Chapter 17: Cytoskeleton Types and Functions: Intermediate Filaments, Microtubules, Actin Filaments
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the primary function of the cytoskeleton?
provides cell shape, movement, adhesion, intracellular traffic, cell division, and other specialized functions.
What are the three types of protein filaments in the cytoskeleton?
Intermediate filaments, microtubules, and actin filaments.
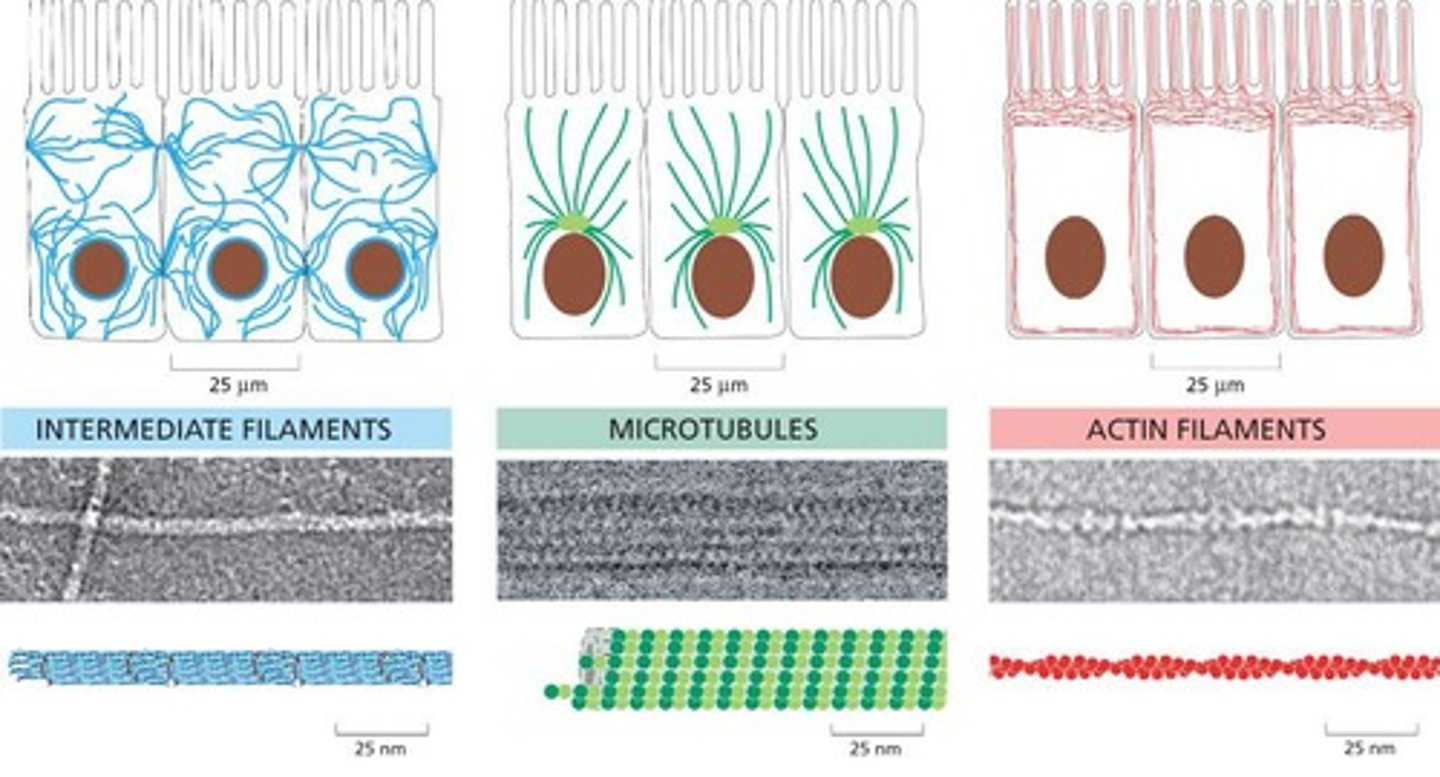
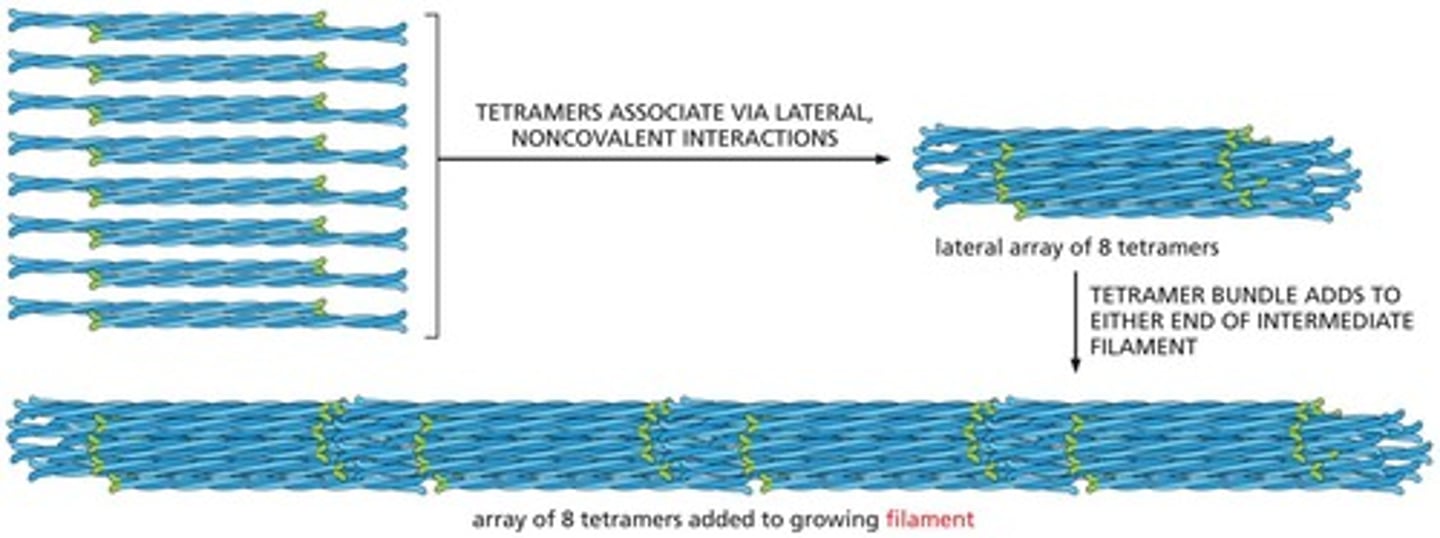
What are intermediate filaments and their main function?
