AP Bio Unit 4: Cellular Communication
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
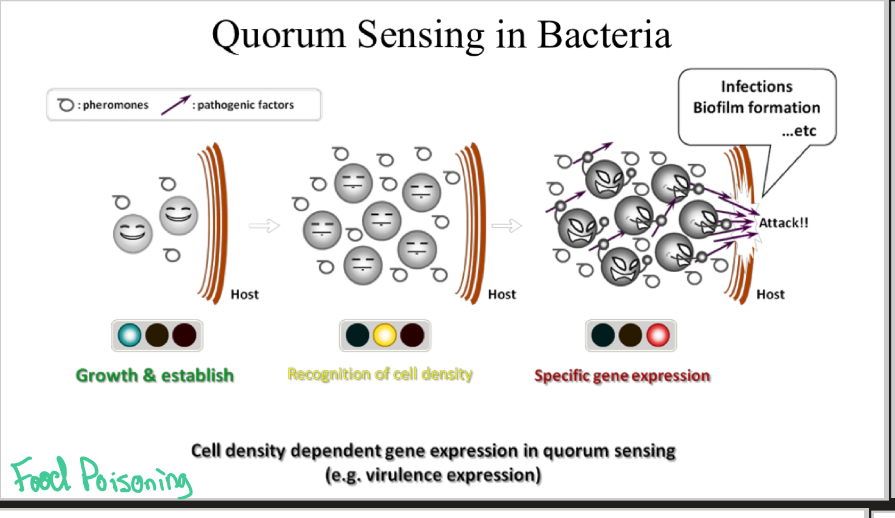
Quorum Sensing
Bacteria grow and establish
Bacteria release pheromones that serve as a population tracker
Once there is a high enough population, start STP with response of releasing pathogenic factors
How to combat quorum sensing?
Inhibit pheromone receptors —> ?? population size —> no pathogen attack
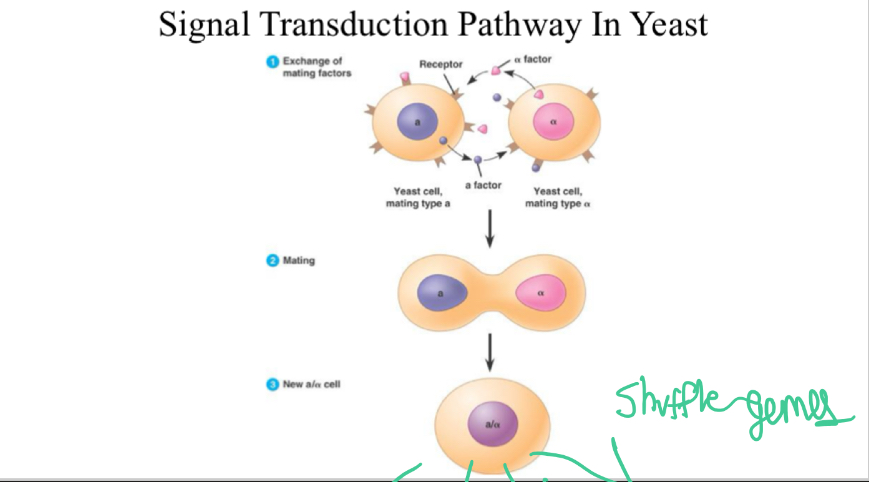
Yeast STP
Exchange chemical factors from 2 cells during reception
2 cells combine
Response: The combined cell now splits into more cells, promoting genetic diversity
Local Signalling
Type of cell communication through signal transduction pathways between nearby cells. Examples include Quorum sensing and yeast cell division.
plasmodesmata
proteins in the plasma membrane of cells that transport carbs from one cell to another across cell walls.
