quiz and tophat questions
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
which cells are found in the white matter of the spinal cord
oligodendrocytes
where is the occipital lobe located with respect to the parietal?
caudal
a 41-year old male presents to the ER with paralysis involving the left arm and hand. imaging shows a small lesion in his cerebral cortex. which lobe is the lesion located in?
frontal lobe
why do cortical layers vary in size across different regions of the cortex?
different cortical regions are specialized for distinct functions, requiring varying amounts of input, output, and processing capacity
which of the following statements is correct regarding the rising phase (upstroke) of the action potential?
a. the membrane potential becomes more negative
b. there is an influx of Na+ through non-gated ion channels
c. Na+ flows into the neuron through voltage gated Na+ channels
d. K+ flows into the neuron through voltage-gated K+ channels
c. Na+ flows into the neuron through voltage gated Na+ channels
why is the resting potential in a neuron typically around -70 mV instead of being equal to the equilibrium potential of K+ (~-90 mV)?
the resting cell membrane has some permeability to Na+
what would happen to the typical neuronal membrane resting potential if the extracellular concentration of K+ was increased?
the resting potential would become more positive
a neuron codes for the intensity of a stimulus by:
a. increasing or decreasing the amplitude of the action potential
b. increasing or decreasing the duration of the action potential
c. increasing or decreasing the frequency of action potentials
d. decreasing the rate of potassium influx
e. both a and b
c. increasing or decreasing the frequency of action potentials
you are recording from 2 different axons and want to determine which of them is myelinated and which is unmyelinated. which characteristics would you expect ONLY the myelinated axon to have?
a. the presence of nodes of Ranvier
b. faster conduction of action potentials
c. equal distribution of voltage-gated sodium channels along axon
d. lower membrane resistance to the leak of ions
e. both a and b
both a and b
which value would give you the best estimate of the relative number and complexity of synaptic inputs to a given neuron?
the extent and complexity of that neuron’s dendritic branches
you have suffered an injury to the brain which has led to cell damage and death. which type of nervous system cell is most important in clearing away the accumulated cellular debris?
microglia
according to the principle of dynamic polarity, which of the following best describes the flow of information in a neuron?
dendrites to cellbody to axon to axon terminal
myelination:
increases the speed of axonal conduction
in general, afferent nerves carry sensory information
towards the central nervous system
the principal region of the neuron for receiving information is the:
dendrite
which region of the neuron is typically myelinated?
axon
in a typical synapse, the presynaptic side is the ___ and the postsynaptic side is the ___
axon terminal; dendritic spine
which type of neurons are specialized to communicate with other neurons located in a different or distant CNS region?
projection neurons
which of the follow is False regarding neural stem cells?
a. they are self renewing
b. they can give rise to all cell types, similar to embryonic stem cells
c. they are found in developing and some adult tissue
d. they are neuroectodermal cells
e. all of the above are true
b. they can give rise to all cell types, similar to embryonic stem cells
hippocampus function
involved in memory formation
limbic system function
group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and the emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
basal ganglia function
group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
cerebellum function
important for motor planning and learning
medulla function
coordinates basic life support systems including respiratory rhythms
one of parietal lobes function
somatosensory (touch and pain)
one of frontal lobes functions
planning and signaling movements
one of occipital lobes functions
early-stage vision
one of temporal lobes functions
hearing, memory, language
which of the following is false regarding the blood brain barrier?
a. it protects the brain from substances in the blood
b. it is formed by tight junctions between capillary endothelial cells in the brain and spinal cord
c. the tight junctions are maintained by oligodendrocytes in the CNS
d. there are no substances which can pass through the BBB
e. c and d are false
e. c and d are false
true or false: humans have 12 pairs of cranial nerves that all serve motor functions
false
true or false: sensory information enters the dorsal portion of the spinal cord
true
a membrane potential is the difference in electrical charge between
inside and outside of a cell
in its resting state, a neuron is said to be
polarized
potassium ions have a ___ charge and are in excess _____ the cell; sodium ions have a _____ charge and are in excess ____ the cell
a. negative, inside, positive, outside
b. positive, inside, positive, outside
c. negative, outside, negative, inside
d. positive, outside, negative, inside
positive, inside, positive, outside
increasing the amount of sodium in the extracellular fluid will ____
a. make the resting potential more negative
b. make the resting potential more positive
c. first hyperpolarize the membrane, then repolarize it
d. have no effect on the resting potential
have no effect on the resting potential
the resting membrane potential of a neuron is -65 mV and changes to -75 mV. what is the most likely cause of this change in voltage? assume each answer is physiologically possible to occur
a. the permeability to sodium increased
b. the activity of the sodium-potassium pump greatly increased
c. the equilibrium potential for potassium increased from -90 mV to -70 mV
d all of the above could contribute to this change
e. none of the above would cause this change
the activity of the sodium-potassium pump greatly increased
the Na+/K+ ATPase…
a. moves Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradients
b. makes the resting membrane potential more negative
c. requires energy in the form of ATP
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
all of the above
which of the following conditions exist when a neuron is at a resting membrane potential:
a. all ions are in equilibrium
b. only sodium ions are moving across the membrane
c. the number of positive charges on the inside of the membrane is equal to the number of positive charges on the outside of the membrane
d. the inside of the cell is positive relative to the outside of the cell
e. the rate of influx of ions is equal to the rate of efflux of ions
the rate of influx of ions is equal to the rate of efflux of ions
which of the following does NOT contribute to the resting membrane potential of neurons?
