EGRB 310 - Unit 1 Terms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
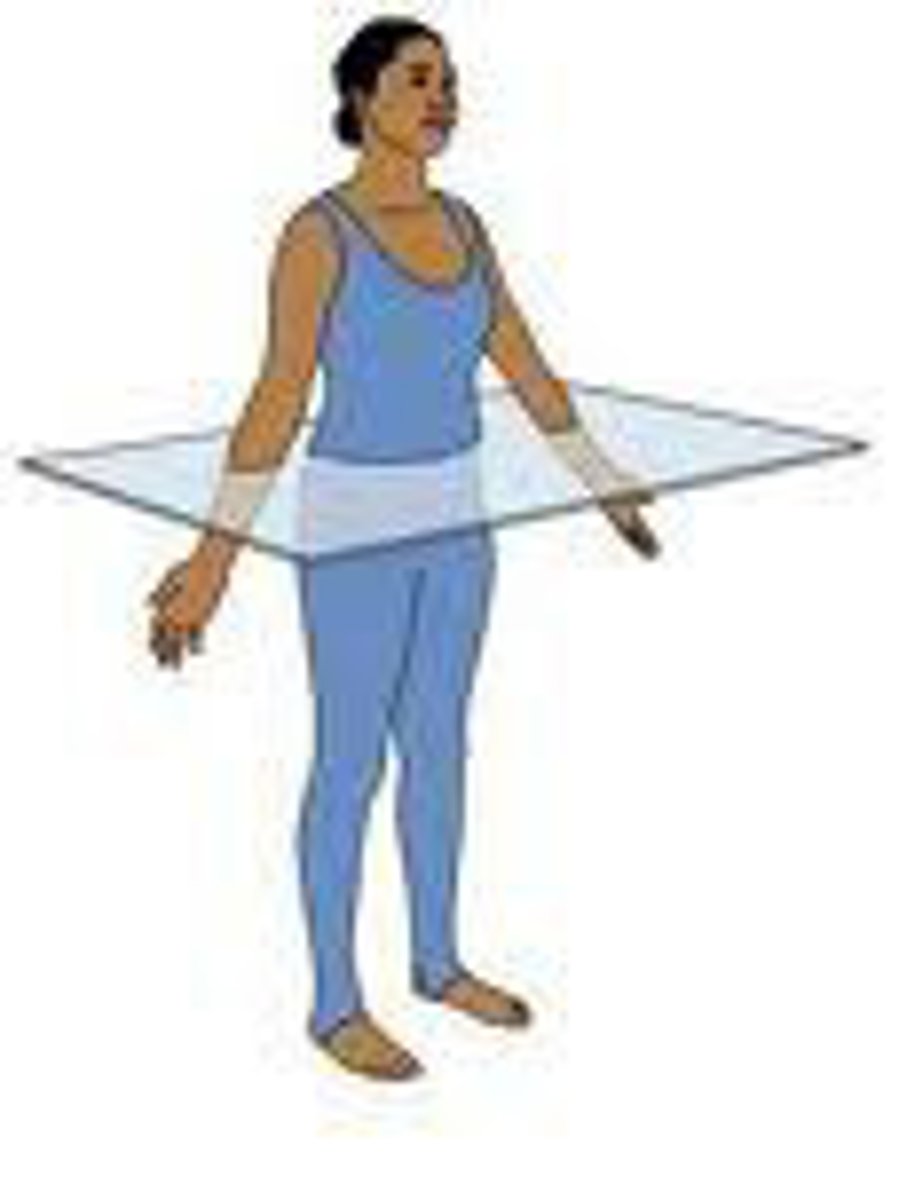
Transverse
Plane of the body that slices parallel to the ground.