They are strong, rope-like fibers that provide mechanical support to cells, enabling them to withstand stress.
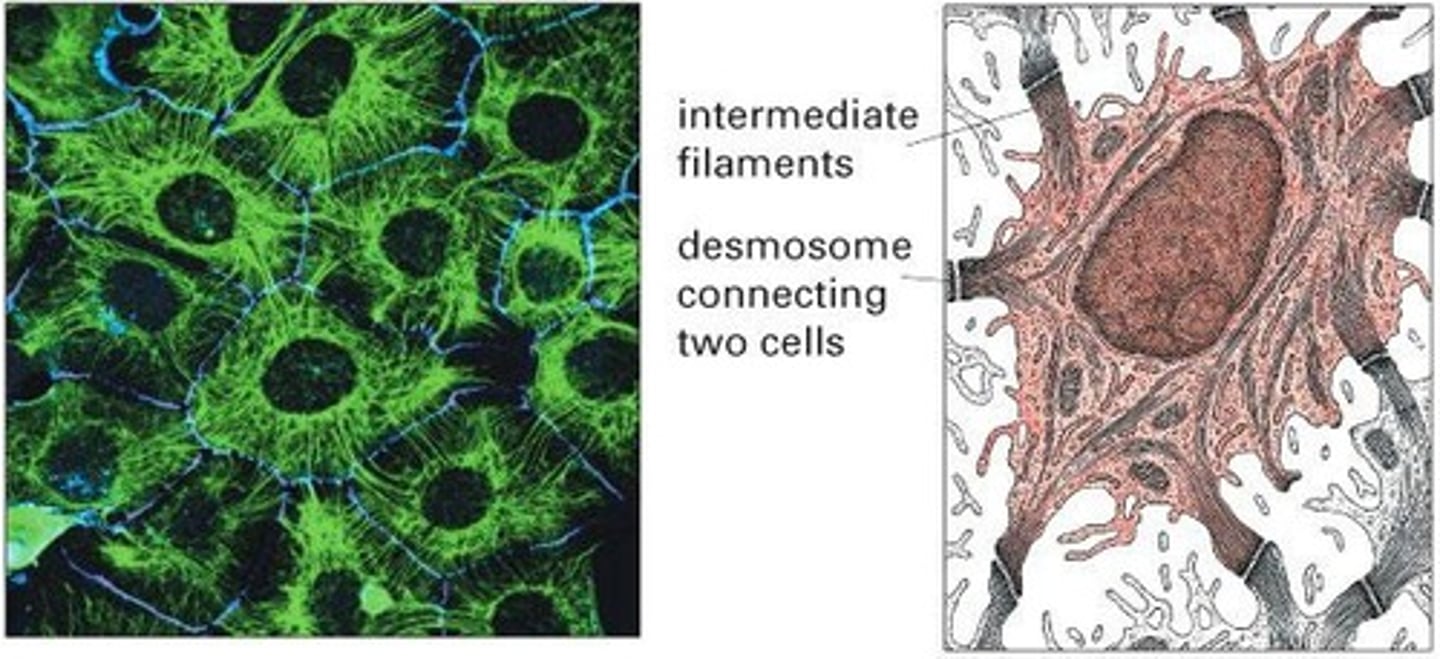
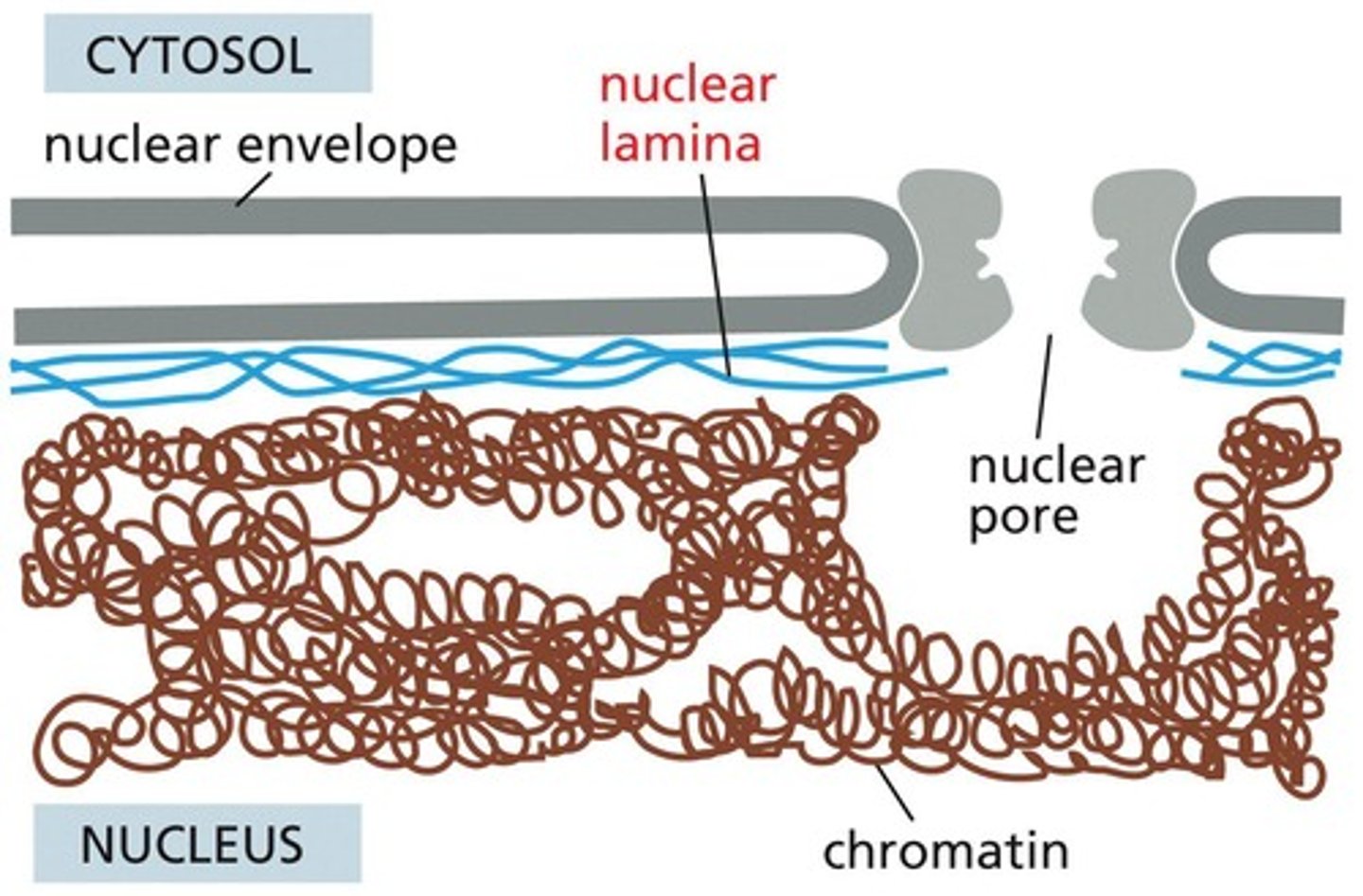
What is the nuclear lamina?
