unit 1 lab exam review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
cranial cavity
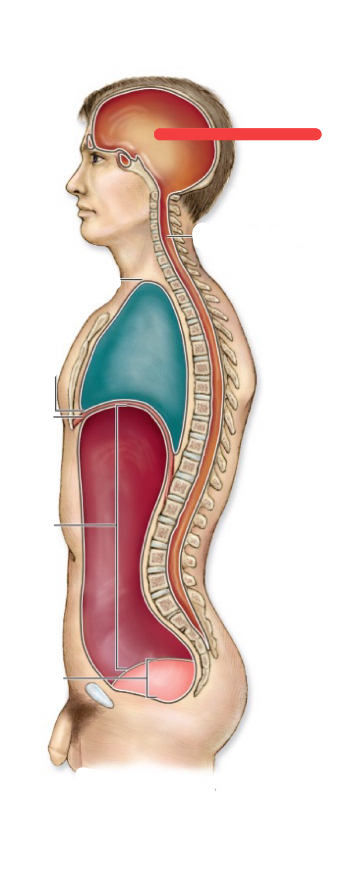
thoratic cavity
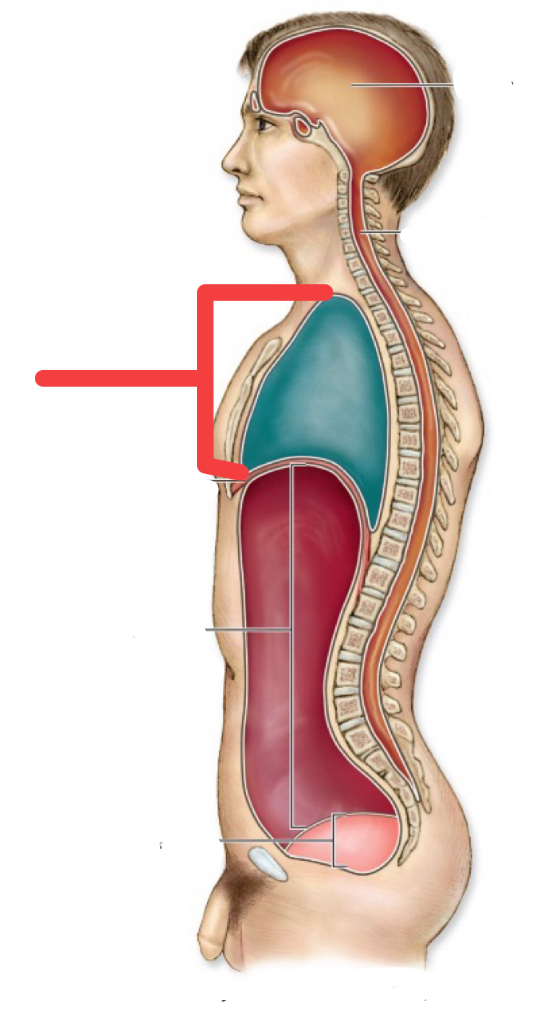
thoratic diaphragm
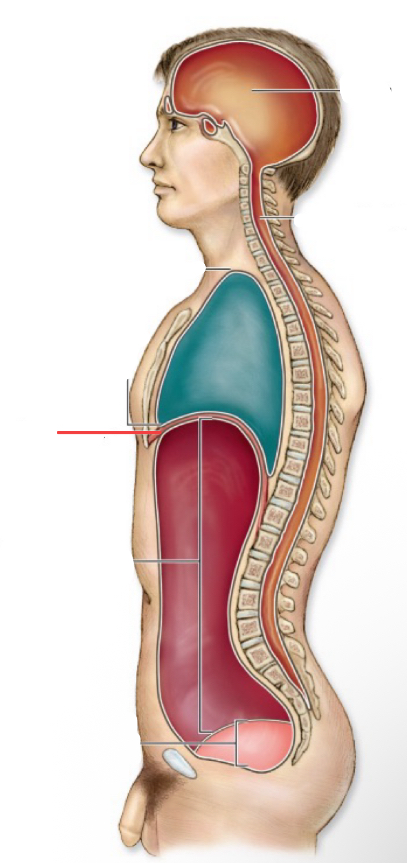
vertebral canal
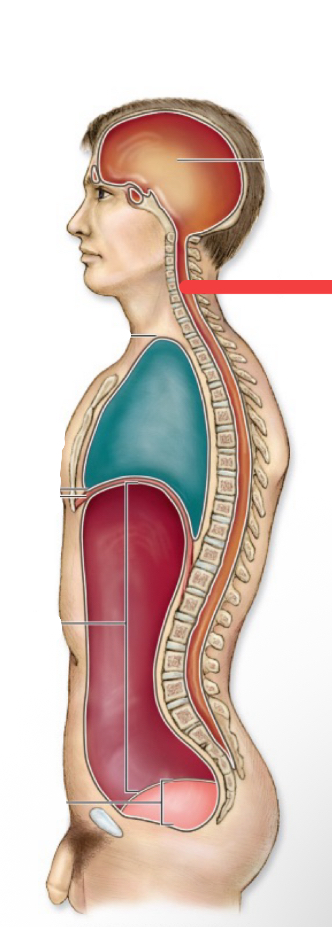
abdominal cavity
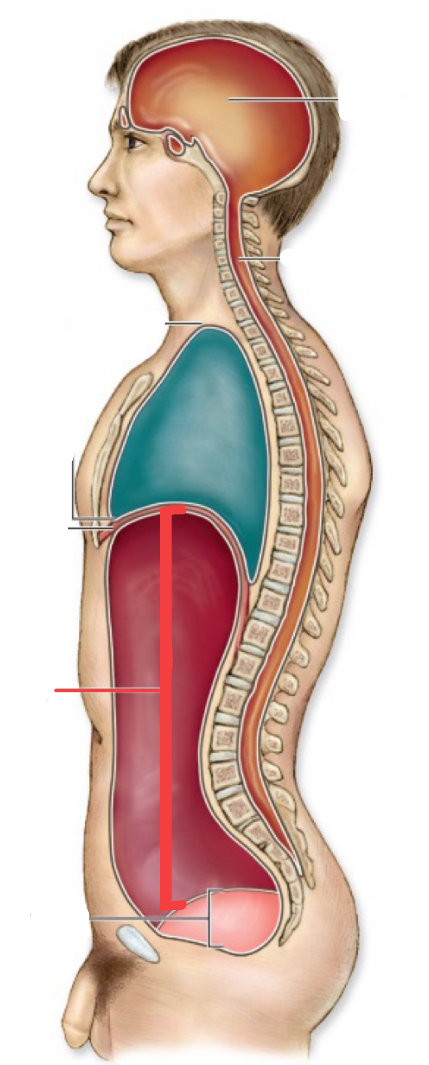
pelvic cavity
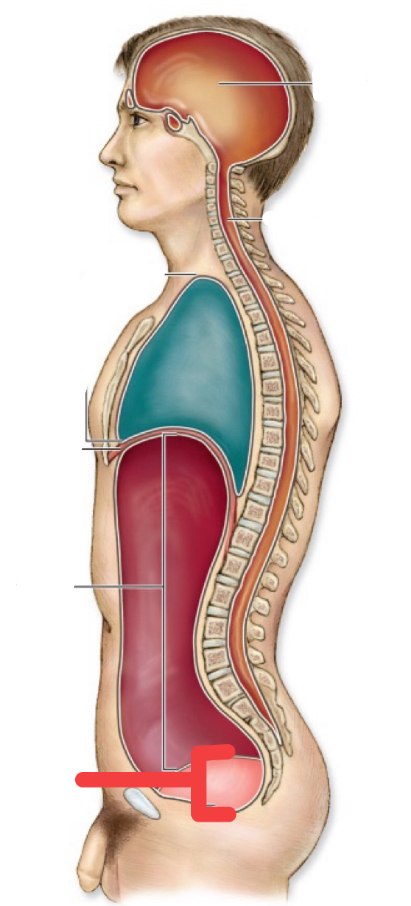
abdomnipelvic cavity
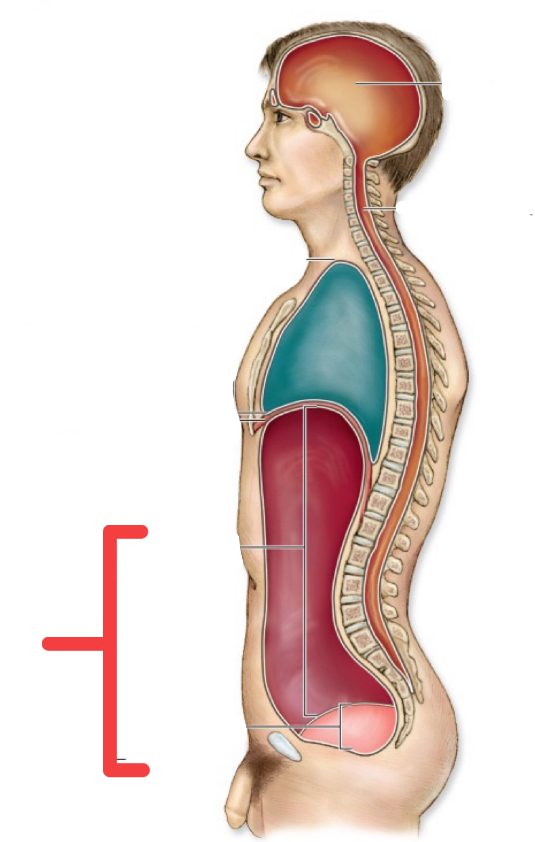
ventral cavity
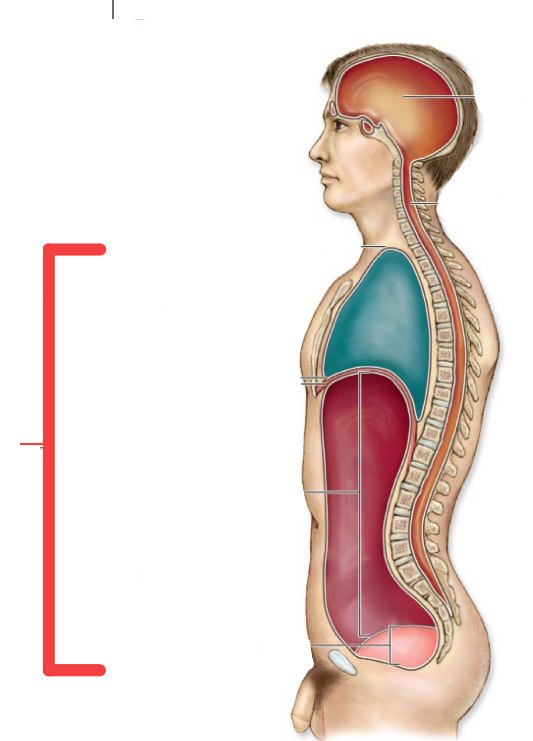
what does the pleura membrane surround
the lungs
what does the pericardium membrane surround
the heart
parietal
outer lining