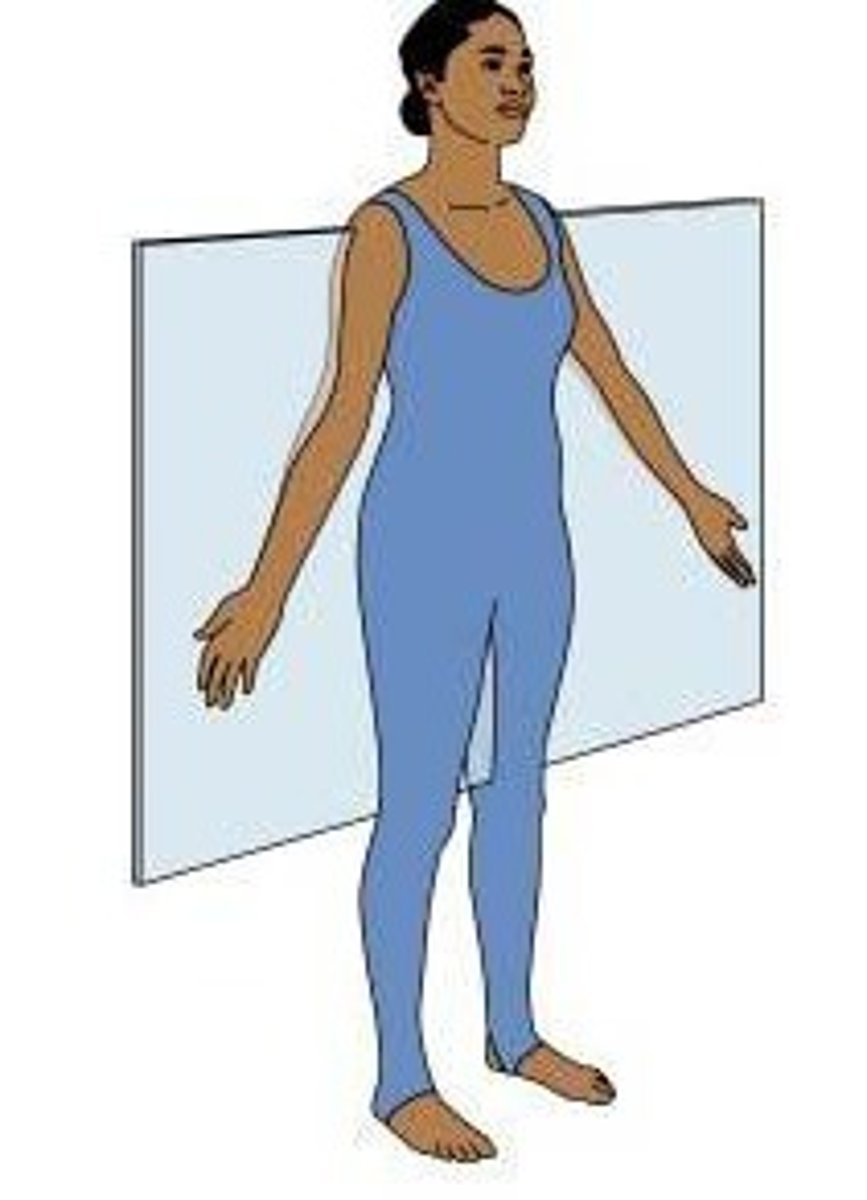
Coronal
Plane of the body that shows the front view.