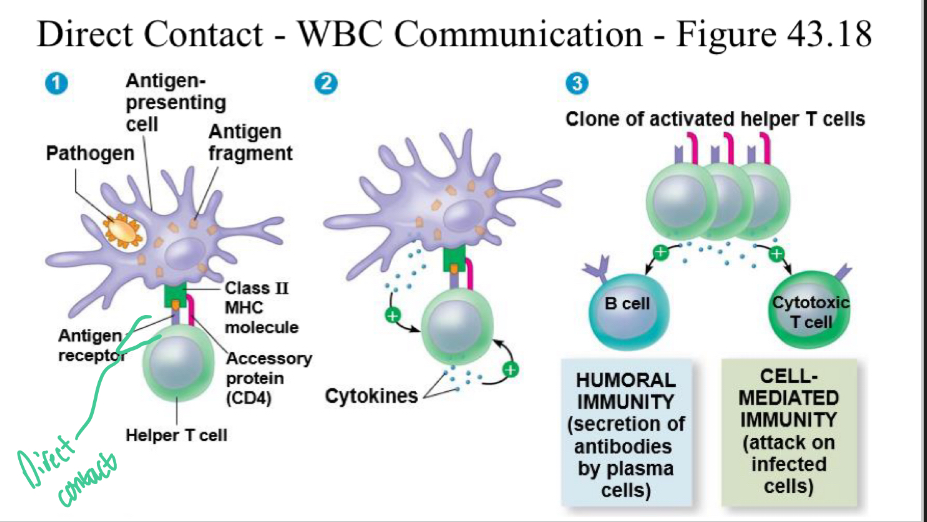
White Blood Cell STP
Reception: White blood cells secrete antibodies, which bind to infected cells
Transduction: Through the exchange of cytokines, killer T cells are signalled to the infected cell
The T cell forces the infected cell to commit apoptosis
Direct Contact
A type of cell signalling wherein the target cells are directly touching and exchanging molecules. Examples include plasmodesmata and white blood cells and antigens.
Autocrine Signalling
A cell secretes a ligand that binds ontoo a receptor from the same cell, triggering a response in the cell that secreted a ligand. An example includes cancer cells, releasing their own growth hormones to signal the cell to grow and divide.
Paracrine Signalling
The cell secretes a ligand that travels a short distance, eliciting an effect on cells in nearby areas.These ligands are also referred to as local regulators because they only affect cells in the immediate vicinity.
Paracrine
Plants signalling apoptosis for infected cells (PAMP) and cell differentiation are examples of _____ signallining.
Endocrine Signalling
Type of cell signalling that sends ligands long distances to target cells.
Hormones
The ligands in endocrine signalling are called ___
Endocrine
Insulin production in response to increased blood sugar levels, glucagon production in response to low blood sugar levels, ethylene, and human growth hormone are examples of this type of signalling
Positive feedback loop
A chemical pathway wherein its products cause more of the same products to be made, amplifying the response. An example includes ethylene gas ripening bananas and oxytocin in stimulating more uterus contractions for child birth.
Synaptic Signalling
A type of paracrine signalling that uses neurotransmitters as the ligand to communicate between neurons.
Negative Feedback Loop
A metabolic pathway wherein the products of the pathway inhibit production of the same products, in an attempt to return a system to its original state; homeostasis.
ligand
name for signal molecule that attaches to receptor proteins
amplifies signal with each reaction
why have multistep STPs?
hydrophilic, polar, hydrophobic, nonpolar
_____ ligands cannot cross the plasma membrane due to their ____ nature, and as such must bind to receptors located on the outside. ____ ligands are _____, so they can pass the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptor proteins, allowing them to eventually cross the nuclear membrane and bind to DNA, impacting gene expression.
Reception: aldosterone binds to a receptor within the nucleus
Transduction: Transcription of genes to MRNA happens
Response: proteins that regulate water and sodium balance are produced
describe the STP for aldosterone
kinase
enzyme that transfers phosphate groups to ther molecules, activating them
phosphatase
enzyme that removes phosphate groups to ther molecules, deactivating them
hormones
first messenger in a signalling pathway
cAMP and Ca2+
second messenger in a signalling pathway
epinephrine and glycogen metabolism
cytoplasmic response examples
aldosterone and gene activation
nuclear response example
receptor protein, specialized
two different tissues can be influenced by the same ligand yet have different responses because they have the same _____ and are _____cells with unique enzymes and genes
diverge
A STP can ___ resulting in two or more cellular response
converge, cross talk
A STP can ___ resulting in one common cellular response. This is called ____
scaffolding proteins
proteins that help other proteins maintain their structure and function.
apoptosis
programmed cell death by receiving an external or internal signal. The lysozyme spills digestive juices and dissolves organelles.
adenylyl cyclase
produces the secondary messenger cAMP. If inhibited the secondary messenger would not be made, stopping rest of pathway
chromosomes
coiled form of DNA, only in this state for cell division
chromatin
uncoiled form of dna, noodle like, must be in this form for gene expression
centromere
region of chromosome where sister chromatids are connected
kinetochore
place on chromosome where spindle fibers attach
46 chromosomes in each, 92 sister chromatids in G2
number of chromosomes and sister chromatids in G1 vs G2
two daughter cells with identical number of chromosomes as parent cell
result of mitosis
binary fission
cell division in prokaryotes: hint loook for chromatin
interphase
prep for cell division phase
G1 phase
Duplicate all raw materials and organelles, 46 non duped chromosomes are present
S phase
all genetic chromosomes are duplicated, resulting in 92 sister chromatids but still 46 chromosomes.
