Topic 14 - Dynamic Earth Part 2: Volcanoes
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is a volcano?
a buildup of volcanic material into a hill or a mountain, the material has come out of a crack (a vent) in the ground
What comes out of a volcano?
lava, ash, gases (CO2, WV, and more), dust, steam - never smoke, and rocks of all sizes
what is magma?
melted rock material below the ground, under a lot of pressure, lots of dissolved gases
what is lava?
melted rock material above the ground, the pressure is decreased, the gases are released
what are the distinct types of lava in Hawaii?
AA and Pahoehoe
what is AA?
if lava cools quickly and moves fast it can tear into chunky pieces
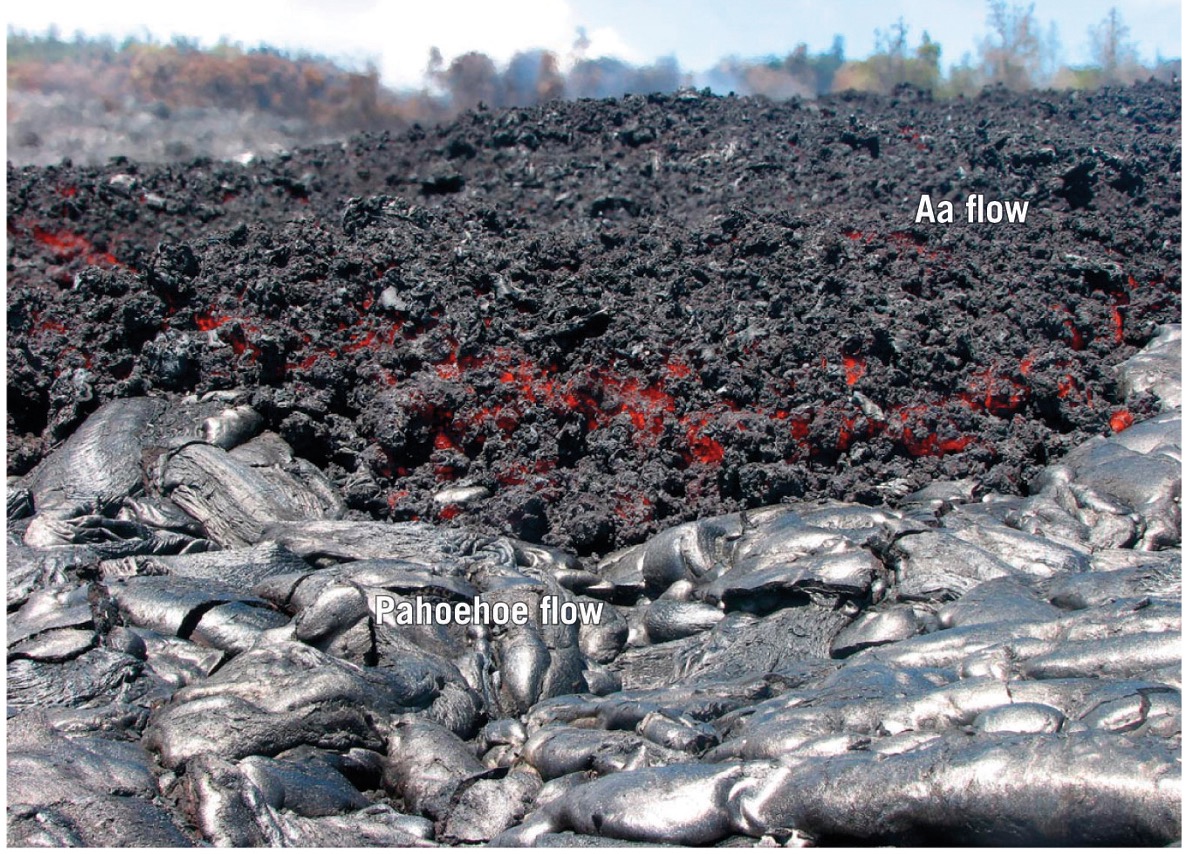

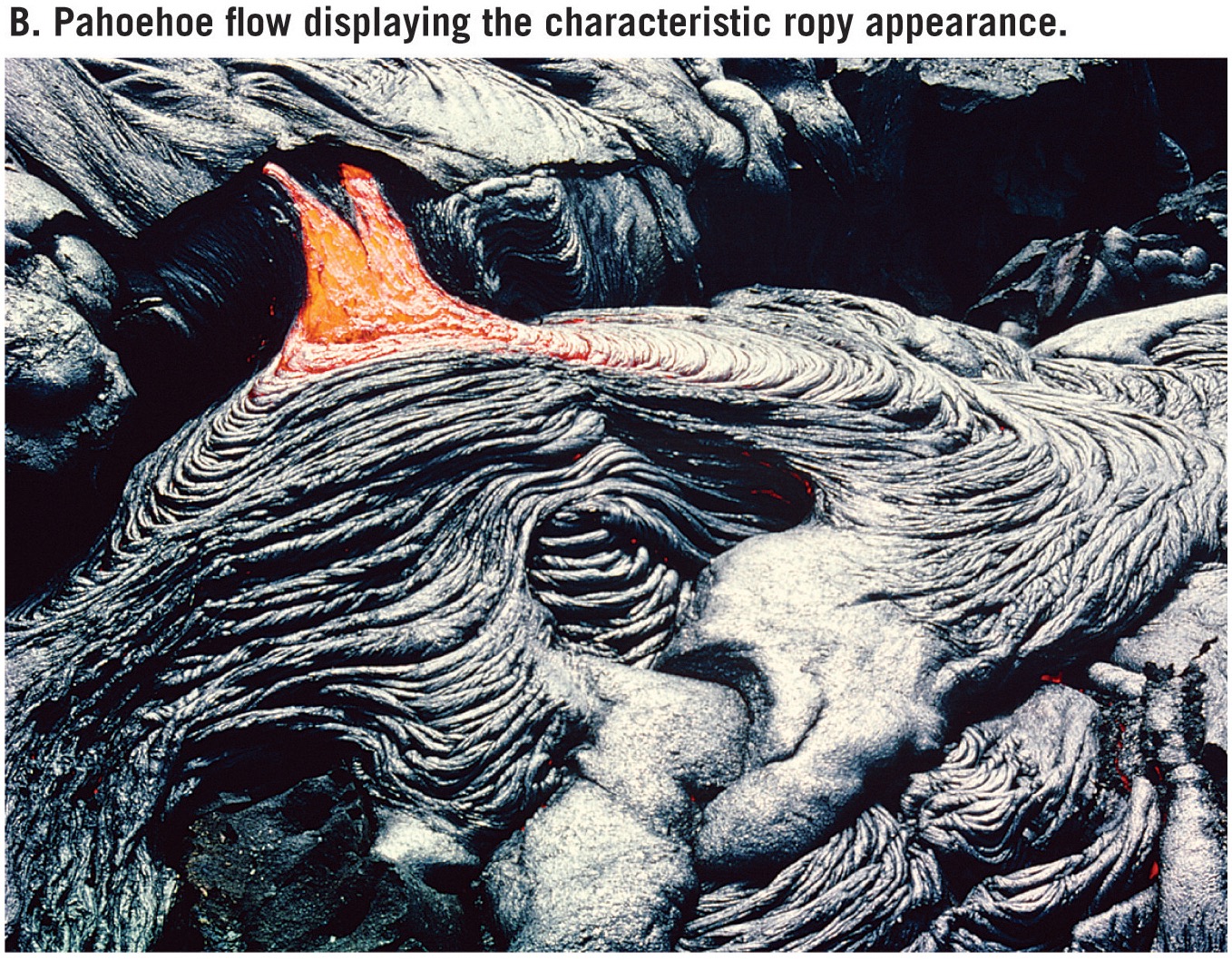
