Sensory Spinal Cord (Pavlick)
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pavlick
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Somatosensation
1st order neuron in _____-
2nd order neuron in ________
3rd order neuron in ________
Terminate in somatosensory cortex (post-central gyrus)
DRG
Spinal cord (decussates)
Thalamus
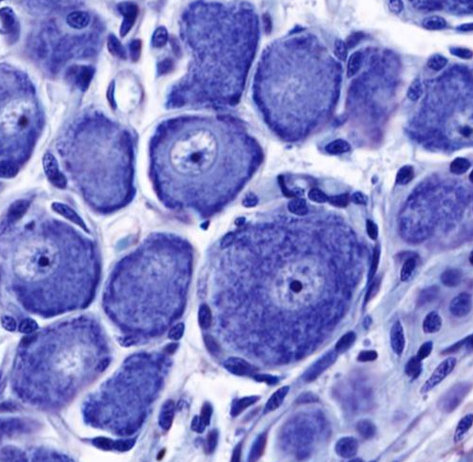
DRG
egg with halo of satellite cells
Pacinian corpuscle
Vibration
Ruffini ending
Skin stretch
Free nerve ending
nociception
Meissner’s corpuscle
movement across skin (slippage)
Merkel disc
light pressure, edges (reading Braille)
Golgi tendon organ
tension
Muscle spindle
changes in muscle length and rate of length change
First order neuron that conveys ________ stimulus
environmental
Proprioception, 2-point discrimination, vibration
Dorsal Column- Medial Lemniscus
Dorsal Column- Medial Lemniscus detects
Proprioception, 2-point discrimination, vibration
Nociception (pain), temperature, crude touch
Spinothalamic (Anterolateral)
Spinothalamic (Anterolateral) detects
Nociception (pain), temperature, crude touch
Unconscious proprioception/balance
Spinocerabellar tracts
Spinocerabellar tracts does
Unconscious proprioception/balance
Dorsal column in spinal cord get name change in sensory decussation in caudal medulla to the _____ ______
medial lemniscus
not actively thinking about needing to stay in the center and which muscles to contract
Spinocerabellar tract
Responsible for transmitting proprioception, 2-point discrimination, and fine touch
Dorsal-Column Medial-Lemniscus (DCML)
Dorsal-Column Medial-Lemniscus (DCML) above T6 travels through _____ fasciculus
Dorsal-Column Medial-Lemniscus (DCML) below T6 travels through _____ fasciculus
cuneate
gracile
gracile fasciculus
What DCML travels through below T6
cuneate fasciculus
What DCML travels through above T6
2nd order neuron for DCML
cuneate or gracile nucleus in caudal medulla
Decussate to ascend contralaterally as medial lemniscus and synapse on 3rd order neurons in VPL of thalamus
DCML
VPL
Ventral posterior lateral
4th order neurons in
primary sensory cortex
Depending on which part of the body it comes from different synapse point in primary _____ cortex
sensory
Incomplete SCI affecting the dorsal columns
Posterior Cord Syndrome
Demyelinating disorders (e.g., B12 Deficiency, multiple sclerosis)
External compression (e.g., tumor)
Loss of blood supply from posterior spinal artery
Neurosyphilis → tabes dorsalis
Causes of posterior cord syndrome
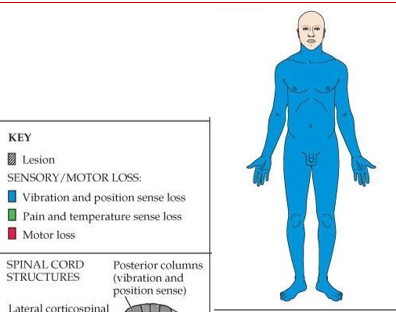
Posterior cord syndrome
Sensory ataxia (coordination difficulties, particularly when visual cues are absent)
Decreased sensation of vibration and fine touch
Posterior cord syndrome
tabes dorsalis
Neurosyphilis
posterior cord syndrome
Responsible for transmitting proprioceptive information
Spinocerebellar tracts
Spinocerebellar tracts 2nd order neuron
nucleus dorsalis
Spinocerebellar tract ascend to enter
cerebellum through cerebellar peduncles
Spinocerebellar tract is from spinal cord to ______
cerebellum
Responsible for transmitting nociception, temperature, and crude touch
Spinothalamic Tracts
Spinothalamic tracts 2nd order neuron is in
substantia gelatinosa
Spinothalamic tract decussates within 1-2 levels through
anterior white commissure
Synapses on 3rd order neurons in VPL of thalamus
DCML and Spinothalamic tracts
Spinothalamic tracts project to 4th order neurons in
primary sensory cortex
With respect to somatosensory homunculus
Noxious stimulus damage to tissues
Nociception
another name for the spinothalamic tract?
