Benign Oral Epithelial Neoplasms
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
list the 4 benign oral epithelial lesions related to HPV infection:
1. squamous papilloma
2. condyloma acuminatum
3. verruca vulgaris
4. focal epithelial hyperplasia
describe the morphology of HPV:
double stranded DNA virus of Papvavirus subgroup A
able to integrate in host cell DNA
what HPV subtypes are associated with squamous papilloma?
6, 11
what HPV subtypes are associated with condyloma acuminatum?
6, 11, 16, 18
what HPV subtypes are associated with verruca vulgaris?
2, 4, 40
what HPV subtypes are associated with focal epithelial hyperplasia?
13, 32
what is the area HPV insert their DNA into a host cell?
E6 and E7
this area would make them malignant if they were strains 16 or 18
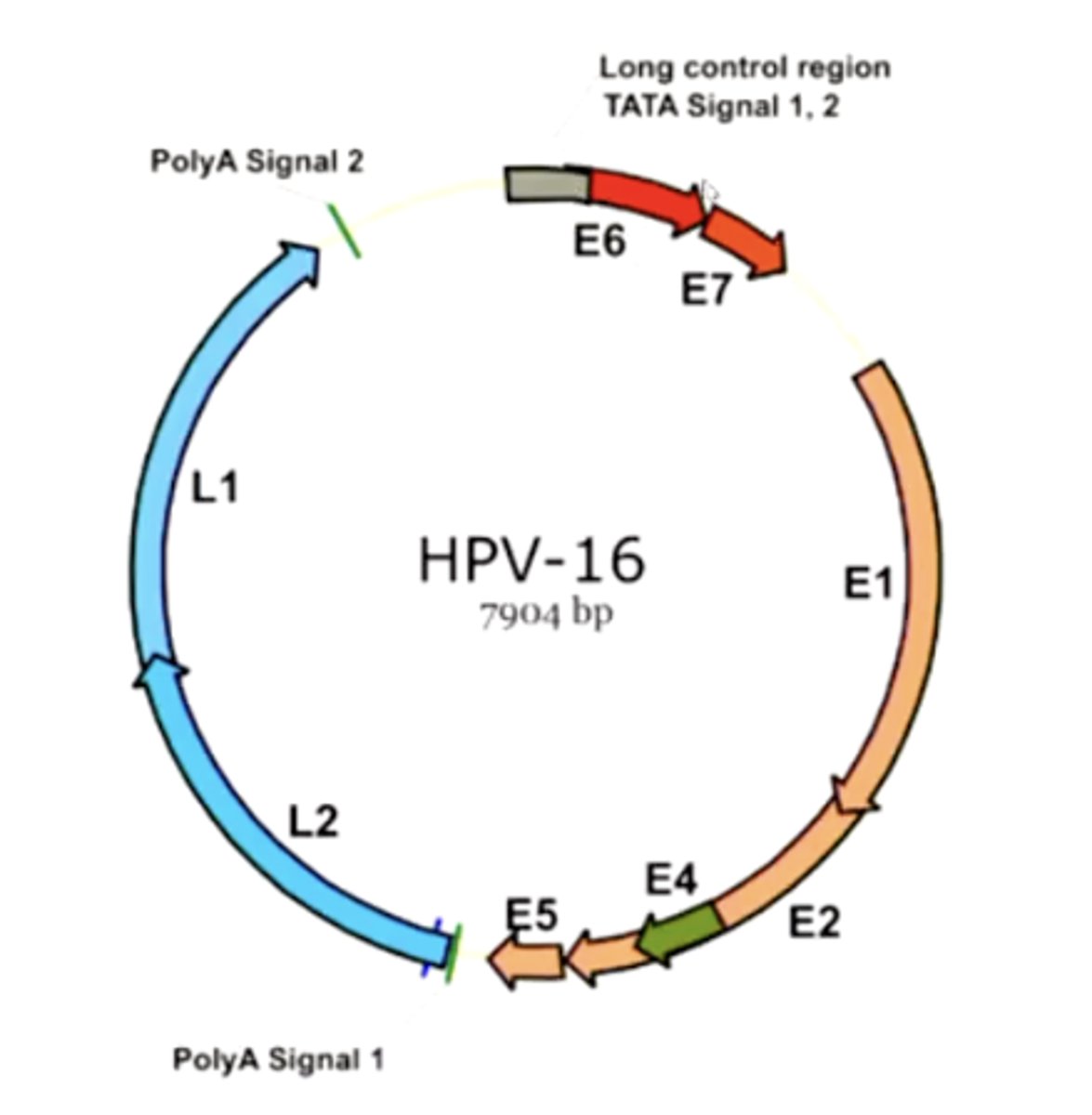
what is a squamous papilloma?