what is pahoehoe?
If lava cools slowly and does not move too fast, it forms smooth ropy lava
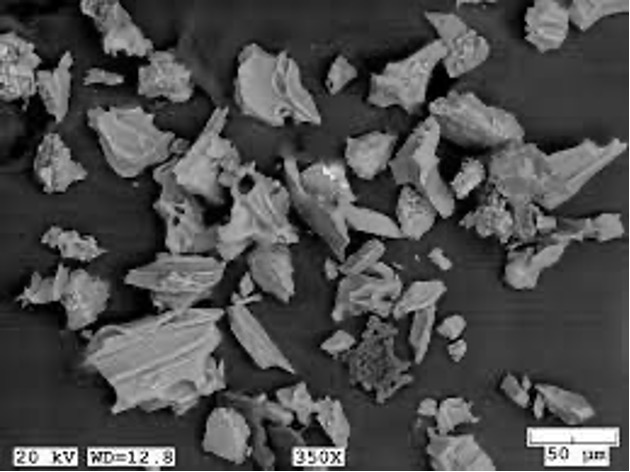
what is ash?
pulverized volcanic glass
what is dust?
pulverized rock (blasted out of the volcano)
what are the three different ways volcanoes are classified?
active, dormant and extinct
what is an active volcano?
it has erupted within recorded history
what are some examples of active volcanoes?
Mount St. Helens, Mauna Loa, Mt. Etna, Mt. Pinatubo, Yellowstone NP
what is a dormant volcano?
the volcano is sleeping, has not erupted in “a while” but shows signs that it could erupt – ground rumbling, small quakes, there is heat in the area
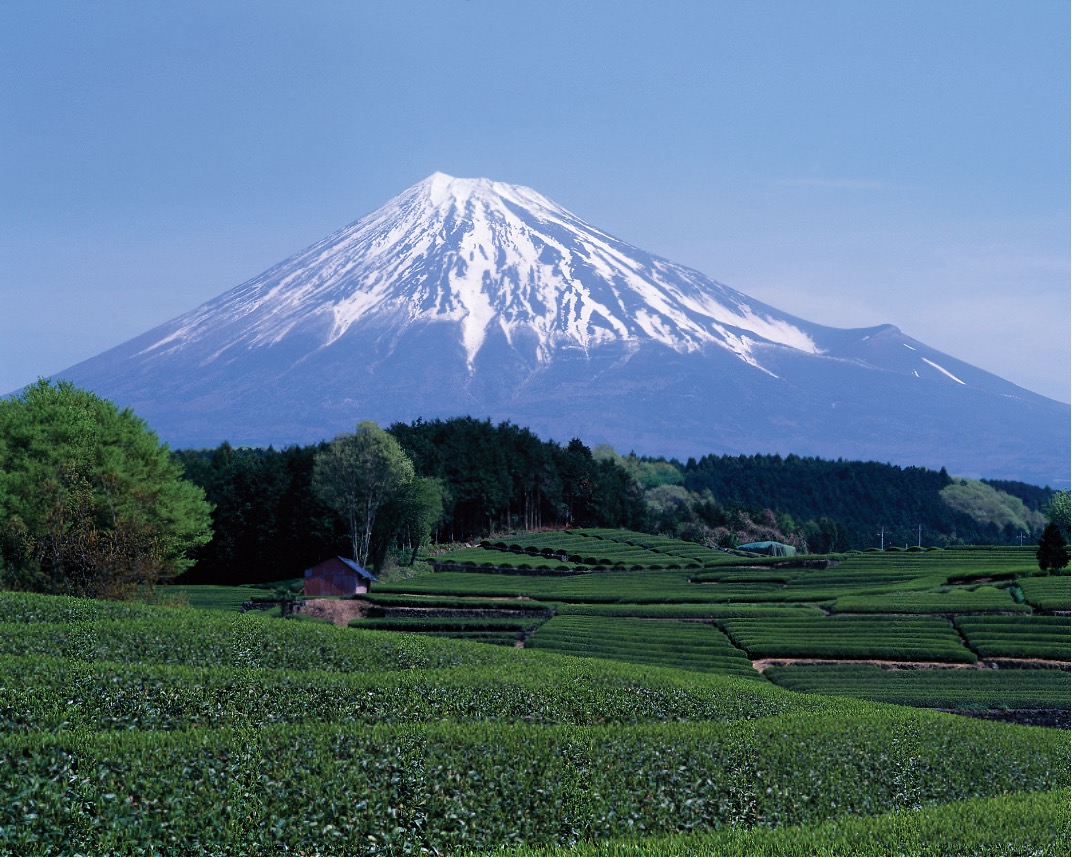
what are some examples of dormant volcanoes?
