Organic Chemistry I Synthesis Definitions - Dr. Straumanis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O/THF
2. NaBH4
-Oxymercuration/demarcation
-converts alkene to alcohol (breaks double bond + adds H and OH)
-Markov regio
-Anti stereo
1) Hg(OAc)2, HOR, THF
2) NaBH4
-Oxymercuration/demarcation
-breaks double bond + adds H and OR
-Markov regio
-Anti stereo
1) BH3, THF
2) H2O2, NaOH
- breaks double bond
- anti-Markovnikov addition of OH
1) HBr
2) ROOR' (peroxide)
- breaks double
- anti-Markovnikov addition of Br
1) Br2
- trans addition only
- breaks double bond
- forms epoxide ring before adding second Br
1) MCPBA
- breaks double bond
- alkene -> epoxide
1) strong base 2) dilute acid
- breaks epoxide ring and adds O- and OR (trans)
- dilute acid: replaces O- with OH
1) H3O+, HOR 2) Br2, HOR
- breaks the double bond
- Adds OR and Br in a trans way
1) CHCl3, KOH
- breaks the double bond
- adds CCl2 cyclopropane ring
1) CH2I2, Zn(Cu)
- breaks the double bond
- adds CH2 cyclopropane ring
1) BH3, THF
2) H2O2, NaOH, H2O
- breaks double bond
- anti-Markovnikov addition of OH
Catalytic Hydrogenation: H2, Pd metal or Pt medal
reducing an alkene by adding molecular hydrogen to double bond with aid of metal catalyst. e.g. pt, pd, ni. takes place on surface of metal so it does syn addition
1) H2/ Pt or Pd metal
