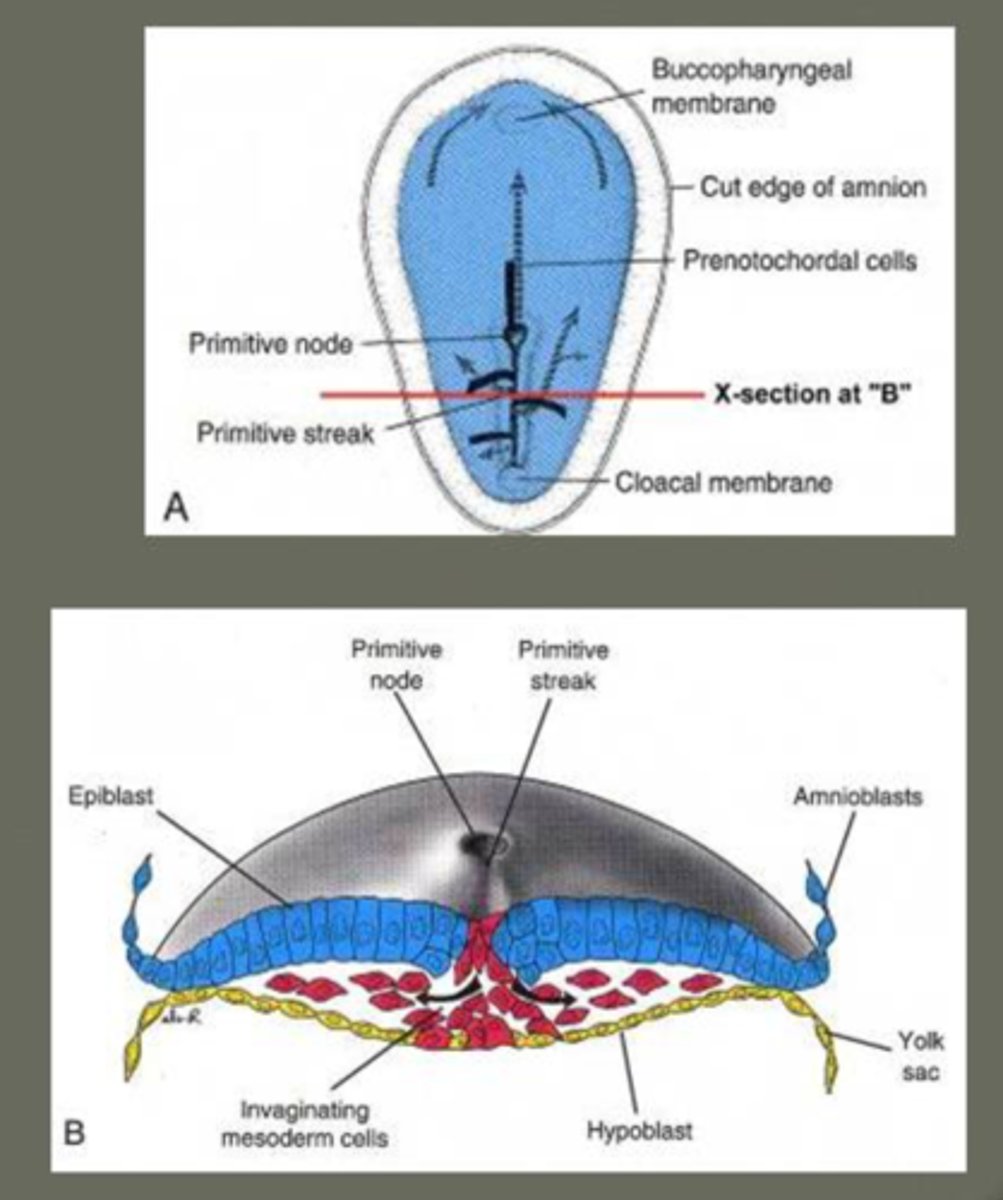
What forms the primitive streak?
Cells in the epiblast move toward the midline and dive down, creating a groove called the *primitive streak*. It marks the embryo's head-to-tail axis.
What is the function of the primitive streak?
It's the entry point for migrating epiblast cells that will form the new germ layers. It defines symmetry and body orientation.
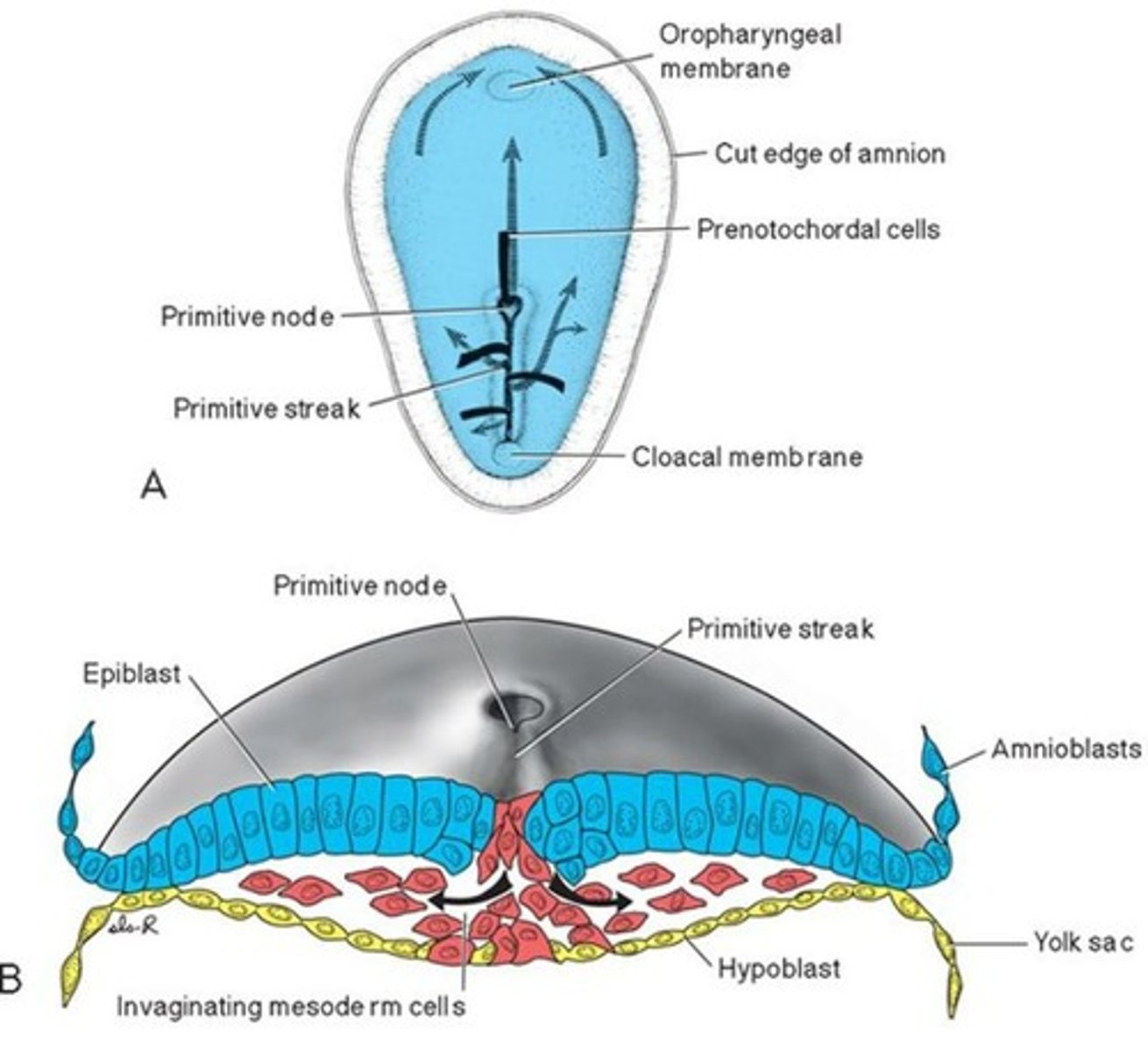
What is the primitive node?