Mt. Fujiyama, Mount Rainier, Mt. Kilimanjaro
what is an extinct volcano?
dead, no energy left to cause it to erupt. Cold, quiet
what are some examples of extinct volcanoes?
Some of the Hawaiian islands and others nearby
can the status of a volcano change?
yes, Vesuvius was thought to be dormant until the 1940’s
what are the different types of volcanoes (7)?
lava plateaus, shield, composite, cinder cone, dome, caldera and crater
what is a lava plateaus?
also called flood basalts, thin - runny lava not explosive

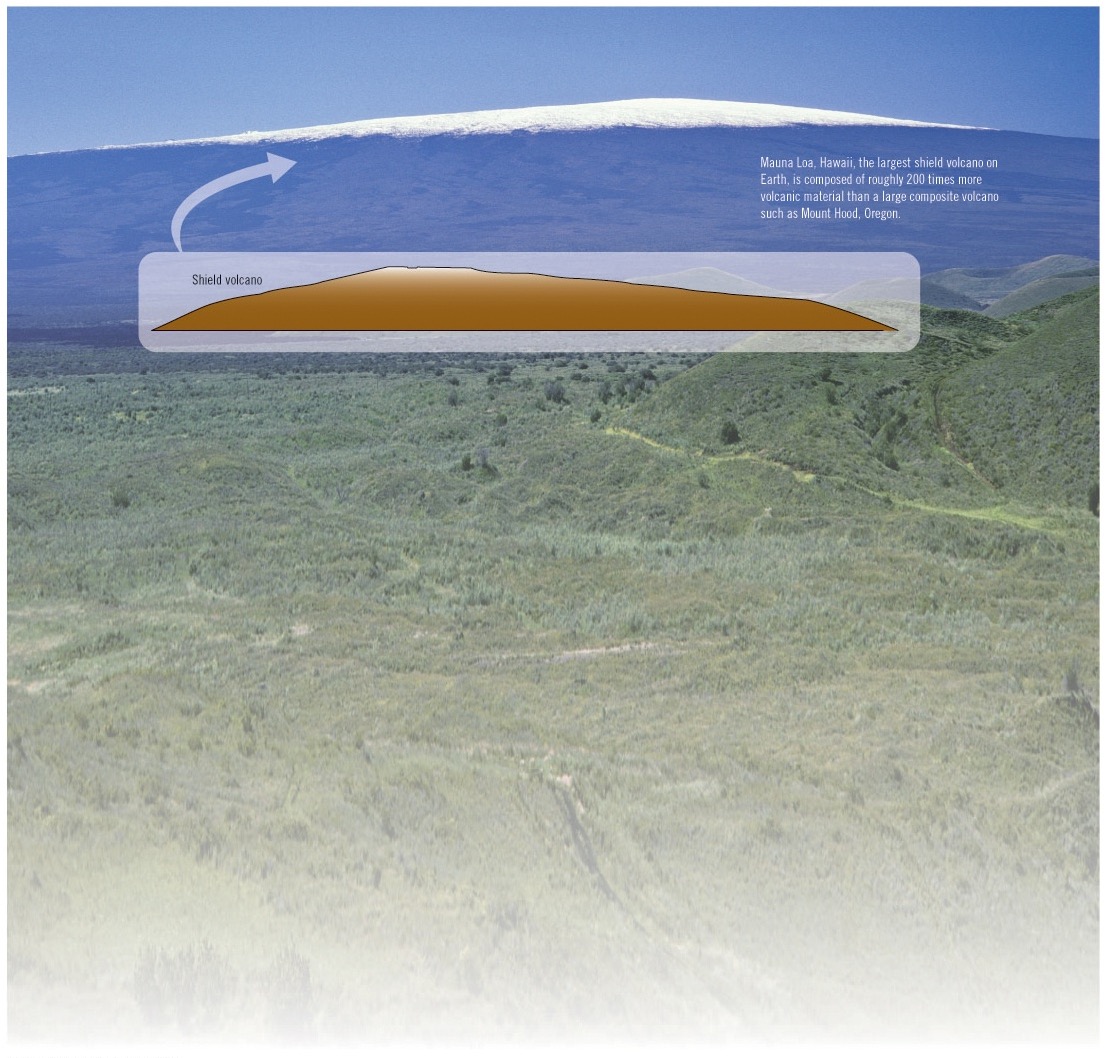
what is a shield volcano?