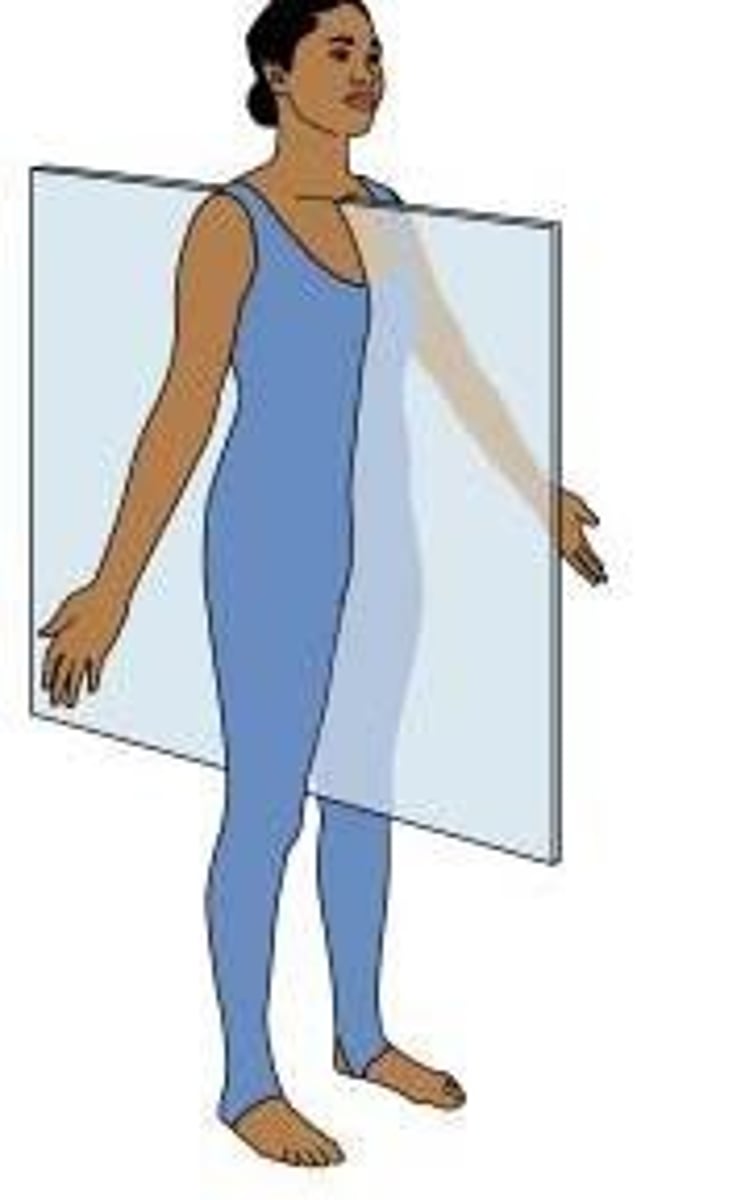
Sagittal
Plane of the body that shows the side view.
Superior
Upward (hip to head) direction in the coronal view.
Inferior
Downward (hip to feet) direction in the coronal view.
Lateral
Away from the midline in the coronal view. Also describes rotation in that direction.
Medial
Towards the midline in the coronal view. Also describes rotation in that direction.
Anterior
Away from the body in the forwards direction, sagittal view.
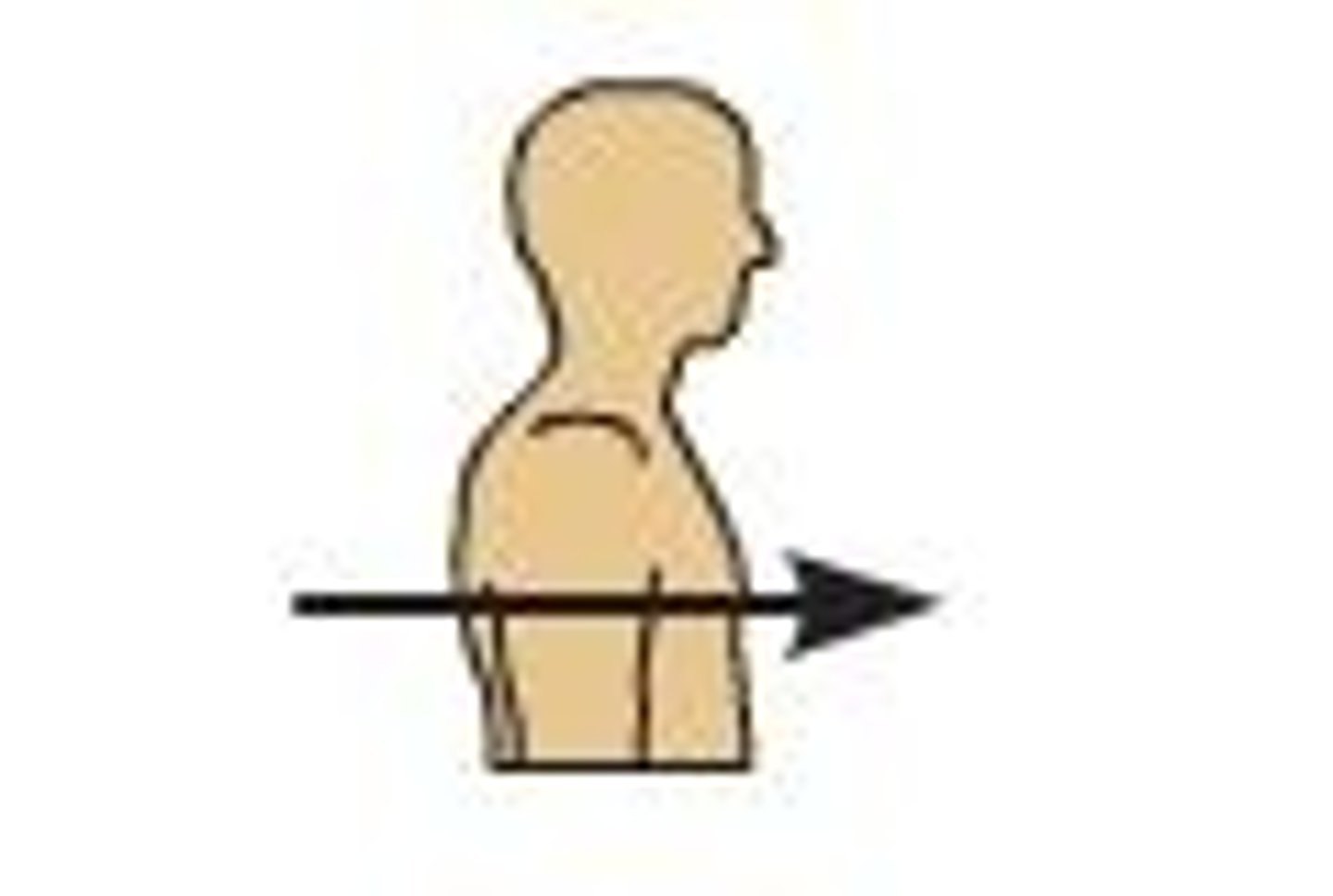
Posterior
Away from the body in the backwards direction, sagittal view.