visceral
inner lining
what does the peritoneum membrane surround
the abdomnipelvic cavity
right hypochondriac
epigastric
left hypochondriac
hypogastric
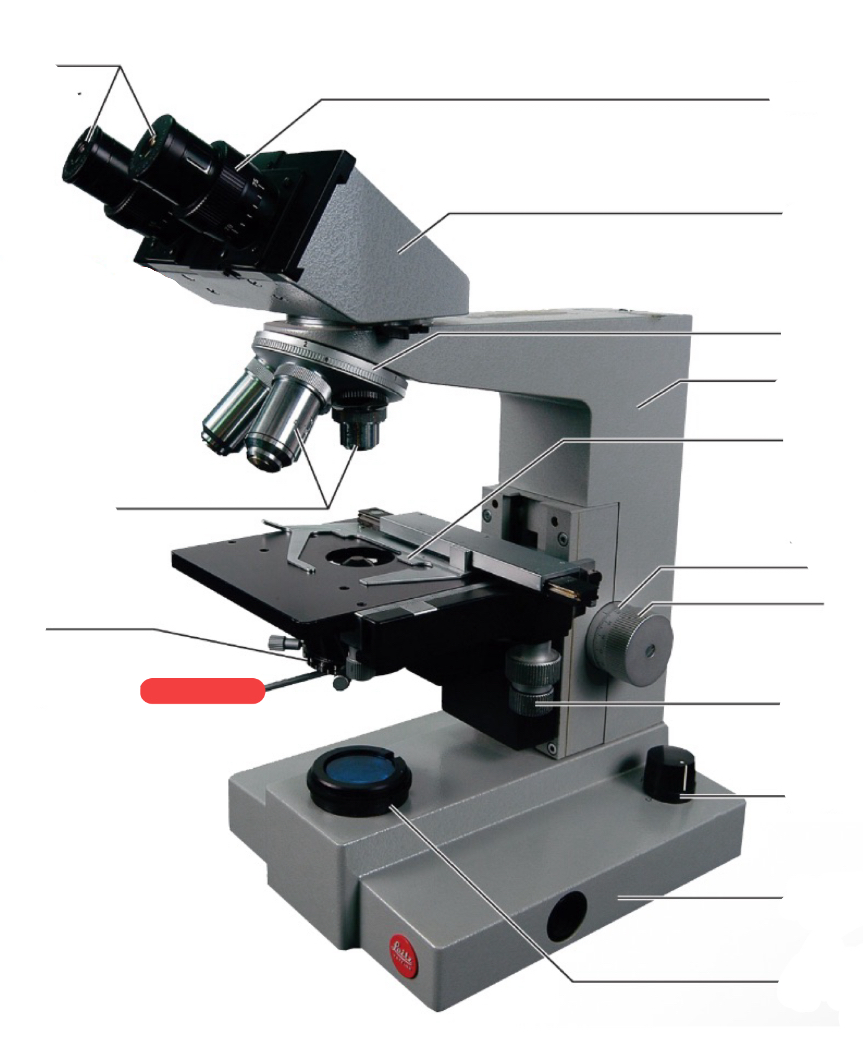
nose piece
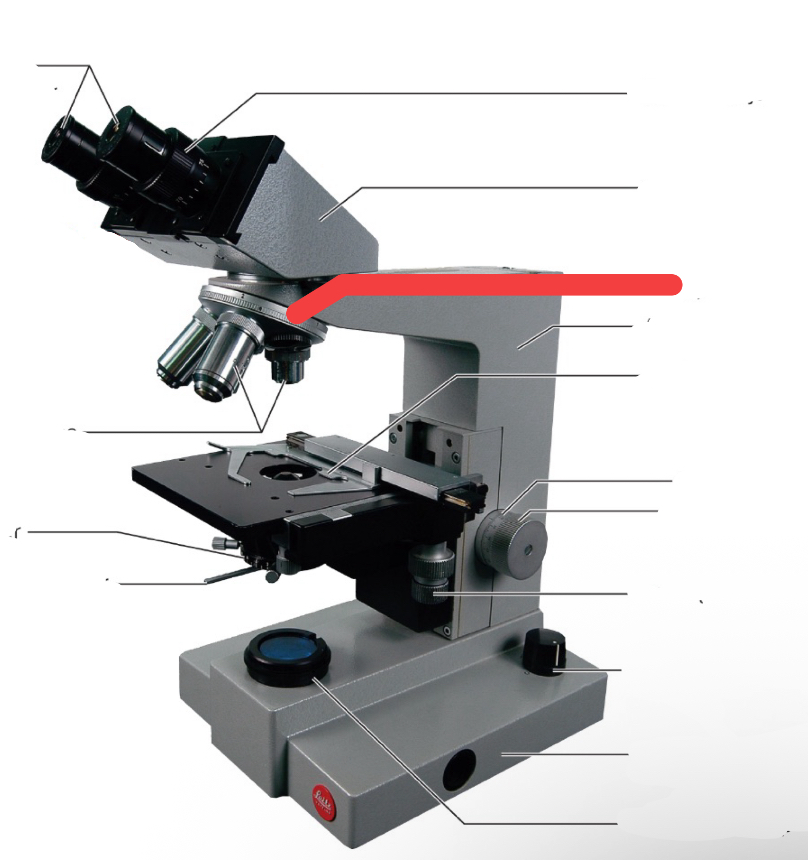

condenser
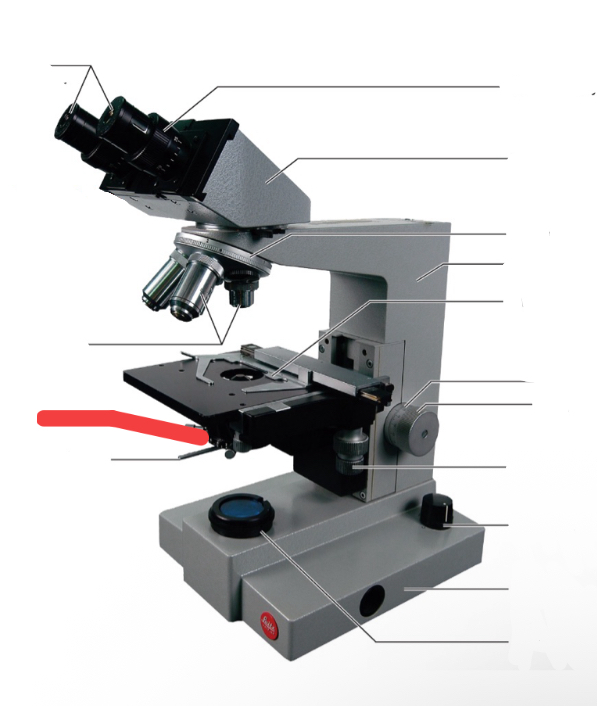
iris diaphragm lever
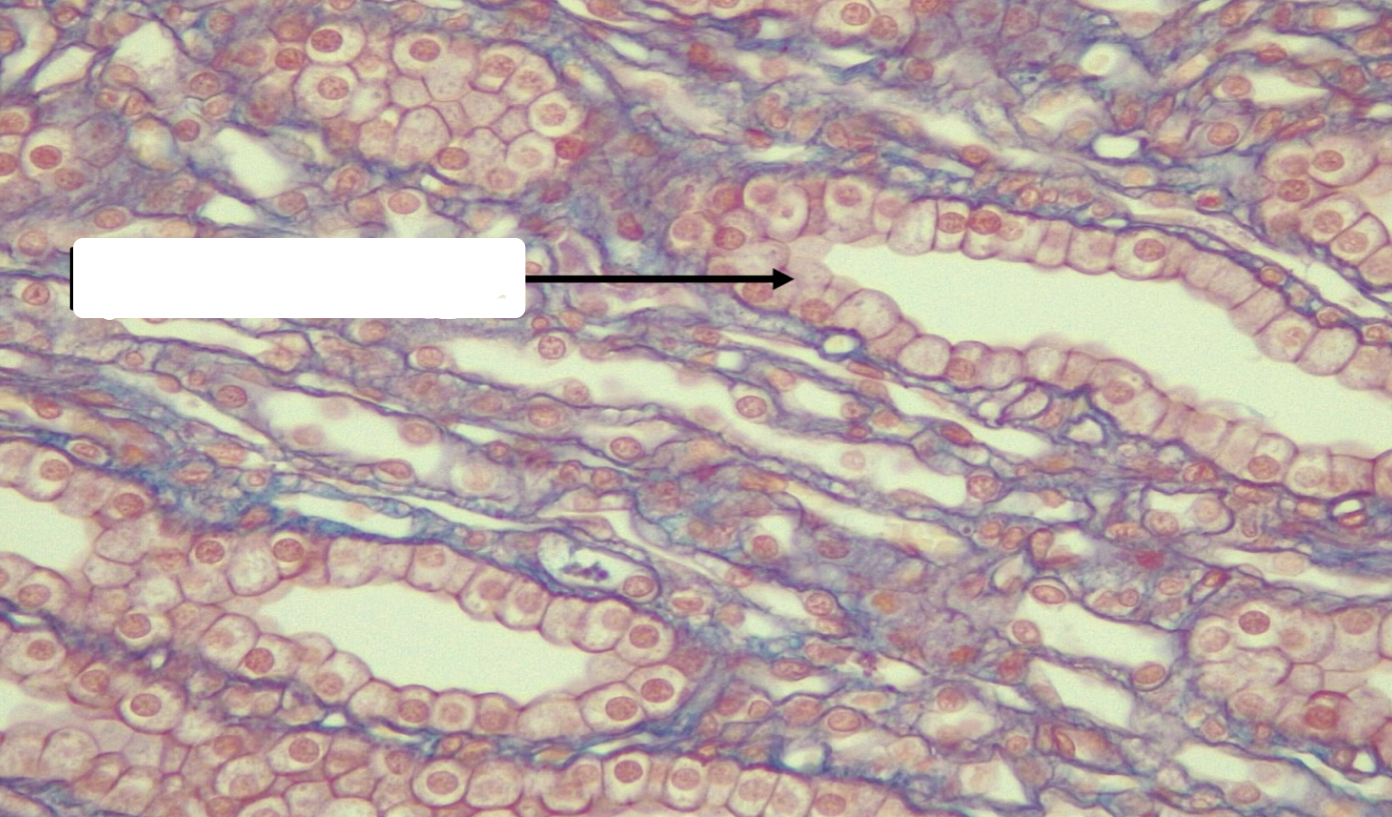
simple squamous epithelia
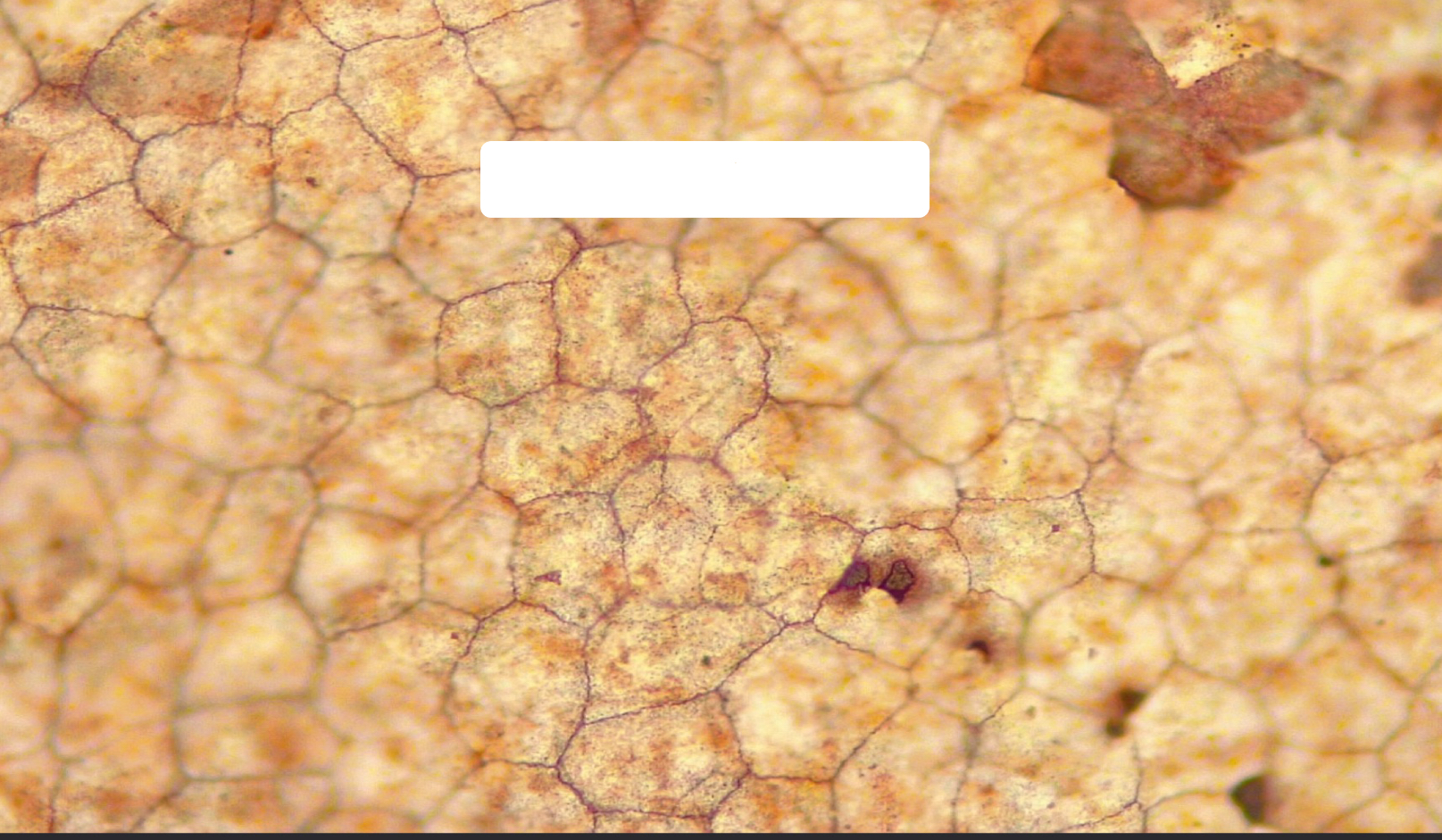

simple cuboidal epithelia
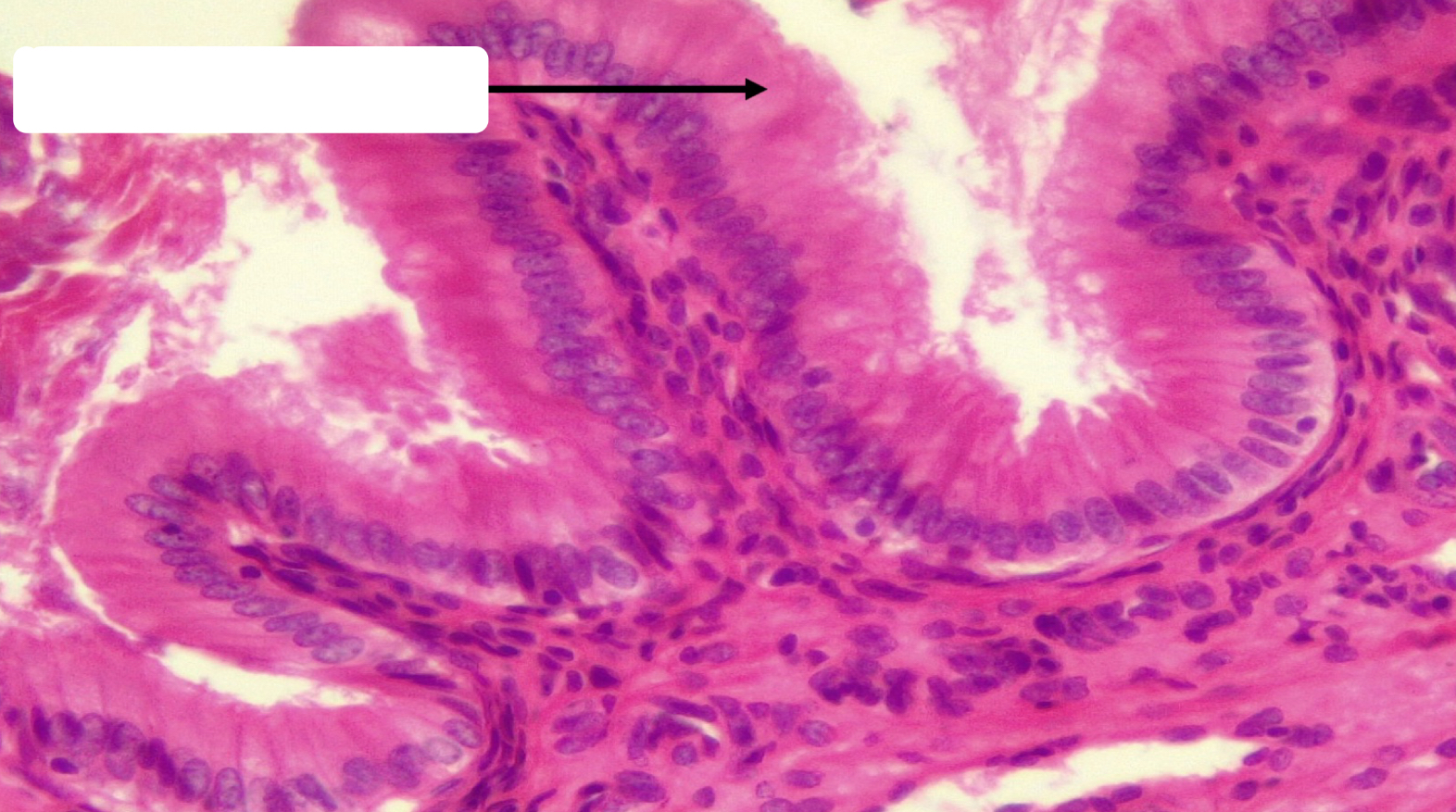
simple columnar epithelia
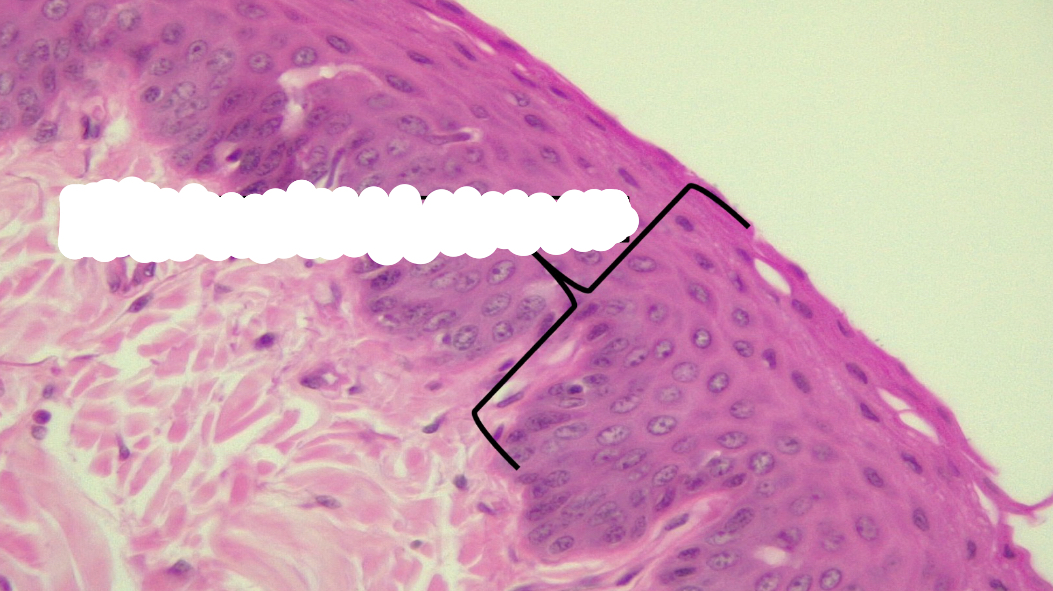
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelial
areolar connective tissue