G2 phase
synthesize more proteins and enzymes, copy centrioles for making spindle fibers
interphase
dna is uncoiled in chromatin, G1, S, and G2 happen
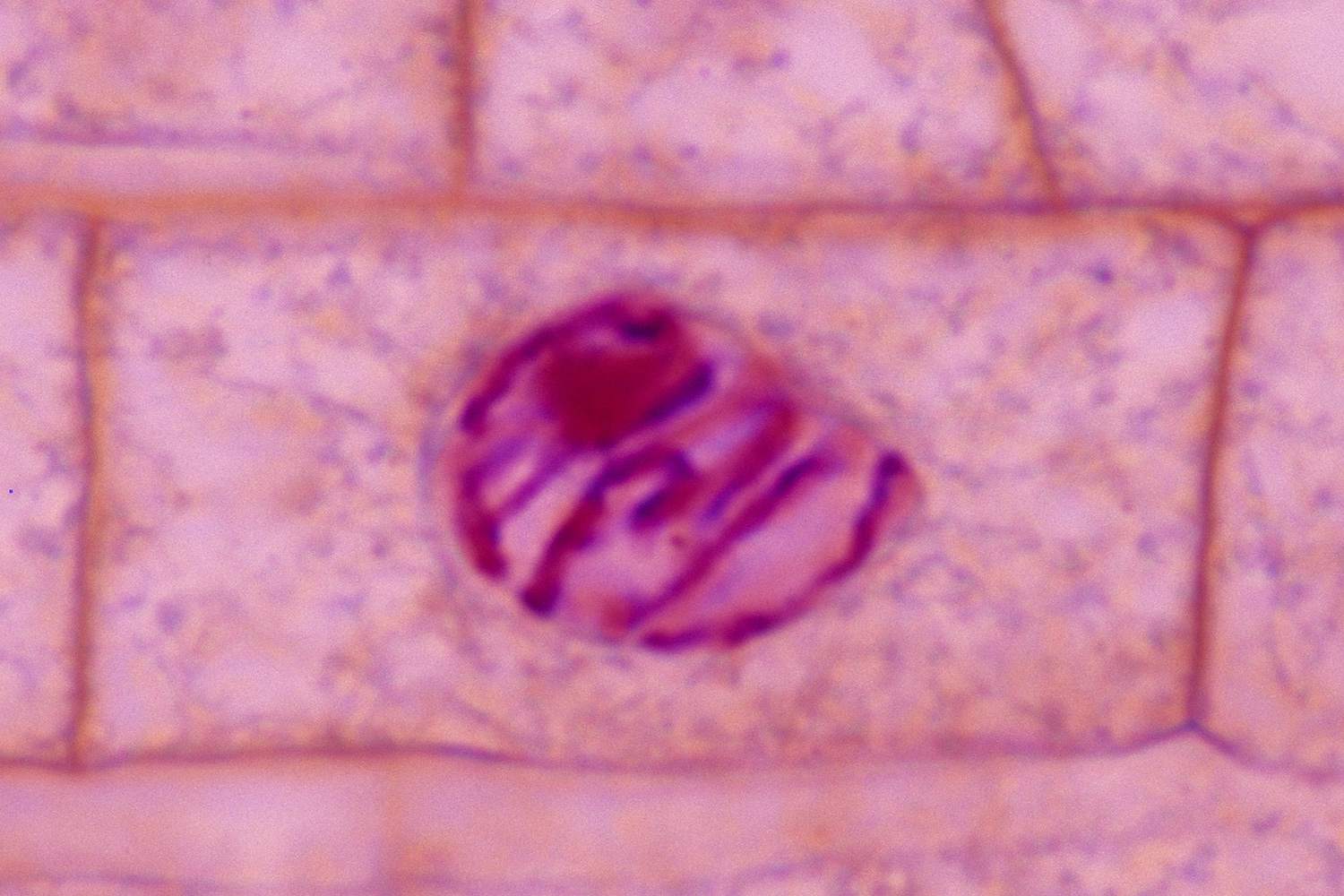
prophase
chromatin begins coiling into chromosomes via histone proteins, spindle fibers beegin to form
Prometaphase
nuclear envelope begins dissolving, kinetochore starts forming to attactch to spindle fibers
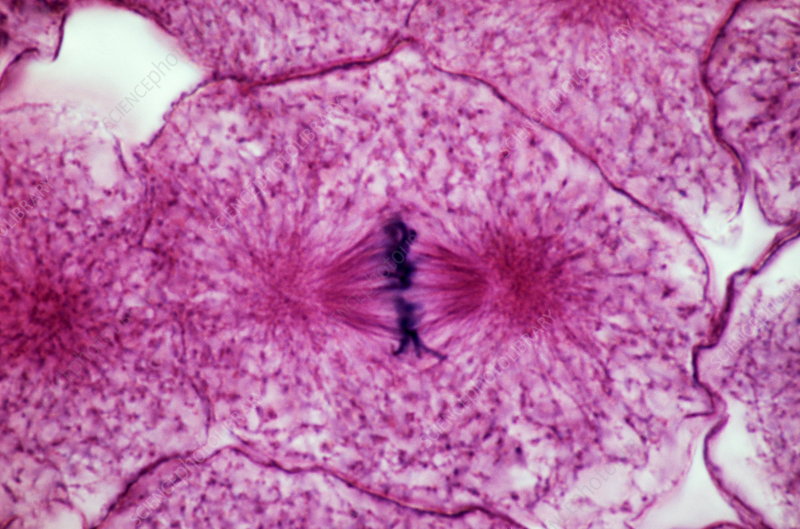
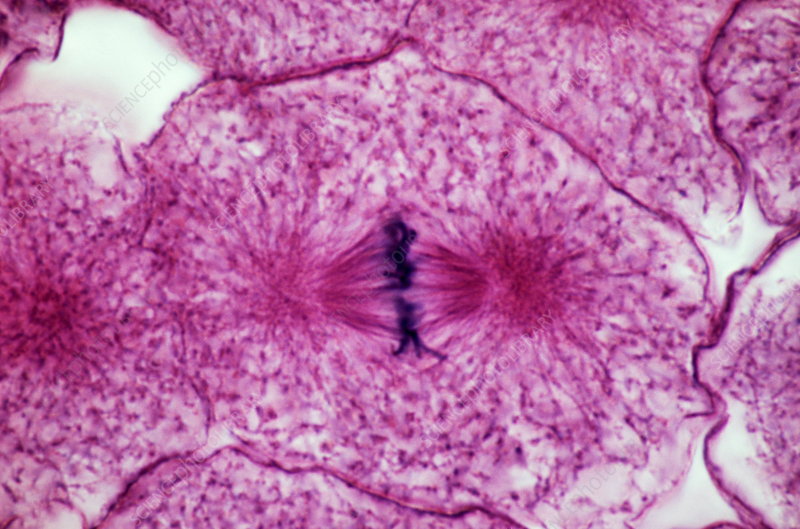
Metaphase
chromosomes are fully coiled and aligned at metaphase plate (equator of cell), spindle fibers attach to kinetochore and prepare to move to poles
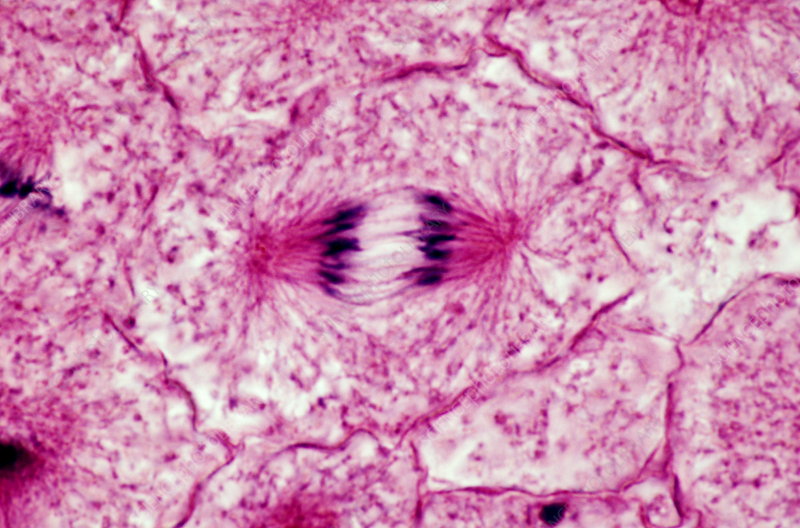
Anaphase
Signals tell cell to move from metaphase to anaphase once spindle is fully formed and connected to kinetochore. Spindles pull sister chromatids to poles
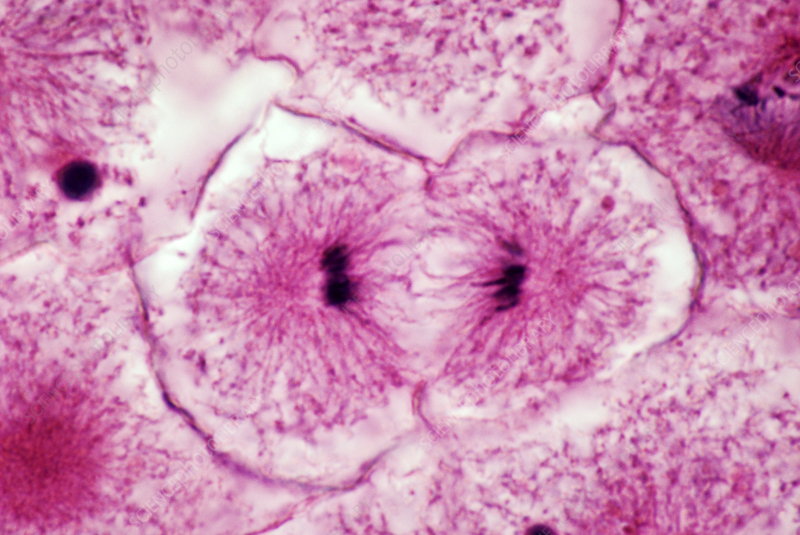
Telophase
nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil into chromosomes, spindle dissolves, and two nuclei are formed
Mitosis