A swelling at the front end of the primitive streak that controls cell movement and signals the formation of the *notochord*. 🎯
How do the germ layers form?
Epiblast cells migrate through the primitive streak: the first replace the hypoblast to form *endoderm, the next spread out to form mesoderm, and the remaining surface cells become ectoderm*.
What is the endoderm?
The innermost layer that lines the gut and respiratory system and forms organs such as the liver and pancreas. 🍽️
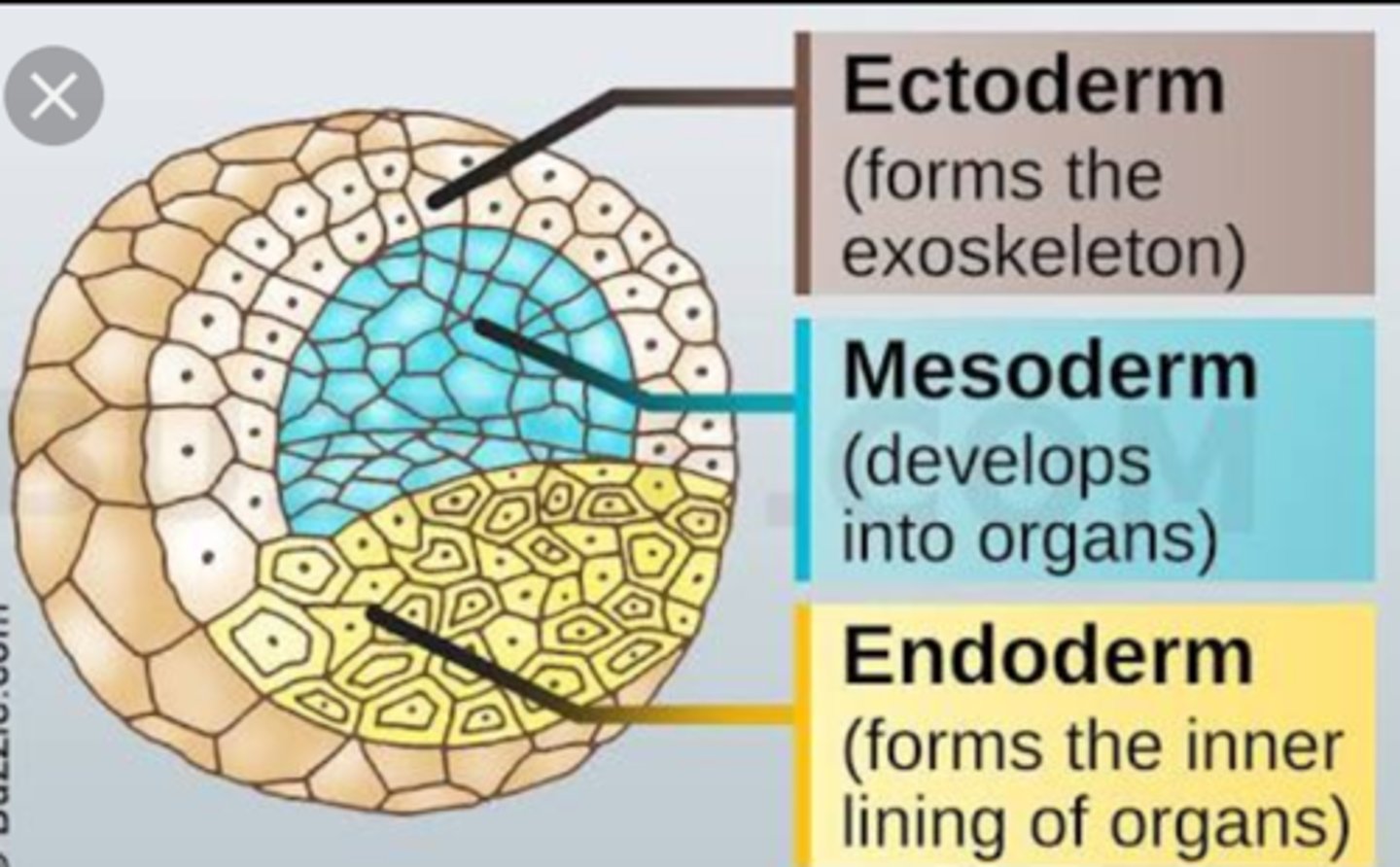
What is the mesoderm?