Anterolateral
Fluid-filled cyst forms within central canal and compromises anterior white commissure (where spinothalamic tract decussates)
Syringomyelia
“cape” distribution of sensory loss
Syringomyelia
central cord syndrome
pain and temperature loss
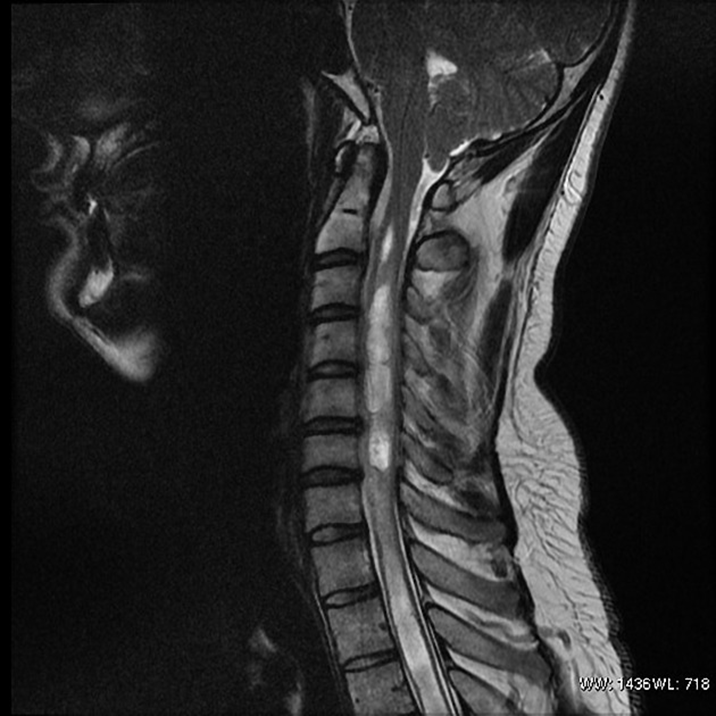
Syringomyelia
central cord syndrome
compromises anterior white commissure of spinothalamic tract
Lesion above motor/sensory decussation will present with motor/sensory deficits ______ to lesion, while lesion below decussation will present with deficits _______ to lesion
contralateral
ipsilateral
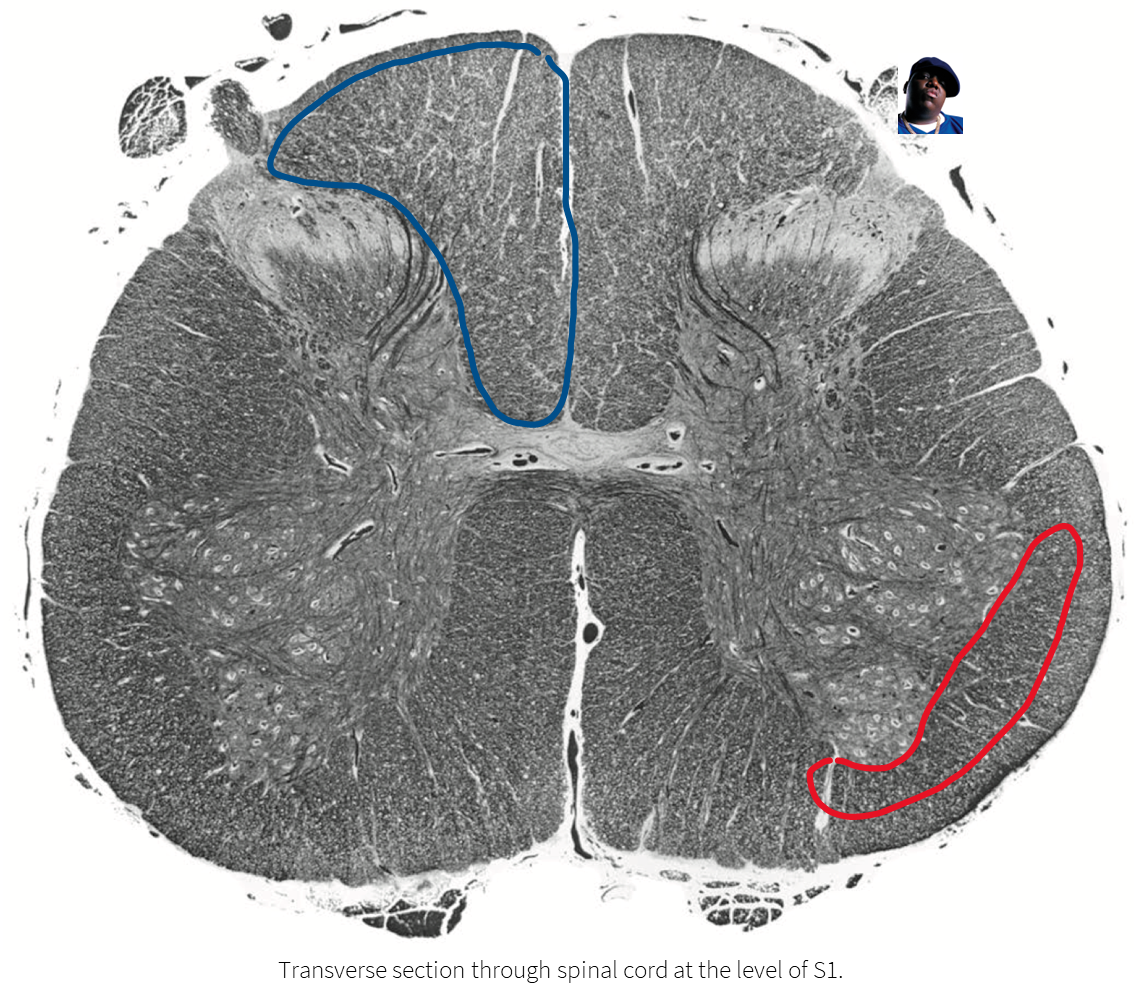
Lumbar spine
Blue DCML
Red ALS spinothalamic tract
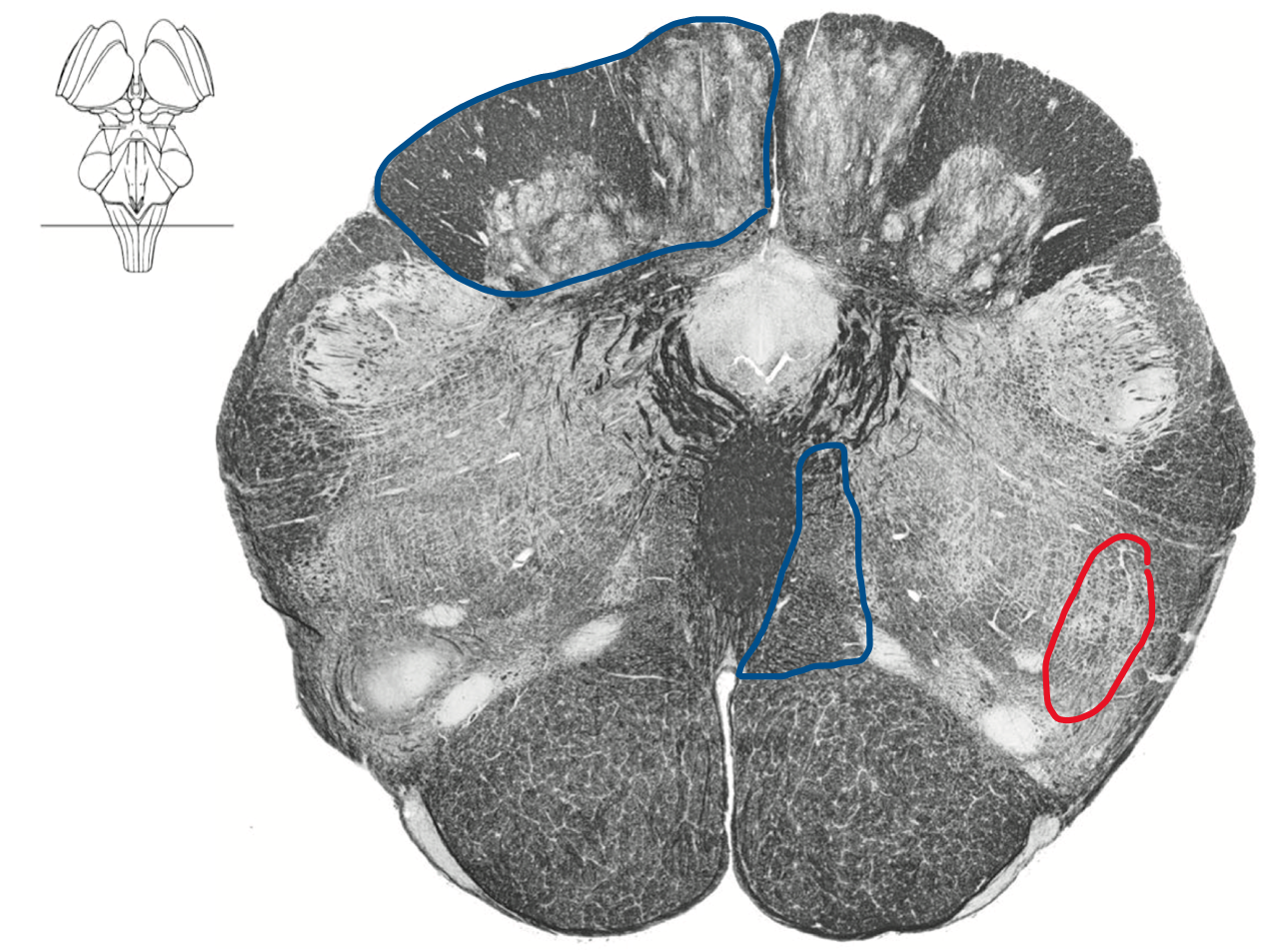
Caudal medulla
Somatic sensory decussation
Blue DCML where dorsal column becomes medial lemniscus
Red ALS spinothalamic tract
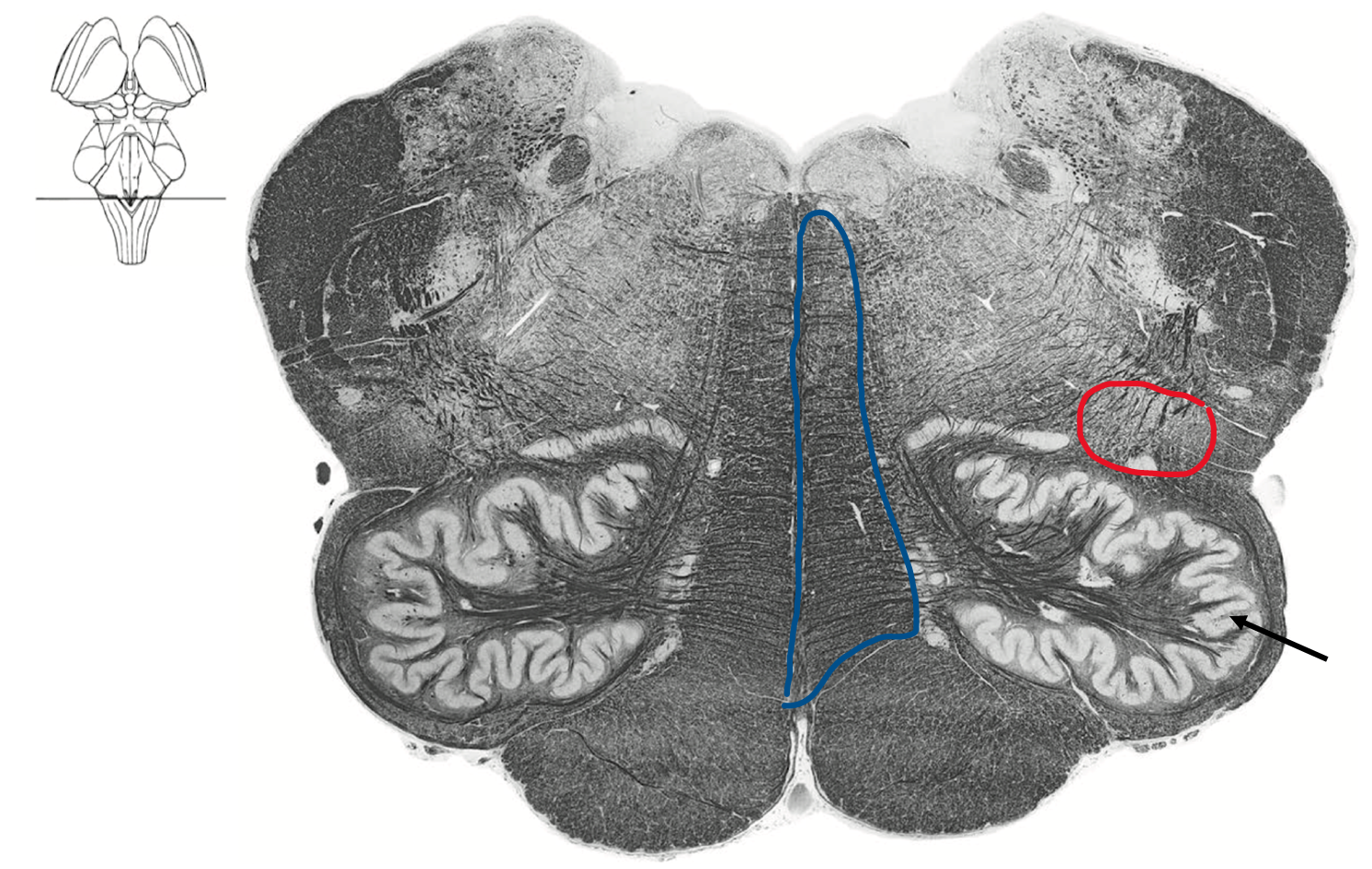