ALKYNE:
- reduces double bond to single completely
1) H2/ Ni2B/Lindlar catalyst
ALKYNE:
- reduces triple bond to double bond
- syn. transformation
1) Na metal, NH3 (l)
ALKYNE:
- reduces triple bond to double bond
- anti. transformation
1) PCC
- turns OH to O with double bond
- 1-degree alcohol -> aldehyde
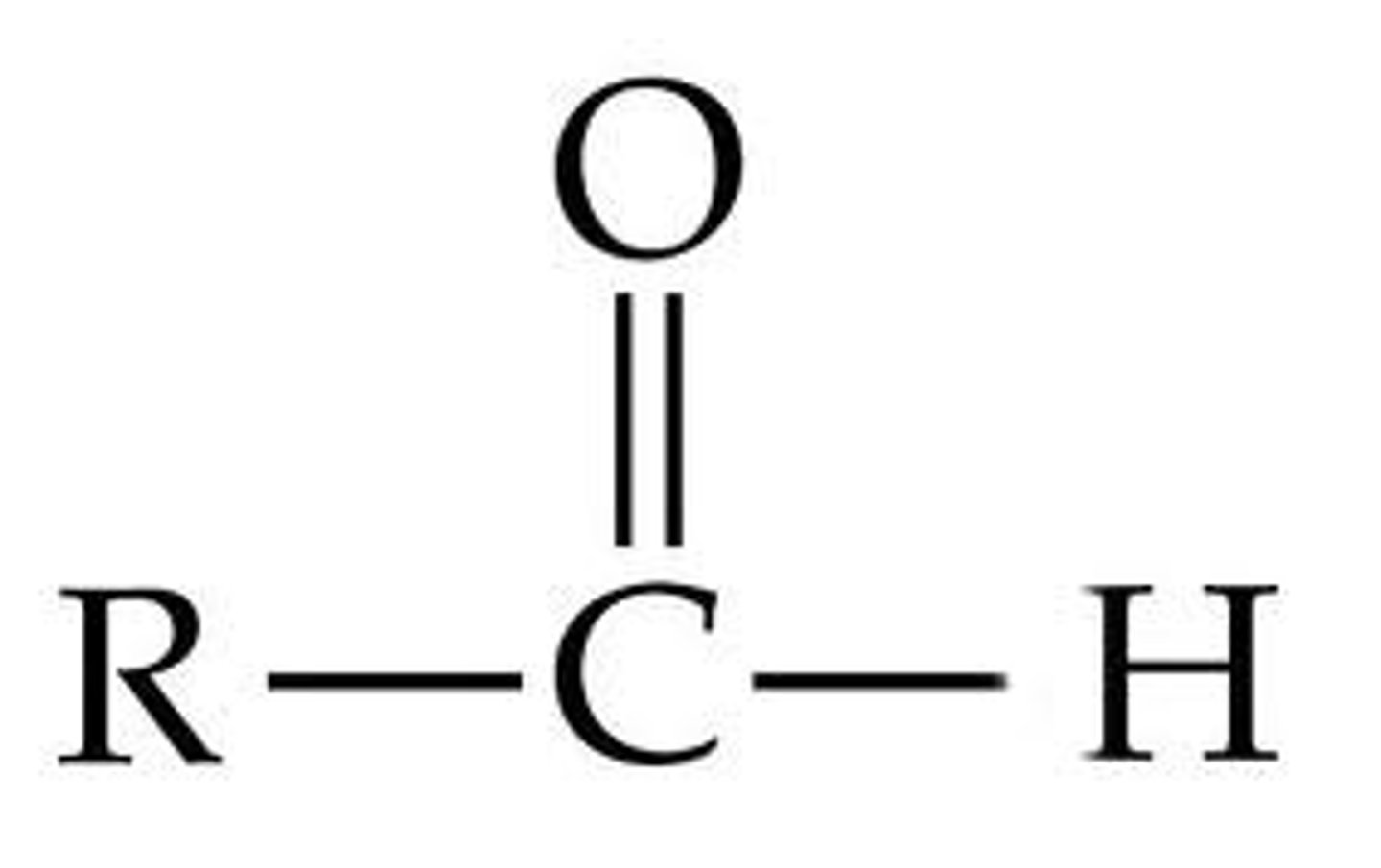
aldehyde
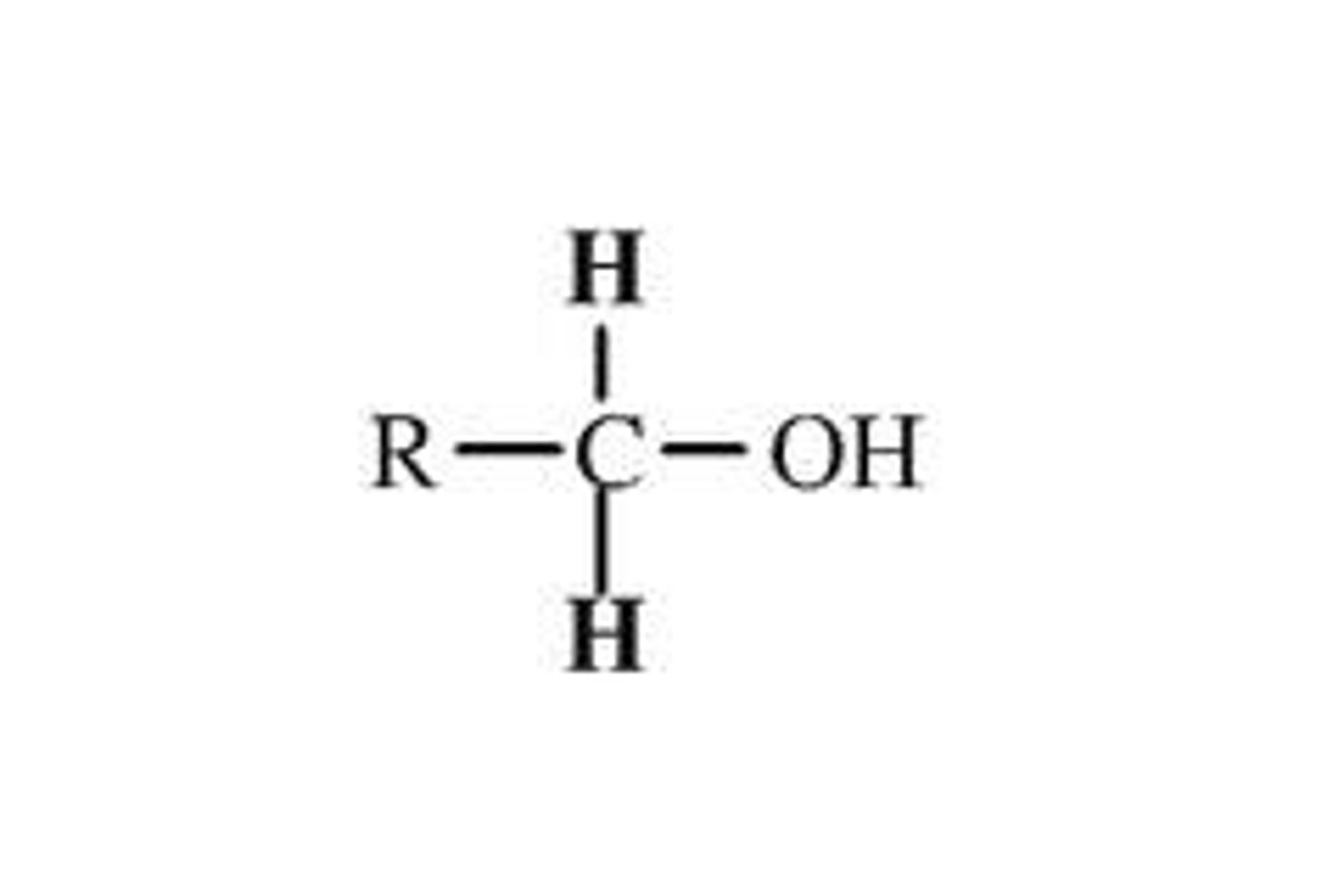
alcohol 1* degree
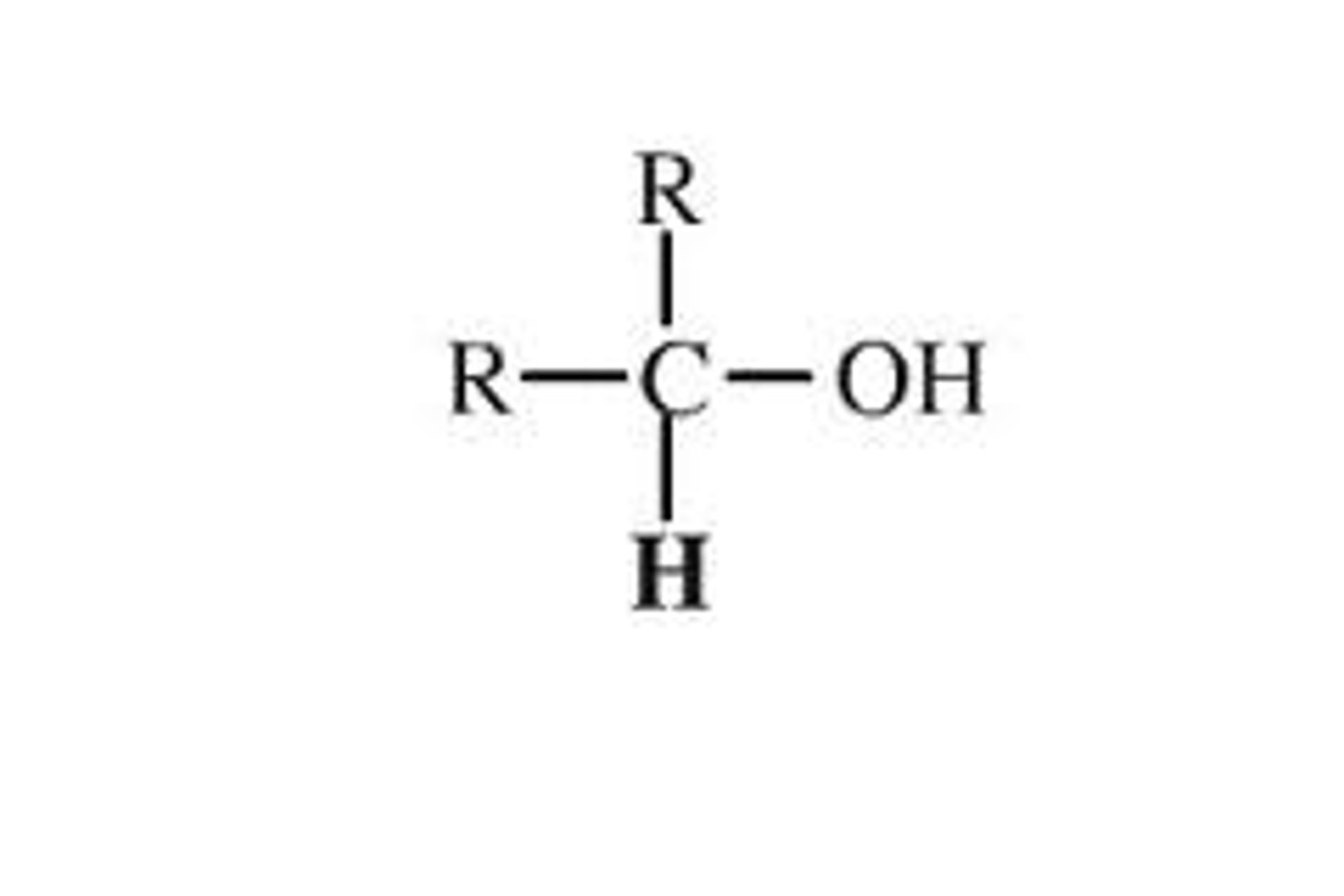
alcohol 2* degree
1) KMnO4 or Na2Cr2O7/acid/water or CrO3/acid/water or PCC
- turns OH to O with double bond
- 2-degree alcohol -> ketone
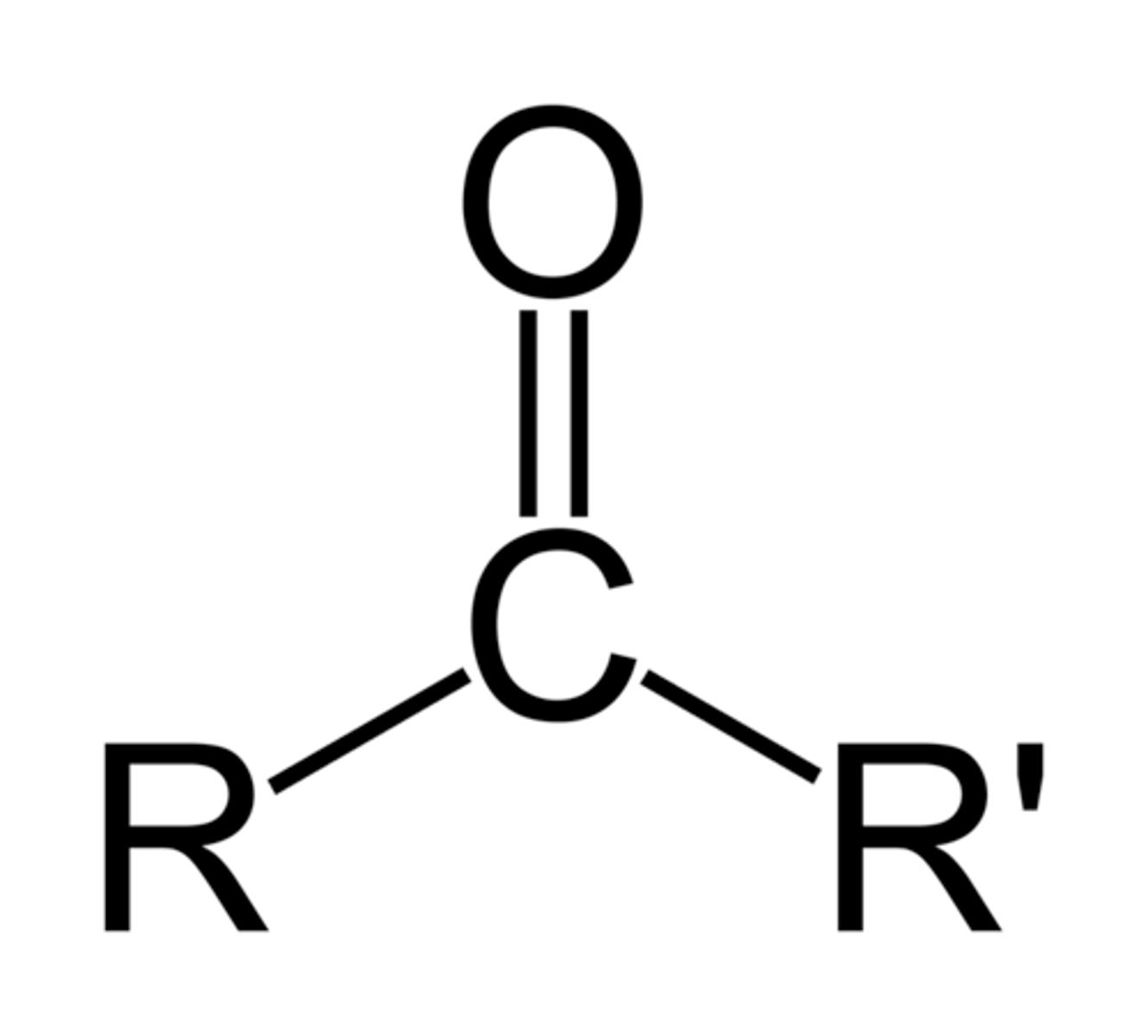
ketone
ROOR
Peroxide