The middle layer forming muscles, bones, blood, kidneys, and connective tissue. 💪 Mnemonic: "Meso → Muscle & Movement."
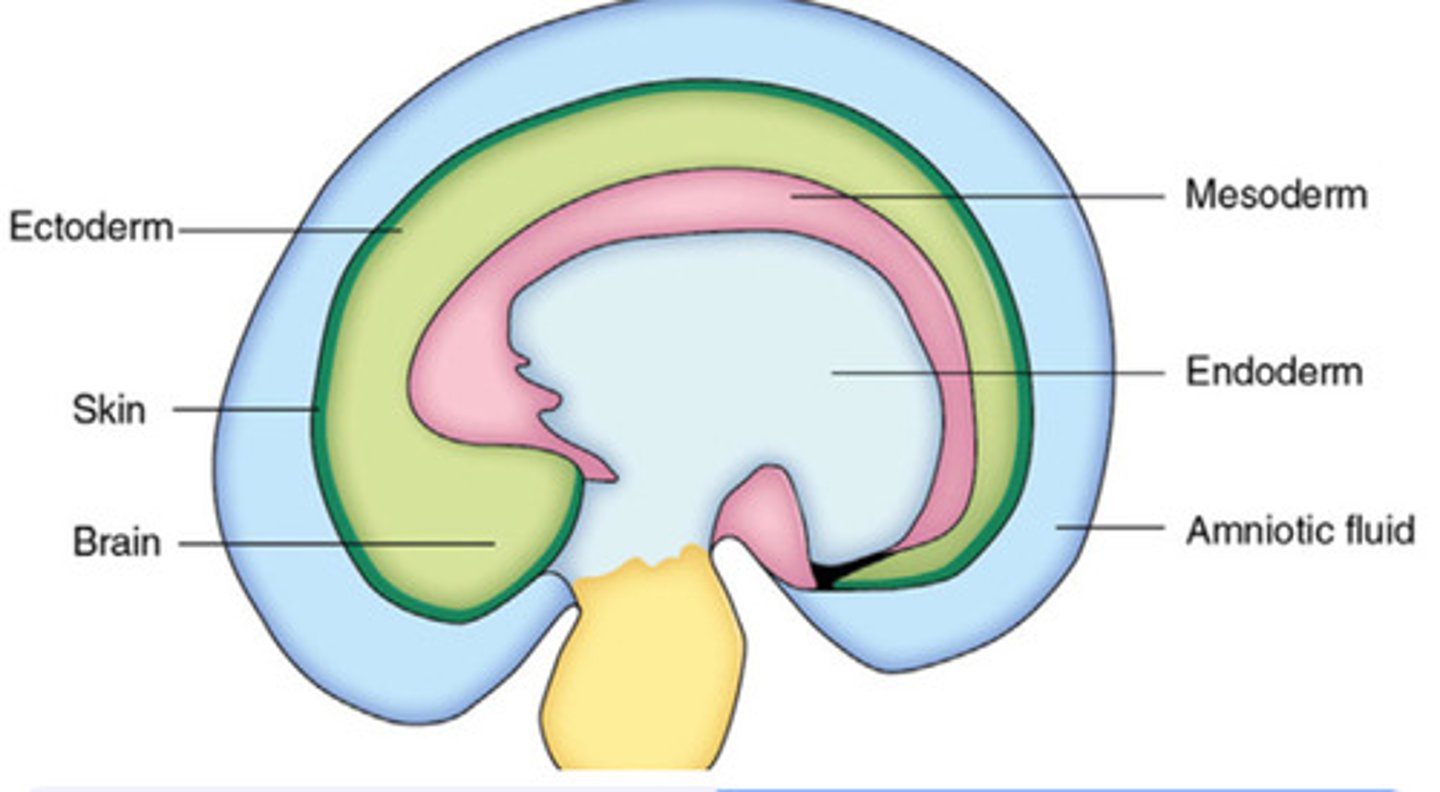
What is the ectoderm?
The outer layer that forms the skin, nervous system, and sense organs. 🌞 Mnemonic: "Ecto = External."
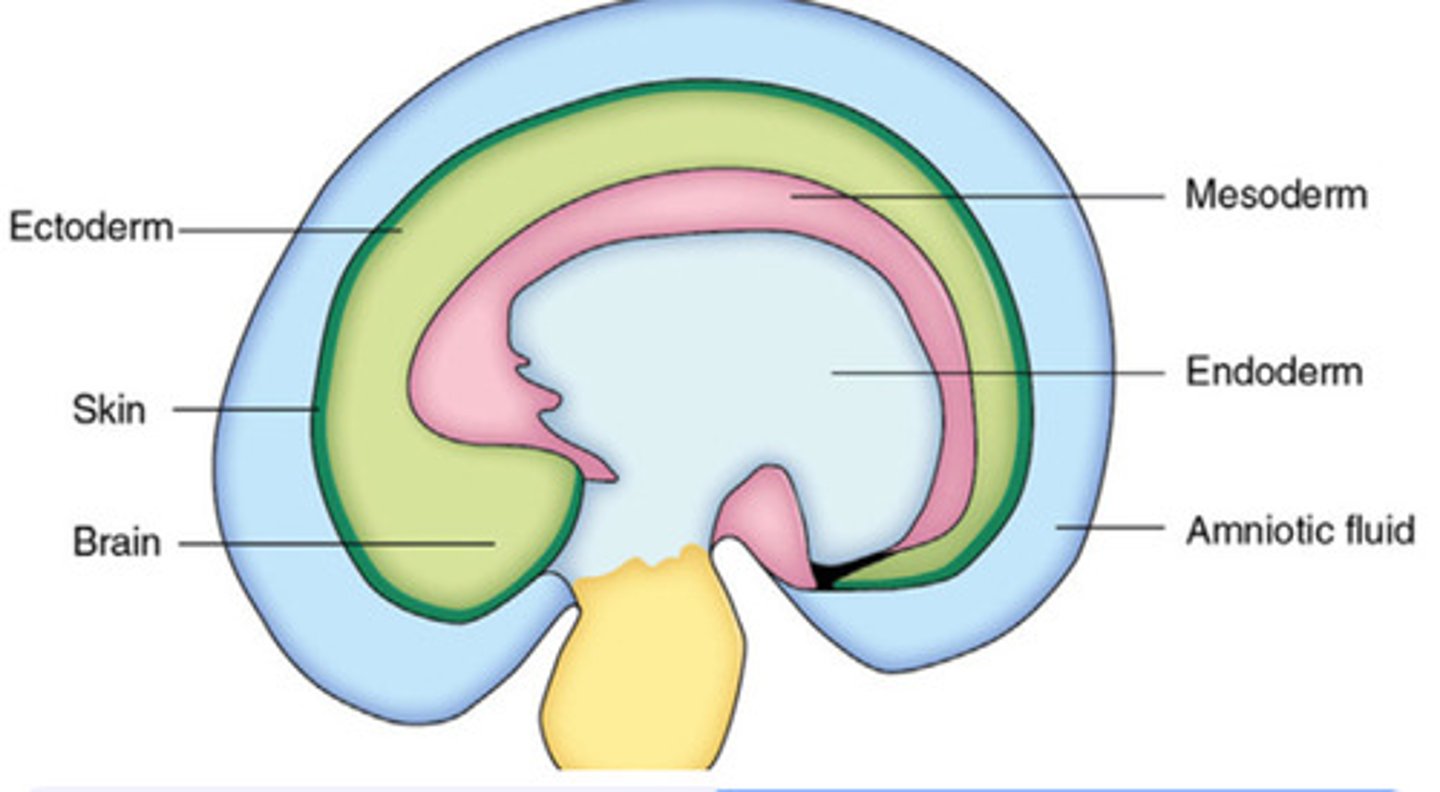
What is the notochord?