A mesh-like network of lamin fibers that provides structural support for the nucleus and attachment sites for chromatin.
What happens to the nuclear lamina during mitosis?
Phosphorylation of lamins causes disassembly of the nuclear envelope, which reassembles into a new nuclear lamina upon dephosphorylation in daughter cells.
What are microtubules and their primary functions?
They are hollow cylinders that aid in cell polarity, intracellular traffic, mitosis, and movement.
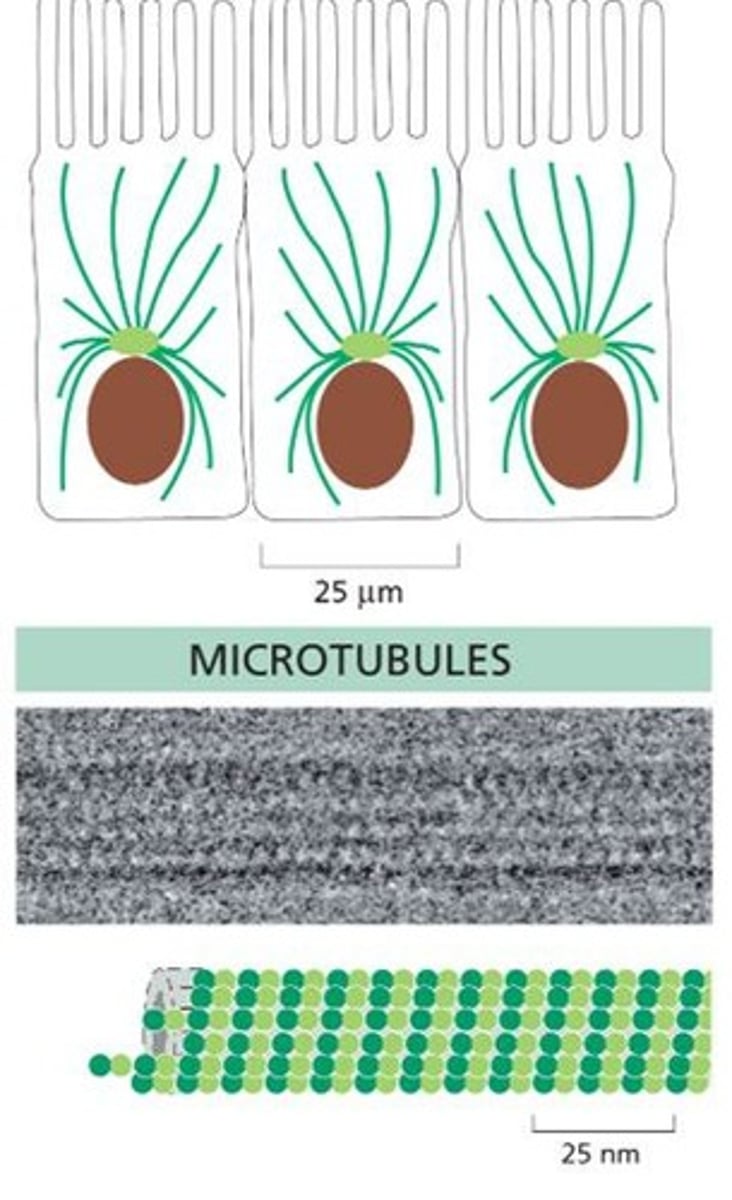
What are the subunits of microtubules?
tubulin dimers, specifically alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin.
