bio120 FINAL
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
dispersal allows organisms to
colonize new areas
escape competition
avoid inbreeding depression
diversity in canada after glacial period is largely from:
dispersal
metapopulation
collection of spatially distinct populations connected via dispersal
if there is dispersal, a locally unstable system can be…
globally stable
P
number of occupied patches
1-P
number of empty patches
formula for patch colonization rate
cP(1 - P)
constant e in patch model
chance that a patch goes extinct / from occupied to unoccupied
Levin’s patch occupancy model
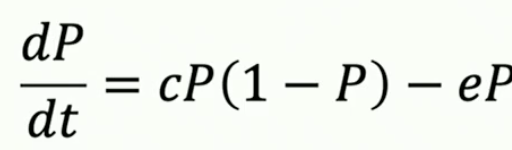
Levin’s patch occupancy model AT EQUILIBRIUM
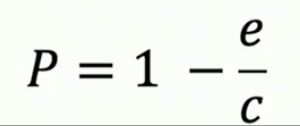
if a is a better competitor than b and they wanna globally coexist then…
b has to be a better disperser
populations can go to extinction through
stochasticity
competitive exclusion
predator prey
allee effects
extinction effects countered by
predation preventing total competitive exclusion (Paine’s sea stars)
non equilibrial conditions, habitat patchiness, rescue by migration, variation in life history strategy
metacommunity
communities linked by dispersal
theory of island biogeography
lotka volterra equation for mutualism
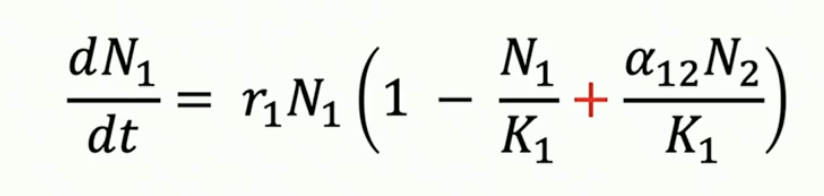
what limits population growth of mutualists?
intraspecific competition
third species e.g. predator
diminishing returns as population grows
invasional meltdown
two non-native species facilitate each other’s spread
survivorship curves examples (I, II, III)
human, bird, bug
geometrical growth model + 𝜆 meaning
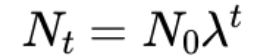
𝜆 = net reproductive rate = (per capita birth rate - per capita death rate)
exponential growth model + r meaning
r = net growth rate
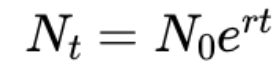
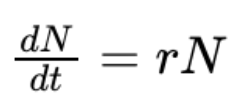
logistic model of density dependence
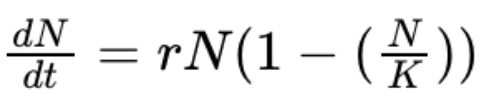
logistic model + allee effect + A meaning
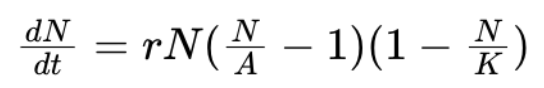
A = allee threshold
equation for R0
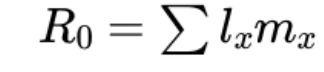
equation for T / generation time + what it means
average age at which a female gives birth
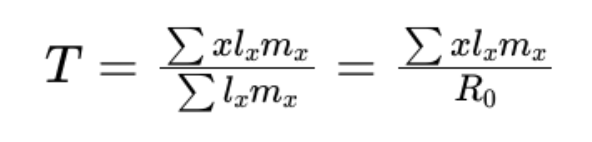
4 possible outcomes of competition
Species 1 outcompetes Species 2
Species 2 outcompetes Species 1
Two species stably coexists, both remaining under K
Competition is unstable, winner depends on starting numbers
𝜆 vs r vs R0
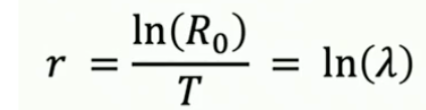
fecundity
number of offspring an individual has
lx
probability of being alive at age x
mx
# daughters born to female of age x between x and x+1
iteroparity
potentially reproduce numerous times
semelparity
reproduce once and then die
vx
expected # of daughters to be produced by a female of age x, now and for the rest of her lifetime
scramble competition
depletion of shared resource
contest/interference competition
direct interactions e.g. battles over territory)
lokta volterra model
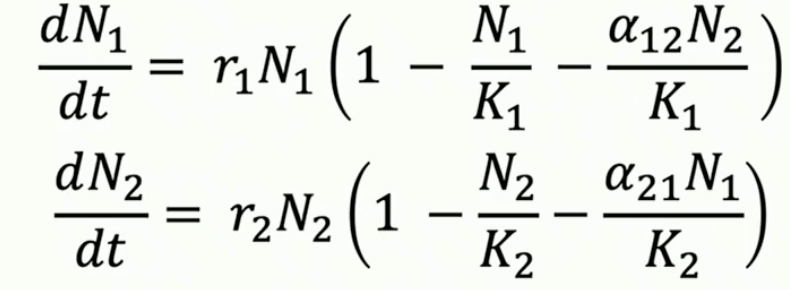
alpha meaning lokta volterra
competition coefficient - per capita effect on one species by the other
e.g. one squirrel is equivalent to 4 sparrows
coexistence requires intraspecific competition __ interspecific competition
>
stability
ignore
stability
ability of system to return to equilibrium following disturbance
principle of competitive exclusion
if two species have same niche one will outcompete the other into extinction
resolving paradox of plankton
lv model to simple
real conditions fluctuate
environmental factors
lv for predator prey predicts
coupled, lagged population cycles
why are predator prey cycles rare irl
they have other prey
hares might be cycling w/ their food
antagonistic coeevolution
arms race —> prey evolves defenses and predators evolve to overcome them
red queen hypothesis (coevolution)
both predator and prey are evolving as fast as they can but that lowkey means they remain in the same place
life dinner principle
predicts prey are under stronger selection to make defenses than predators are to overcome them (life vs. dinner)
enemy release hypothesis
invaders’ impacts results from having fewer natural enemies in their new range
dilution effect
host diversity can dilute disease risk to humans or animals
amplication effect
more host / vector species can support larger populations of disease causing organisms