Lymphocyte Pathophysoiology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Lymphoblast
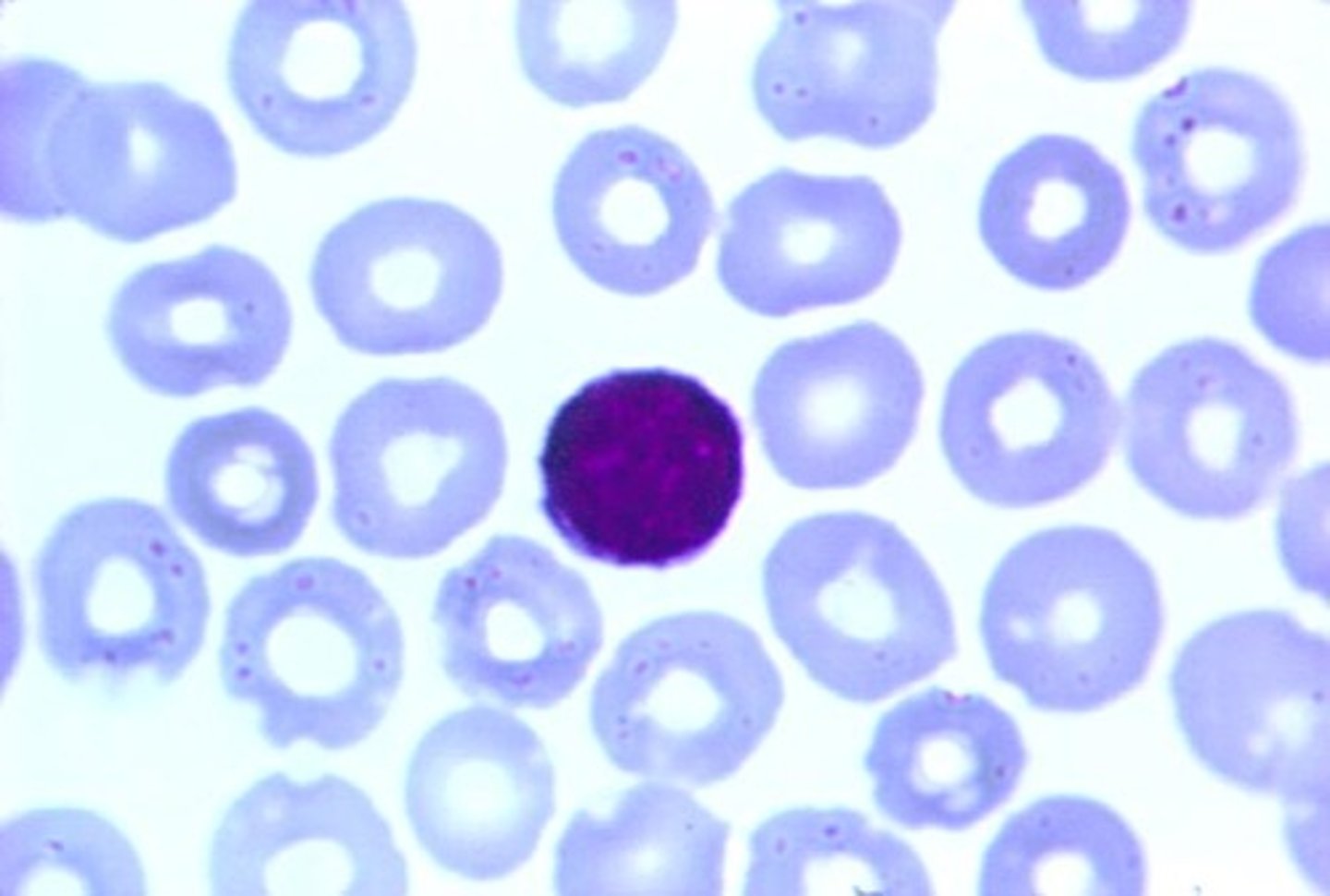
Prolymphocyte
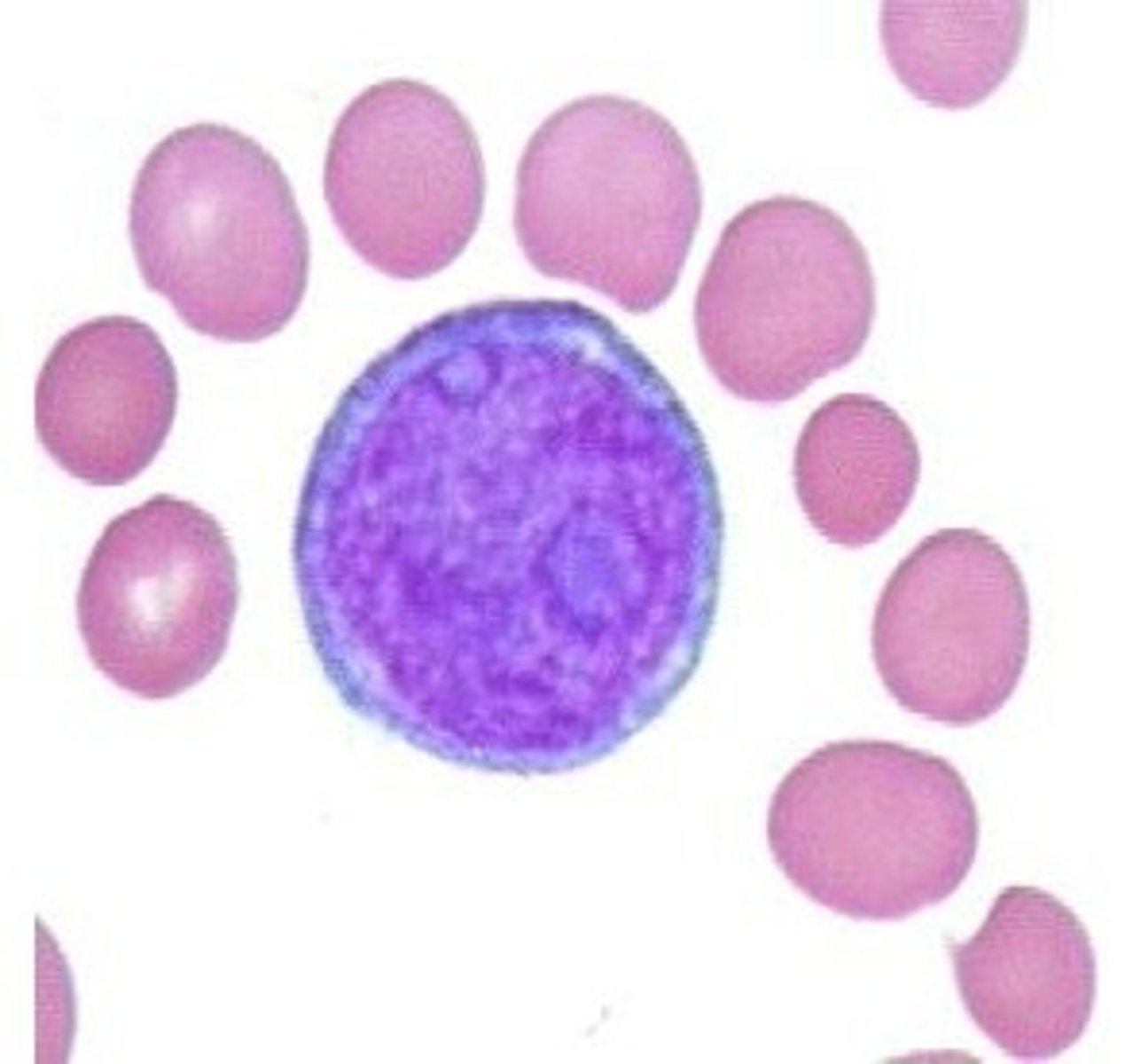
mature lymphocyte
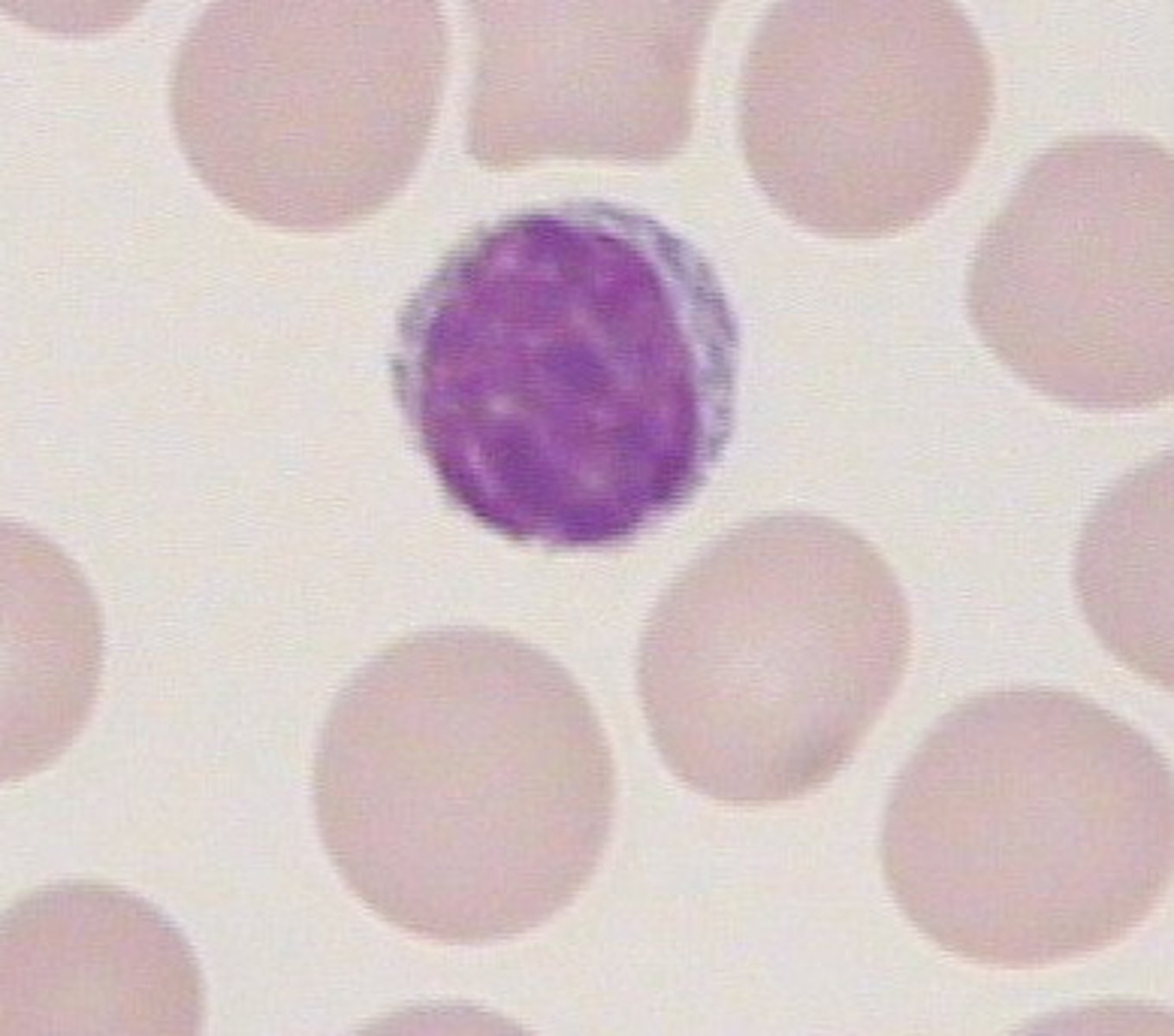