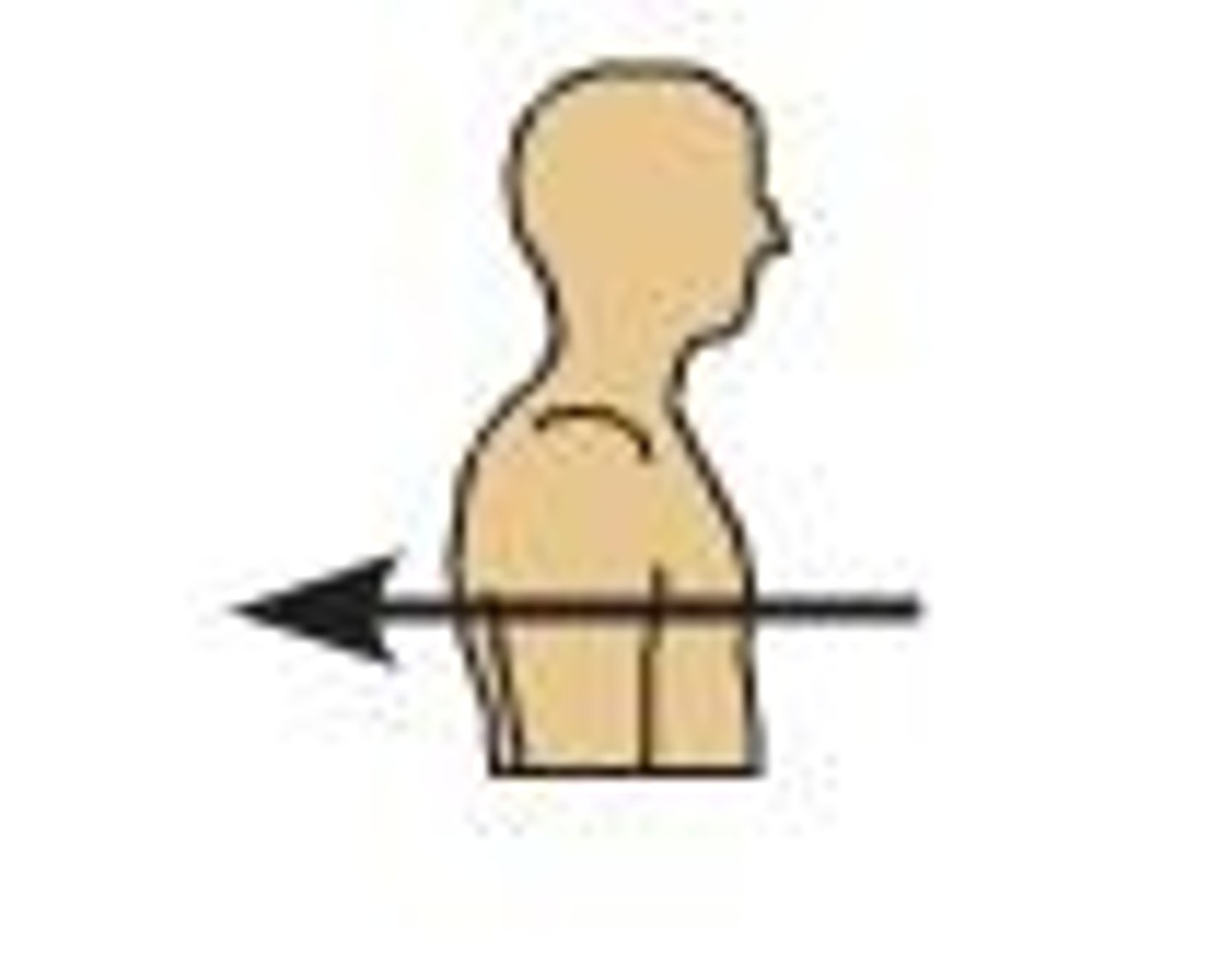
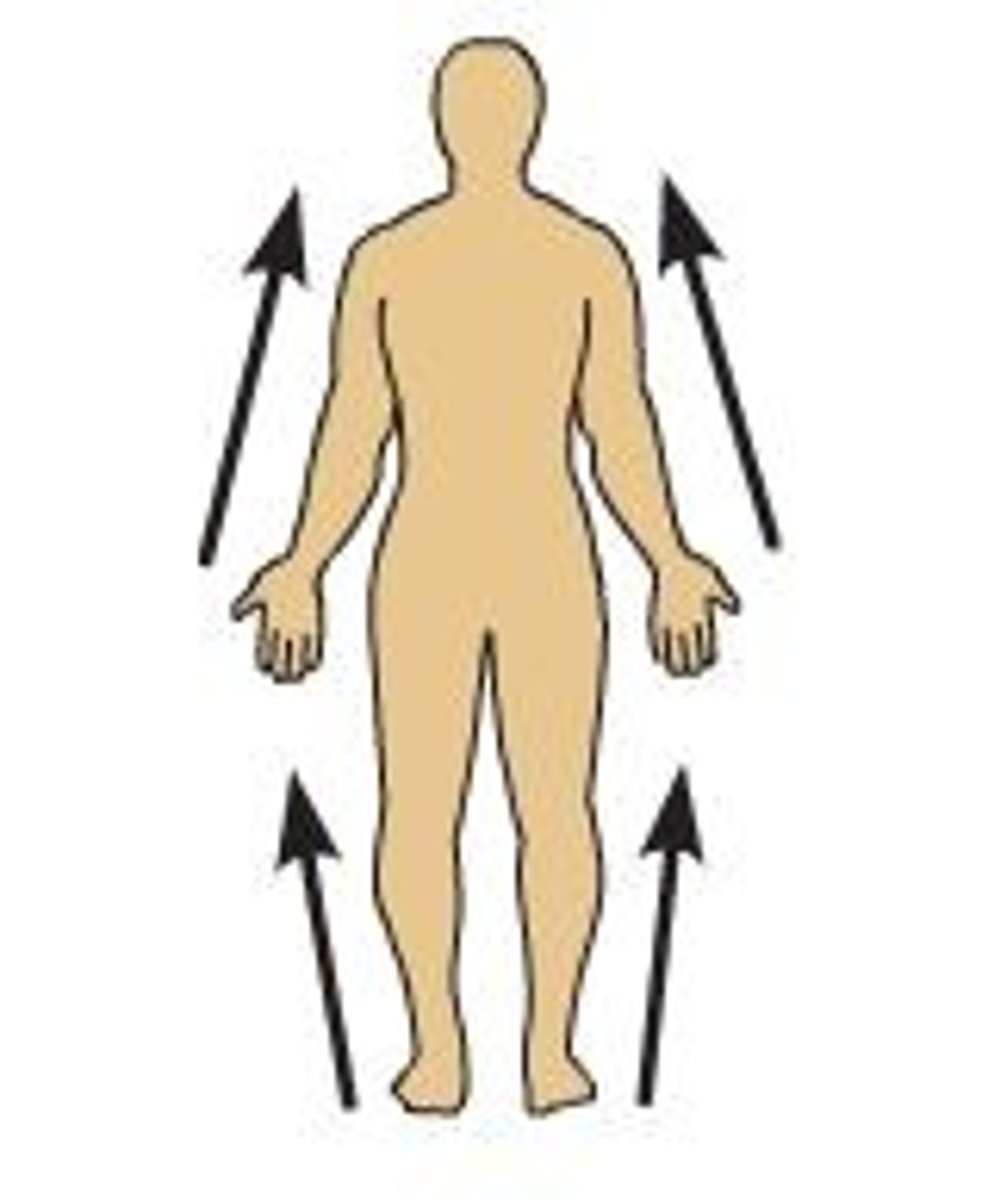
Proximal
Direction towards the body, along a limb.
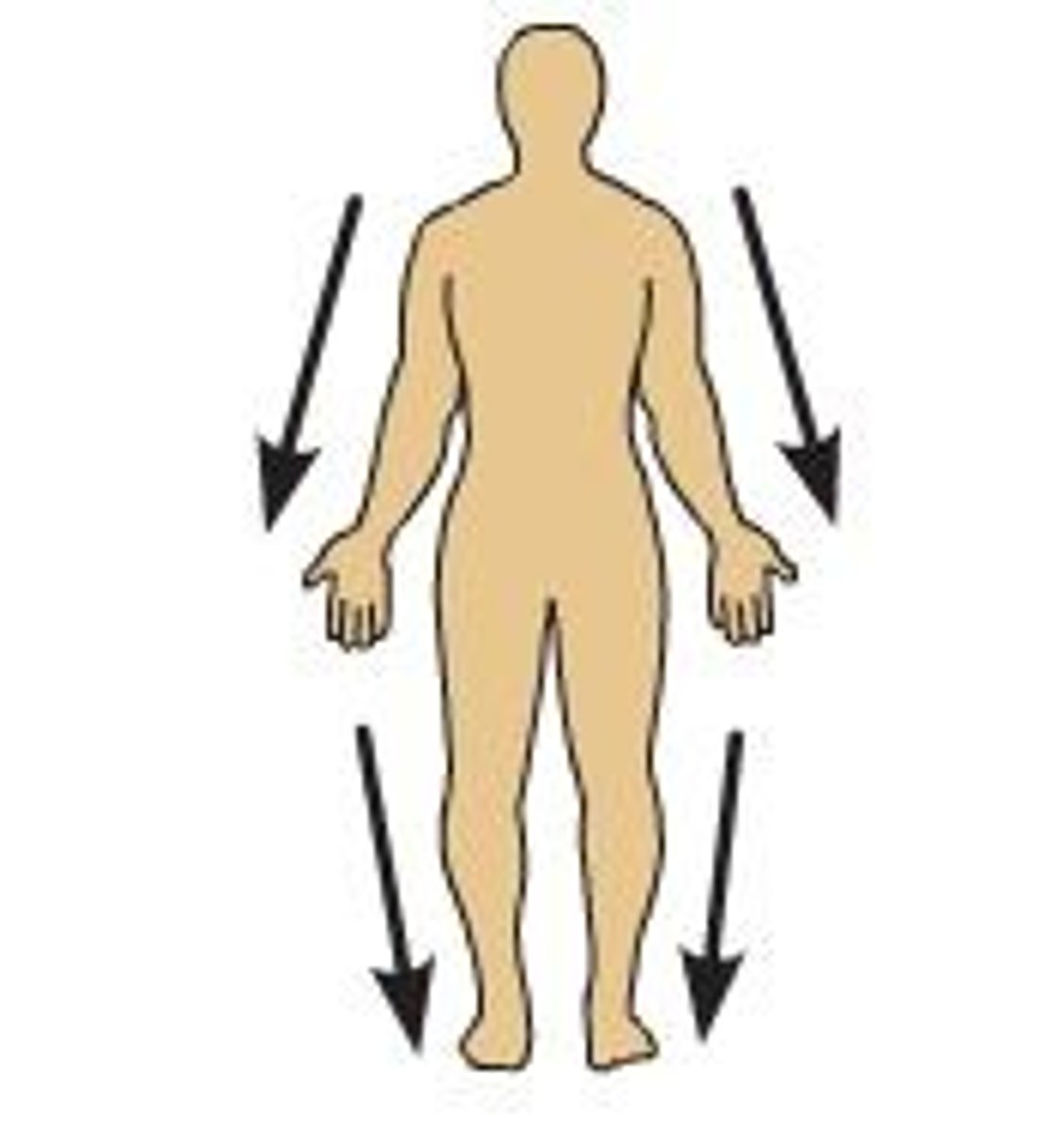
Distal
Direction away from the body, along a limb.
Flexion
Movement that closes the joint.
Extension
Movement that opens the joint.
Abduction
Movement away from the body.
Adduction
Movement towards the body.
Pronation
Rotational movement in the arm that turns the palms down.
Supination
Rotational movement in the arm that turns the palms up.
Synarthrodial
Type of joint with effectively no motion.