thin - runny lava, builds up into a shield shape, not explosive (called effusive)

what is a composite volcano?
well-known volcano shape, alternating layers of thick lava and volcanic ash – the escaping gas causes the strong eruptions

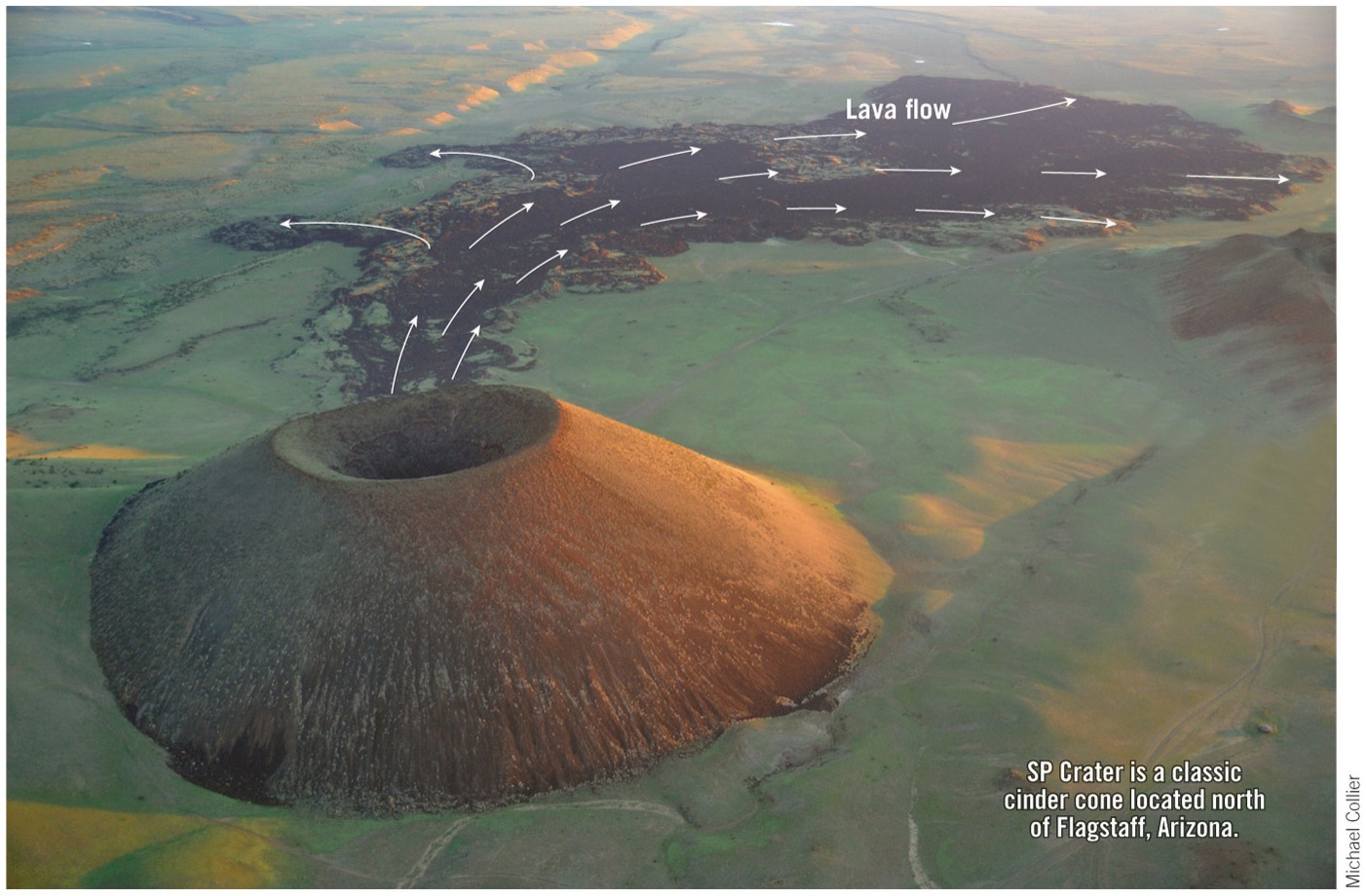
what is a cinder cone volcano?