a benign, papillary projection of any shape (looks like a little cauliflower sticking out)
there will commonly be hyperparakeratosis and acanthosis present
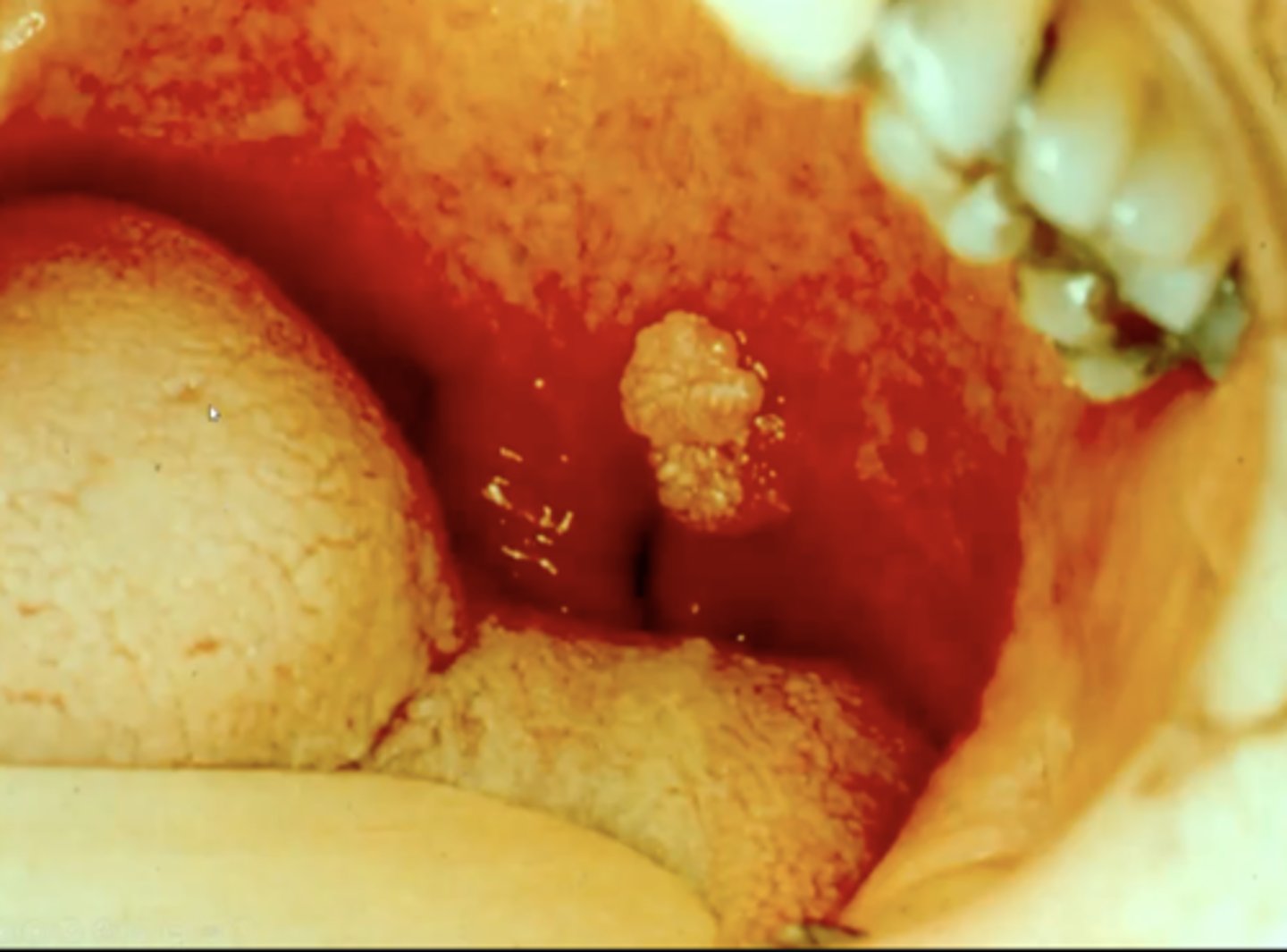
what is verruca vulgaris?
