Swallowing: Muscle Cont... & Normal Swallowing
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Larynx: Extrinsic Muscles - Suprahyoids
Muscles from hyoid & above ELEVATES
Hyoid to mandible
- Anterior belly of digastrics
- Mylohyoid
- Geniohyoid
Hyoid to skull
- Posterior belly of digastrics
- Stylohyoid
Hyoid to tongue
- Hyoglossus
Larynx to skull
- Stylopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus
- Salpingopharyngeus
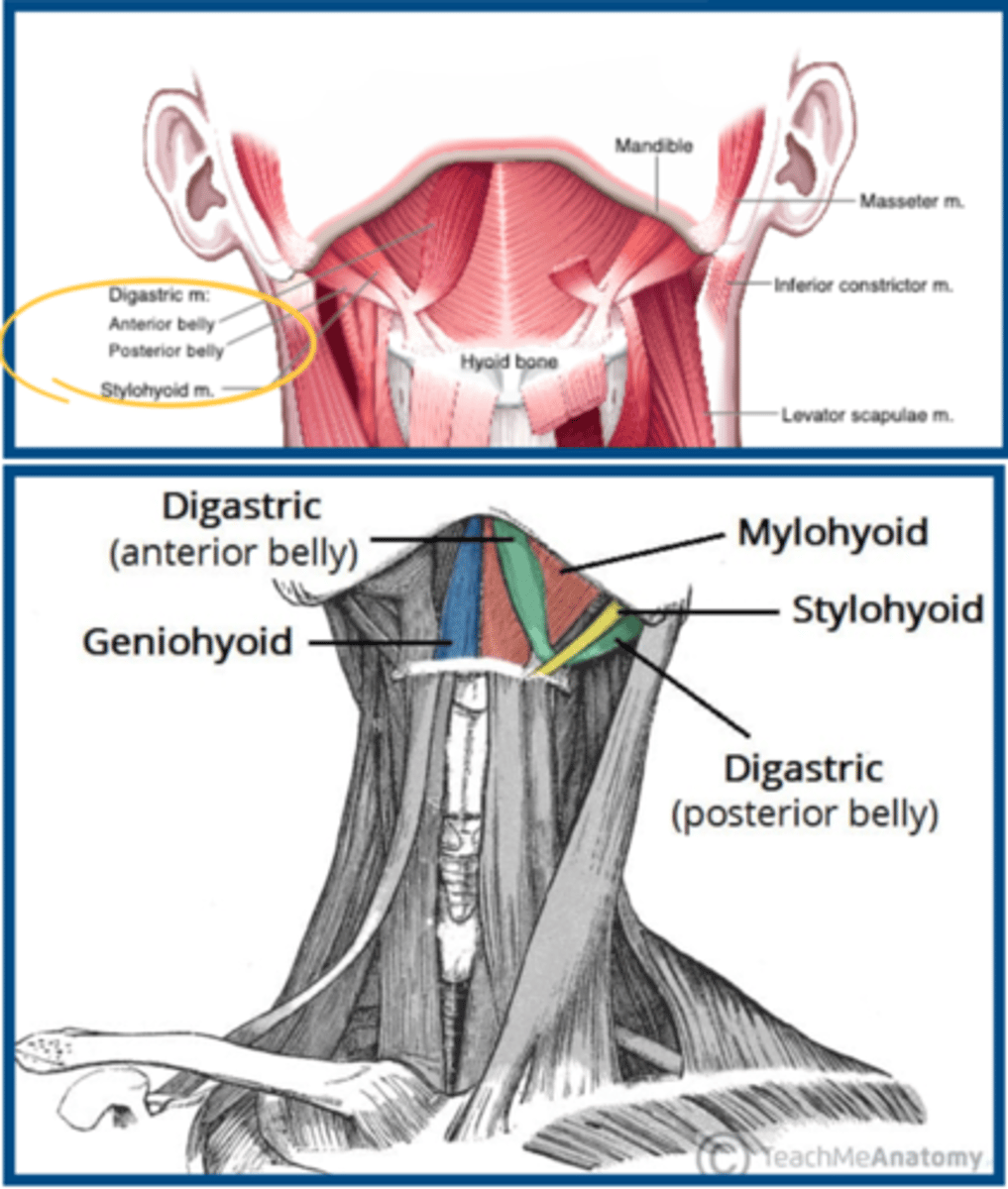
Larynx: Hyoid to mandible - CN?