smallest types of built-up volcano, cinders blast out of vent and accumulate close by, explosive eruptions

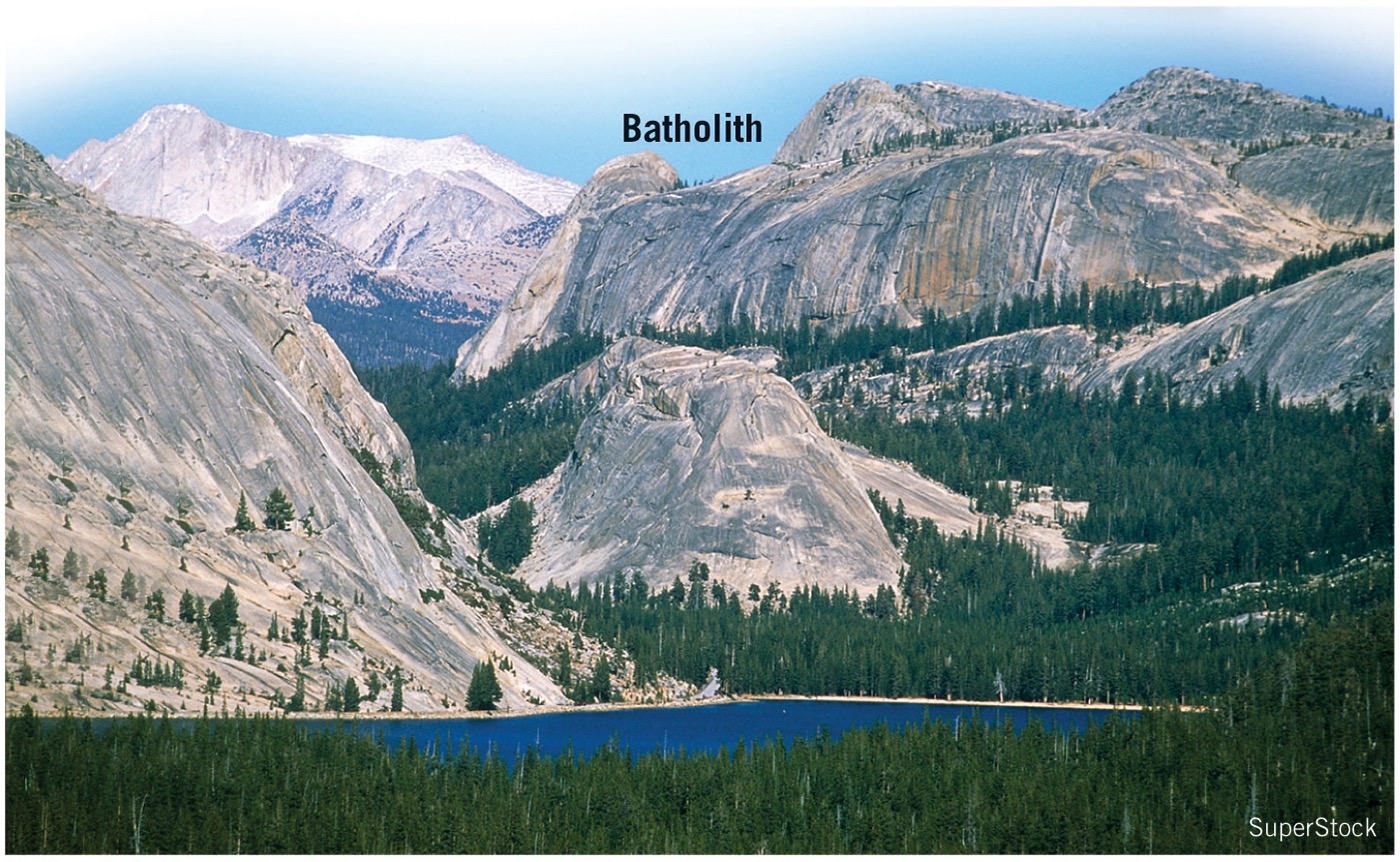
what is a dome?
form beneath the surface, magma chamber below ground, never erupted through the vent

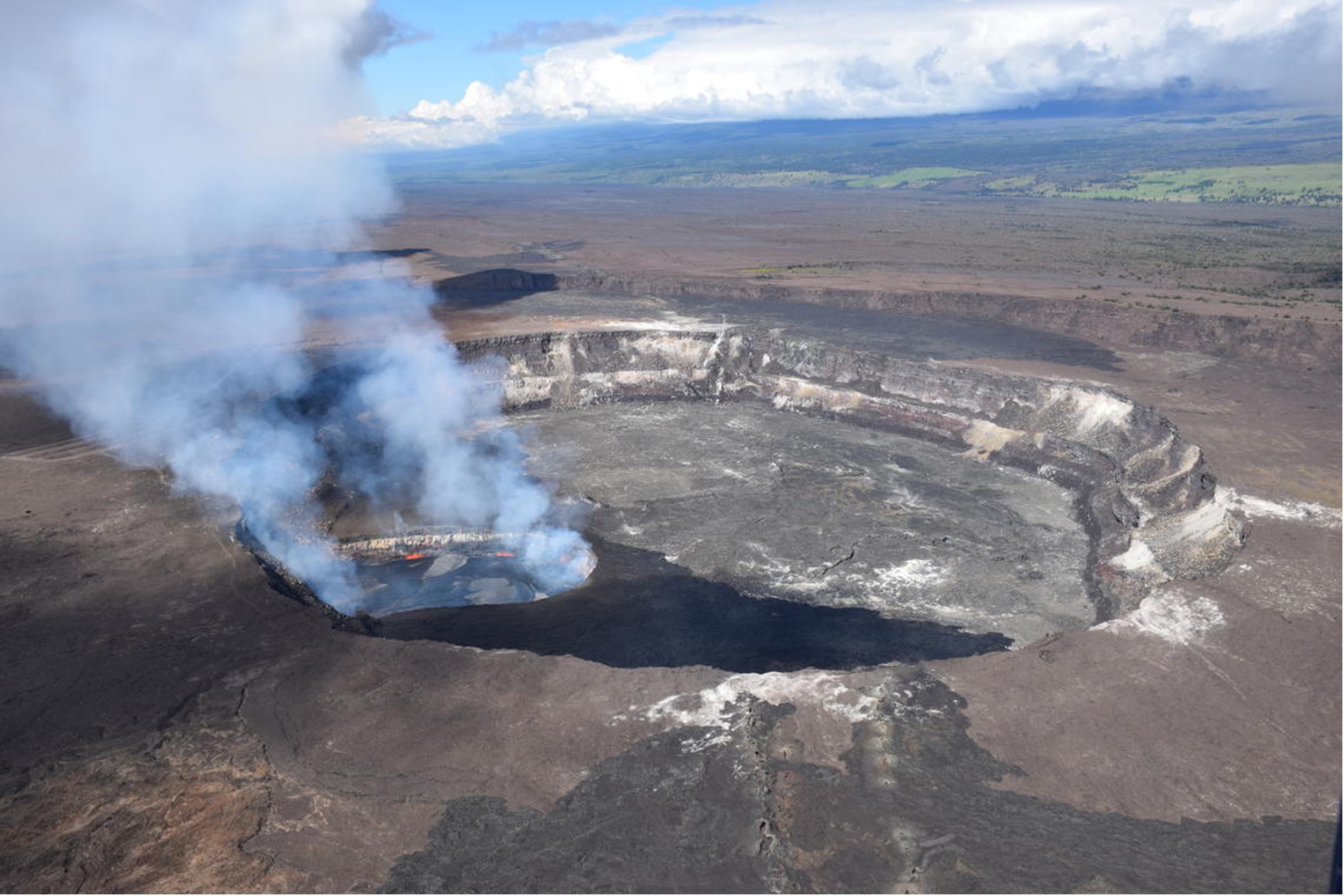
what is a caldera?