the common wart
these look very white in the oral cavity
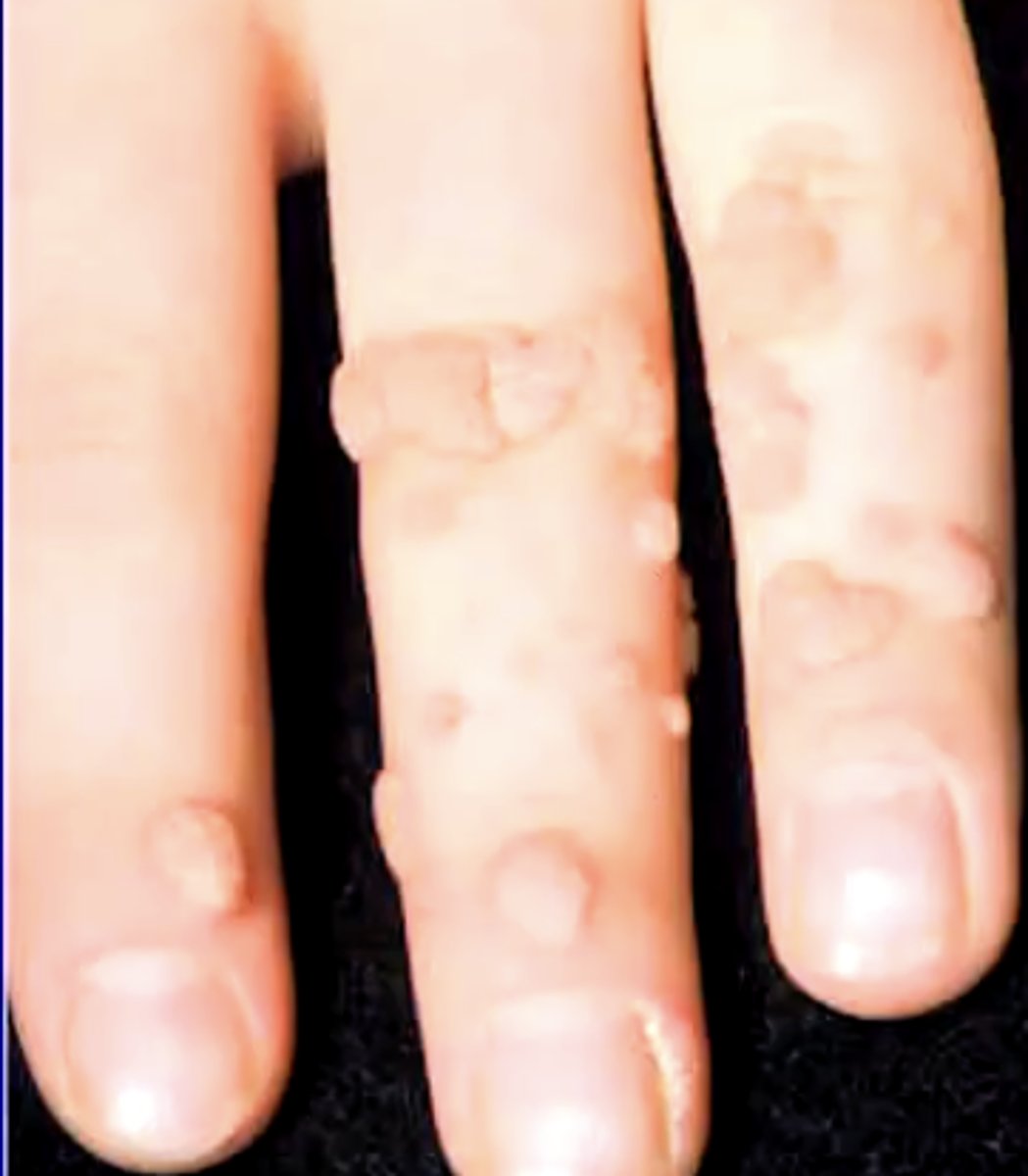
T/F: verruca vulgaris is sexually transmitted
false
spreads mostly from autoinnoculation
describe the histology of verruca vulgaris:
1. hyperorthokeratosis
2. hypergranulosis
3. convergence of rete ridges toward center
what is the treatment for verruca vulgaris?
conservative excision or cryotherapy
2/3 of them spontaneously disappear
condyloma acuminatum makes up ______% of STDs
20%
what is condyloma acuminatum?