Trigeminal Nerve - CN V
Larynx: Hyoid to skull
Facial Nerve - CN VII
Cervical Plexus
Spinal nerves (C1-C5)
Larynx: Extrinsic Muscles - Infrahyoids
Muscles from hyoid & below DEPRESSES
Cranial Plexus
- Thyrohyoid : C1
- Sternohyoid : C1 - C3
- Sternothyroid: C1 - C3
- Omohyoid: C1 - C3
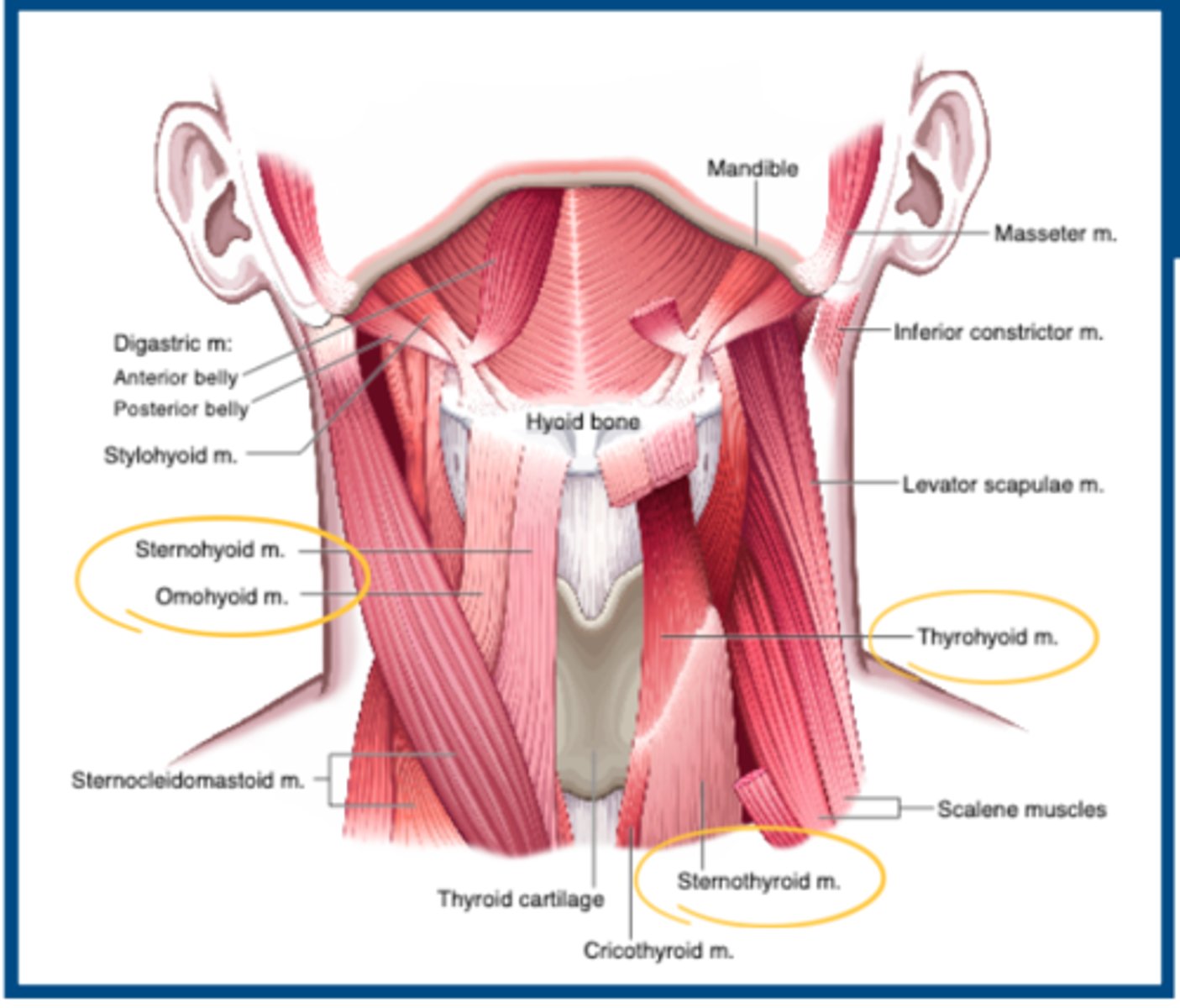
Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES)
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
- Thyropharyngeus
- Cricopharyngeus
- Tonically contracted
- Relaxes during the swallow
Normal Swallow Events
Apnea onset --> Posterior lingual propulsion --> Swallow --> Velar elevation --> Laryngeal vestibule closure --> Pharyngeal constriction + elevation --> UES opening --> Apnea onset
Goals of Swallowing:
Bolus Efficiency: How safely and effectively the bolus moves into the esophagus
Airway Protection: Preventing material from entering the larynx and/or trachea
Oral Phase
Voluntary
Sequential process: Bolus Acceptance --> Mastication --> Bolus propulsion
Oral Cavity
Bolus containment + Preparation
Containment
- Lips: Closure after intake
- Cheeks: Adequate tension
Preparation
- Teeth: Mastication
- Tongue: Posterior bolus propulsion
- Cheeks: Bolus efficiency, midline
- Soft palate: Depresses for airway protection
Posterior lingual: Propulsion
- Quick pressure build
- Moves bolus into pharynx
- Epiglottic inversion
Pharyngeal Phase
Involuntary
Swallow trigger
- Velar elevation
- Laryngeal vestibule closure