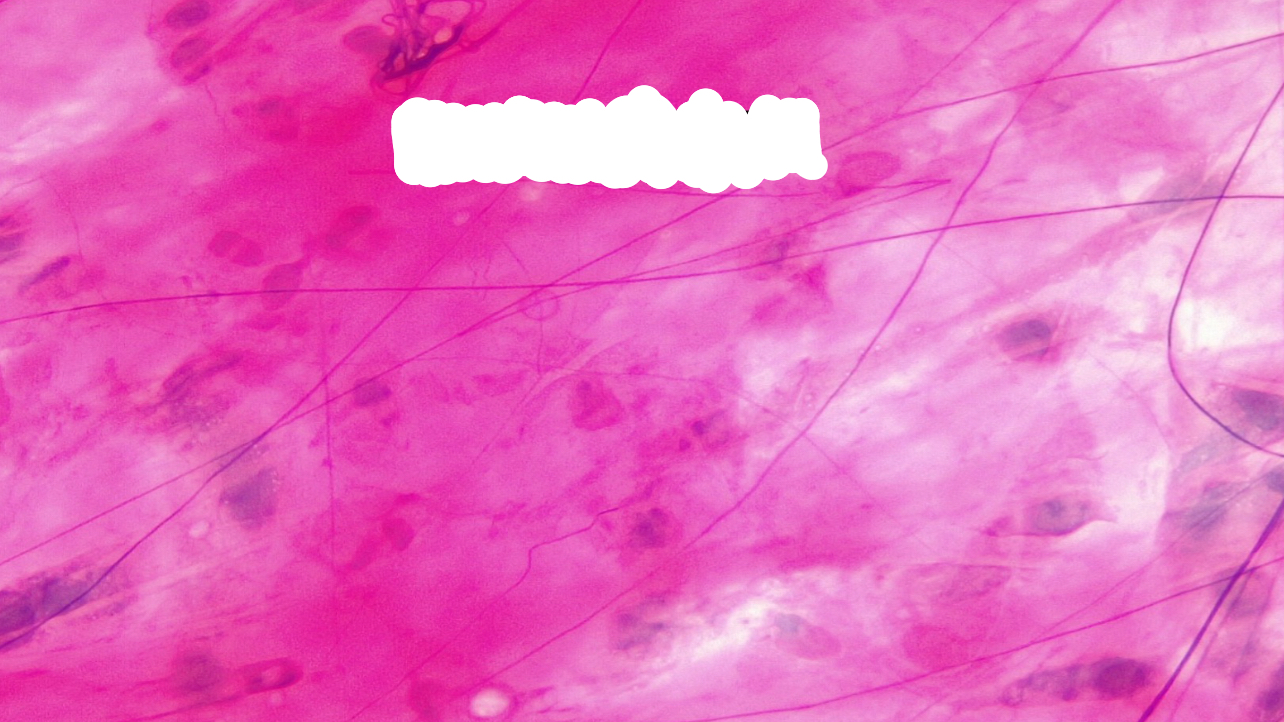

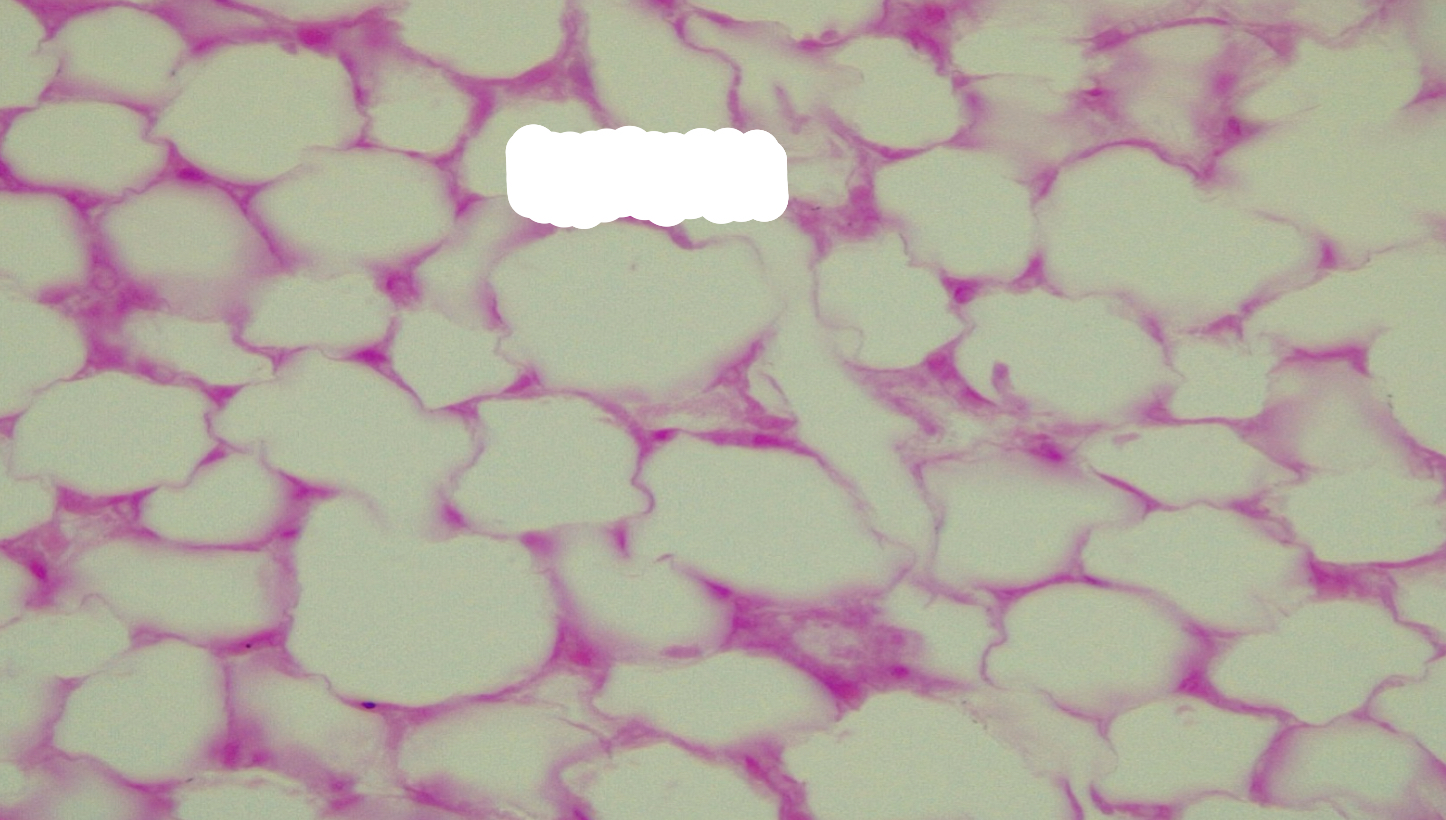
adipose tissue
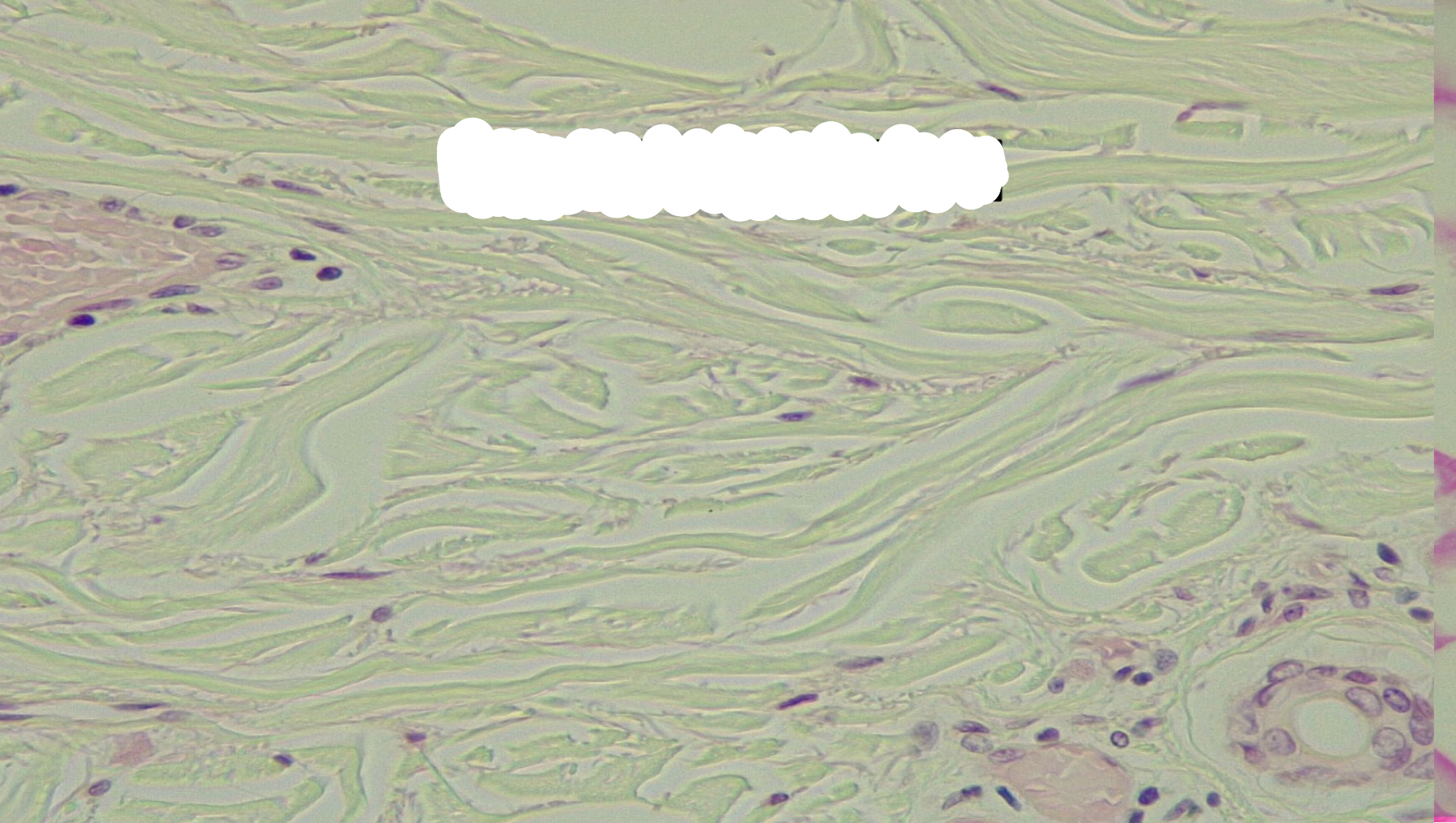
dense irregular connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue
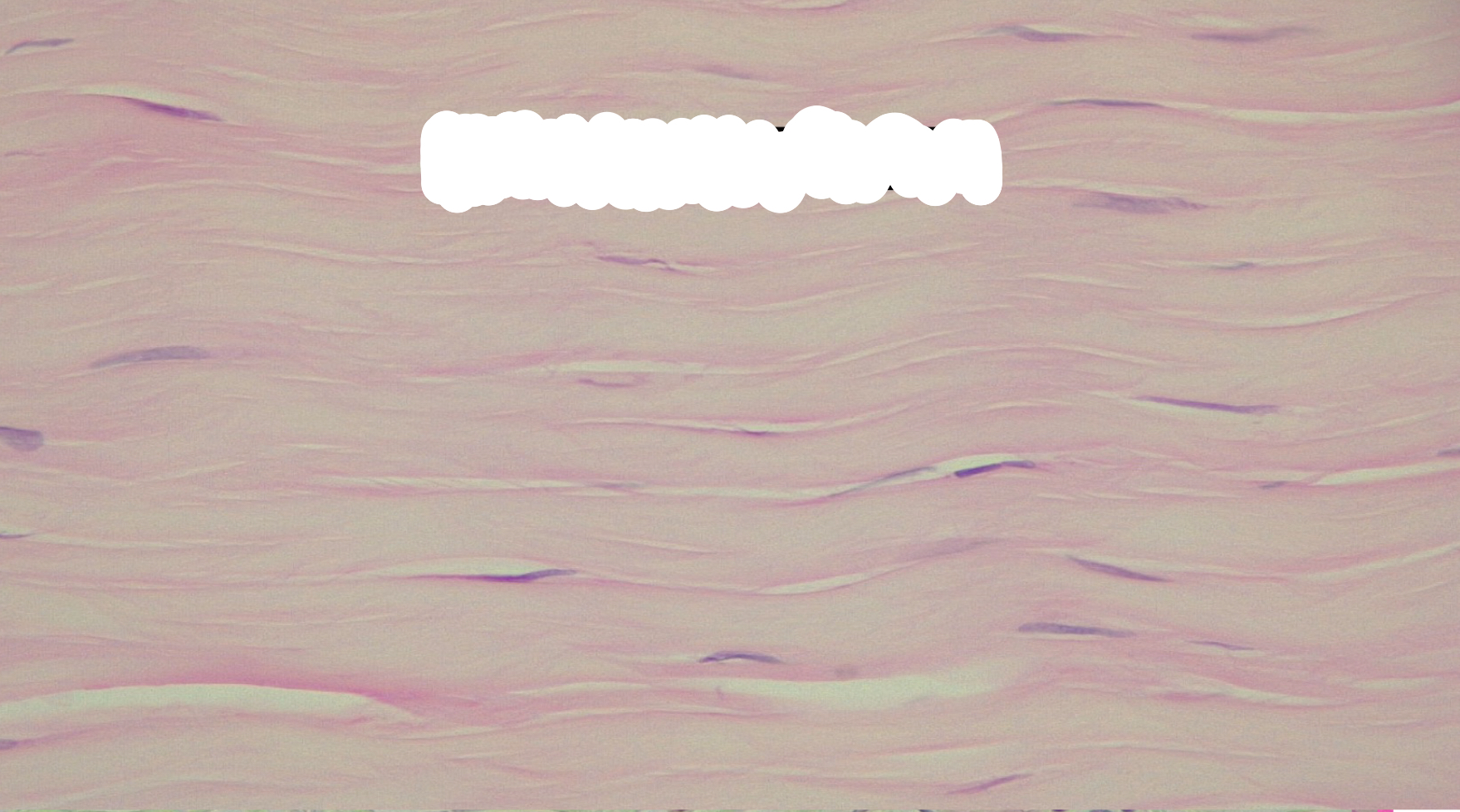

hyaline cartilage
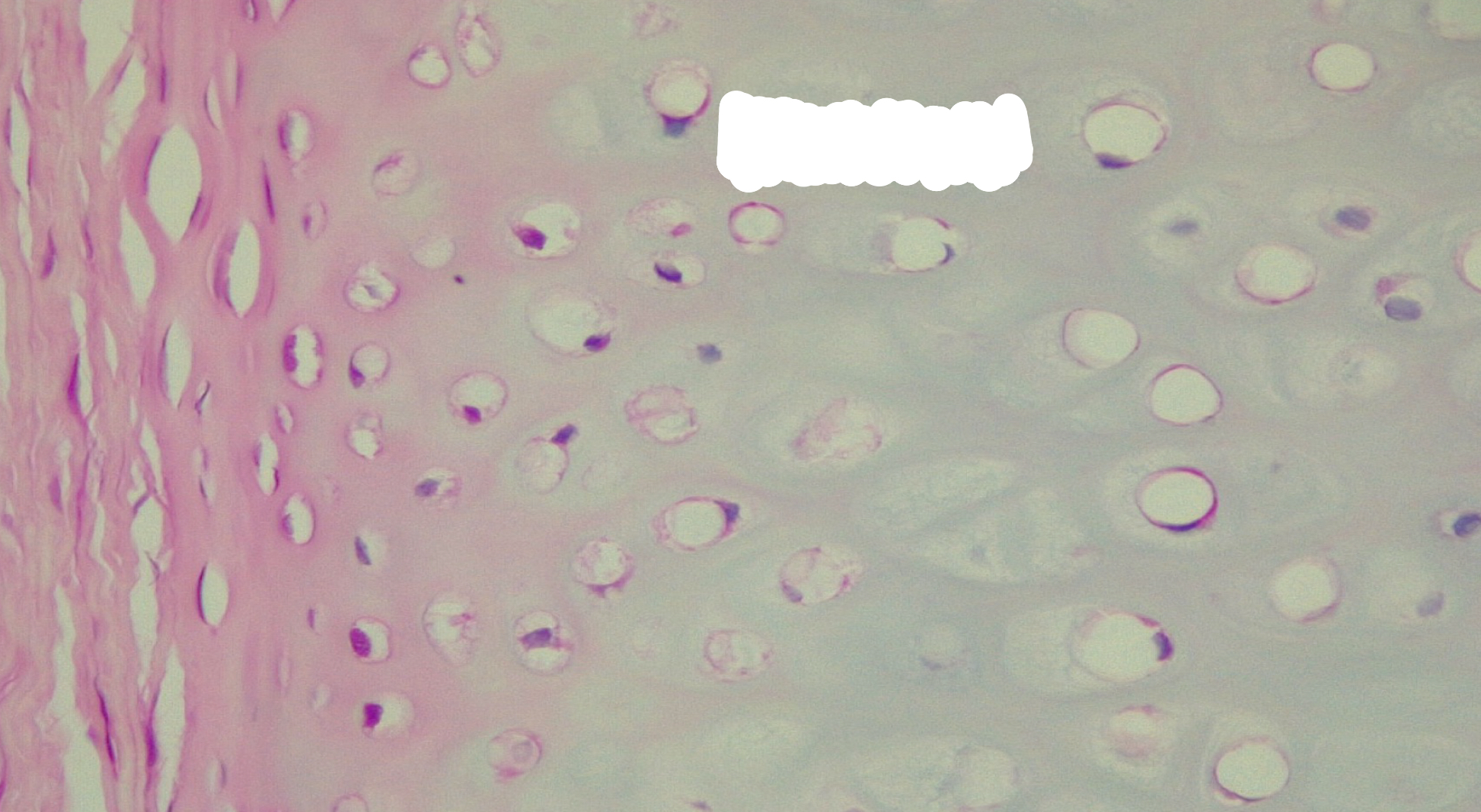
elastic cartilage
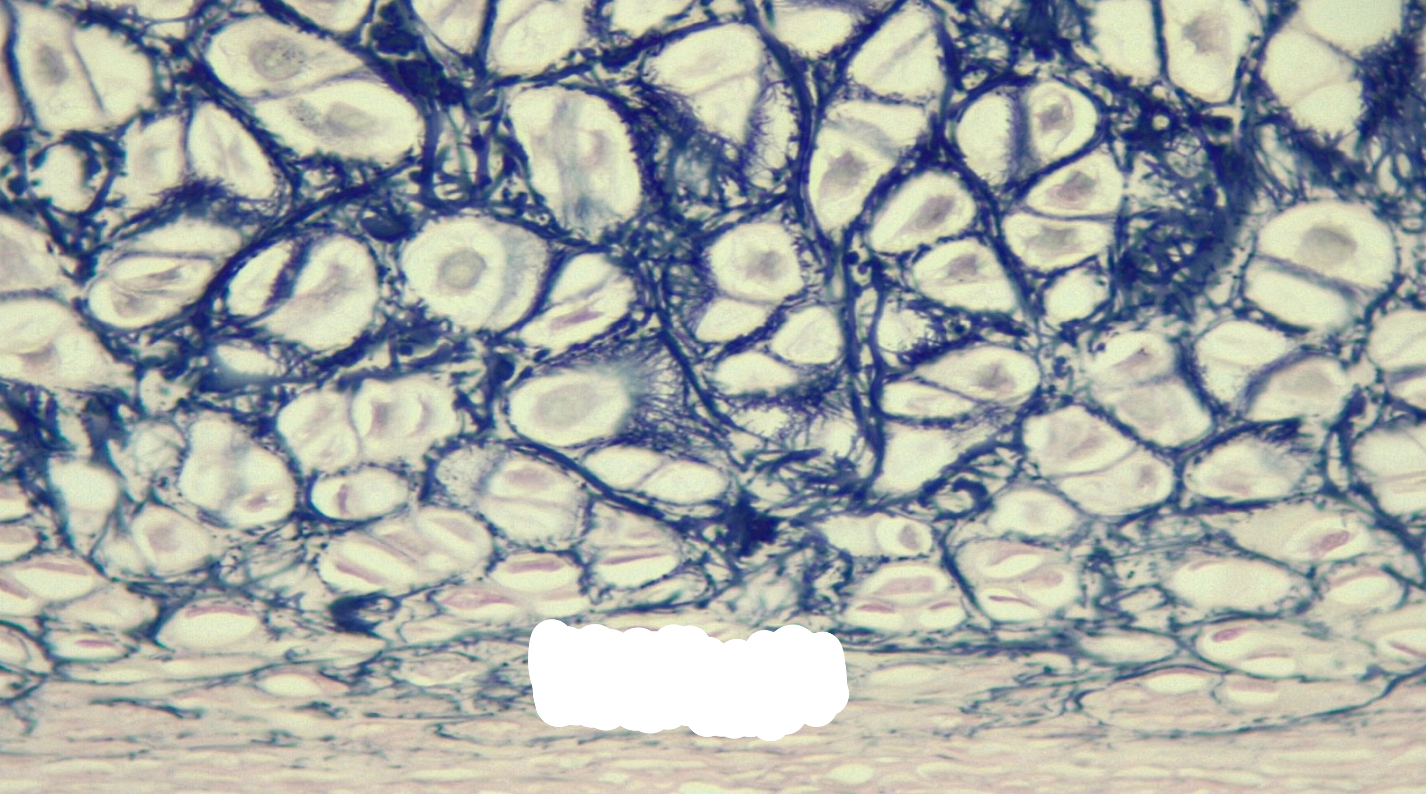
fibrocartilage
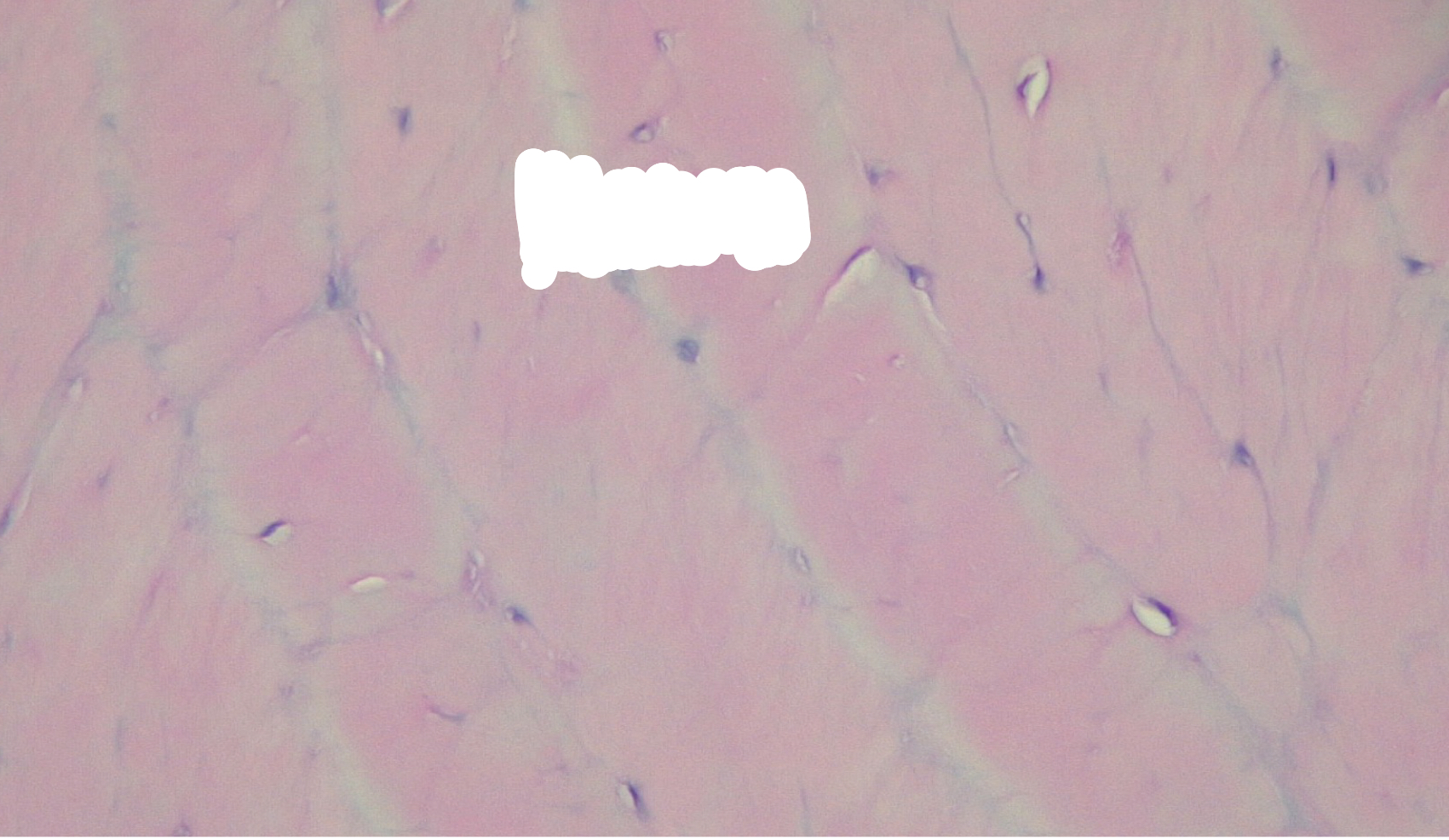
G1
division preparation
centriole replication begins
s phase
DNA replication
G2
last minute protein synthesis, organization & completion of centriole replication
epithelial tissue layers
apical
lateral
basal
basement membrane
simple squamous function