A solid rod of mesodermal cells that defines the body's midline and induces neural tube formation. It later becomes part of the intervertebral discs.
What does the notochord secrete?
It releases *signaling molecules* like Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) to guide neural and vertebral development.
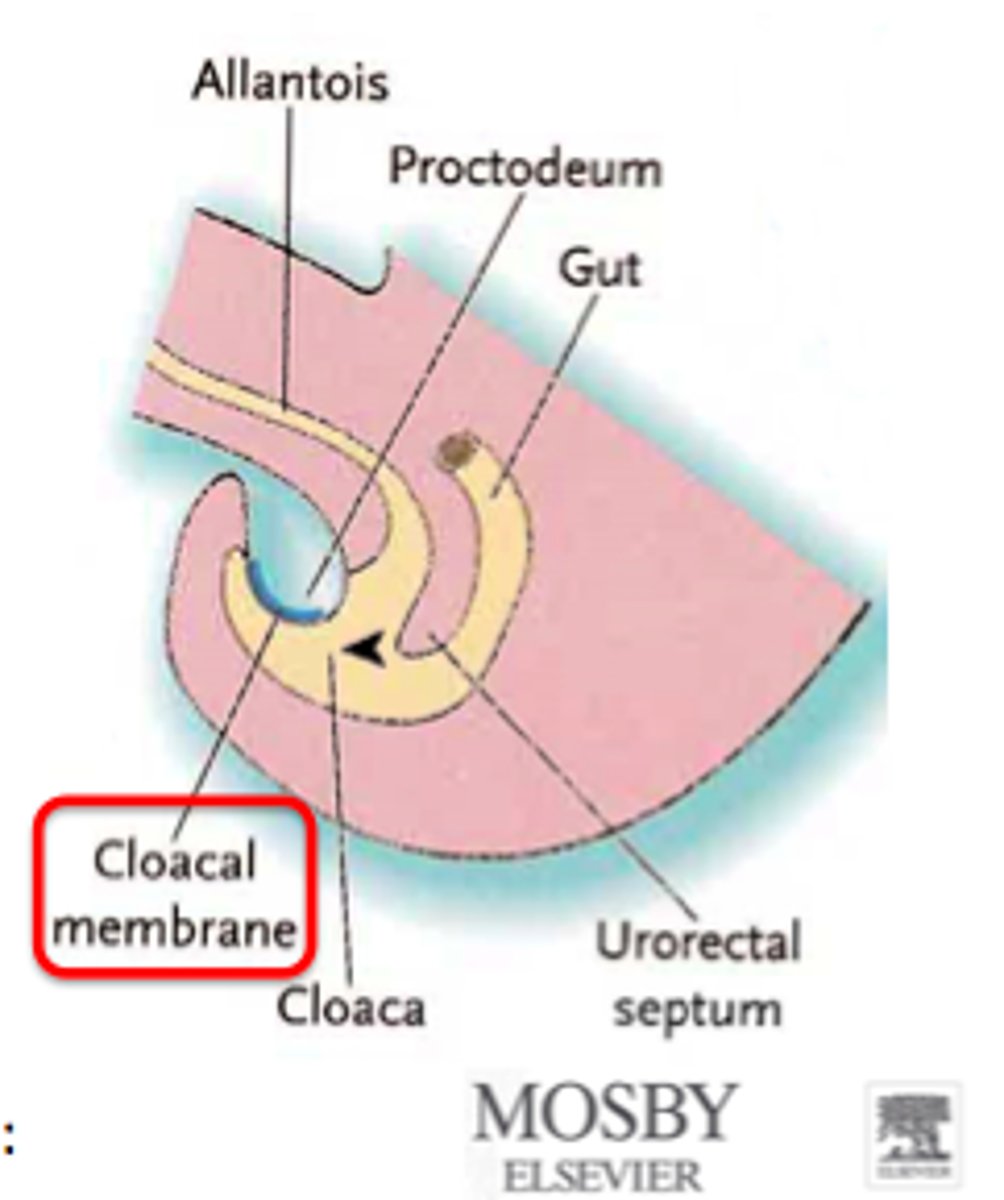
What is the cloacal membrane?
A membrane at the caudal end of the embryo that marks the future openings of the anus and urogenital tract. 🚻
What is the oropharyngeal (buccopharyngeal) membrane?
A membrane at the head end where the mouth will form. No mesoderm lies between ectoderm and endoderm here. 👄
What is body axis formation?
Gastrulation establishes the head-tail, left-right, and dorsal-ventral axes, organizing how the body will fold and grow.
