lec 7 - vestibular system - unfinished
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
vestibular system processs _______ information underlying _____ and ______
_____
_____
_____
sensory information; motor responses to; perceptions of
self-motion
head posiition
spatial orientation relative to gravity
helps to stabilize
gaze, head, posture
key component in
postural reflexes
eye moement
______ critical to ______
“sixth sense”
autonomic behaviors and perception
damage to the vestibular system can cause issues with
balance
stabilizing our gaze while moving head
spatial orientation
what types of acceleration does the vestibular system sense
linear
rotational
vestibular system converts the effects of ____ into neural impulses
gravity
(linear/rotational accelerations)
The three semicircular canals are oriented to detect ______ around the 3 cardinal axes
rotational motion
What are the three cardinal axes? give the names for rotation around these axes.
x, y, z
roll, pitch, yaw
which type of acceleration
otolith organs
semicircular canals
linear
rotational
Approximately _____ of US population will experience some form of dizziness or balance difficulty in their lifetim
40%
Symptom reports of dizziness and imbalance in adults increase with
age
____% of adults—_____Americans—report a chronic problem with balance
4
8 mil
____ of adults (____) report a chronic problem with dizziness
1.1%
2.4 mil
the main peripheral component of the vestibular system
labyrinth
labyritnth and cochlea
works similar to cochlea
continuous with it
the labyrinth converts ______ into ______
physical motion from gravity/linear and rotational acceleartions of the head
neural impulses
parts of the labyrinth
2 otolith organs (linear acceleartions, static head position relative to gravitational axis (head tilts))
3 semicircular canals (rotational)
vestibular hair cells
vestibular hair cells are located
utricle, saccule, ampullae
vestibular hair cells work like
auditory hair cells
some transduction channels are open in the ______
absence of stimulation
vestibular system baseline - high or low
high, lots of spontaneous activity
hair cells in 3 organs are _____ for certain directions
selective
striola
divids hair cells into two population
which way do hair cells point in the
ampulla
sacculus
utricle
same direction
away from the striola
towards the striola
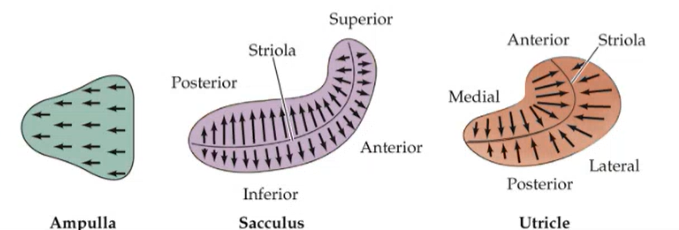
if hair cells are diplaced towards the tallest stereocilia:
smallest steroocilia:
tallest = depol
smallest = hyperpol
K cascade leads to which neurotransmitter release
glutamate
Firing rates of vestibular fibers can increase or decrease in a manner that
Faithfully mimics the receptor potentials produced by the hair cell
otolithic membrane is a _____ layer with small crystals called ____ which _____ hair bundles during tilting motion
gelatinous
otoconia
deflect
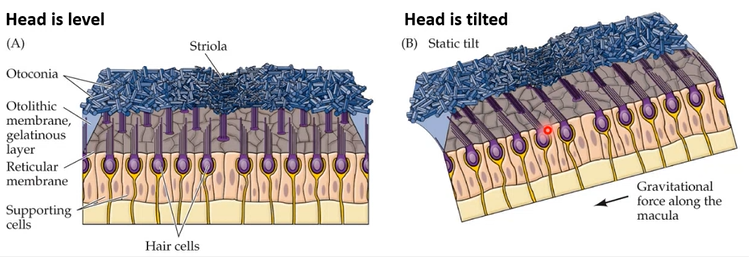
utricle: _____ movements
saccule: _____ movements
horizontal
vertical
depolarizing one otolith organ →
hyperpolarizing the other
utricle
head tilt backwards
head tilt forwards
no head tilt + forward accel
no head tilt + forward decel
depol
hyperpol
depol
hyperpol
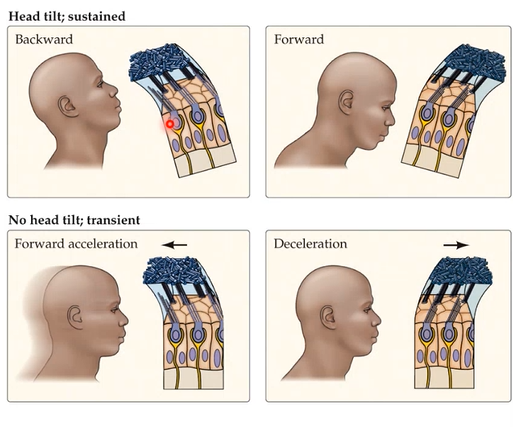
Hair bundle movement occurs
_____ in response to tilting of the head
_____ in response to acceleration
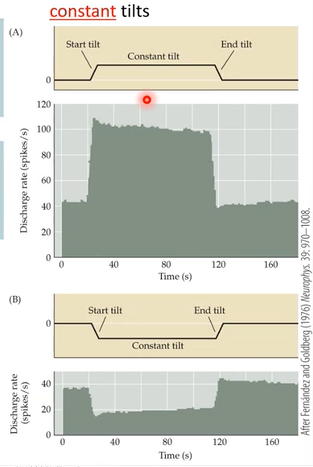
tonically
transiently
constant head tilt = ______ firing
constant

B
bulbous expansion at the base of each canal
ampulla
ampulla of each canal houses ______ that contains the _____
sensory epithelium/crista
hair cells
hair cells extend out of the crista into a gelatinous mass, the ____
cupula
viscous barrier in the semicircular canals through which endolymph cannot circulate
cupula
hair cells/cupulae have ______ orientation on either side of the head
opposite
when the head rotates, fluid in the canal
distorts the cupula
endolymph fluid flow vs head movement
flow goes opposite to head movement
Each semicircular canal works in concert with
The partner located on the other side of the head that has its hair cells are lined oppositely
3 pairs of semicircular canals
right/left horizontal
left ant + right post
right ant + left post
push-pull arrangement - head rotations deform the cupula in _____ dirrections for the two partners, resulting in ____ changes in firing rate
opposite
opposite
(provides info about rotation of head in any direction)
turn head to left - ____ depol and ____ hyperpol
left
right
semicircular canals
acceleration = ____ firing rate
deceleration = ____ firing rate
constant v = ____ firing rate
max
min
baseline

C
Central vestibular processing is inherently _____
multisensory
Many neurons in the vestibular nuclei function as _____ neurons in addition to giving rise to _____
premotor
ascending sensory projections
Central projections from vestibular nuclei are involved in 2 major classes of reflexes:
Helping to maintain equilibrium and gaze during movement
Maintaining posture
vestibulo-ocular reflext
eye movements counter head movements
maintains gaze fixation
VOR pathway




C
Rotating the head elicits _____ which consists of a ____ eye movement _____ the direction of head turning
due to ____
physiological nystagmus; slow; counter to
relative differences in firing
When one canal is damaged, _____ occurs, due to _____
spontaneous nystagmus
the tonic firing of fibers from the opposite canal