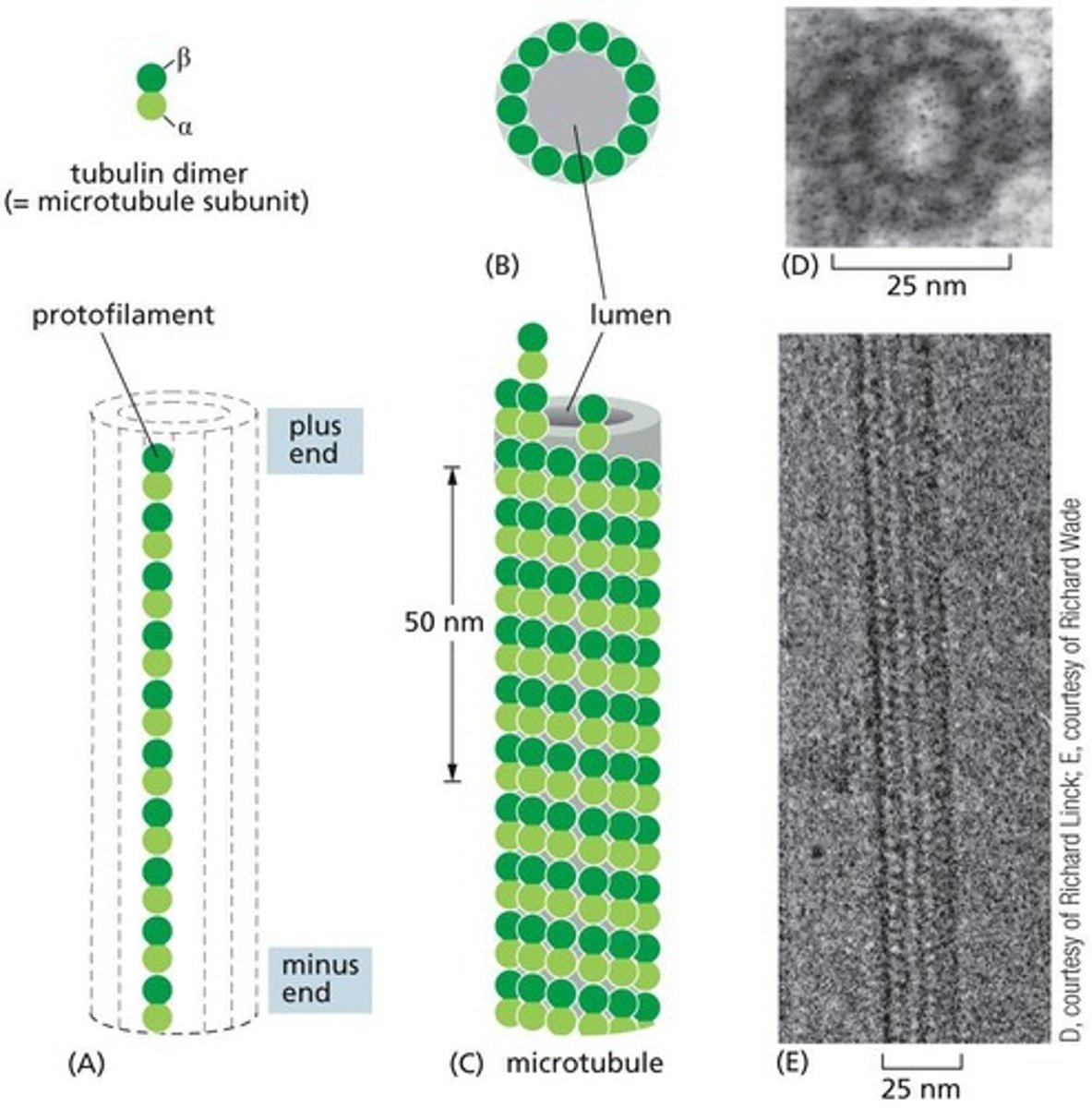
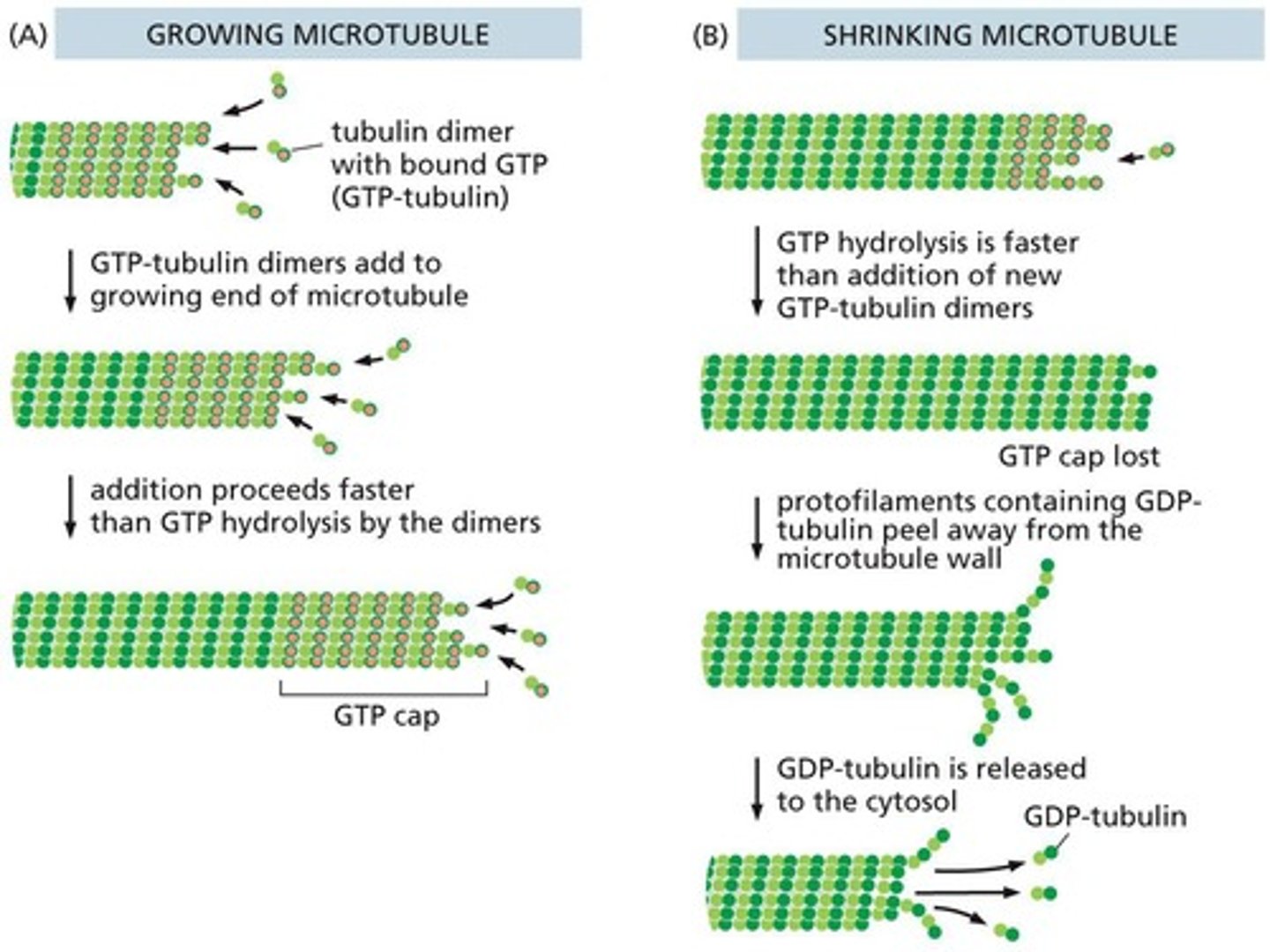
How does GTP affect microtubule dynamics?