small lymphocyte
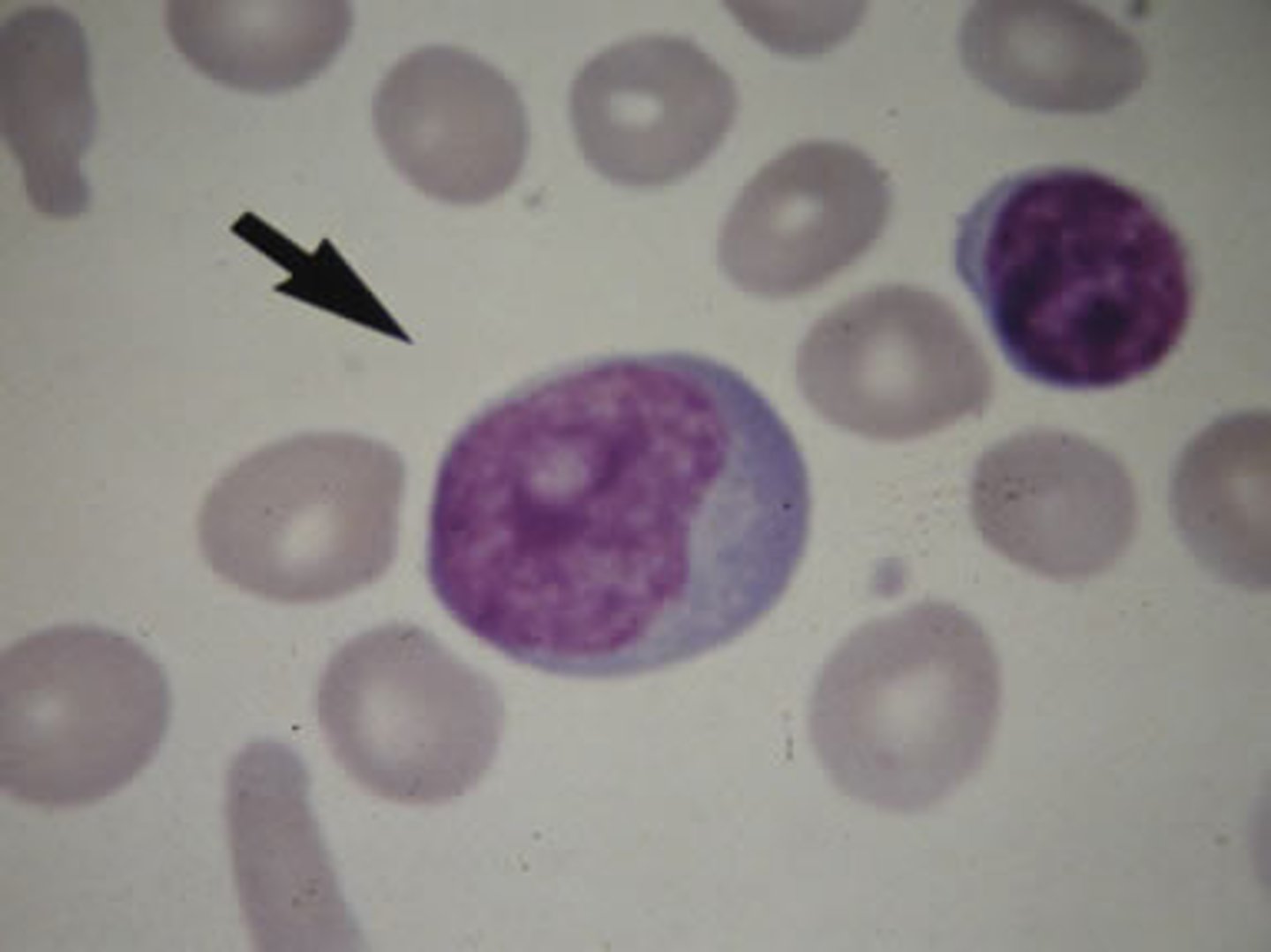
large, atypical lymphocytes
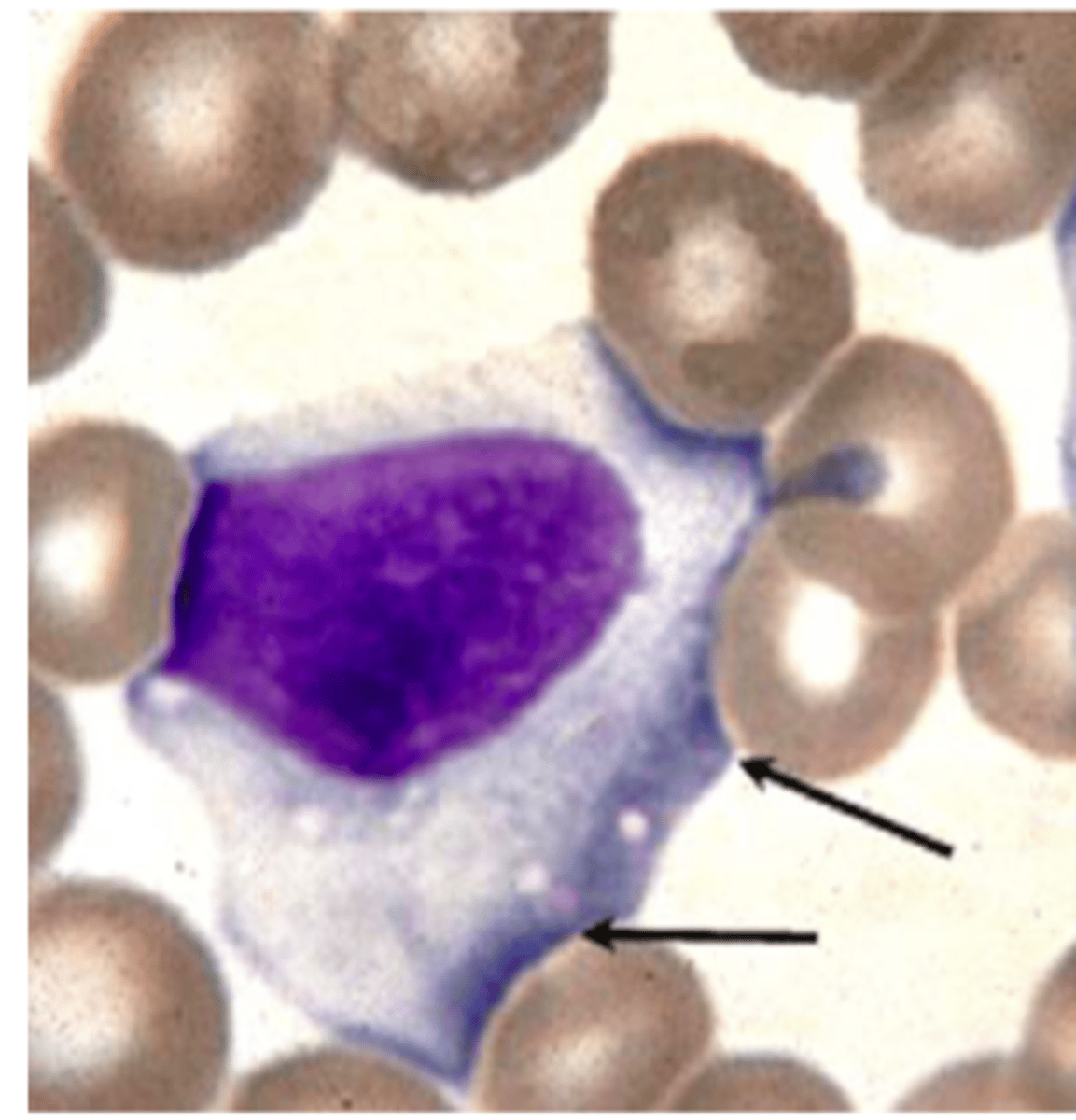
Plasma cells
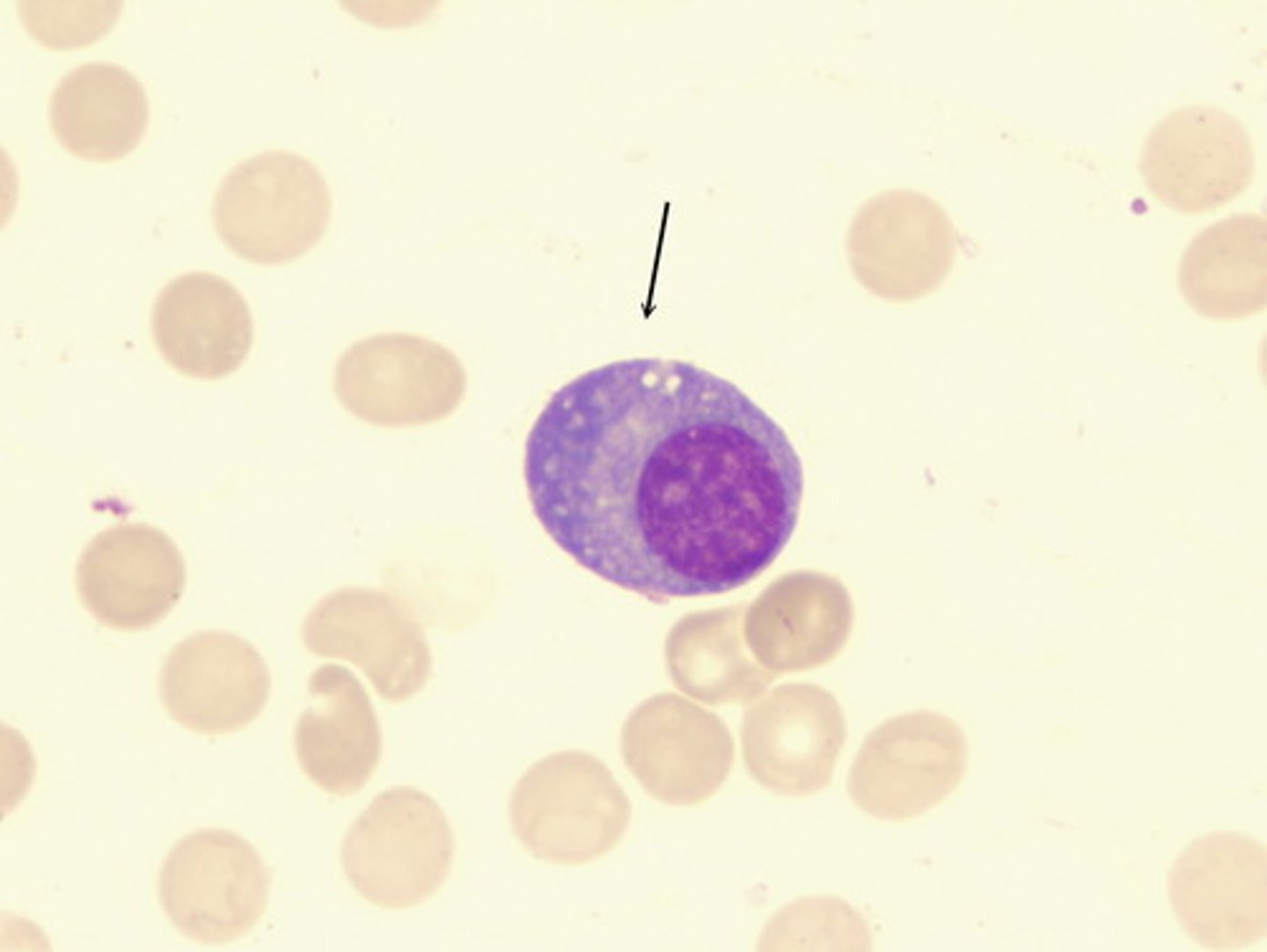
What CD markers are associated with all stages of B cell maturity?
Mature B cells: CD45 (all lymph stages) and CD19-24
stem cells and early precursor B cells: CD34
CD markers associated with T-lymphs
CD45 (all lymphs), CD2,3,7 (all T-lymphs), CD4 and 8 determine functional group
What is the function of B cells?
- precursors for plasma cells
- synthesize and release ONE type of Ab (M/G in secondary lymphoid, A/E in mucosa)
What is the function of T-cells
- cellular immunity/modulators of humoral immunity
- interact with macrophages
- antigen directed response
Null lymphs (percentage/function)
10% of lymph population
represent: undifferentiated stem cell, immature T/B cell, lost surface receptors
Large Granular Lymphocytes (LGL)
- antibody dependent cytotoxicity
- NK (mediate cytotoxic rxns w/o prior sensitization) and K lymphs
Lymphocytopenia values
adult: <1.0 X 10^3/uL
child: <2.0 X 10^3/uL
What are causes of non-malignant lymphocytopenia?