What happens if gastrulation goes wrong?
Abnormal migration can cause *sirenomelia (fusion of lower limbs) or caudal dysgenesis*. ⚠️
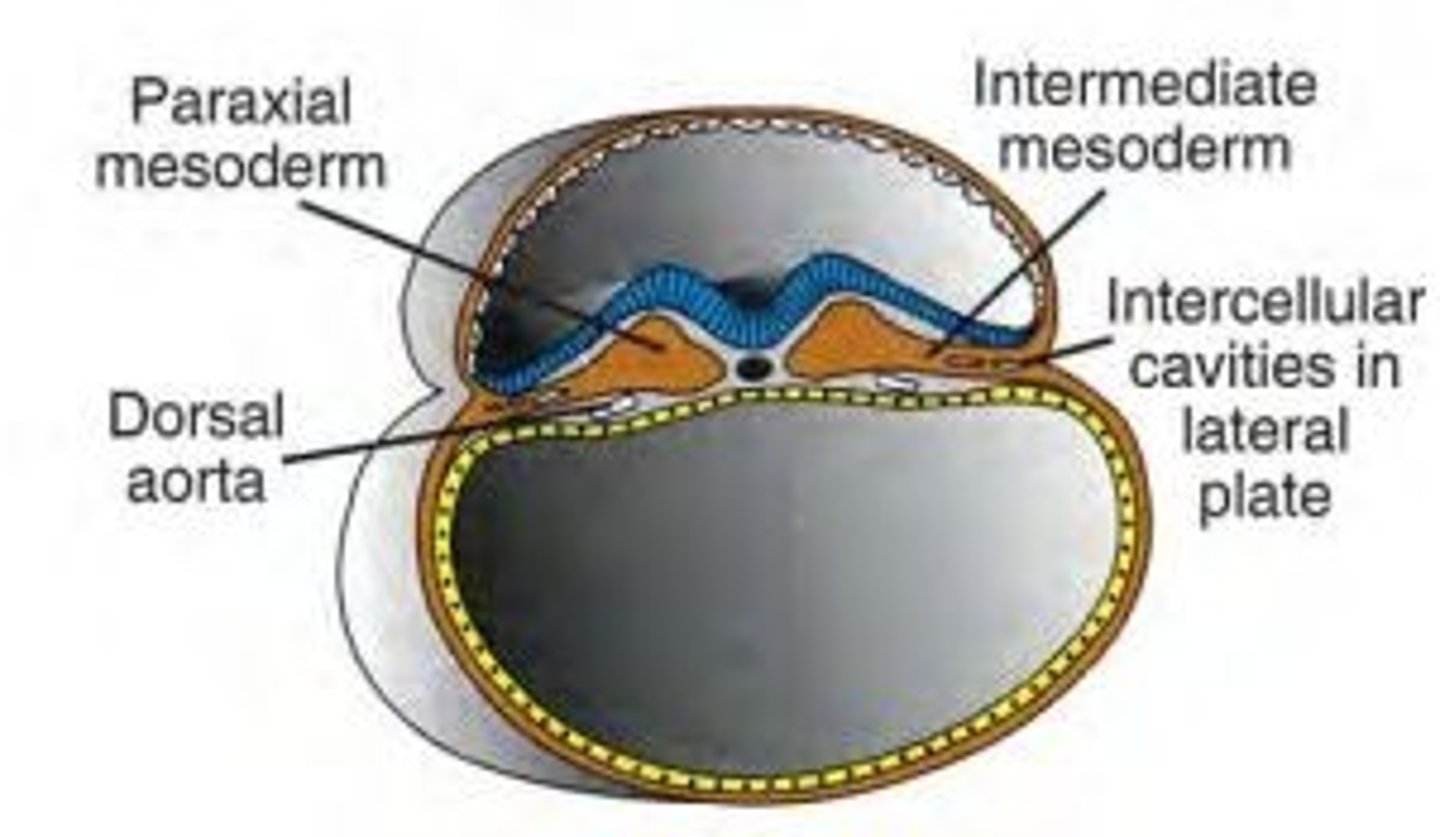
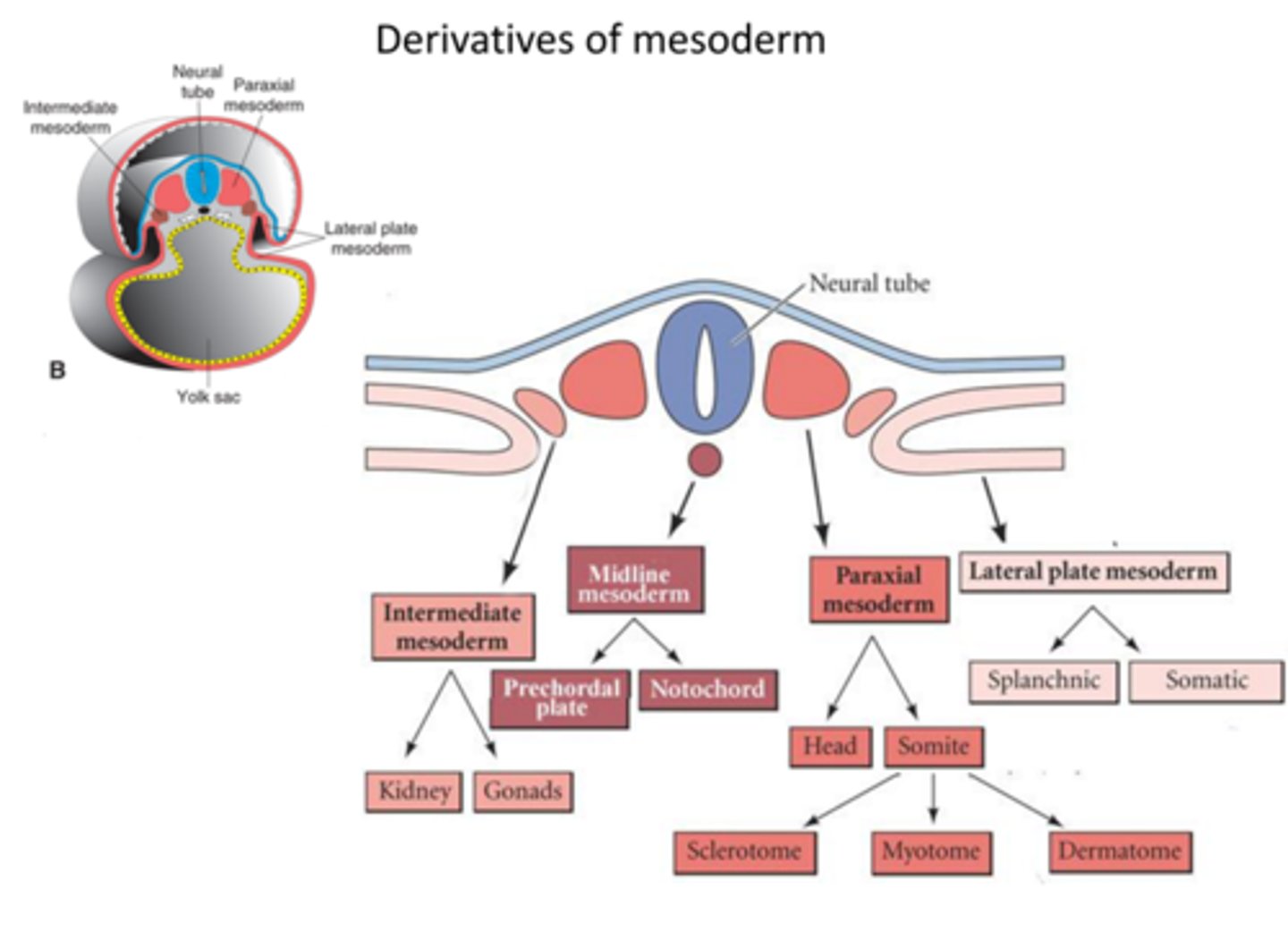
What is mesodermal differentiation?