large circular depression at a volcano's summit, forms when the magma chamber empties, summit collapses inward

what is a crater?
circular, smaller than a caldera, typically forms from the eruption or explosion of a volcano, not collapse
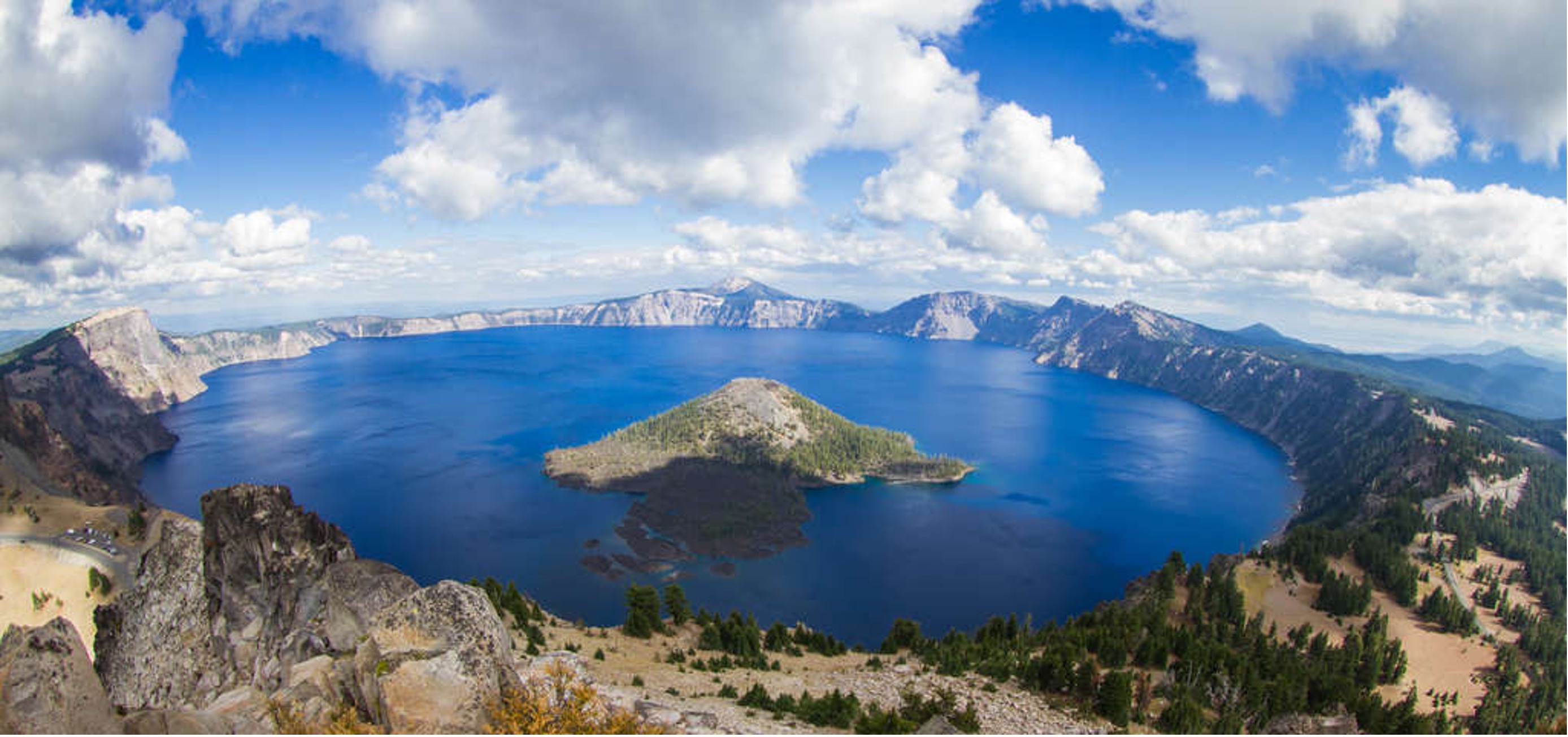

what determines the eruptive activity of a volcano?
temperature and the amount of silica
Cooler lava is …?
thicker - flows less
Hotter lava is …?
thinner - flows easily
The more silica, …?
the thicker the melted material
The less silica, ….?
the thinner the melted material
what comes out of a volcano that can affect people far away from the actual eruption?
gases - held inside the magma by pressure, pressure is released and the gases escape
what are the gases that are released from a volcano?