benign warts found on genitalia or oral cavity that present as pink, short, sessile papillary projections
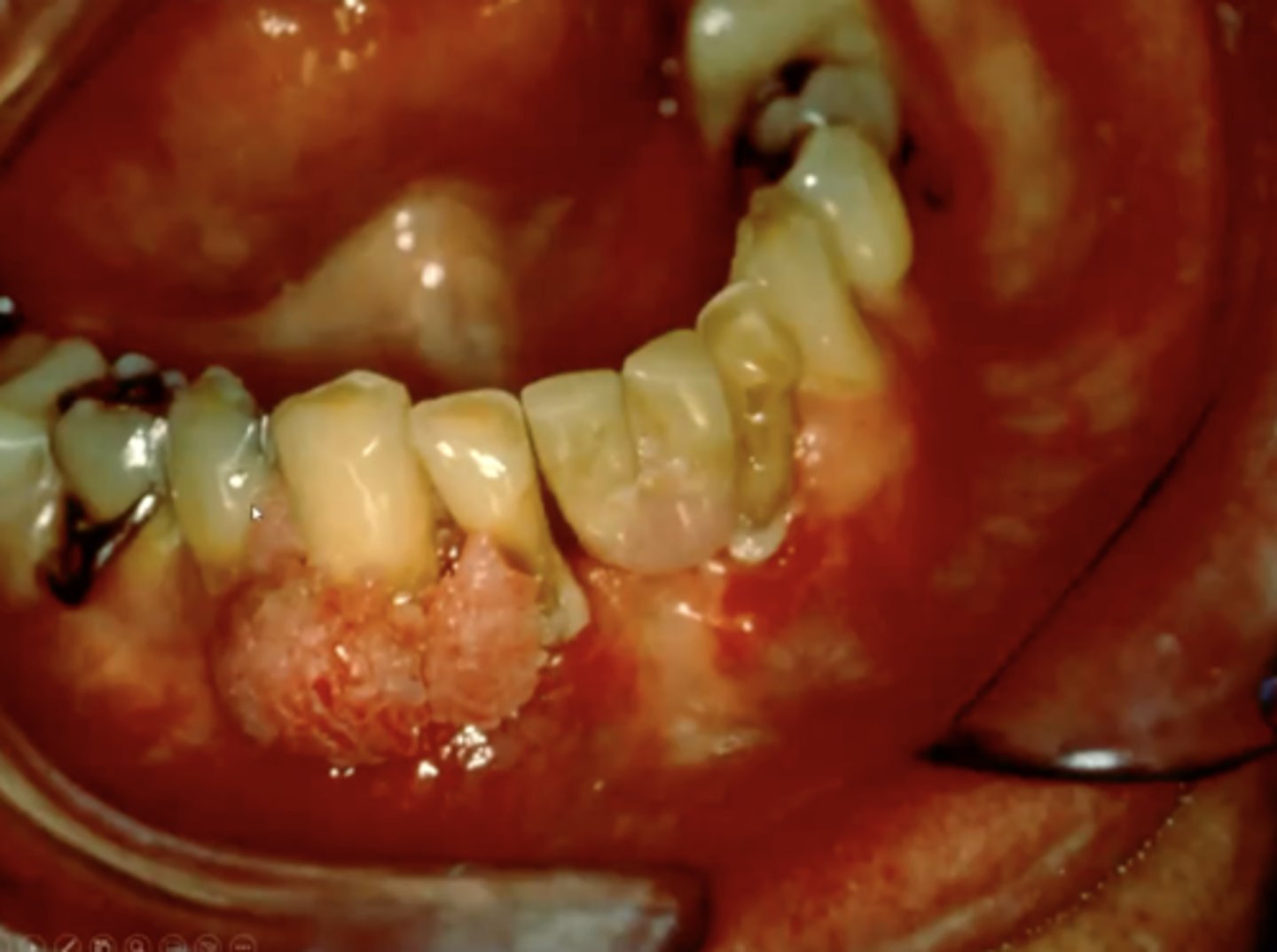
where is condyloma acuminatum commonly found in the oral cavity?