GTP-bound tubulin dimers add to the plus end of microtubules, while hydrolysis to GDP destabilizes the interaction, leading to potential shrinkage.
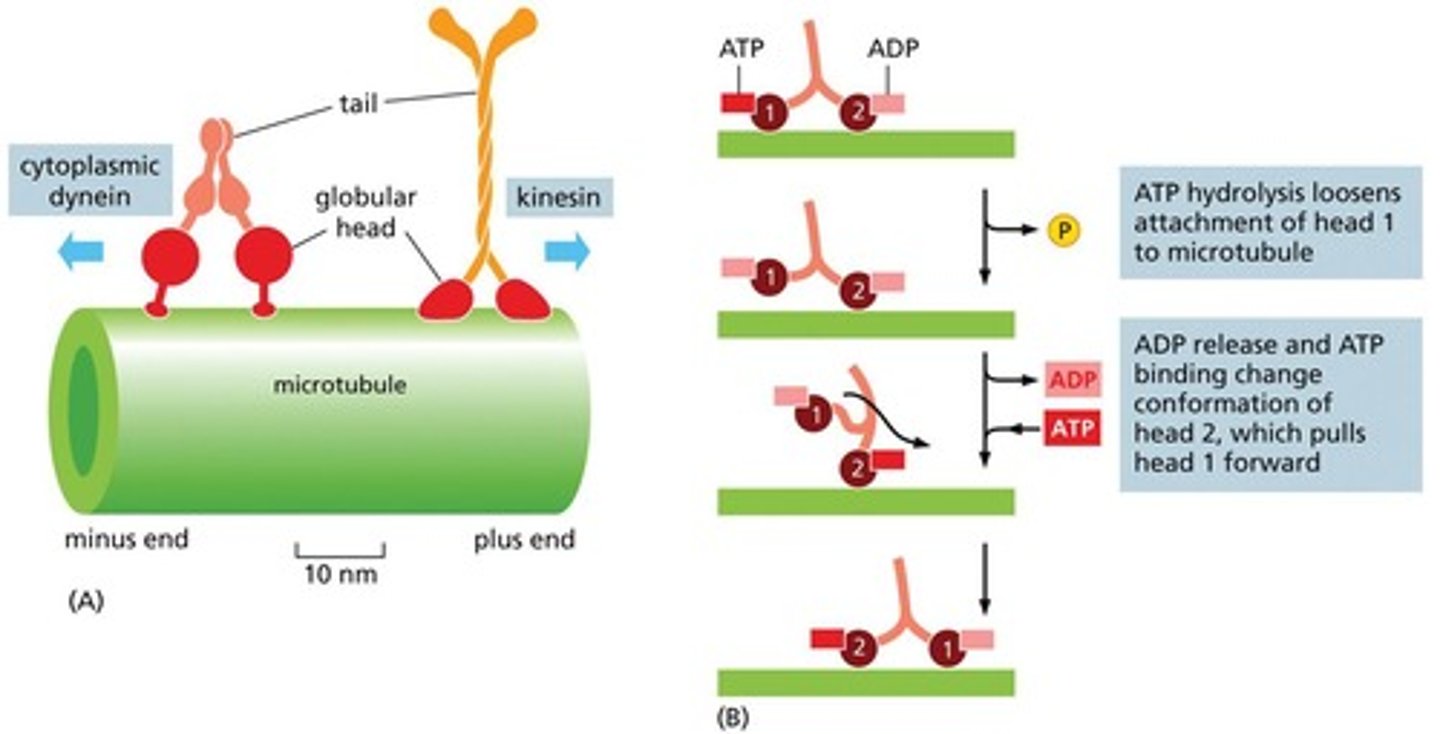
What are the two main types of motor proteins associated with microtubules?
Dynein, which moves toward the minus end, and kinesin, which moves toward the plus end.
