chemical level of organization inorganic compounds
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
element
pure substance that cant be created or broken down by ordinary chemical means
compound
substance composed of 2+ elements joined by chemical bonds
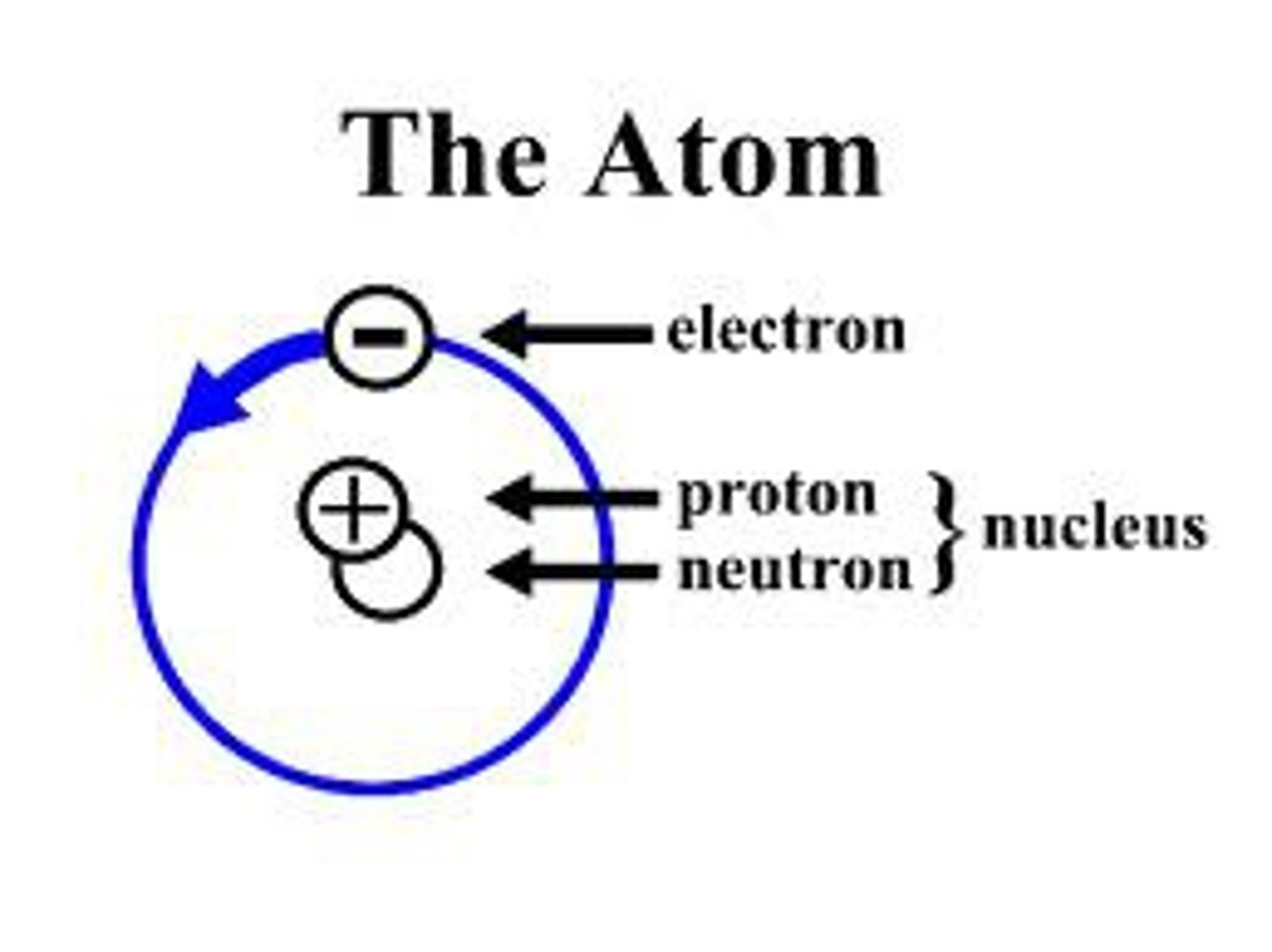
atom
smallest quantity of an element with properties unique to it
consists of protons and electrons
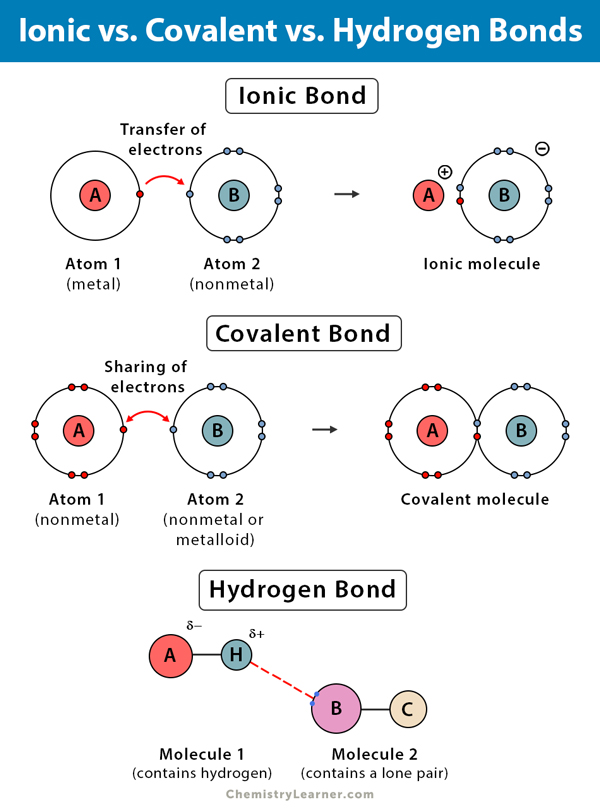
bond
electrical attraction that holds atoms in the same vicinity
3 types of bonds