Caudel medulla at Obex (4th ventricle)
Blue medial lemniscus (DCML)
Red ALS spinothalamic tract
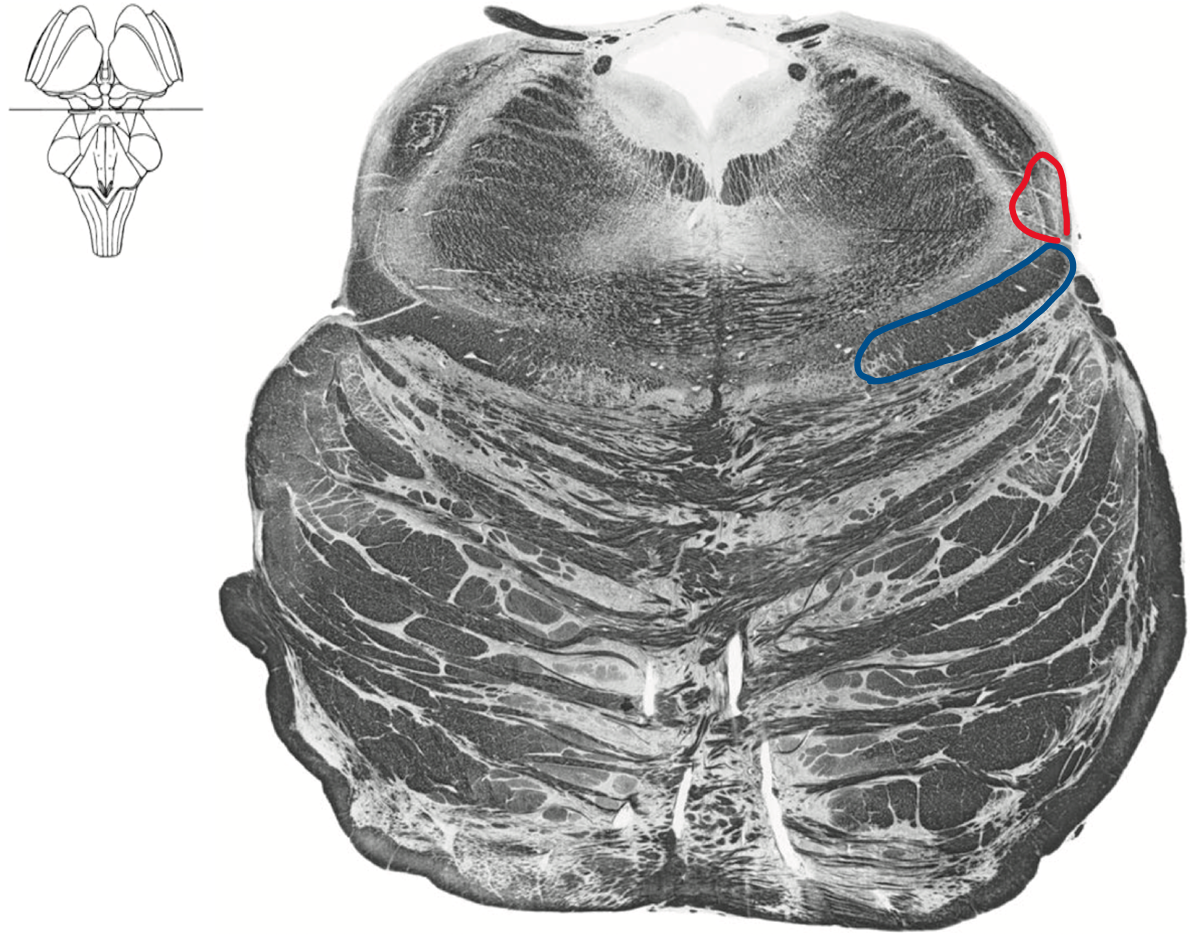
Rostral pons
Boomerang
Blue Ventral medial lemniscus (DCML)
Red ALS spinothalamic tract
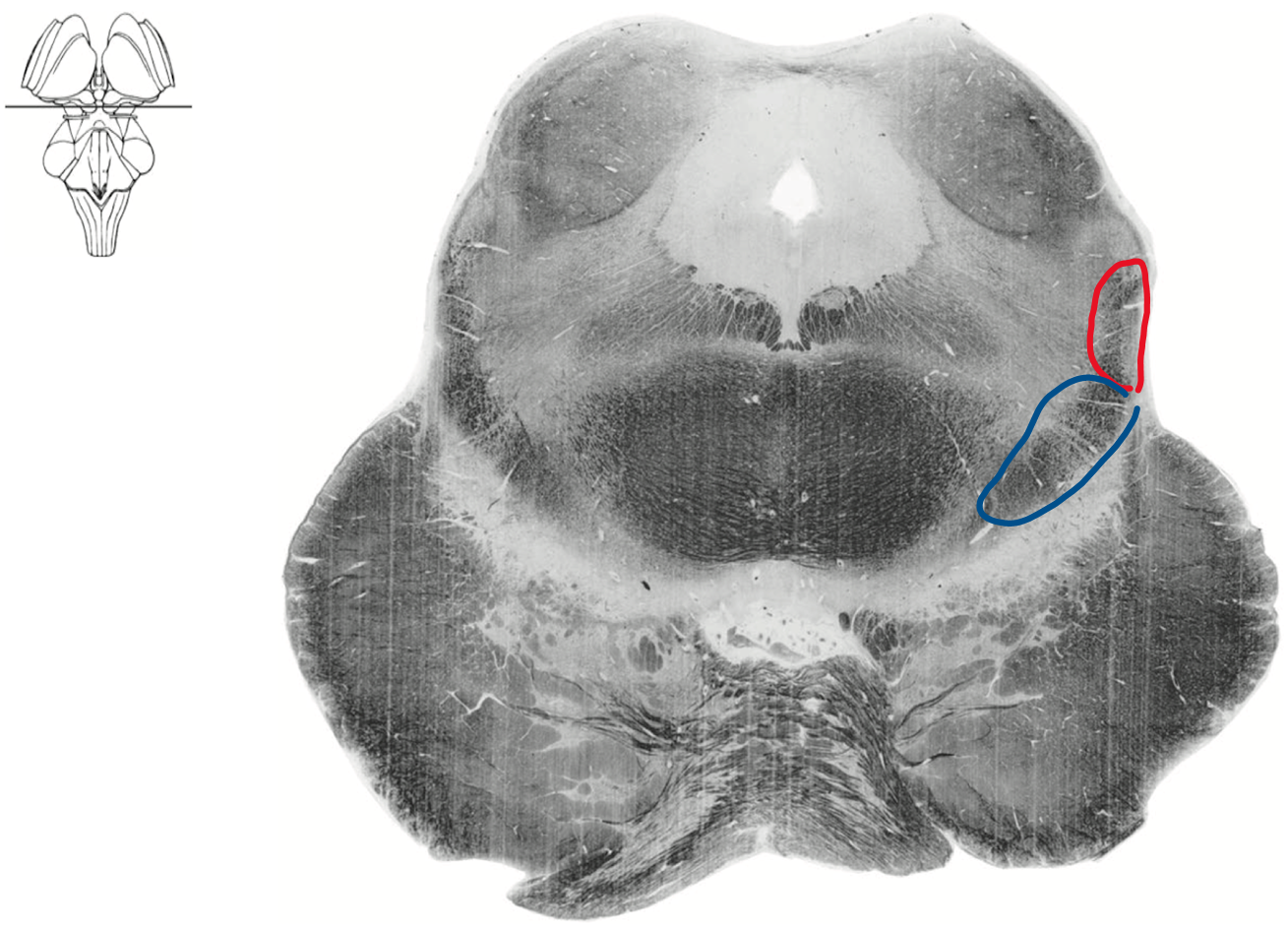
Geisha Caudal midbrain level of inferior colliculus
Boomerang still
Blue medial lemniscus
Red ALS spinothalamic tract
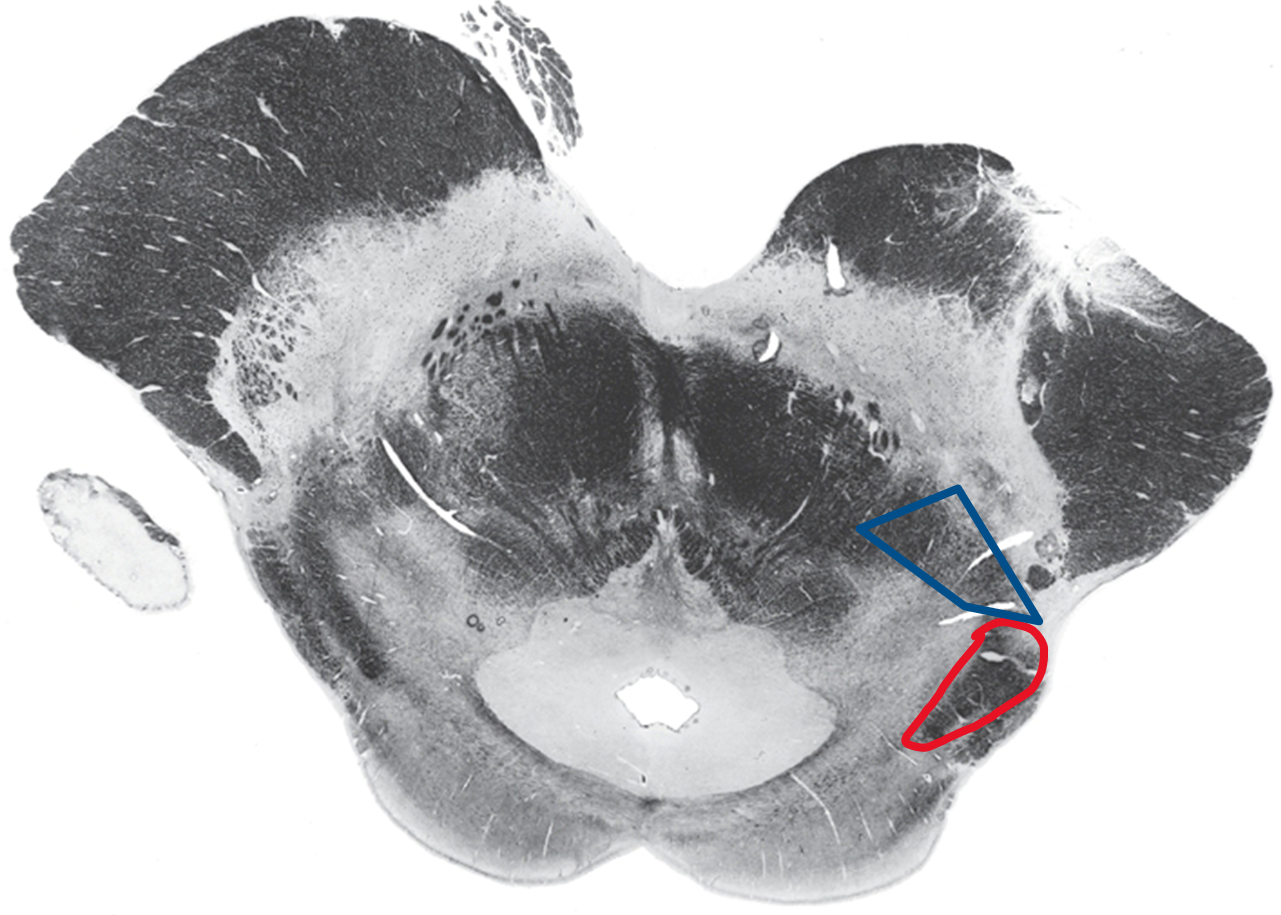
Rostral midbrain level of superior colliculus
Red ALS spinothalamic
Blue Medial lemniscus (DCML)
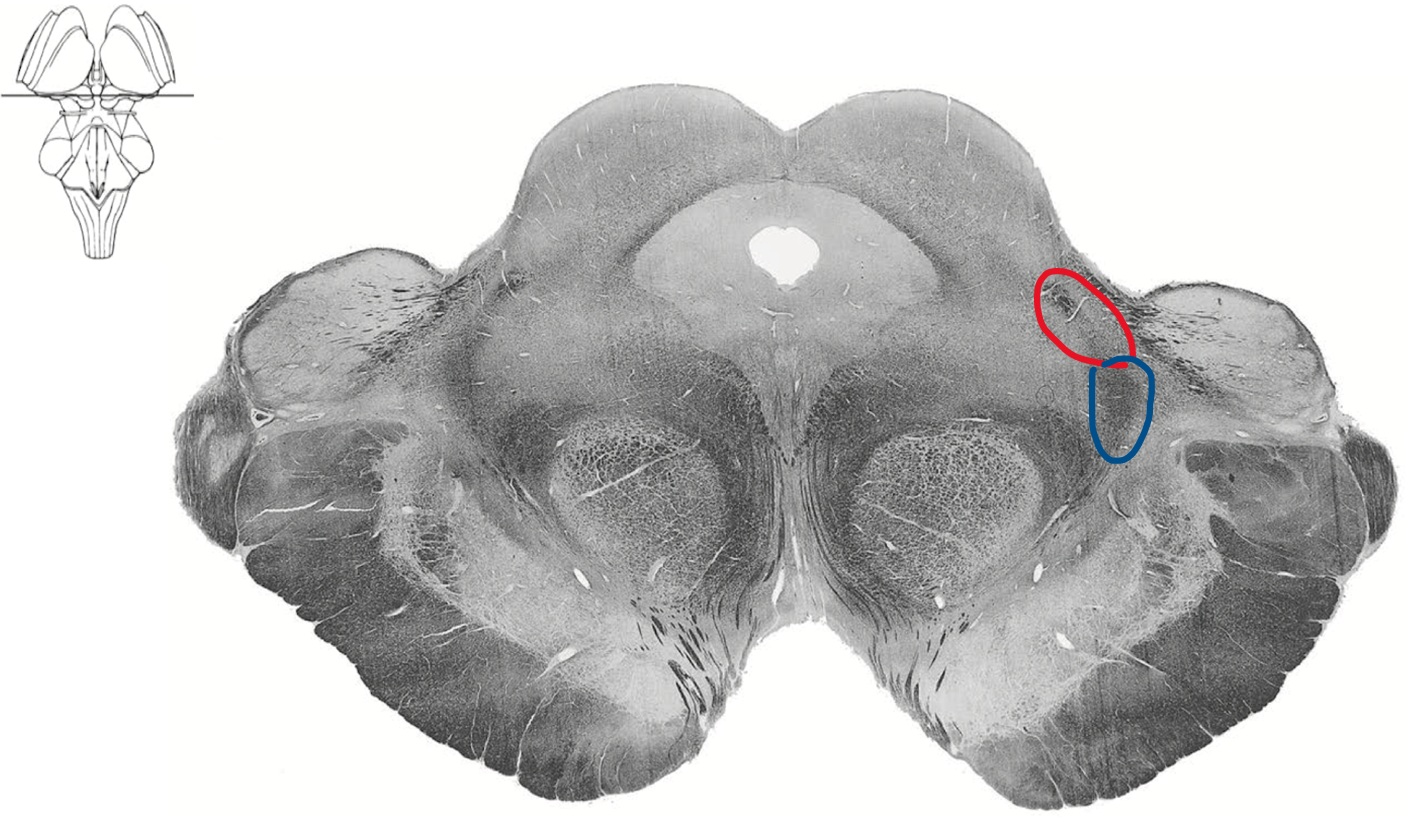
Rostral midbrain level of superior colliculus
Red ALS spinothalamic
Blue Medial lemniscus (DCML)
unpleasant sensory and/or emotional experience which RESULTS FROM THE INTEGRATION of physical stimuli, memory, environment, and/or mental state.
Pain
Pain is a
perception
Midbrain structure which sends descending projections important for pain modulation