Connected with connective tissue.
Ex. suture connections in the skull
Amphiarthrodial
Type of joint that's held together by cartilage.
Ex. vertebral column
Diarthrodial
Type of joint that is able to move, 6 types.
Membrane-bound region of synovial fluid.
Ex. fingers
Hinge
Type of diarthrodial joint with uniaxial flexion/extension (only moves in 1 direction).
Ex. elbow
Pivot
Type of diarthrodial joint with uniaxial rotation (about 1 axis).
Ex. c1-c2 joint in spine (atlantoaxis joint)
Saddle
Type of diarthrodial joint with biaxial motion (motion in 2 directions that combines into circular motion).
Ex. carpometacarpal joint in thumb
Condyloid
Type of diarthrodial joint with biaxial motion (motion in 2 directions that combines into circular motion).
More restricted movement.
Ex. knee
Ball + Socket
Type of diarthrodial joint with multiaxial movement that allows for full rotation.
Ex. shoulder, hip
Plane
Type of diarthrodial joint with multiaxial movement caused by sliding planes.
Ex. acromioclavicular joint
Skeletal
Muscle type with voluntary movement and striated structure.
Smooth
Muscle type with involuntary movement and unstriated structure.
Ex. stomach walls
Cardiac
Muscle type with involuntary movement and striated structure.
Ex. heart
Concentric
Type of muscle contraction that causes the muscle to shorten.
Eccentric
Type of muscle contraction that causes the muscle to lengthen.
Isometric
Type of muscle contraction that doesn't change the length.
Agonist
Type of muscle that causes movement through contraction.
Antagonist
Type of muscle that opposes the action of another muscle.
Synergist
Type of muscle that compliments the contraction of other muscles.
Fossa
Cavity/depression in the bone.
Process
Extension off a bone.