a. negatively charged proteins inside the neuron
b. the sodium/potassium pump
c. potassium flows through leak channels
d. higher concentration of potassium ions outside than inside the of the cell
e. higher concentration of sodium ions outside than inside the cell
higher concentration of sodium ions outside than inside the cell
the intracellular concentration of potassium is decreased 3-fold. what effect will this have on the potassium concentration gradient and the potassium equilibrium potential?
a. decrease, more positive
b. decrease, more negative
c. increase, more positive
d. increase, more negative
e. only the concentration gradient will be changed, no effect on the equilibrium potential
decrease, more positive
which of the following does NOT happen at the threshold potential?
a. an action potential is triggered
b the membrane is depolarized relative to resting potential
c. voltage-gated sodium channels are open
d. potassium ions enter the cell through ion channels
e. all of the above happen at the threshold potential
potassium ions enter the cell through ion channels
which of the following statements is true regarding saltatory conduction?
a. it is slower than propagation in unmyelinated axons
b. action potentials are regenerated at nodes of ranvier
c. salutatory conduction occurs in both myelinated and unmyelinated axons
d. salutatory conduction means the action potential travels in both directions down the axon
e. all of the above are true
action potentials are regenerated at nodes of ranvier
which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the absolute refractory periods?
a. the absolute refractory period comes before the relative refractory period
b. the absolute refractory period is cause by sodium channel inactivation
c. the absolute refractory prevents the action potential from reversing direction
d. during the absolute refractory period, the neuron can fire again, if it receives a strong enough stimulus
e. all of the above are true
during the absolute refractory period, the neuron can fire again, if it receives a strong enough stimulus
the after-hyperpolarization phase of the action potential (AHP) occurs because:
a. ligand-gated Na+ channels are inactivated and cannot be opened
b. the K+ equilibrium is below the resting membrane potential
c. voltage-gated K+ channels become inactivated
d. all of the above
e. both b and c
the K+ equilibrium is below the resting membrane potential
action potentials begin by the:
a. opening of voltage-gated sodium channels
b. closing of ligand-gated chloride channels
c. closing of ligand-gated potassium channels
d. opening of ligand-gated potassium channels
e. all of the above
opening of voltage-gated sodium channels
the brief period of time immediately after the initiation of an action potential when its absolutely impossible to initiate another one in the same neuron is called the ____
absolute refractory period
the conduction of an action potential along ANY axon is mediated by the action of
voltage-gated ion channels
put the following action potential events in order.
i. regenerative Na+ influx occurs at the threshold potential
ii. weak Na+ influx and strong K+ efflux
iii. continuous K+ efflux causes the membrane potential to become more negative than resting potential
iv. strong Na+ influx and weak K+ efflux
i, iv, ii, iii
which of the following is true for electrical synapses but NOT for chemical synapses?
i. they have cells joined by connexons
ii. current can flow in either direction
iii. can pass positive or negative current
iv. transmission is calcium-dependent
v. transmission requires a presynaptic action potential
i, ii, and iii
when an action potential reaches the axon terminal, release of neurotransmitter is triggered by….
a. movement of sodium ions into the axon terminal
b. movement of calcium ions into the axon terminal
c. movement of sodium ions into the neuron at the nodes of Ranvier
d. movement of calcium ions into the neuron at the nodes of Ranvier
e. either b or d
movement of calcium ions into the axon terminal
A student is experimenting to decide whether two neurons have an electrical synapse or a chemical synapse. After performing a variety of tests, which results would provide evidence that the synapse is, in fact, an electrical synapse.
a. there was less than a millisecond (ms) between the pre-synaptic neuron action potential and the post-synaptic neuron response.
b. there was a flow of current detected from the pre-synaptic cell in the post-synaptic cell without an action potential fired.
c. the synapse passes both positive and negative current.
d. all of the above
e. B and C only
all of the above
Neurotransmitters are often stored in:
a. ribosomes
b. vesicles in the presynaptic neuron
c. vesicles in the postsynaptic neuron
d. nodes of ranvier
e. both B and C
vesicles in the presynaptic neuron
EPSPs are:
a. graded responses
b. transmitted decrementally
c. hyperpolarizations
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a and b only
The process of neurotransmitter release is referred to as:
a. Excitation
b. Exocytosis
c. Endocytosis
d. Synthesis
e. metabolism
exocytosis
After release, neurotransmitters are removed from the synapse by:
a. reuptake
b. enzymatic degradation
c. G proteins
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a and b only
Which process involves the integration of signals from multiple presynaptic neurons at different locations on the postsynaptic neuron's dendrites or cell body?
a. axonal Conduction
b. temporal summation
c. spatial summation
d. synaptic inhibition
e. both b and c
spatial summation
which of the following is true regarding electrical synapses?