1. labial mucosa
2. soft palate
3. lingual frenum
4. uvula
focal epithelial hyperplasia is also known as ________
Heck's disease
what is focal epithelial hyperplasia?
benign oral lesion associated with HPV that presents with a slightly papillary appearance
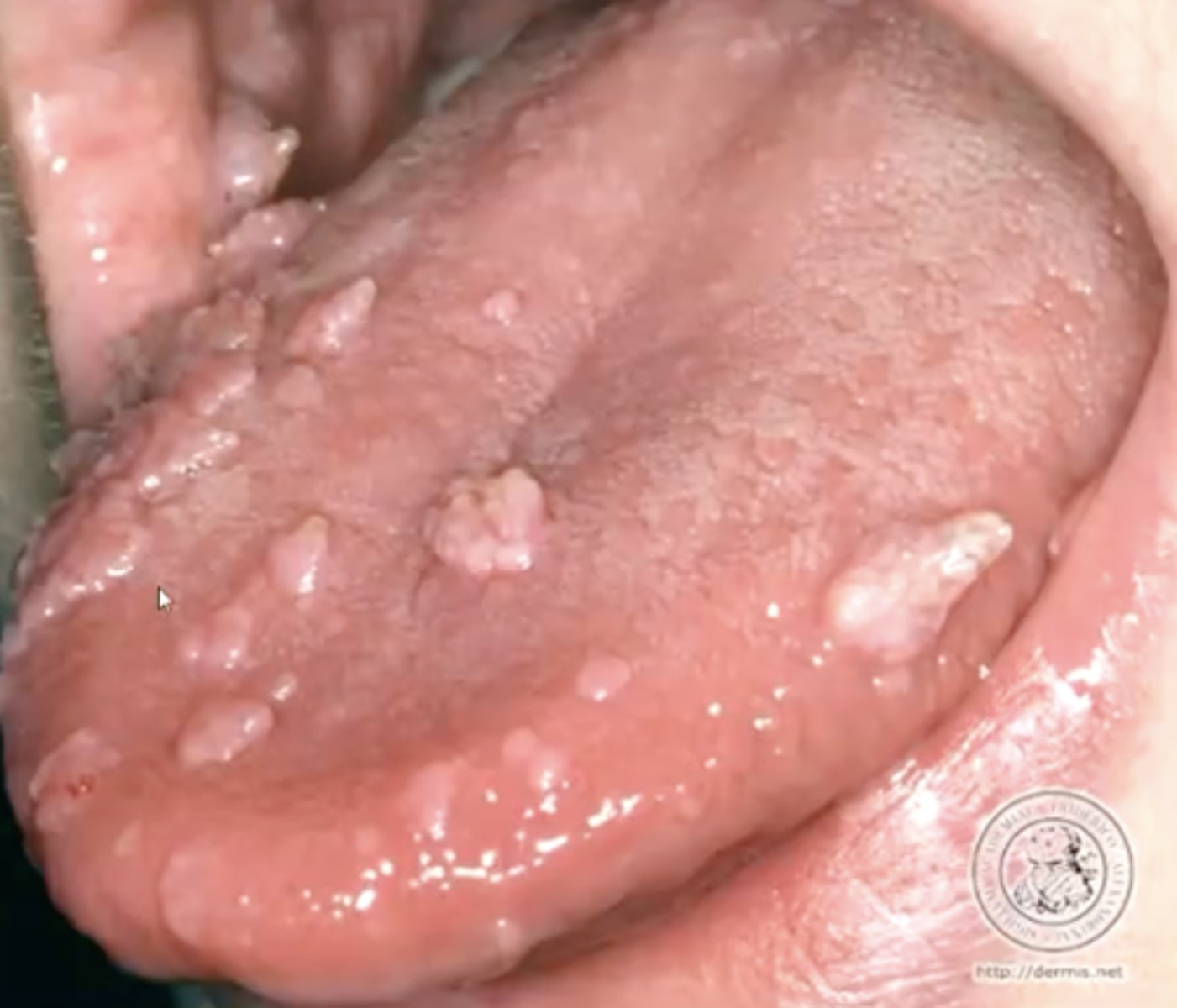
describe the histology of focal epithelial hyperplasia:
1. acanthosis
2. broad rete ridges
3. mitosoid or mitotic cells in spinous layer
what are the 3 ways HPV can be detected?