- radiation
- acute stress
- cortisol
- chemotherapy
- AIDS
- Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders
X-linked Agammaglobulinemia (Bruton)
defects of B cells (mostly male babies), depleted B cell zones, recurrent infections
Hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
B cell deficiency (delayed development/dec Igs), recurrent infection, self-correcting by 2 y/o
Late onset variable primary hypogammaglobulinemia
B cell deficiency (30 y/o), defect in differentiation of B cells into plasma cells, Inc infection and autoimmune disorders
Selective Immunoglobulin deficiency
acquired dec in 1 Ig subtype, IgA most common, associated with anaphylactic reactions
Thymic Aplasia (Di George's Syndrome)
defect of thymus gland, depleted T cell zones, normal serum Ig levels
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Syndrome
inherited, T and B lymph deficiency, complete loss of humoral and cellular immunity
Lymphocytosis values
adults: > 4.0 X 10^3/uL
children: > 7.0 X 10^3/uL
infants: > 9.0 X 10^3/uL
What are the viral causes of infectious lymphocytosis?
Coxsackievirus A and B6, Echoviruses, Adenovirus
What symptoms/presentations are associated with viral infectious lymphocytosis?
vomiting, fever, abdominal discomfort, NO atypical lymphs, eosinophilia
Pertussis (whooping cough)
- bordetella pertussis
- lymphocytosis (small mature lymphs)
- LPF from pertussis organism
Infectious Mononucleosis (IM)
- EBV
- oral contact
- B cells have cell receptors specific for EBV, later T cells
- lymphocytosis, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy (self-limit)
What are the complications associated with IM?
rash w/ ampicillin treatment, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, mild thrombocytopenia, jaundice/hepatitis, splenomegaly
Hematologic features of IM
- leukocytosis
- neutrophilia (metas, toxic granulation, Dohle body)
- abundant reactive lymphs
Serological findings for IM
heterophile Ab (absorbed by beef RBC), EBV-specific abs, autoimmune cold agglutinins (anti-i)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- symptoms same as IM
- inc risk w/ transfusions and transplants
- close contact infection
- leukocytosis involving lymphocytosis
How would you differentiate CMV from IM?
- negative for heterophile Abs
- CMV abs
- cause congenital viral infections
Toxoplasmosis
- symptoms similar to IM
- Toxoplasma gondii
- absolute lymphocytosis and reactive lymphs
- = for heterophile/EBV Abs
How is toxoplasmosis diagnosed?
toxoplasmosis Abs (common host: house cat)
What are some other causes of lymphocytosis w/ reactive lymphs?
syphilis, smallpox, PAS hypersensitivity, phenytoin/mesentoin hypersensitivity
Hypergammaglobulinemia
levels of one or more serum Igs are increased above normal levels (may have abs. lymphocytosis)
Multiple Myeloma (MM)
- evolves from MGUS
- monoclonal gammopathy
- proliferation of plasma cells in BM
Symptoms of MM
- older and more men (2X more in AA pop.)
- bone pain/fractures
- increased calcium
- major cause of death: infection/renal failure
Multiple Myeloma lab profile
N/N anemia, rouleaux, inc ESR, hypervolemia/bleeding, BM: 1-90% plasma cells
What acronym goes with multiple myeloma's lab profile?
C- hyperCalcemia R-Renal insufficiency A-anemia B-bone lesions
What proteins are associated with MM (where do they show on electrophoresis?)
Bence Jones (gamma region M spike)
Multiple Myeloma treatment
melphalan-based high dose chemo (newer: angiogenesis inhibitors)
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
- lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL) and BM involvement
- proliferation of B and plasma cells
- IgM inc in serum
What population has high prevalence of WM?
older white men
Symptoms of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
cell proliferation/inc blood viscosity: nuero problems, renal insufficiency, heart failure, clotting probs
NO lytic bone lesions
WM lab profile
N/N anemia, thrombo/pancytopenia, lymphocytosis w/ normal WBC count, Rouleaux and inc ESR, IgM > 1, small normal lymphs and plasma cells in BM
WM treatment
chemo w/ alkylating agents, nucleoside analogues, and Rituximab
What are heavy chain diseases?
disorders related to production and excretion of the Ig heavy chains w/o light chains
Gamma Heavy Chain Disease
- > 50 y/o
- leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, atypical lymphs, plasma cells
- serum protein spike in beta-gama region (hypogamma)
Alpha Heavy Chain Disease
- more common (younger age group)
- intestinal involvement (malabsorption, diarrhea, infiltration in intestinal mucosa), lack of BM/lymph node involve
- normal protein electrophoresis
Mu Heavy Chain Disease
similar symptoms to Gamma-HCD