The mesoderm splits into regions: *paraxial, intermediate, and lateral plate mesoderm*, each forming specific tissues.
What does the paraxial mesoderm form?
It segments into *somites* that give rise to the vertebrae, ribs, skeletal muscles, and dermis. 💪
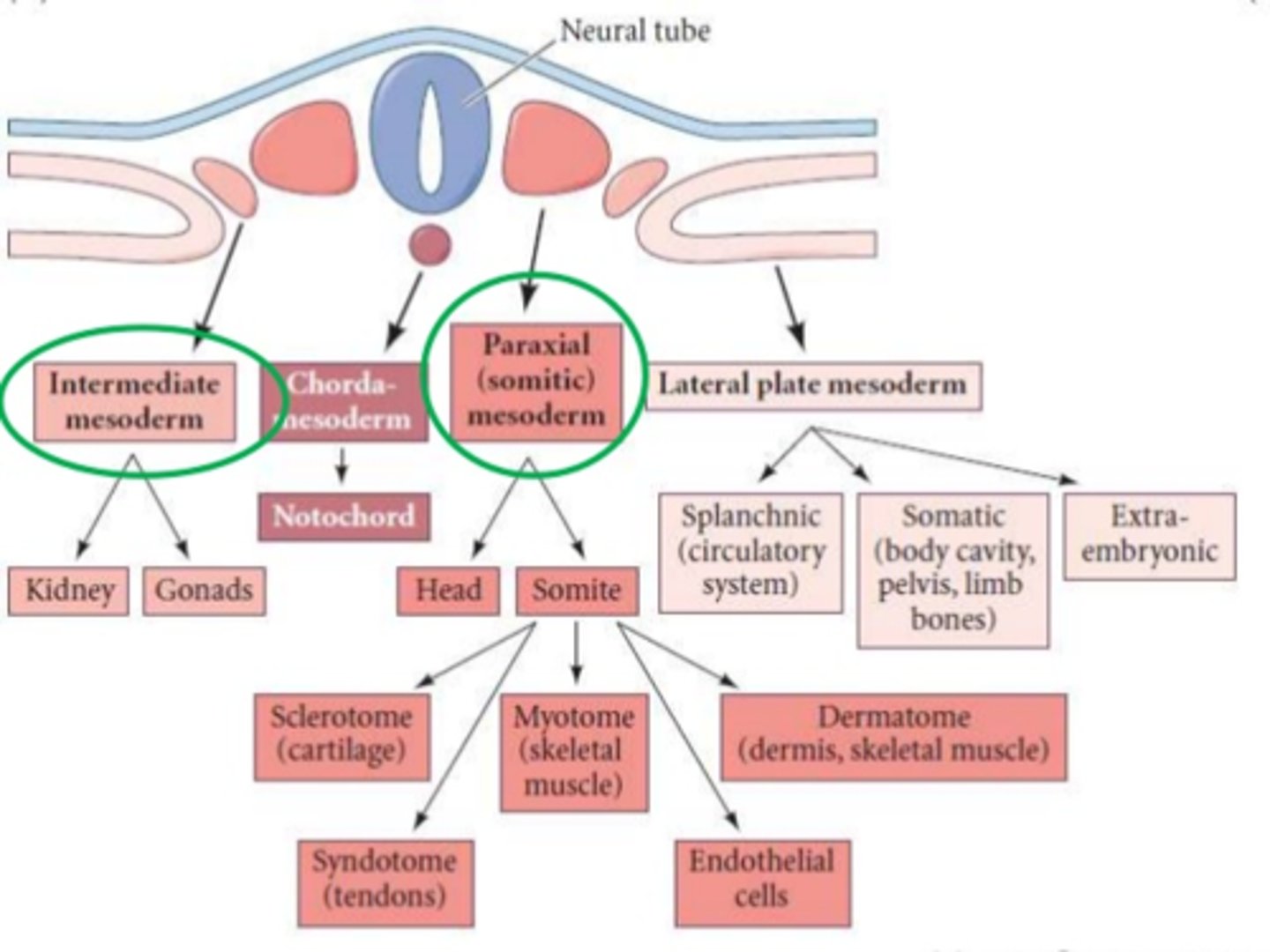
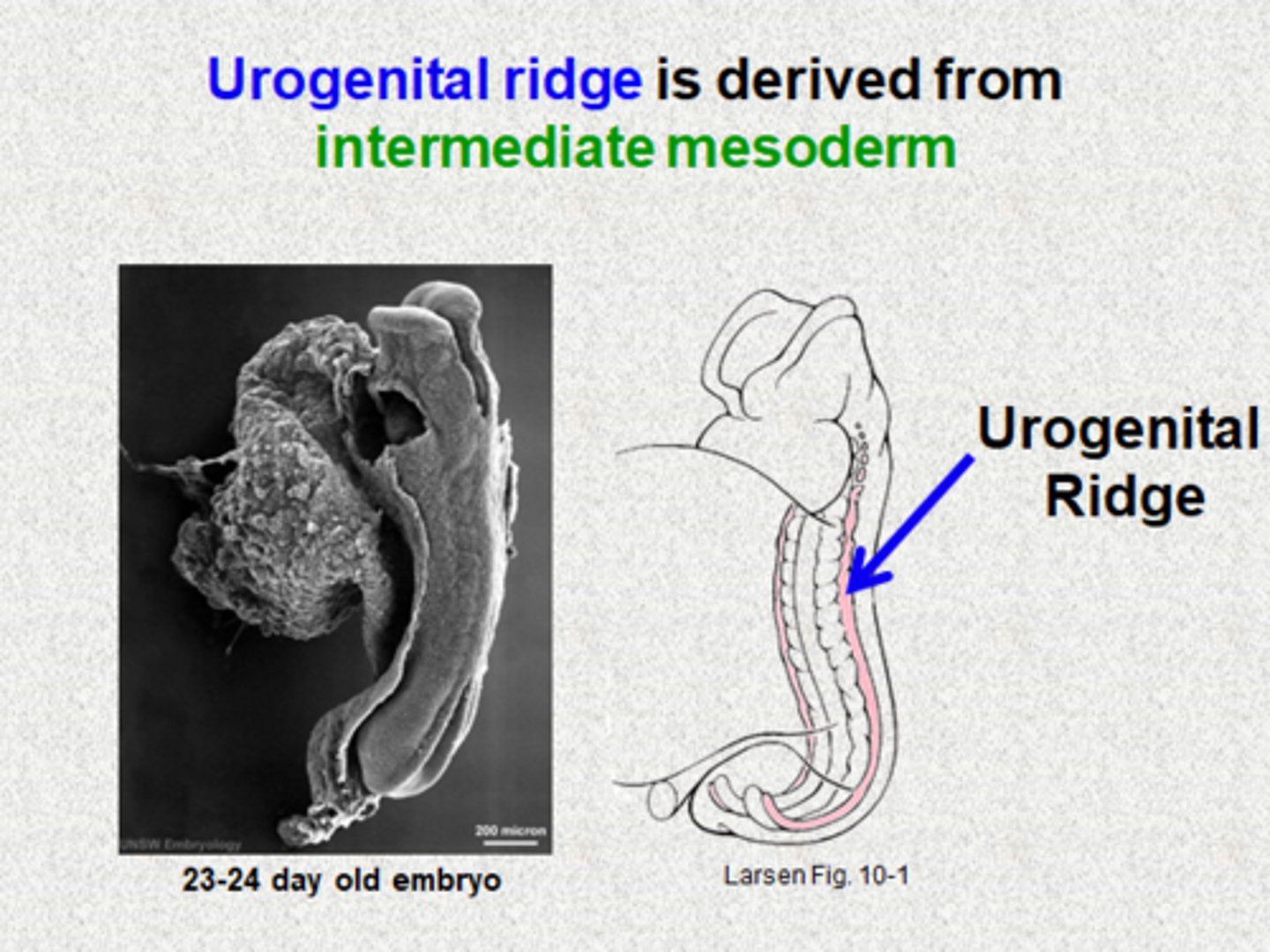
What does the intermediate mesoderm form?
It develops into the *urogenital system* — kidneys and gonads. 💧