Periaqueductal Gray
important for pain modulation
Periaqueductal Gray
Midbrain structure which sends descending projections important for pain modulation:
Reticular formation
Raphe nuclei
Locus coeruleus
Descending pain control tracts from higher centers (e.g., hypothalamus, forebrain)
Periaqueductal Gray
As afferent pain signals ascend, collateral axons synapse with __________ ____ to activate release of pain modulating products
Periaqueductal gray
area that sends descending projection through brain stem and spinal cord for pain modulation to try to reduce perception of pain.
Periaqueductal Gray
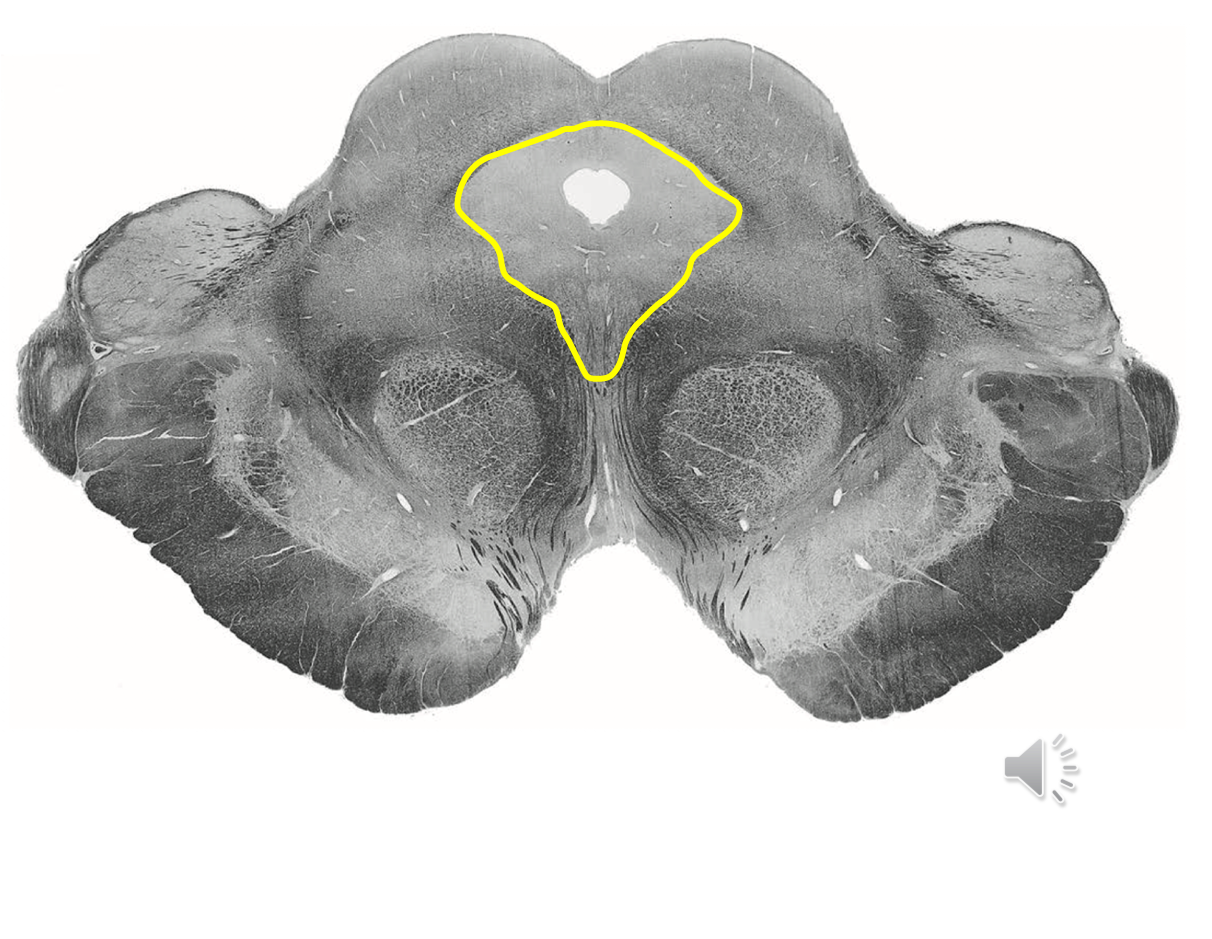
Yellow Periaqueductal gray in brainstem
Pain modulation
Pain modulating products activated by periaqueductal gray
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Endogenous opiate peptides (e.g., enkephalins)
