Stage 1: Dilation Stage
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Timeframe
Can last up to 29 hours (longest stage)
Begins: Onset of true labor contractions.
Ends: Full cervical dilation (10 cm) and 100% effacement.
How many phases are there?
2 phases: Latent Phase and Active Phase
Latent Phase
0–6 cm
Contractions: Irregular → become more regular.
Mom: Excited, talkative, some nesting behavior.
Discharge: Bloody show, mucous plug loss.
Cervical change = effacement first, then dilation.
Active Phase
6–7 cm (8-10cm is transitional)
Contractions: Stronger, every 2–3 minutes.
Pain more intense → increased need for support.
Fetal presenting part descends.
Mom: More focused, may become anxious.
Maternal Changes
↑ Cardiac output, stroke volume, and heart rate (returns to baseline between contractions).
↑ Oxygen use → risk of hyperventilation.
Delayed gastric emptying, N/V possible.
↑ Proteinuria, risk of incontinence.
Endocrine: ↑ estrogen, prostaglandins, oxytocin.
Fetal Adaptations
Transient hypoxia with contractions.
↓ fetal breathing movements.
Head molding, sutures overlap.
May pass meconium.
Nursing Care
Assess contractions: frequency, duration, intensity, resting tone.
Monitor fetal heart rate and variability (110–160 bpm is normal).
Vaginal exam (dilation, effacement, station, membranes).
Labs: GBS, Rh, HIV, Hep B, CBC, rubella, STIs.
Comfort: breathing techniques, ambulation, positioning, hydration, hygiene.
Pain: consent, epidural, IV meds as ordered.
Support: education, encouragement, reassurance.
Maternal Care
Encourage ambulation, upright positions (walking, squatting, kneeling).
Monitor VS, contractions, fetal heart rate.
Vaginal exam for dilation, effacement, station, and membranes.
Pain relief: breathing techniques, meds, epidural.
Support, reassurance, hydration, hygiene.
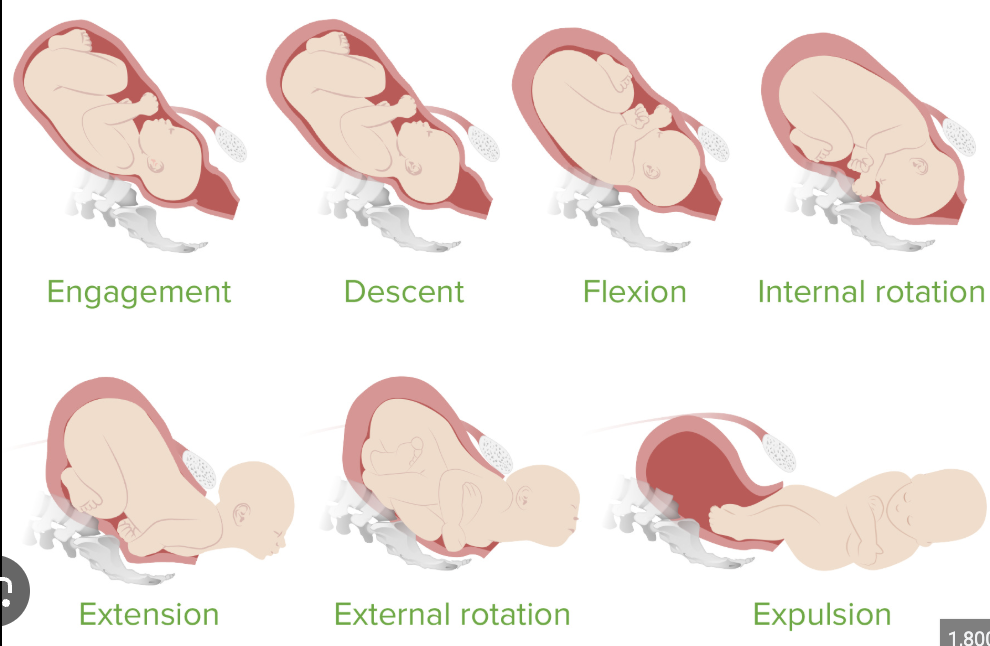
Labor Stages
Engagement
Descent
Flexion
Internal Rotation
Extension
External Rotation
Expulsion