All About Igneous Rocks! (GEOL 101)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What can you mainly see in Granite?
Quartz, Feldspar, and Biotite
What are the 3 kinds of Rocks?
Igenous, Metamorphic, and Sedimentary
What kind of rock is the crust mostly made of?
Igenous and Metamorphic rocks
What is the most abundant rock on the surface?
Sedimentary rocks
How do Igenous Rocks form?
Solidification of magma or lava

What is the name of this rock?
Granite

What is the name of this rock?
Gabbro

What is the name of this rock?
Rhyolite porphyry

What is the name of this rock?
Basalt
What is Intrusive (Plutonic) Magma
Rocks formed beneath the surface by magma
What is Extrusive (Volcanic) lava?
Rocks formed at the surface by lava
What is Magma?
Molten rock below Earth’s surface.
What is Lava?
Molten rock on earth’s surface.
What is a Country Rock?
The rock that magma intrudes into
What are Igenous Rocks classified by?
Texture and Composition
What does Texture mean?
The size of mineral crystals
What does Composition mean?
What mineral it’s made of
Define Texture
As magma or lava cools, it solidifies, and minerals crystalizes
What are mineral crystals inside a rock sometimes called?
Mineral grains
What determines how large a mineral crystal grows?
Amount of time
What happens when magma cools slowly?
You can easily see mineral crystals
What happens when lava cools quickly?
Minerals are microscopic
What is a fine-grain texture?
An igneous rock made of microscopic mineral crystals
What is a coarse-grained texture
An igneous rock made of large mineral crystals
What is the 2 stage cooling process for some Igneous Rocks?
They start to cool slowly as a magma and then, they reach the surface, and grow microscopic mineral crystals
What is a Porphyritic Texture?
Rocks that have have both large and microscopic crystals.
What is a Porphyry?
A rock with a porphyritic texture
What is a glassy texture?
When lava cools too quickly the atoms do not have time to arrange themselves into a crystalline structure
What happens when lava cools too quickly?
The lava forms glass
What is Pillow Lava?
lava that erupted under water
What results from a pillow lava?
A rock with both a glassy (outside) and fine-grain (inside) texture

What kind of texture does this rock have?
Fine grain

What kind of texture does this rock have?
Coarse Grain

What kind of texture does this rock have?
Porphyritic

What kind of texture does this rock have?
Glassy
What are some common Igneous Rock Minerals
Quartz, Feldspar, Muscovite, Biotite, Amphibole, Pyroxene, and Olivine
Out of the common igneous rock minerals, which are felsic?
Quartz, Feldspar, Muscovite, Biotite, and Amphibole
Out of the common igneous rock minerals, which are mafic?
Pyroxene and Olivine
What does Felsic mean?
More silicon
What does Mafic mean?
Less silicon
What do Felsic Rocks have?
Higher Silicon Concentrations, Lower Melting Temperature, Higher Viscosity, and Light Colored
What does High Viscosity mean?
It does not flow easily
What color are Felsic rocks usually?
Light colored (pink and or gray)
What do Mafic Rocks have?
Lower Silicon Concentrations, Higher Melting Temperature, Lower Viscosity, and Dark Colored
What does Low Viscosity mean?
Flows easily
What color are Mafic rocks usally?
Dark colored (black)
What is helpful to determine if a rock is felsic or mafic?
Color