What does the lateral plate mesoderm form?
It splits into *somatic (parietal) and splanchnic (visceral)* layers forming body walls and circulatory components.
What are somites?
Paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm appearing on either side of the neural tube. They determine the segmented pattern of muscles and vertebrae. 📏
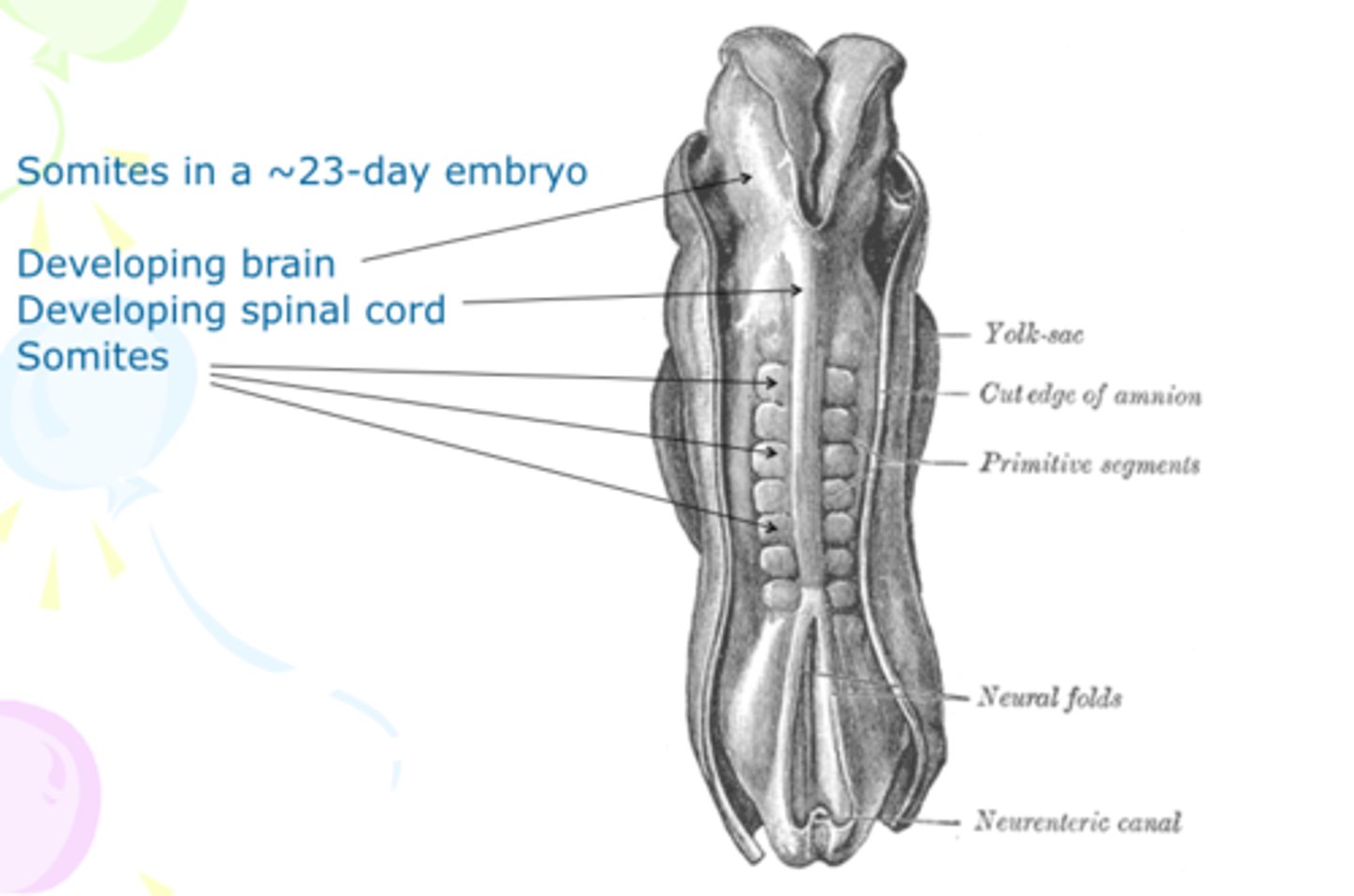
When do somites first appear?