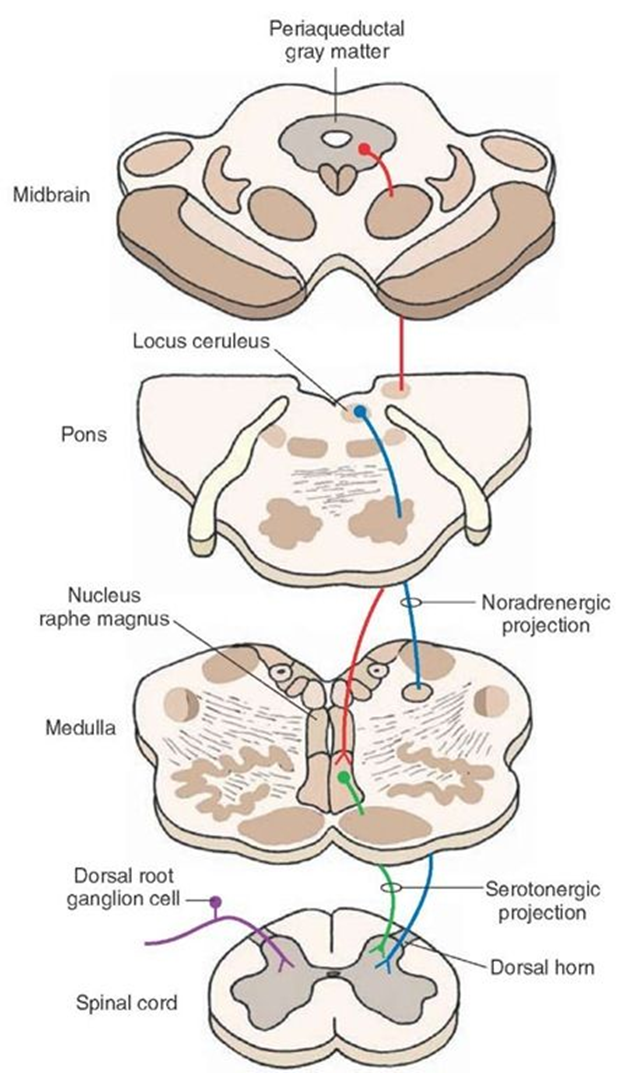
Periaqueductal Gray
for pain modulation
you just stubbed your pinky toe what do you do after you scream and cuss? Rub it. Why do we rub our stubbed toe?
Gate Theory of Pain Modulation
Override nociceptive signals coming through the spinal cord by highjacking the second order neurons
Pain signals can be interrupted in the _____ _______ of the spinal cord which acts as a gate
substantia gelitanosa
Pain fibers sensing pain signal excites to continue pathway. Rubbing the toe uses a different pathway activating _____ instead of spinothalamic tract. Activating _______ sends excitatory signals to some interneurons that release _______ signals onto the pain pathway.
DCML; DCML
inhibitory
Signals from the DCML pathway are faster than pain signals. Therefore it is not able to react to the pain signal.
Pain activates _______ tract.