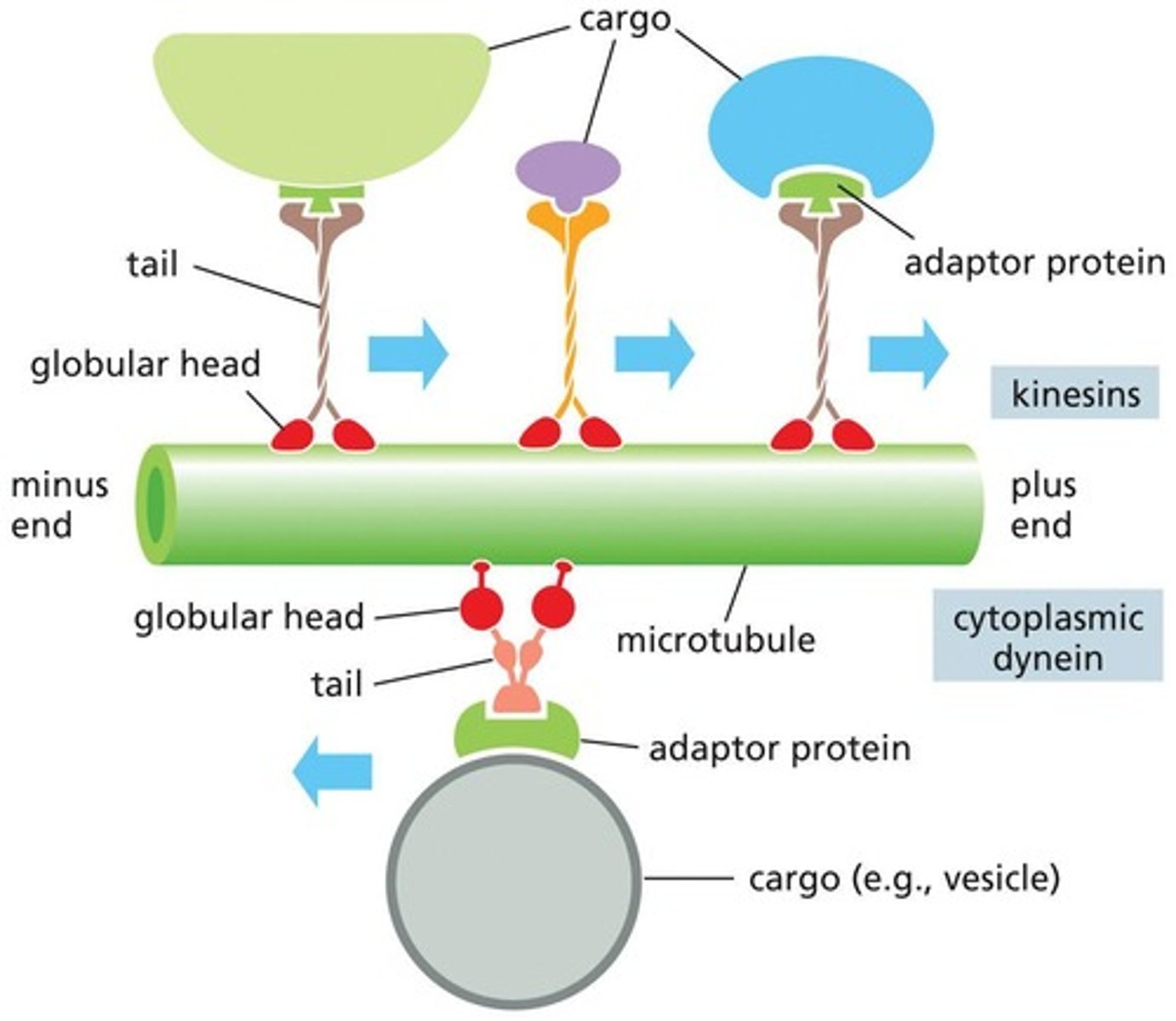
What is the role of motor proteins in vesicular transport?
transport vesicles along microtubules, using energy to move along the filament tracks.
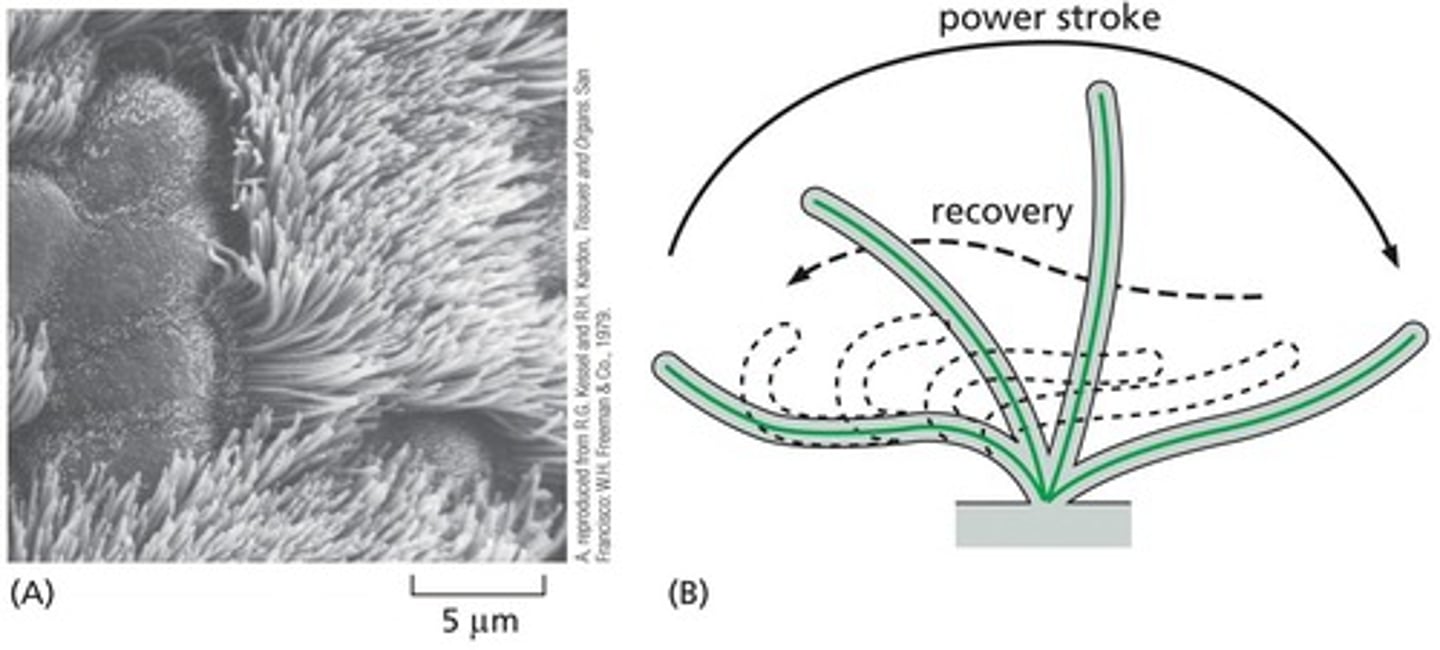