What kind of texture does Rhyolite have?
Fine grain

Is Rhyolite Mafic or Felsic?
Felsic

What kind of texture does Basalt have?
Fine grain

Is Basalt Mafic or Felsic?
Mafic

What texture does Granite have?
Coarse Grain

Is Granite Mafic or Felsic?
Felsic

What texture does Gabbro have?
Coarse grain

Is Gabbro mafic or felsic?
Mafic
What is an example of a ultramafic rock?
Peridotite
What is Peridotite mostly made up of?
Olivine
What is the mantle made up of?
Peridotite
What are Pyroclasts?
Lava that gets exploded from Volcanic eruptions that solidifies before it hits the ground
What is Volcanic Ash?
A type of pyroclast that has small fragments of glass formed by escaping volcanic gases
What is Pumice?
A type of pyroclast that has a frothy mass of glass with a large number of vesicles
How are pyroclasts deposited after an eruption?
In thick layers
How does Tuff form?
Pyroclasts that were hot enough to weld together
What is Tuff?
a hard igneous rock that is made up of welded pyroclasts
What 2 ways is magma usually formed?
Decompression Melting and Water-Induced melting
What is Decompression Melting?
Hot rocks rise near the surface, pressure is lowered, so the melting temperature decreases.
Where does Decompression Melting usually happen?
On Divergent Boundaries
What is Water-Induced Melting?
When water reduces the melting temperature of rocks. If “wet” rock enters the Earth and heats up, it will easily melt.
Where does Water-Induced Melting usually occur?
On Convergent Boundaries
As Pressure increases what happens to melting temperatures?
It gets higher
As Water Content increases what happens to melting temperatures?
It gets lower
What is Partial Melting?
The incomplete melting of a rock that occurs because the minerals that compose it melt at different temperatures
What happens if Peridotite is partially melted?
It forms Gabbro and Basalt
What is a Pluton?
Large igneous body of rock formed in the crust
What are the 2 kinds of Plutons?
Batholith and Stock
What is a Batholith?
A type of large Pluton
What is a Stock?
Anything smaller than a Batholith
What is a Sill?
A intrusion of Igneous rocks that are Parallel to the country rock
What is a Dike?
A intrusion of Igneous rocks that cut across the country rock
What was the most active and explosive Volcano in the US?
Mt. Saint Helens
How many months did Mt. Saint Helen gives clues to an eruption?
2 months
What is Mt. Saint Helens part of?
The Cascade Mountains
What are the Cascade Mountains?
A volcanic arc
What kind of convergent boundary are the Cascade Mountains on?
Ocean-Continent Convergence
What is another Volcano on the Cascade Mountains?
Mount Rainier
What are Volcanic Eruptions Preceded by?
Earthquakes, Swelling, and Increased Temperatures
What causes the early signs of eruptions in Volcanoes?
The rising of magma beneath the Volcano
Does Volcanism only happen on Volcanoes?
No
What is Volcanism?
The process by which magma rises through the crust and emerges at the surface as lava
What is a Volcano?
A hill or mountain constructed by an accumulation of lava and pyroclasts.
Where does MOST Volcanism usually occur?
On Divergent Boundaries
Where do Volcanoes usually form?
On Subduction Zones (Convergent Boundaries)
Where does SOME Volcanism Occur?
Interplate Volcanism (hotspots)
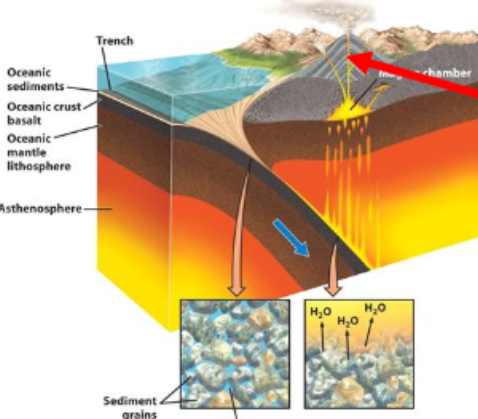
What is this?
A subduction zone
What is an example of hotspot volcanism?
The Hawaiian Islands
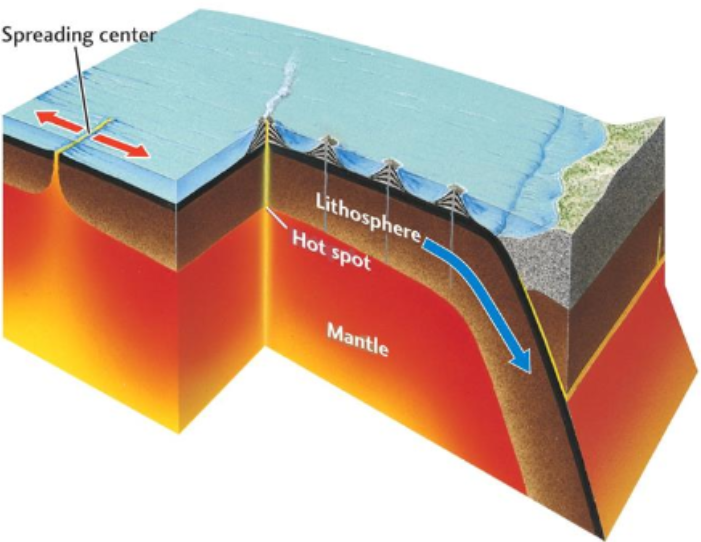
What is this?
Hotspot
What is a possibly explanation for Interplate Volcanism?
The Mantle Plume Theory
What is the Mantle Plume Theory?
Hot plumes of rock rise from the deep mantle (perhaps the core-mantle boundary) and reach the surface, forming hotspots
What is Basaltic Lava?
Hot, fast flowing, non-explosive lava
What are the kinds of Basaltic lava?
Flood basalts, Pahoehoe, Aa, and Pillow lavas