a. they are the most common type of synapse in the nervous system
b. gap junctions only allow for current to move in one direction
c. action potentials are not required for current flow in the postsynaptic neuron
d. electrical synapses are only seen in fully developed nervous systems
e. none of the above are true
action potentials are not required for current flow in the postsynaptic neuron
dopaminergic neurons in the nucleus accumbens contain nictonic receptors on their axon terminals. these receptors are permeable to Ca2+. what effect will smoking cigarettes have on these dopaminergic synapses?
a. decreased stimulation of postsynaptic dopamine receptors
b. decreased release of dopamine
c. prolong presynaptic action potential
d. increased release of dopamine
e. decreased influx of Ca2+ into dopaminergic axon terminal
increased release of dopamine
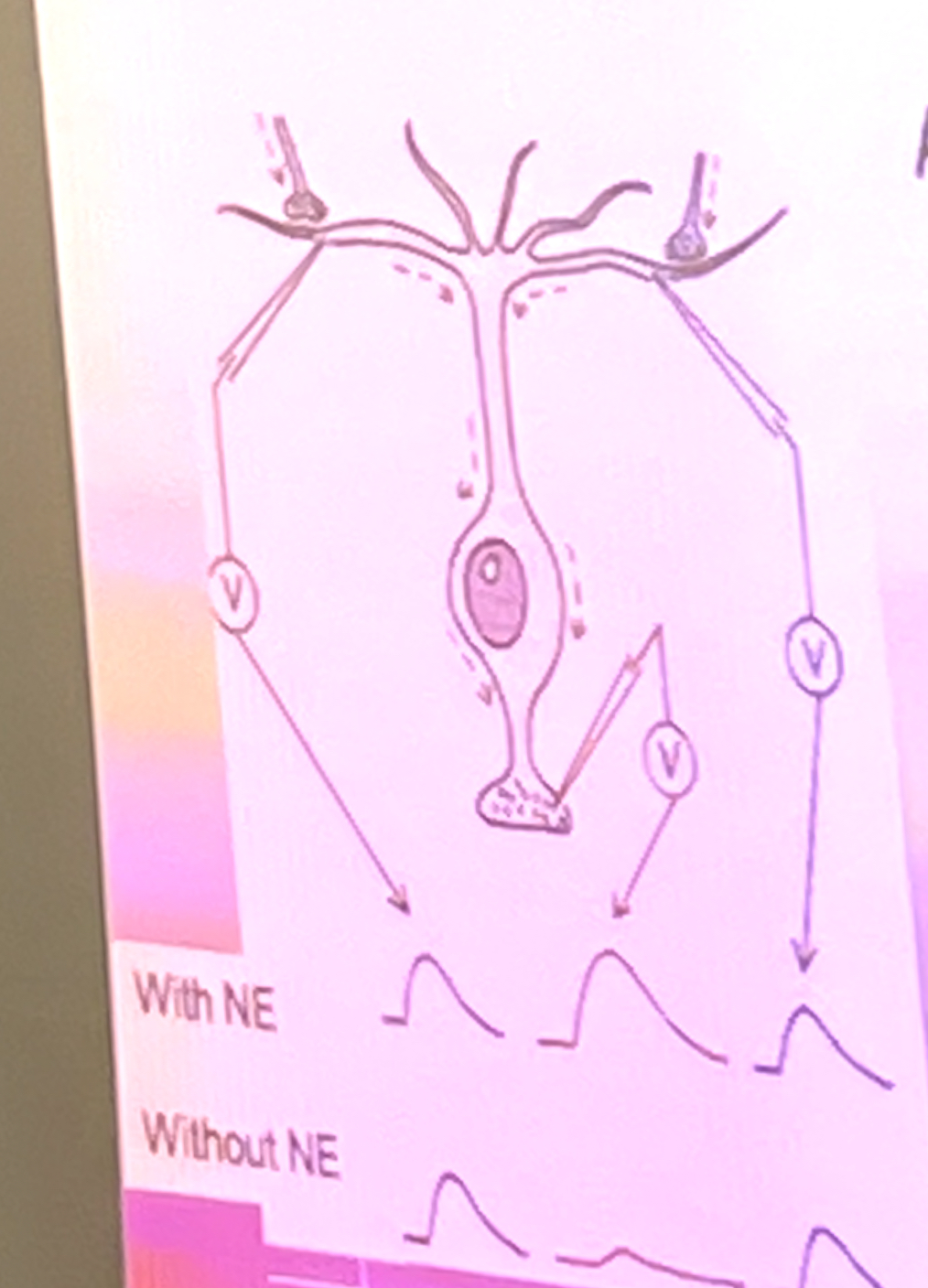
The diagram below indicates the EPSPs generated at 2 different dendrites of the same neuron and the resulting EPSPs recorded at the axon hillock in the presence or abundance of norepinephrine (NE). from the results we can coduce that norepinephrine:
a. decreased temporal summation
b. opened K+ channels in the membrane
c. decreased the excitability of the neuron
d. decreased spatial summation
e. increased the probability of firing an action potential
increased the probability of firing an action potential