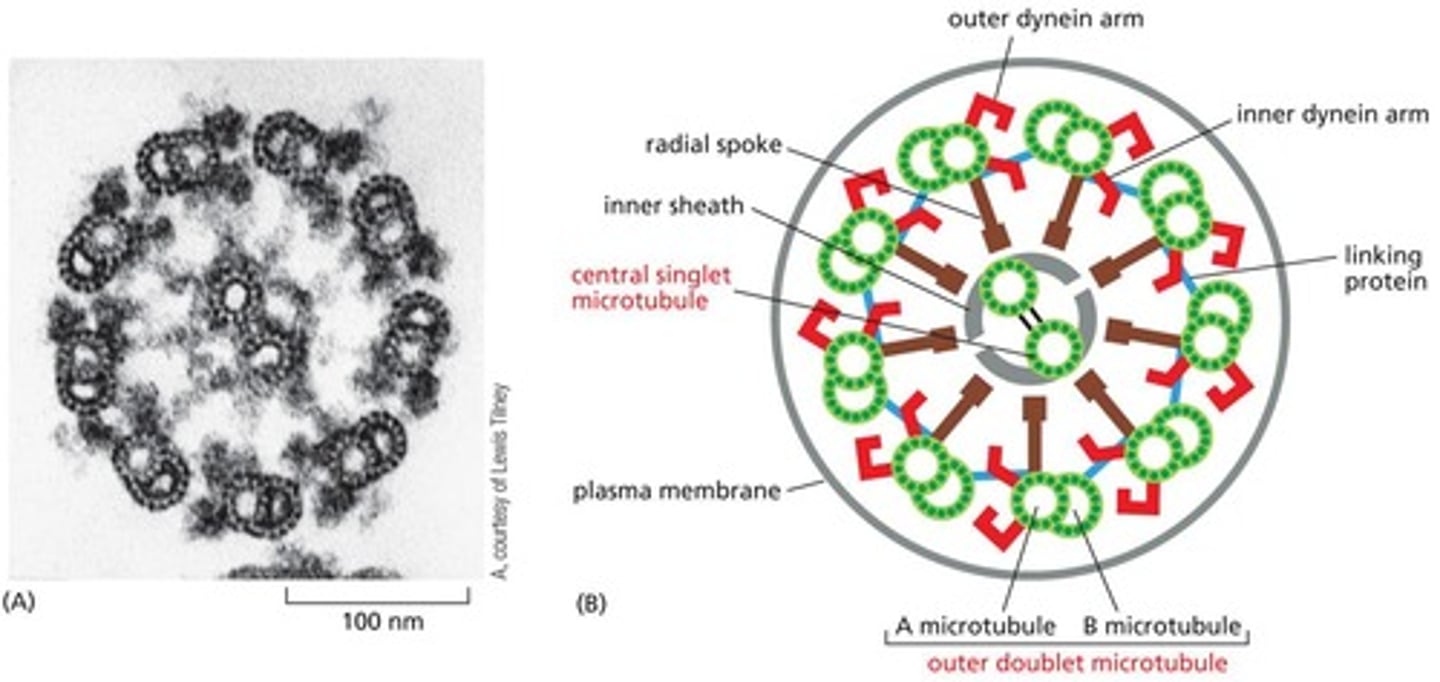
What are cilia and flagella composed of?
They are composed of microtubules arranged in a specific pattern, allowing for movement.
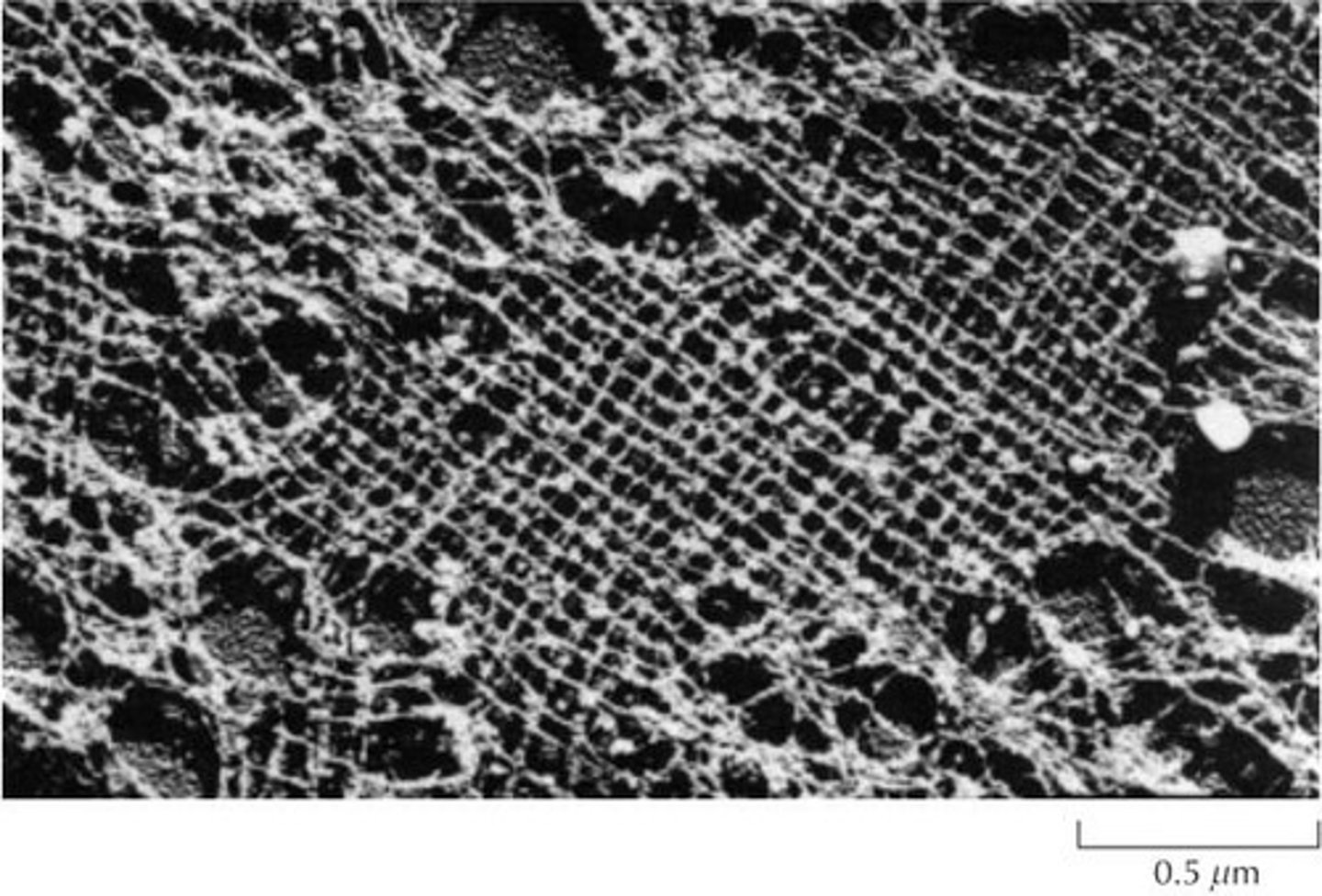
What are actin filaments and their functions?