CO2 (carbon dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), WV, SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide)
what are pyroclastic materials?
hot broken rocks released from a volcano during an eruption
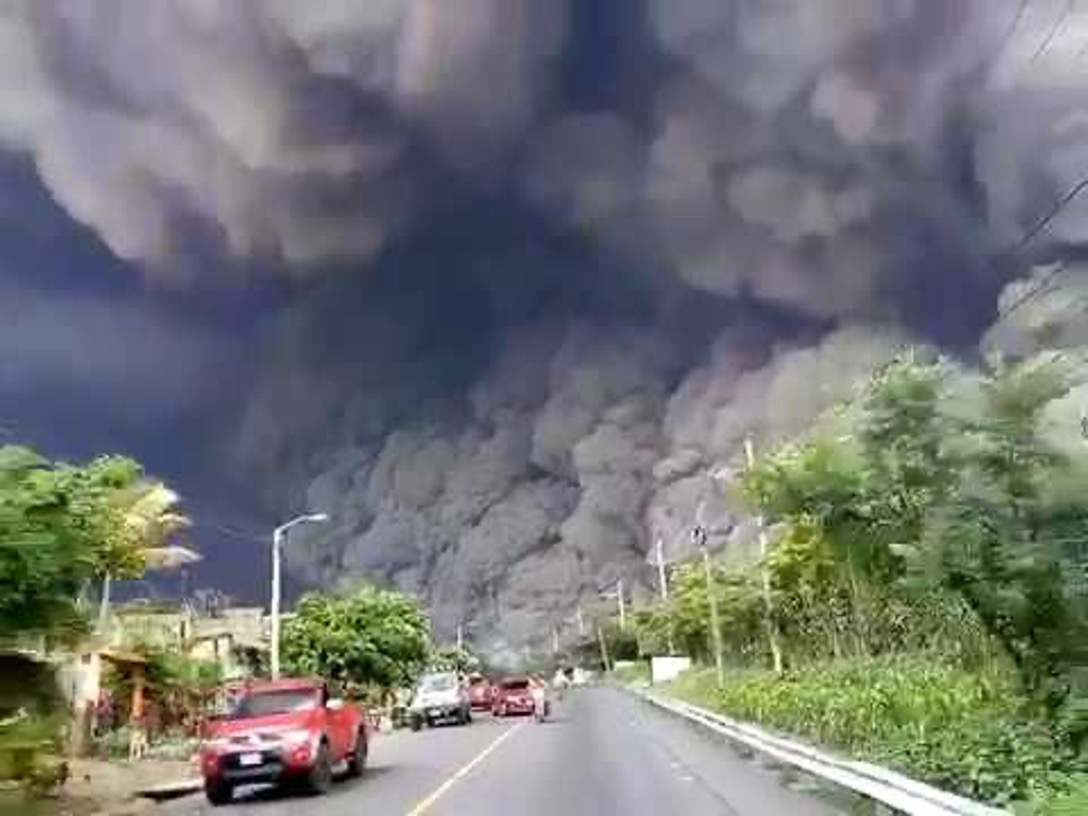

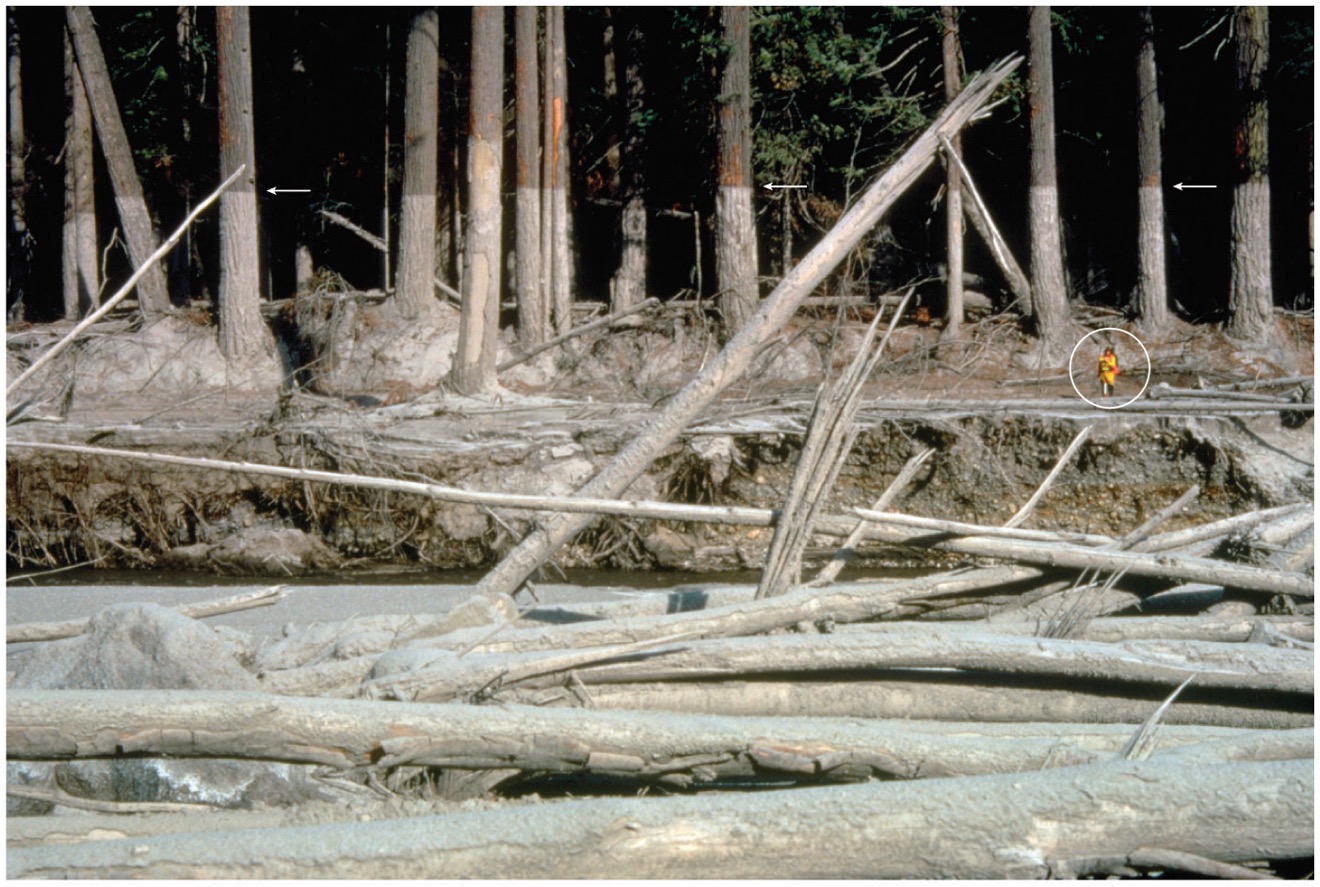
What is a lahar?