thinnest possible barrier to allow for rapid diffusion and filtration; secretion in serous membranes
simple squamous location
air sacs in lungs (alveoli); lining of lumen of blood vessels and lymph vessels (endothelium); serous membrane of body cavities (mesothelium)
simple cuboidal function
absorption and secretion; forms secretory tissue of most glands and small ducts
simple cuboidal location
lining of kidney tubules; thyroid gland follicles; surface of ovary; secretory regions and ducts of most exocrine glands
simple columnar function
absorption and secretion
simple columnar location
lining of most gastrointestinal (digestive) tract (stomach, small intestine, and large intestine)
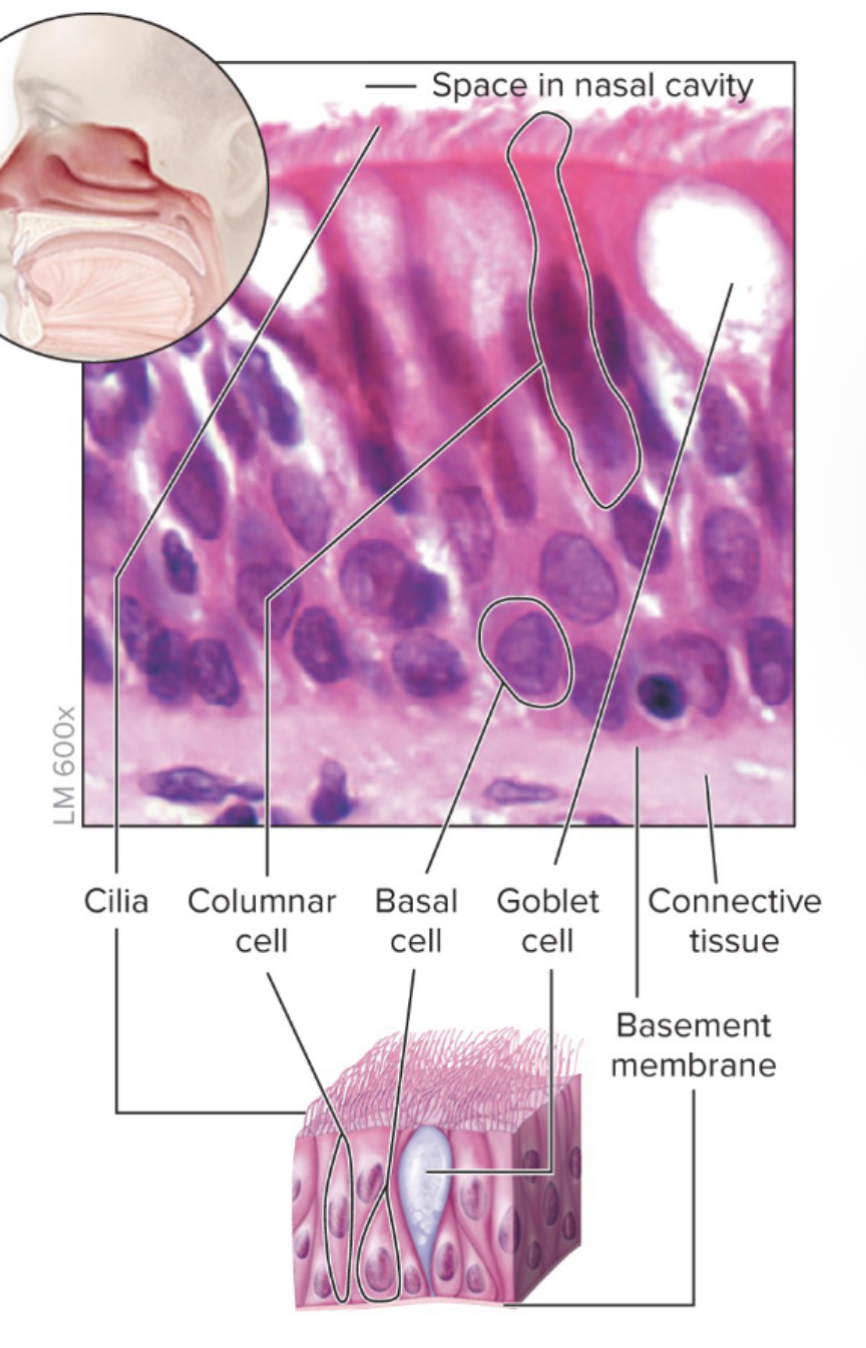
ciliated pseudostratified function
protection; secretion of mucin and movement of mucus along apical surface of epithelium by cilia
ciliated pseudostratified location
lining of the larger airways of respiratory tract, including nasal cavity, part of pharynx, parts of larynx, trachea, and bronchi
ciliated pseudostratified
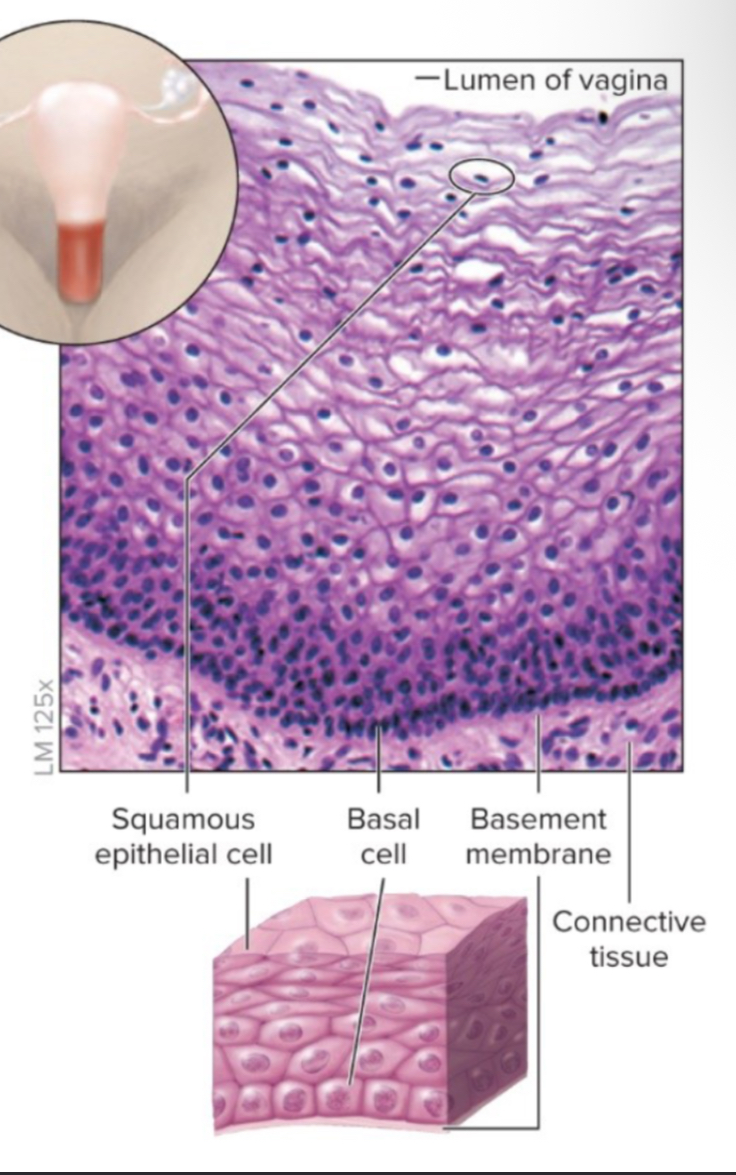
non-keratinized stratified sqamous epithelia function
protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
non-keratinized stratified sqamous epithelia location
lining of oral cavity, part of pharynx, parts of larynx, esophagus, lining of vagina, and anus