Are helical polymers that play roles in cell shape, movement, and division.

What is the structure of actin filaments?
They are made of globular actin (G-actin) that polymerizes to form filamentous actin (F-actin).
What is treadmilling in actin filaments?
refers to the dynamic process where actin filaments grow at one end while simultaneously disassembling at the other.
How do myosin motor proteins interact with actin filaments?
They walk toward the plus end of actin filaments, facilitating movement and contraction.
What triggers muscle contraction?
The release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which interacts with the troponin complex.
What is the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
blocks myosin binding sites on actin; its relocation exposes these sites for myosin interaction during contraction.
What is progeria and its relation to the cytoskeleton?
A premature aging disorder caused by mutations in lamin A genes, affecting the stability of the nuclear lamina.
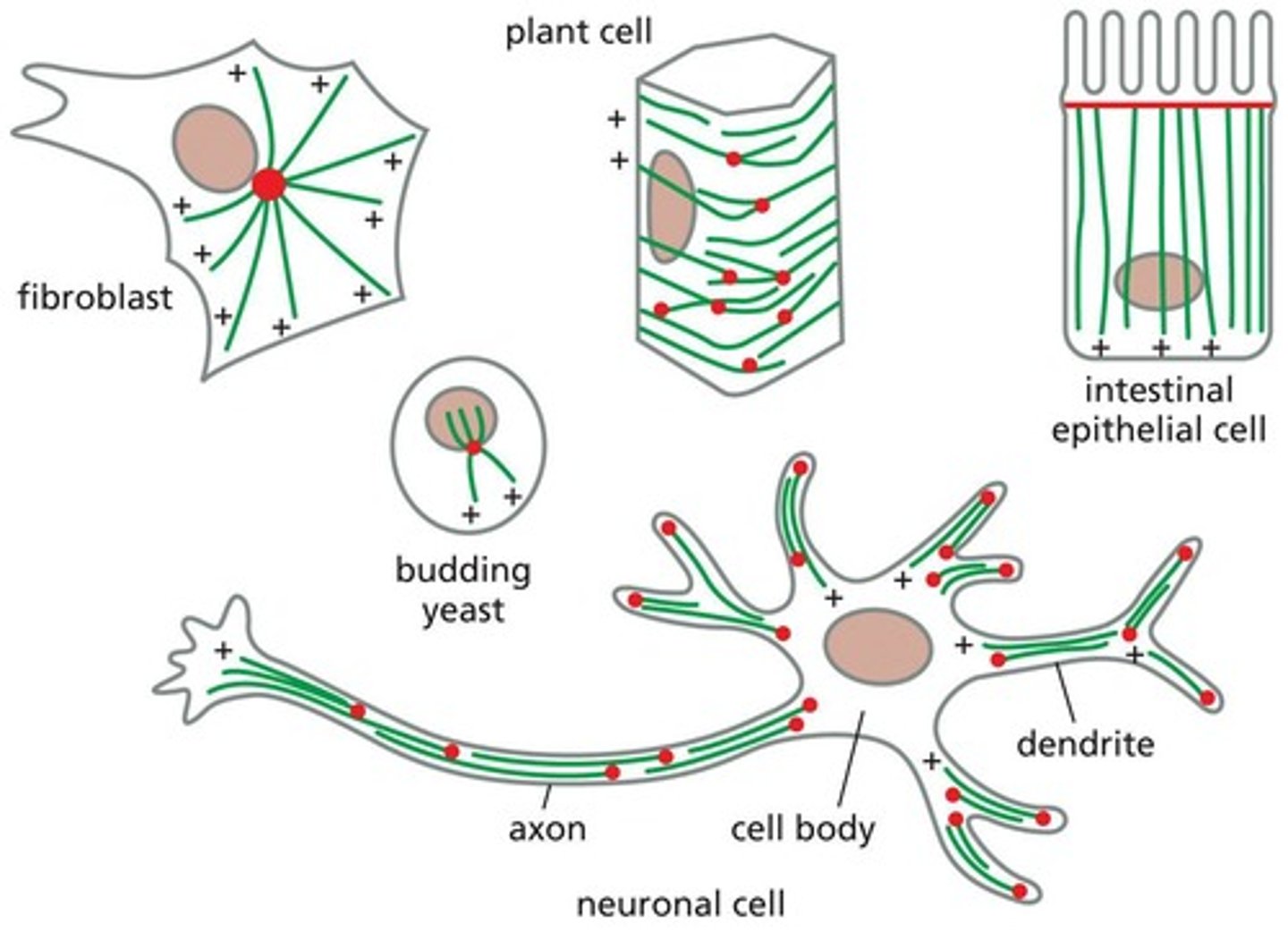
What is the significance of microtubule organization in neuronal axons?
In neuronal axons, microtubules are arranged with their plus ends toward the axon terminal, facilitating the transport of vesicles.
How does the concentration of GTP-tubulin affect microtubule stability?
High concentrations of GTP-tubulin promote microtubule growth, while low concentrations lead to shrinkage due to increased dissociation rates.
What is the structure of myofibrils in muscle cells?
composed of actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments), which interact to produce muscle contraction.
What are the roles of actin-binding proteins?
regulate actin polymerization, depolymerization, and interactions with other proteins, including motor proteins.
What is the role of dynein in cilia and flagella movement?
Causes linked microtubules to slide against each other, resulting in bending and movement of cilia and flagella.