Microscopes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
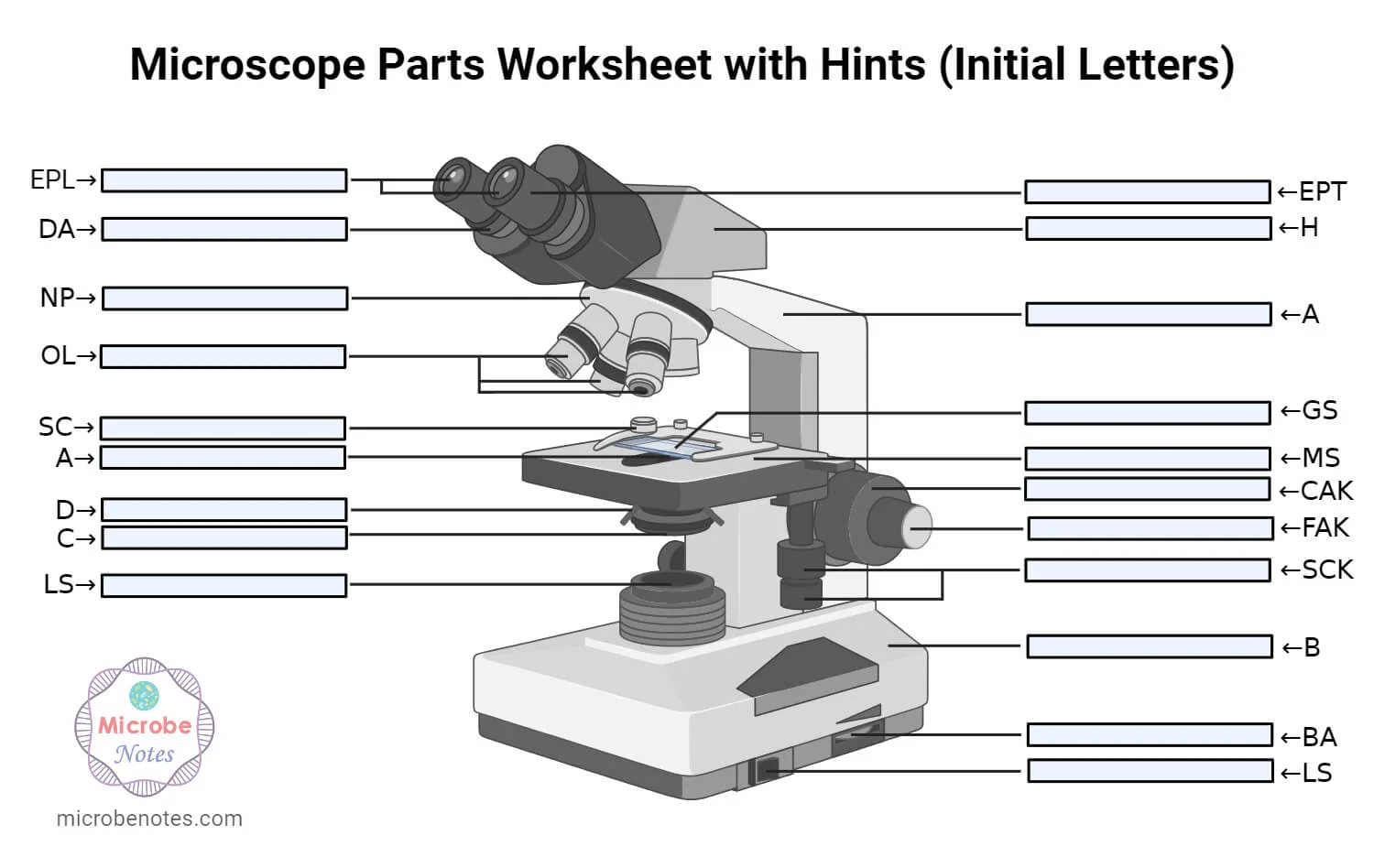
Head
is a cylindrical metallic tube that holds the eyepiece lens at one end and connects to the nose piece at other end. It is also called a body tube or eyepiece tube.
Arm
This is the part connecting the base to the head and the eyepiece tube to the base of the microscope. It supports the head of the microscope and is also used when carrying the microscope.
Base
is the lowermost part of the microscope that supports the entire microscope structure. It provides stability for the microscope.
Eyepiece
is closest to the viewer’s eye. They are located at the top of the microscope. This part is used to look at the specimen. These lenses come in different magnification powers from 5X to 30X, but the most common ocular lenses are of 10X or 15X magnification. They magnify the image for the second time.
Eyepiece tube
It’s the eyepiece holder. It carries the eyepiece just above the objective lens.
Diopter Adjustment
is a control knob present only in the binocular microscope that is used to change focus on one eyepiece. It is used to correct any difference in vision and compensate for the differences in vision between the viewer’s two eyes.
Nose piece
a movable circular structure that houses all the objective lenses. It is also called the revolving turret. It is connected to the body tube and lies just above the stage. It can be rotated clockwise or counterclockwise to increase or decrease the magnification.
Objective lenses
is the lens that is closest to the specimen. They are fitted on the nosepiece. A standard microscope has 3 to 4 objective lenses of different magnifying powers: 4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X.
Fine Adjustment Knob
It is a smaller knob and is used to move the stage up or down very slowly. The stage covers a very small distance on each rotation of the adjustment knob. It is used to sharpen the image. It is mostly used while viewing under high power.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
is used for focusing the image under low power magnification. It is a larger knob and is used to move the stage up or down very rapidly. The stage is raised or lowered rapidly with the help of a coarse adjustment knob.
Stage
This is the section in which the specimen is placed for viewing. They have stage clips that hold the specimen slides in place. The most common stage is the mechanical stage, which allows the control of the slides by moving the slides using the mechanical knobs on the stage instead of moving them manually.
Stage Control Knobs
are the control knobs used to move the stage mechanically. There are two knobs; one for moving left and right and the other for moving forward and backward. This will move the slide in the field of vision.
Aperature
This is a hole in the microscope stage through which the transmitted light from the source reaches the stage.
Microscopic illuminator
is a light source. In some compound microscopes, a mirror, which reflects the light from an external source to the sample, is used. In other optical microscopes, different electric bulbs of low voltages are used as a constant light source.
Condenser
These are lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen. They are found under the stage next to the diaphragm of the microscope. They play a major role in ensuring clear, sharp images are produced with a high magnification of 400X and above. The higher the magnification of the condenser, the clearer the image.
Diaphragm
It’s also known as the iris. It is found under the stage of the microscope, and its primary role is to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. It’s an adjustable apparatus, hence controlling the light intensity and the size of the beam of light that gets to the specimen.
Condenser focus knob
This is a knob that moves the condenser up or down, thus controlling the focus of light on the specimen.
Abbe condenser
This condenser specially designed for high-quality microscopes makes the condenser movable and allows very high magnification above 400X. High-quality microscopes normally have a higher numerical aperture than objective lenses.