1.ionic bond- bond between ions of opposite charges (donates electrons) ex: NaCl
2.hydrogen bond- weak (+) charged Hydrogen atom already bonded to 1 electro (-) attracted to another ex: H2O (weakest)
3.covalent bond- 2 atoms equally share electrons CO2 (strongest)
chemical energy
potential energy stored in chemical bonds
- energy is only used when bonds are formed and produced when bonds are broken
3 types of reactions
1.synthesis/anabolic - bond formed between 2 simpler substances to form a complex product(requires energy)
2. decomposition/ catabolic- bond broken into simpler products( releases energy)
3. exchange- formation of new compounds through synthesis and decomposition
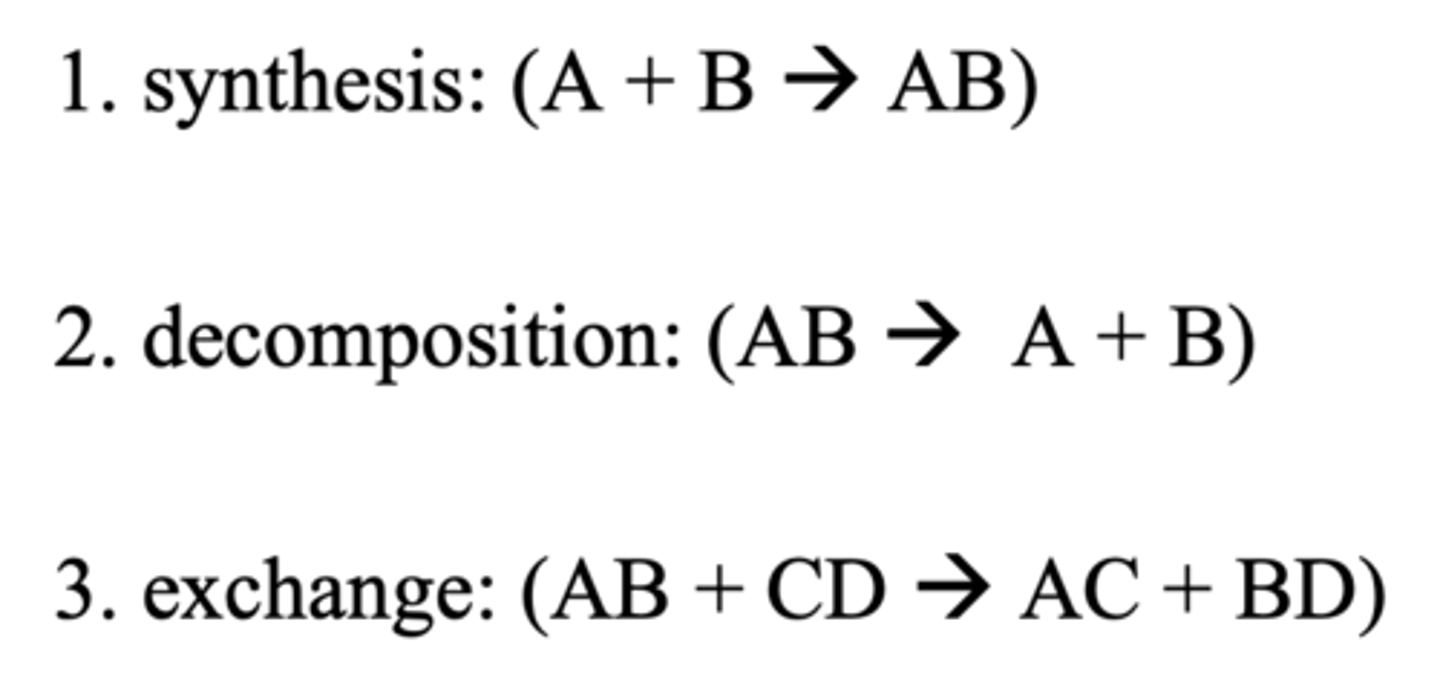
5 factors influencing rate of chemical reactions
1. temperature- rxns faster higher temps
2. concentration- rxn faster higher concentration of reactants
3. pressure- rxn faster with higher pressure of container the reactants are in
4. enzymes -increases rate of rxns
5. properties of the reactants- rxns faster in a gaseous state ,have a larger surface area available for reactants, smaller in size and slower in a solid state