1) PCC 2) 1)KMnO4 or Na2Cr2O7/acid/water or CrO3/acid/water
1 degree alcohol -> aldehyde -> carboxylic acid
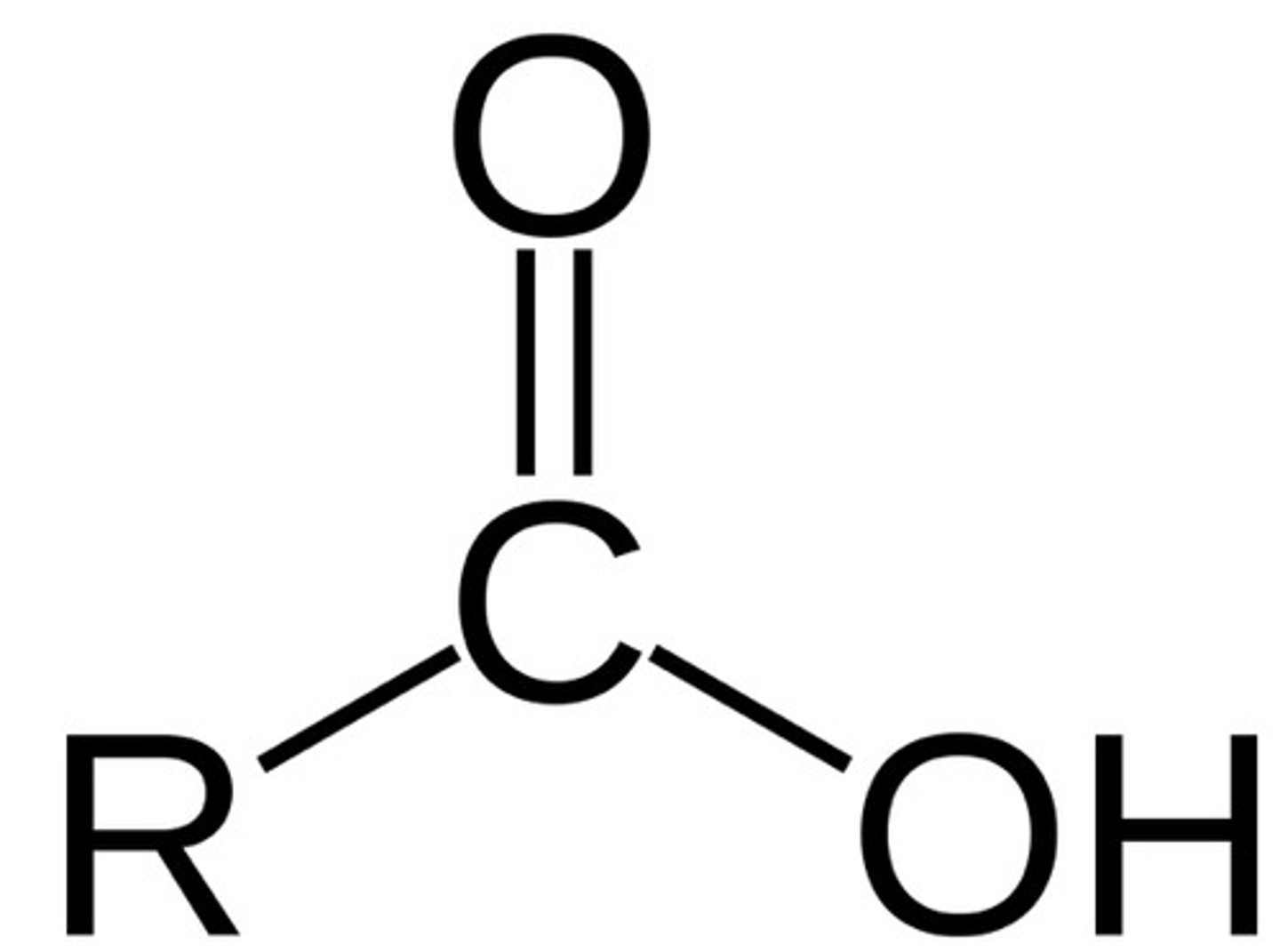
carboxylic acid
R-COOH
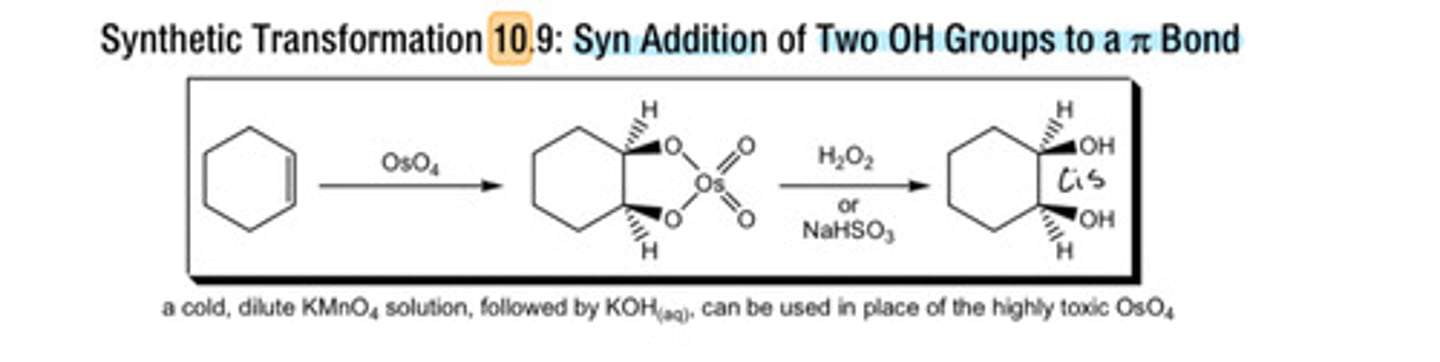
1) OsO4 2)H2O2 or NaHSO3
1) Ozone 2) Zn, acetic acid
cleavage of the entire C=C, add O at the end
- 1 carbon is 3 degrees, the other is 2 with a Hydrogen
1) KMnO4 (hot) 2) H3O+, H2O
cleavage of the entire C=C, add O at the end
- 1 carbon is 3 degrees, the other is 2 with an OH group
1) HX, dark, cold, no peroxides (X = Cl, Br or I)
2) HX, dark, cold, no peroxides
- first one breaks triple bond to double bond and adds X in Markovnikov way