Livia sticks to hypogastric region and emits vibration frequencies that hijack the system and help block/reduce change of pain pathway being activated.
spinothalamic tract
A 42-year-old female presents to the emergency department after being shot in the back by a spear-gun while deep-sea fishing. Her vitals are stable but upon examination you find she cannot extend her right knee and has weakened flexion of the hip. She does not respond to vibratory stimuli on her right lower extremity and does not respond to painful stimuli on her left lower extremity, though motor functions are intact. All motor function and sensation is intact for both upper extremities.
Which of the following best explains her presentation?
a.Left spinal cord hemisection at C4
b.Right spinal cord hemisection at C4
c.Left spinal cord hemisection at T12
d.Right spinal cord hemisection at T12
e.Left spinal cord hemisection at L3
f.Right spinal cord hemisection at L3
g.Left spinal cord hemisection at S1
h.Right spinal cord hemisection at S1
DCML and spinothalamic
below decussation for DCML but at decussation for spinothalamic
f.Right spinal cord hemisection at L3
Motor and sensory deficits. Motor issues are on the right. Sensory issues one on the right and one on the left.
Motor issue cannot extend right need and weak flexion of the hip.
In back below motor decussation so ipsilateral to lesion so the right.
Vibration on the right DCML pathway
Pain on the left spinothalamic tract has different decussation tract so it decussates at the level of where the spinal tract is at so contralateral
Sensory below decussation so also ipsilateral on the right for vibration DCML
What level? Return to motor information myoterms extension of knee and hip flexion is at L3.