1. immunohistochemistry
2. in situ hybridization
3. polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
where are the mitotic figures located in squamous papilloma?
basal layer
describe the surface keratinization of squamous papilloma:
hyperparakeratinized
what type of keratinization pattern is seen in verruca vulgaris?
ortho-keratinized
what are koilocytes and where are they seen?
in verruca vulgaris, they are clear cells found in the granular layer
this is where the virus "hangs out"
describe the configuration of the rete ridges at the base of verruca vulgaris:
converge toward a central point
T/F: one can identify condyloma acuminatum solely on light microscopy
false - need to have it situ hybridization/PCR for HPV 16 and 18
T/F: condyloma acuminatum is considered premalignant
true
what is verruciform xanthoma?
a hyperplastic condition of the epithelium with a characteristic accumulation of lipid-laden histiocytes within the CT
may be due to epithelial trauma
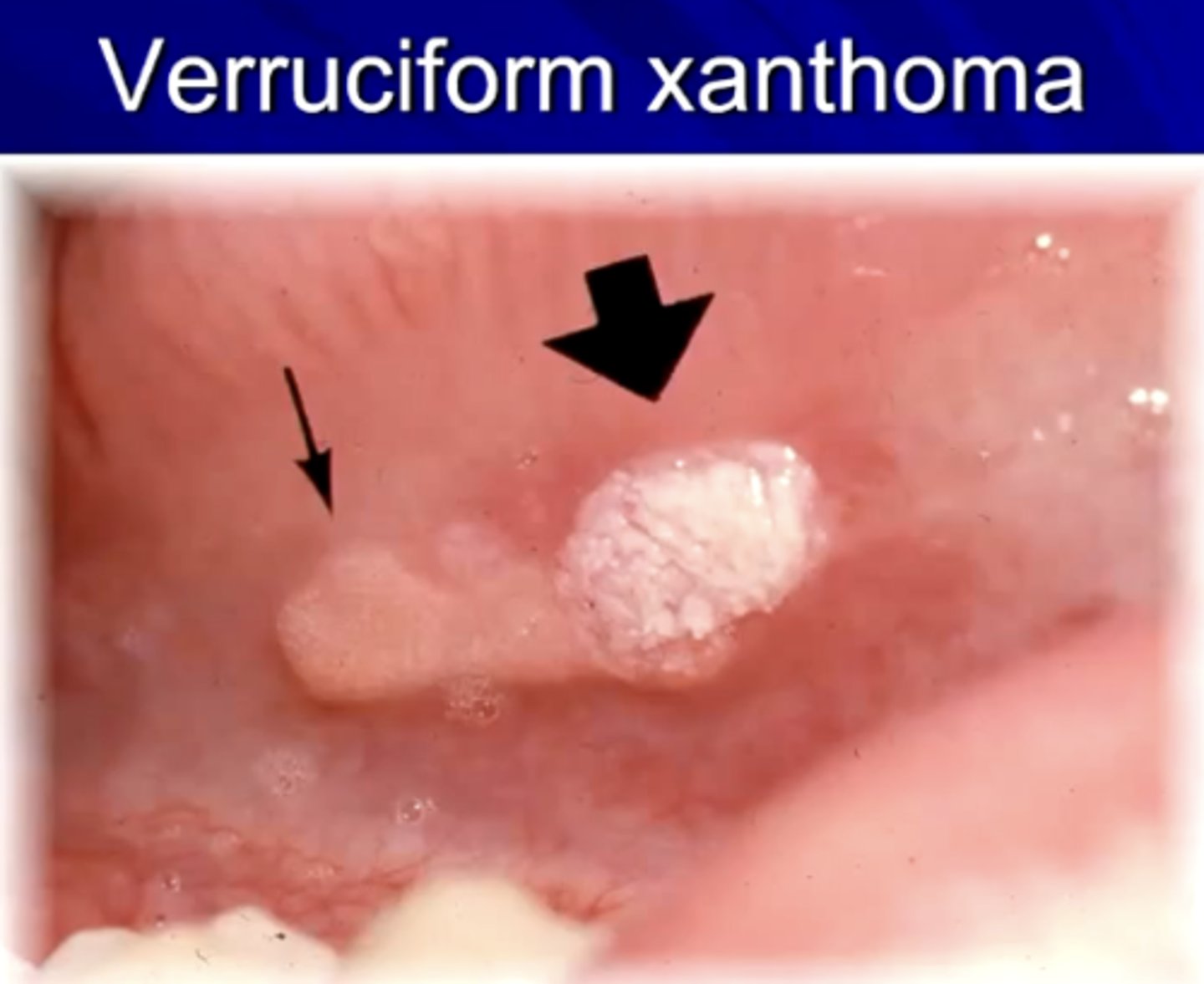
T/F: verruciform xanthoma is associated with HPV
false
how does verruciform xanthoma look clinically?