mixture of ash and meltwater – turns into a “mudslide”, thick dangerous deep river

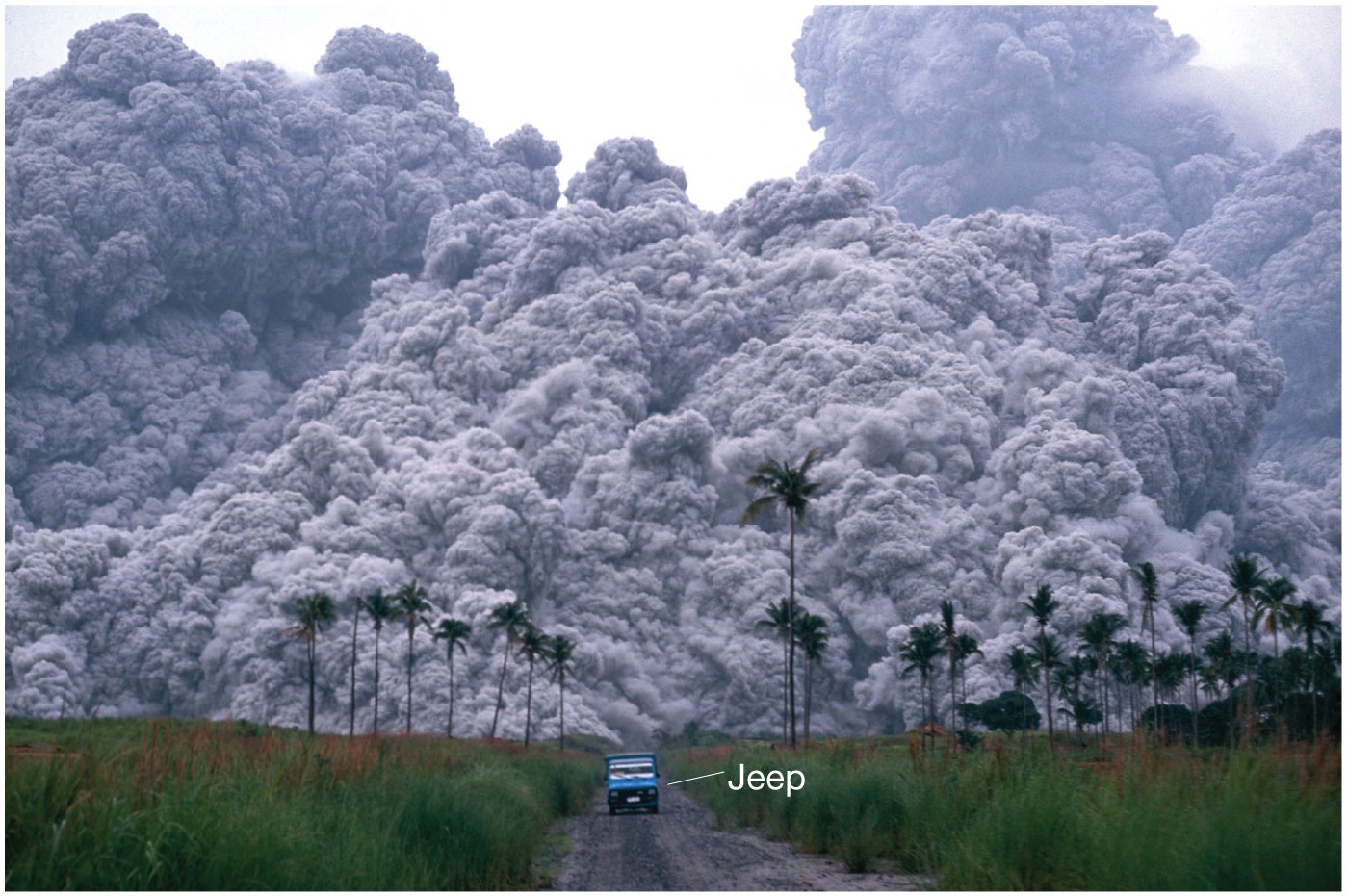
what is a nuee ardent?
glowing or flaming clouds of incandescent (super hot) gas and dust

what effect can dust and ash have in the upper atmosphere?
can affect sunset colors, climate via sunlight insolation and temperatures