- Pharyngeal constriction + elevation
- Upper esophageal opening
Oropharynx
Propulsion + Velopharyngeal
Propulsion
- Soft palate
- Lateral pharyngeal walls
- Base of tongue
Velopharyngeal
- Soft palate: Elevates as tongue propels
- Tongue: Elevates
Swallow trigger: Approximate zone of initiation
- Separates volitional from reflexive events
- Variability is normal
Young adults typically trigger a swallow SOONER than older adults
Velar Elevation
- Prevents nasal regurgitation
- Build downward pressure
- NOT involved in airway protection
Hypopharynx
Propulsion + Larynx
Propulsion
- Pharyngeal constrictors
- Pyriform sinuses
- Cricopharyngeal function
Larynx
- Closure: Glottis, ventricular folds, epiglottis
- Pharyngeal squeeze
- Hyoid elevation
Laryngeal vestibule closure
Hyolaryngeal excursion
- epiglottis moves higher - BOT
- UES stretching
Arytenoid adduction
- forward movement
Aryepiglottic fold bunching
- forward movement
Epiglottic inversion
- BOT + pharyngeal constriction
Pharyngeal constriction: Elevation
Sequential
1. superior PC
2. middle PC
3. inferior PC
Pharyngeal stripping wave
Laryngeal elevation, epiglottic inversion
Esophageal phase
Involuntary
Final Phase
- UES opening
- Peristalsis
- LES opening
Esophagus
Cricopharyngeus (CP) relaxes
Laryngeal elevation
Bolus passage
Sequential contraction of esophagus
Relaxation empties bolus into stomach
1. UES opening
2. Primary peristaltic wave
3. Secondary peristaltic wave
4. LES opening