Around *day 20*, new pairs form daily, totaling about 42-44 pairs. 📅
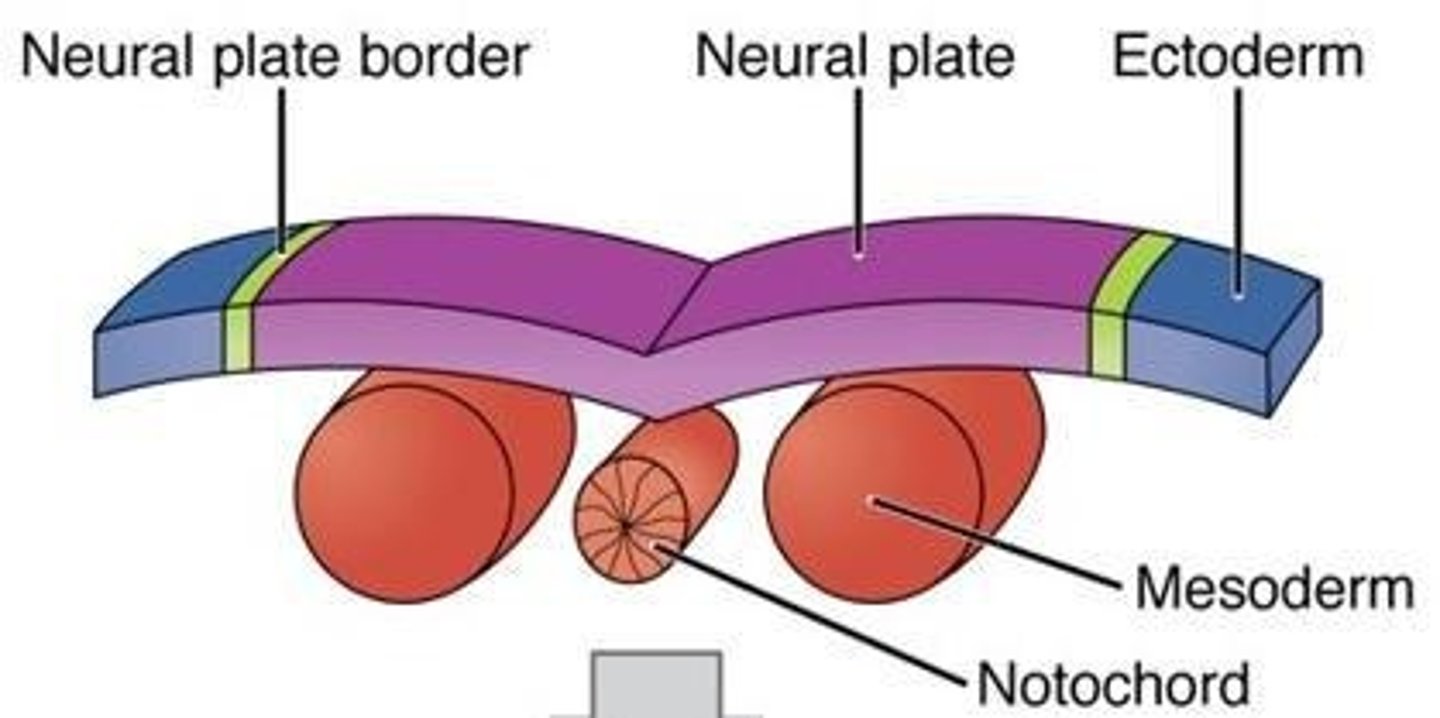
What induces neural plate formation?
The *notochord signals the overlying ectoderm to thicken into the neural plate*, starting neurulation.
Why is gastrulation called the most important stage?
Because it sets up all future tissues and organs — every structure in the body originates from these three layers. 🌍
Which germ layer forms the nervous system?
The *ectoderm* forms the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. ⚡
Which germ layer forms the heart and blood vessels?
The *mesoderm* forms the cardiovascular system, including heart muscle and blood cells. ❤️
Which germ layer forms the lining of the gut and lungs?
The *endoderm* forms the epithelium of the digestive and respiratory tracts. 🍽️
What is intraembryonic mesoderm?
It's the mesoderm between ectoderm and endoderm inside the embryo, distinct from the extraembryonic mesoderm of the membranes.
What happens to the primitive streak later?
It shrinks and disappears by the end of week 4. Persistent streaks can form *sacrococcygeal teratomas* (tumors with mixed tissues). ⚠️