Portion of cell division from Prophase to Telophase resulting in nuclear divison. Aka m phase
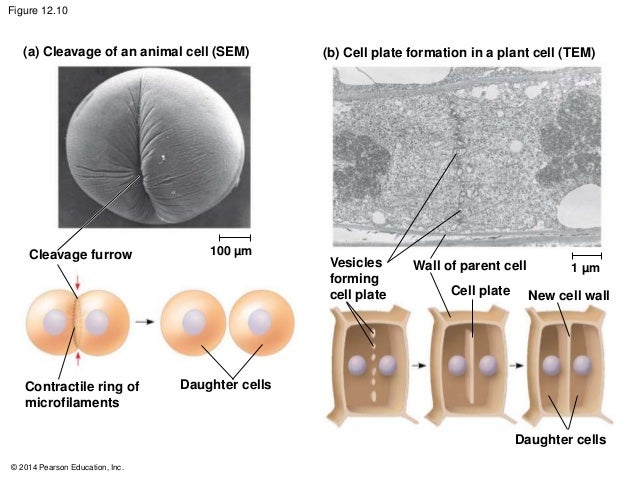
Cytokinesis
Contractile pinches cytoplasm in half, forming a cleavage furrow in animal cells and a cell plate (new cell wall) in plant cells.
cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs)
enzymes dependent on activation by cyclin. Give go ahead signals at G1 and G2 checkpoints if active, constant concentration but activity depends on cyclin.
cyclins
concentration in cells rises and falls for different stages, but activate cdks
G0 phase
state of limbo in cell division for cells who lack the nutrients or go ahead signal to proceed. Will not divide unless unpaused. Examples include mature nerve cells.
G1 Checkpoint (Restriction Point)
checkpoint between G1 and S. Cell checks to see if there is adequate nutrients, cell size, DNA damage, growth factors/hormones before giving go ahead signal. If check is failed, cells enter G0 until further notice.External Signal
S Checkpoint
checkpoint in between S and G2. Cell checks to see if there is DNA damage or tangling before proceeding. If cells proceed without the go ahead signal, defective genese/gene activation struggles may occur.
G2 Checkpoint
During G2, checks to see if cell is adequate in size and organelles, DNA replication has occurred before proceeding. Internal SIgnal from cyclins and cdks
M Checkpoint
Metaphase checkpoin. Ensures that spindles are fully formed, kinetochores are attaching chromatids to spindle fibers, and aligned in equator of cell. If proceeding without go ahead signal, there may be unequal chromosome count in daughter cells. Internal Signal kinetochores
Anaphase Telophase Checkpoint
Checkpoint between anaphase and telophase. Ensures chromosomes are at the poles before dividing nucleus. If go ahead signal is ignored, chromosome damage may occur during nuclear division.
apoptosis, cancer
If the cell cycle fails to regulate the cell cycle properly, ____ or ___ is a likely outcome
activating genes, enzymes, altering cell shape
Ways to identify response in STP