properties of water
1. universal solvent-capable of dissolving more substances than any other liquid
2. lubricates and cushions-protects against trauma and friction
3.high specific heat-can lose or gain large amount of heat with little change of its own temperature
4.role in chemical rxns- breaking and creation of H2O molecules
hydrolysis rxn
breakdown of H2O
intracellular fluid
water inside the cells (largest body fluid compartment)
-higher concentration of potassium, protein anions
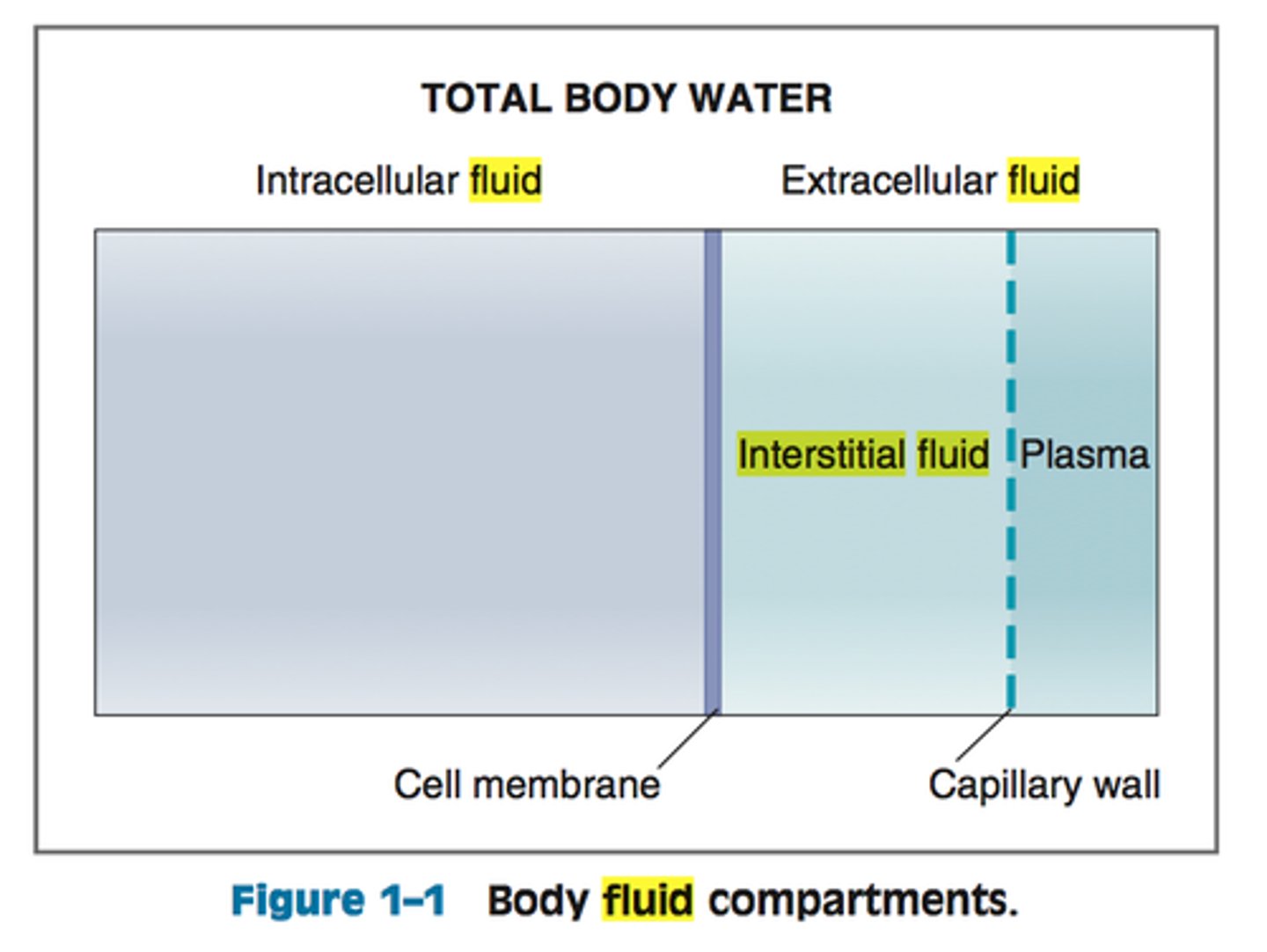
extracellular fluid
water outide the cells, transports substances to and from the cells
-higher concentration of bicarbonate, sodium
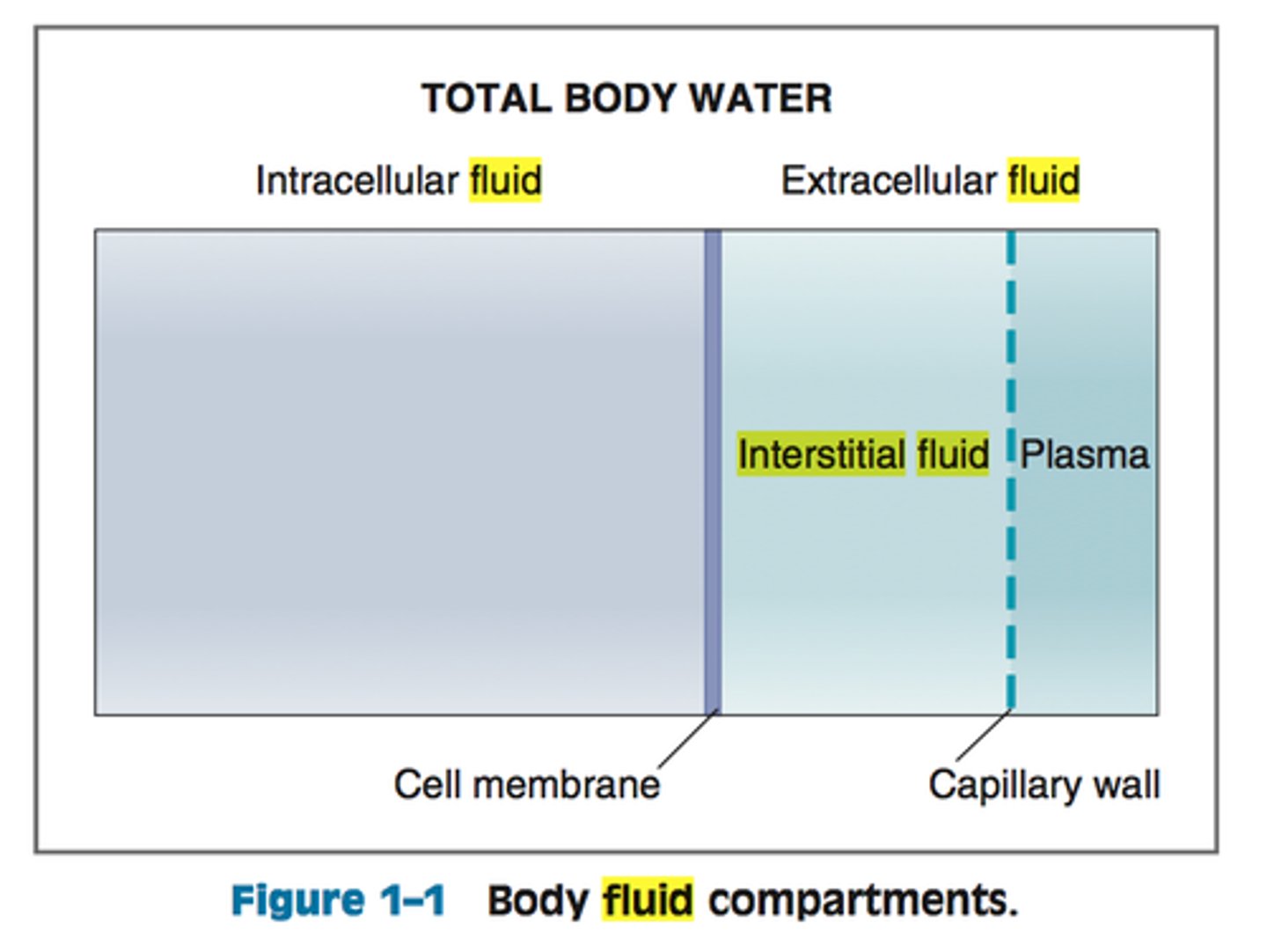
plasma
fluid component of blood
interstitial fluid
fluid that surrounds all cells not in the blood
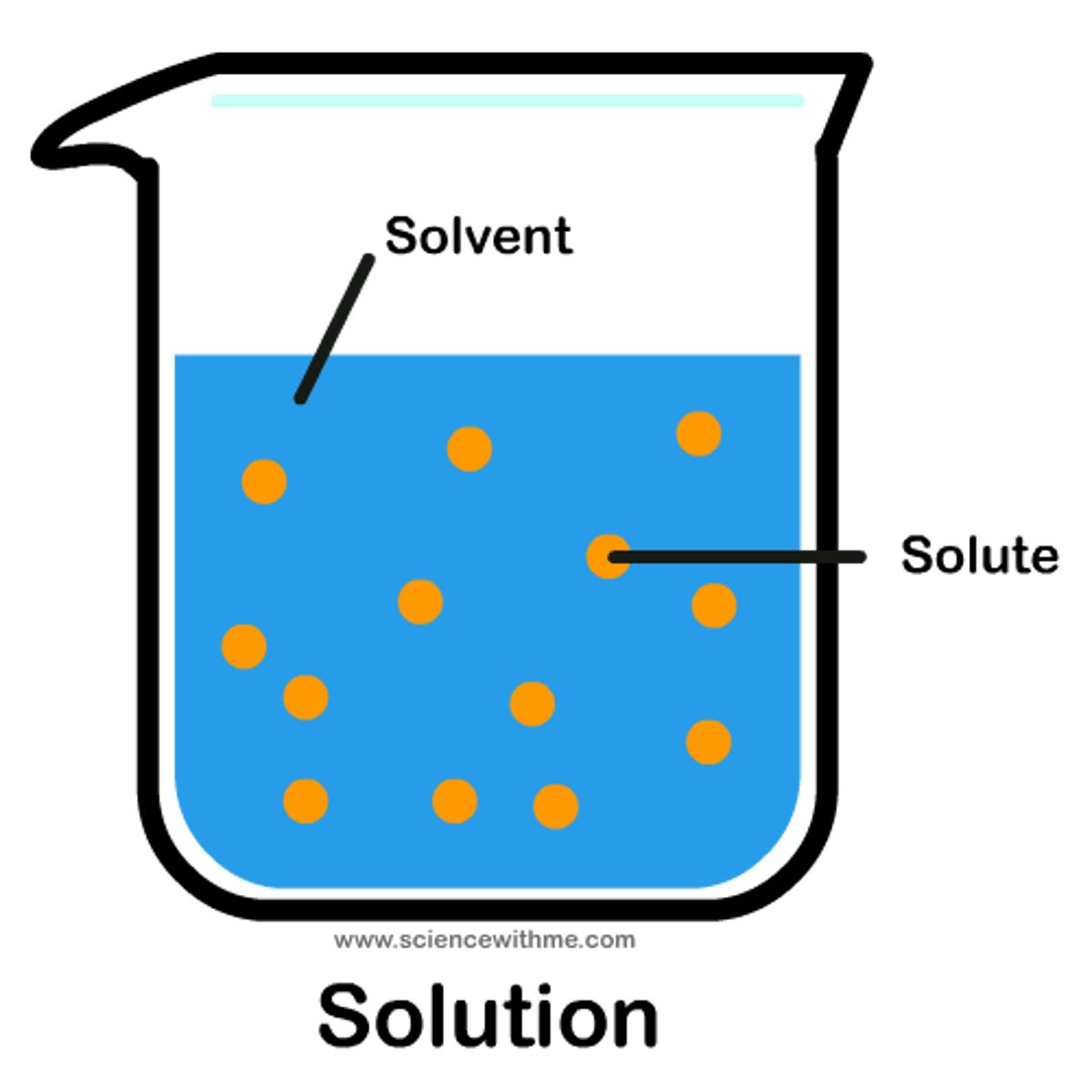
solutes
dissolved substances in a solution ex: salt
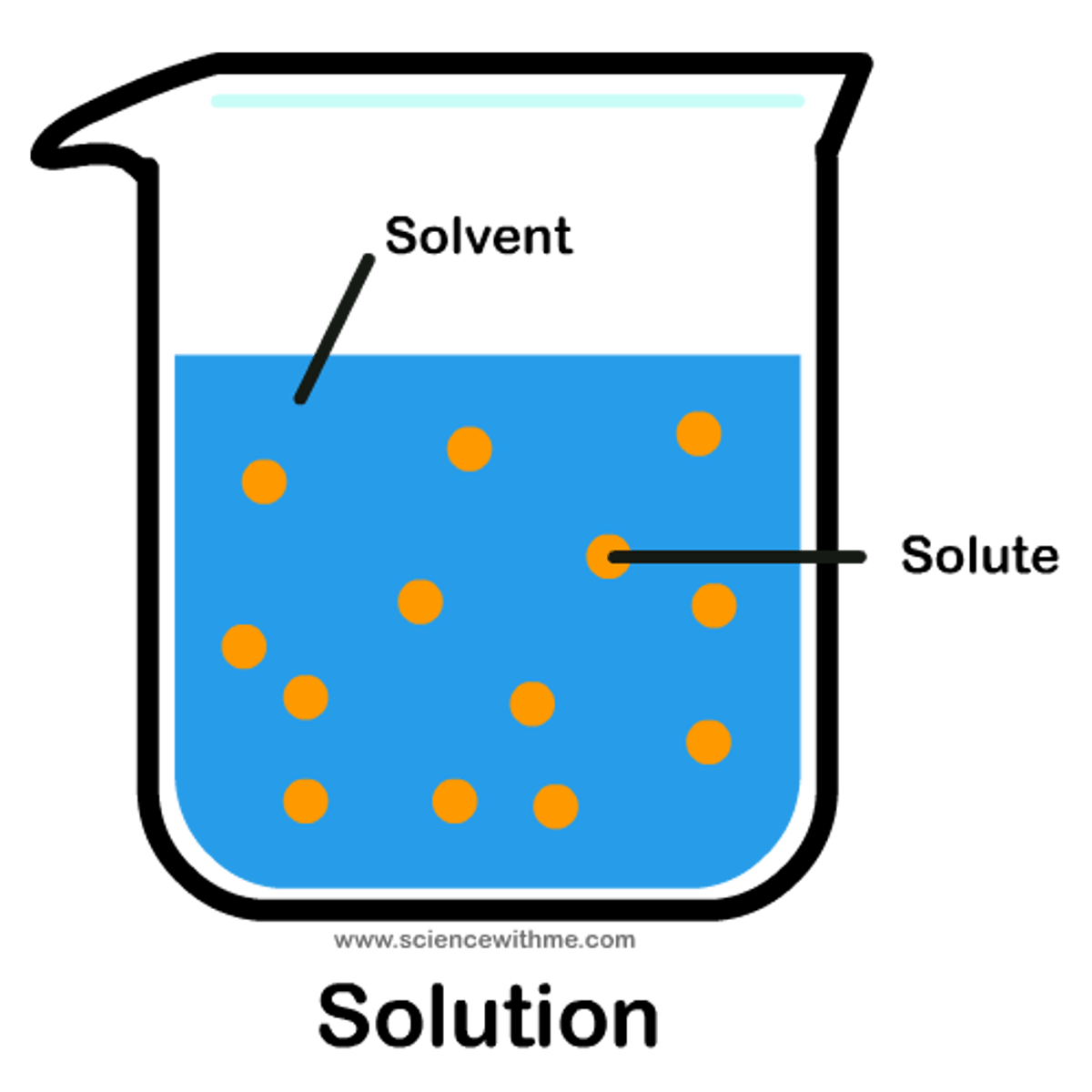
solvent
solution that solutes are dissolved in ex: water
anion
substance with a (-) charge
cation
substance with a (+) charge
acid
substance that dissociates into a hydrogen ion and anions
- pH of lower then 7
base
substance that dissociates into a hydroxyl ion and cations
-pH of greater then 7
salt composed of ...
anions and cations ex:NaCl
pH of ______ means
7 is neutral ex: water
buffer
solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components
oxygen
-required to complete decomposition rxns
-cause the release of energy in the body
carbon dioxide
- waste product
-maintain acid-base balance in the body