non-keratinized stratified sqamous epithelia
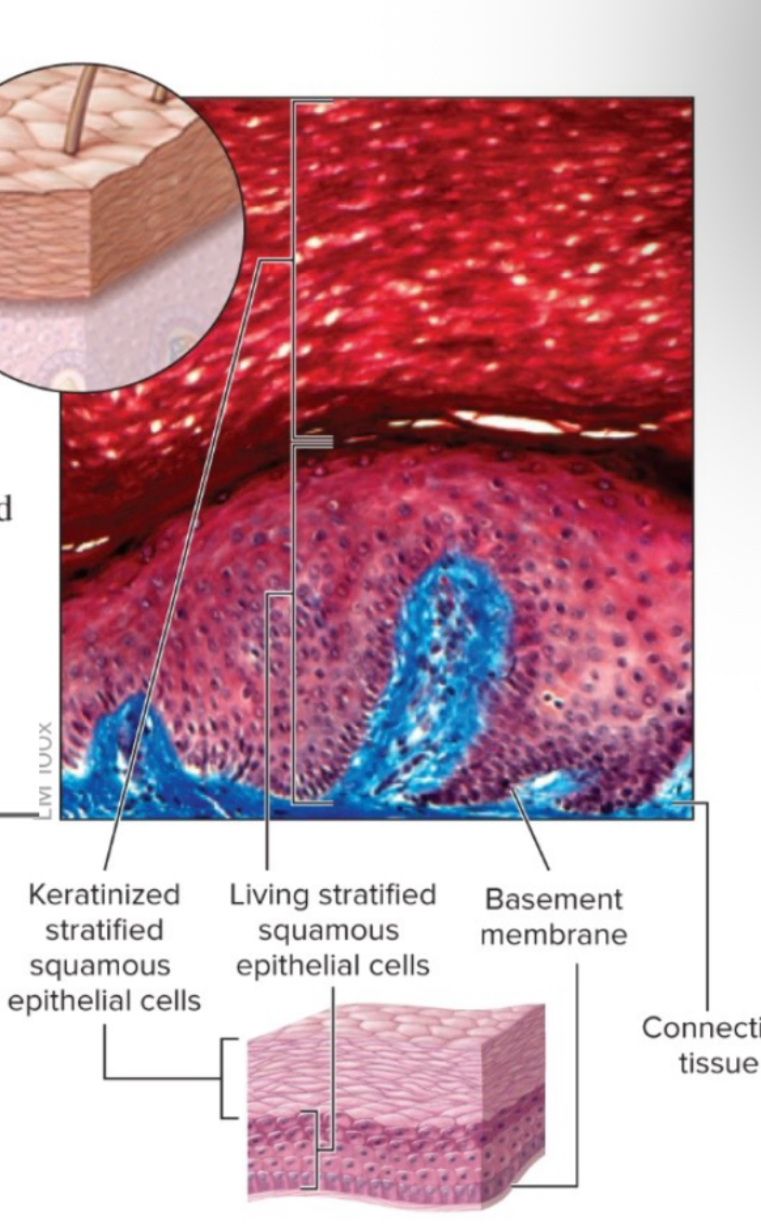
keratinized stratified squamous epithelia function
protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
keratinized stratified squamous epithelia location
epidermis of skin
keratinized stratified sqamous epithelia
areolar connective tissue function
protect tissues and organs; find skin and some philia to deeper tissue; provide space for blood vessels and nerves
areolar connective tissue location
capillary layer of the dermis (skin); subcutaneous layer (deep to skin); surrounds organs, nerve cells, some muscle cells, and component of blood vessel walls
adipose connective tissue function
stores energy; insulates, cushions and protects
adipose connective tissue location
subcutaneous layer; surrounds and covers some organs
dense regular connective tissue function
attaches bone to bone (most ligaments) as well as muscle to bone (tendon); resists stress applied in one direction
dense regular connective tissue location
tendons & ligaments
Dense, irregular, connective tissue function
With Stan stresses applied in all directions; durable
Dense, irregular, connective, tissue location
reticular layer of the dermis: epimysium covering skeletal muscle; epineurium covering nerves; periosteum covering bone; perichondrium, covering cartilage; some organ capsules
hyaline cartilage function
provide support; forms most of fetal skeleton
hyaline cartilage location
Tip of nose; trachea; bronchi; most of larynx, coastal cartilage; both of the epiphyseal (growth) plates and articular ends of long bones; most of fetal skeleton
fibrocartilage function
Weight-bearing cartilage that resists compression; acts as a shock absorber in some joints
fibrocartilage location
intervertebral discs; pubic symphysis; menisci of knee joints
Elastic cartilage function
maintain shape while permitting extensive flexibility
elastic cartilage location
external ear; epiglottis of larynx