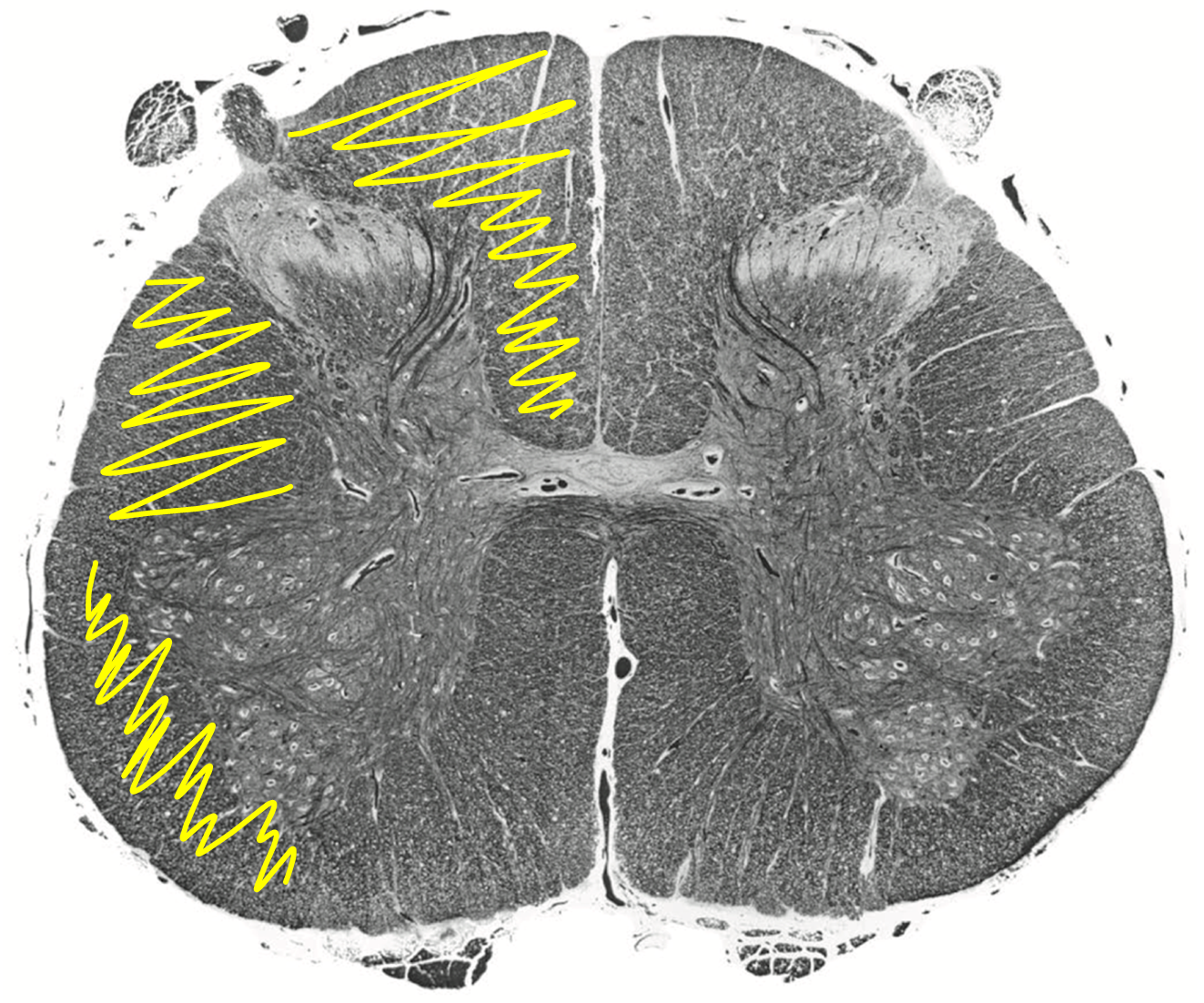
Lost corticospinal tract on that side laterally
Lost Dorsal column
Lost spinothalamic tract.
Loss of contralateral pain/temperature below level of lesion
Loss of ipsilateral vibration and/ or proprioception below level of lesion
Loss of ipsilateral motor function below level of lesion
Lost spinothalamic tract.
Lost Dorsal column
Lost spinothalamic tract.
Centrally located lesions (i.e., syringomyelia) results in _____ loss of pain/temperature sensation
bilateral
If lesion boundaries are T1-T2, deficits will be observed bilaterally from T2-T3 dermatomes
T1 and T4 dermatomes are “safe”
Spinothalamic tract additional info
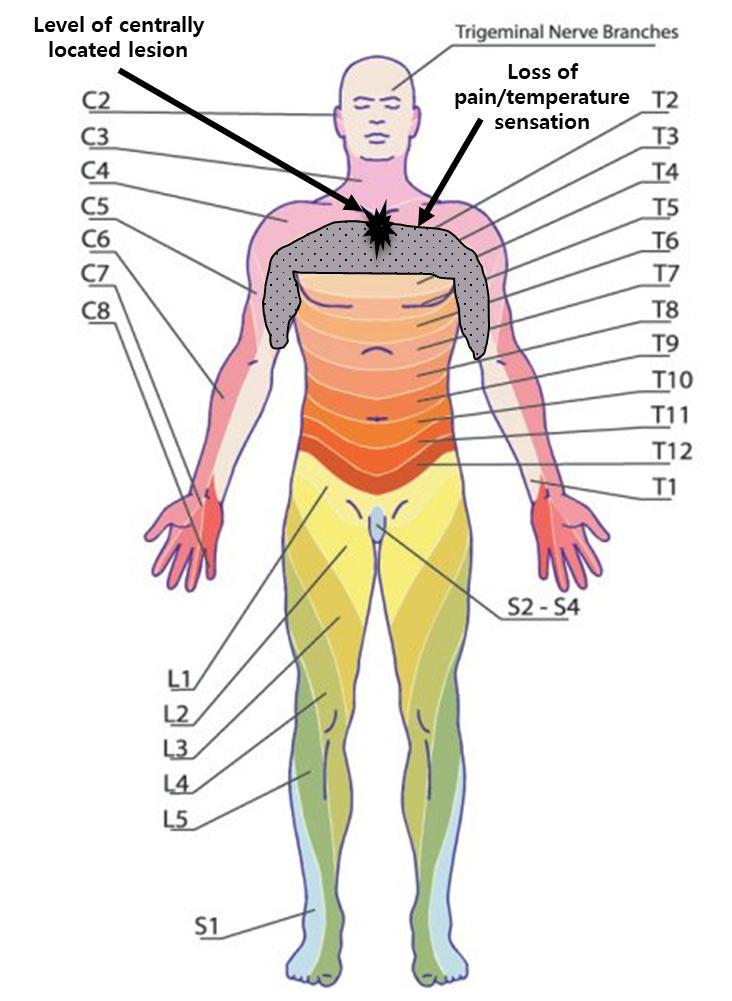
Unilateral lesions results in ______ loss of pain/temperature sensation
contralateral