- second one breaks double bond to single bond and adds another X in Markovnikov way
1) X2
2) X2 (excess)
- first one breaks triple bond to double bond and adds 2 Xs in a trans way
- second one breaks double bond to single bond and adds another 2 Xs in a trans way
1) H2O, H2SO4, HgSO4
turns C(triple bond)C to O=C-CH3
permanganate
MnO4-
H2SO4, H2O
turns C(triple bond)N to O=C-OH
H2O2, NaOH, H2O
tautomerizes
HX
replaces Oh group with X, has a step in between that shows the X- (X as an anion)
SOCl2
replaces OH group with Cl
PBr3
replaces OH group with Br
Any nucleophile
replaces leaving group with Nuc
NaOH or KOH
replaces leaving group with OH
Na metal + alcohol (ROH) = NaOR
replaces leaving group with OR
NaNH2 + any molecule with a LG
replaces leaving group with the carbon anion
Cl2+ light (hv)
creates two products of one Cl on the least substituted carbon and one Cl on the most substituted carbon
Br2 + light (hv)
creates 1 product of Br on the most substituted carbon + HBr
radical initiator (NBS/heat or Br2/light) + Br2
Addition of 1 Br on the carbon NEXT to the double bond
Does not break double bond
Br2, Cold, dark, no peroxides
trans addition of 2 Br,
Breaks double bond
radical initiator (benzoyl peroxide) + HBr
Anti-addition of Br
Breaks double bond
HBr, Cold, dark, no peroxides
Markov addition of Br
Breaks double bond