painless, sessile, with a roughened surface
color may vary from white to yellowish-red
what is keratoacanthoma?
a firm, non-tender, well-demarcated nodule with a central keratin plug that is caused by sun damage or HPV 26, 37
can look yellowish, brown or black
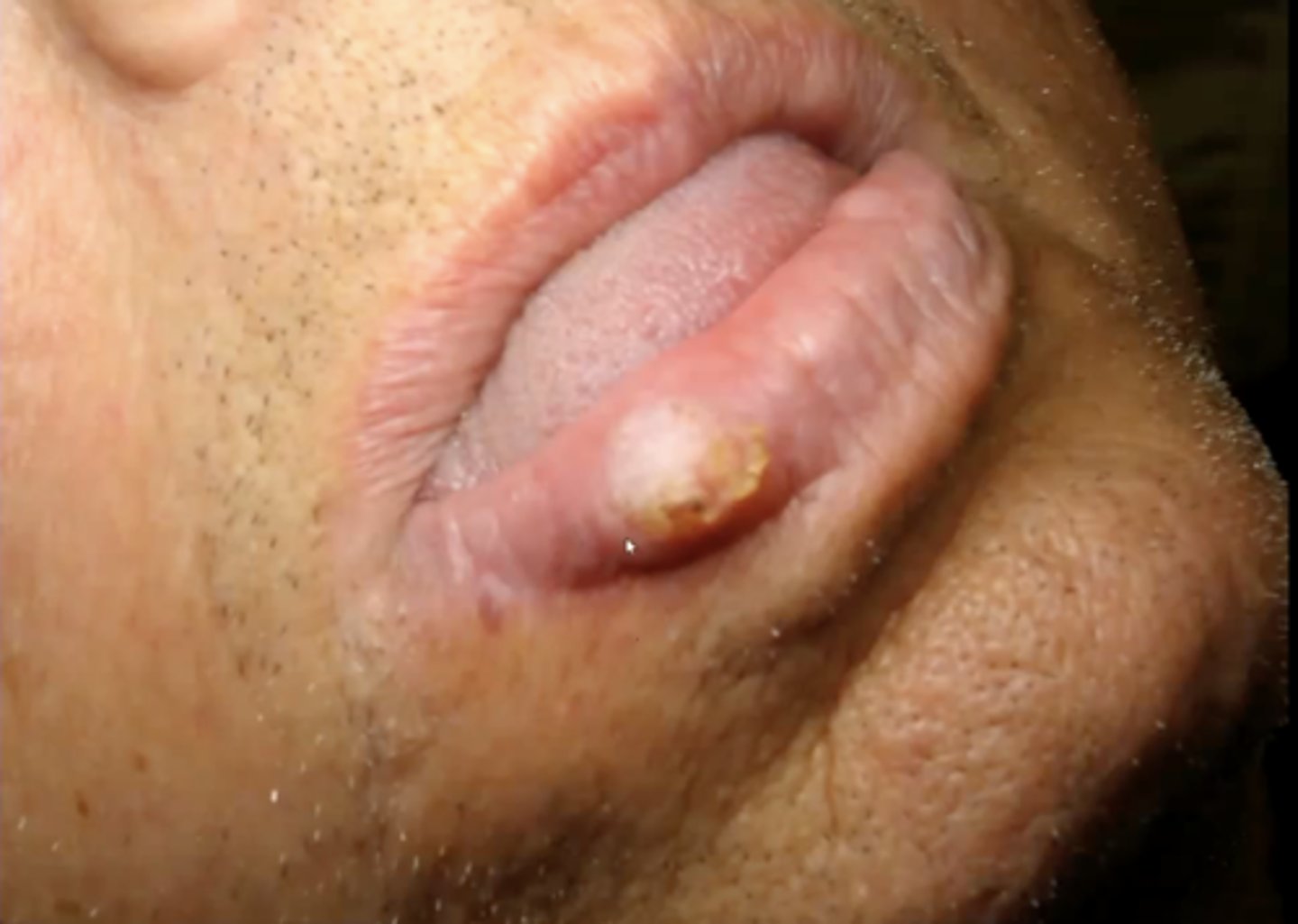
the "self-healing" benign epithelial neoplasm is?
keratoacanthoma
this will regress spontaneously with scarring
where is keratoacanthoma commonly located?
on the vermillion border
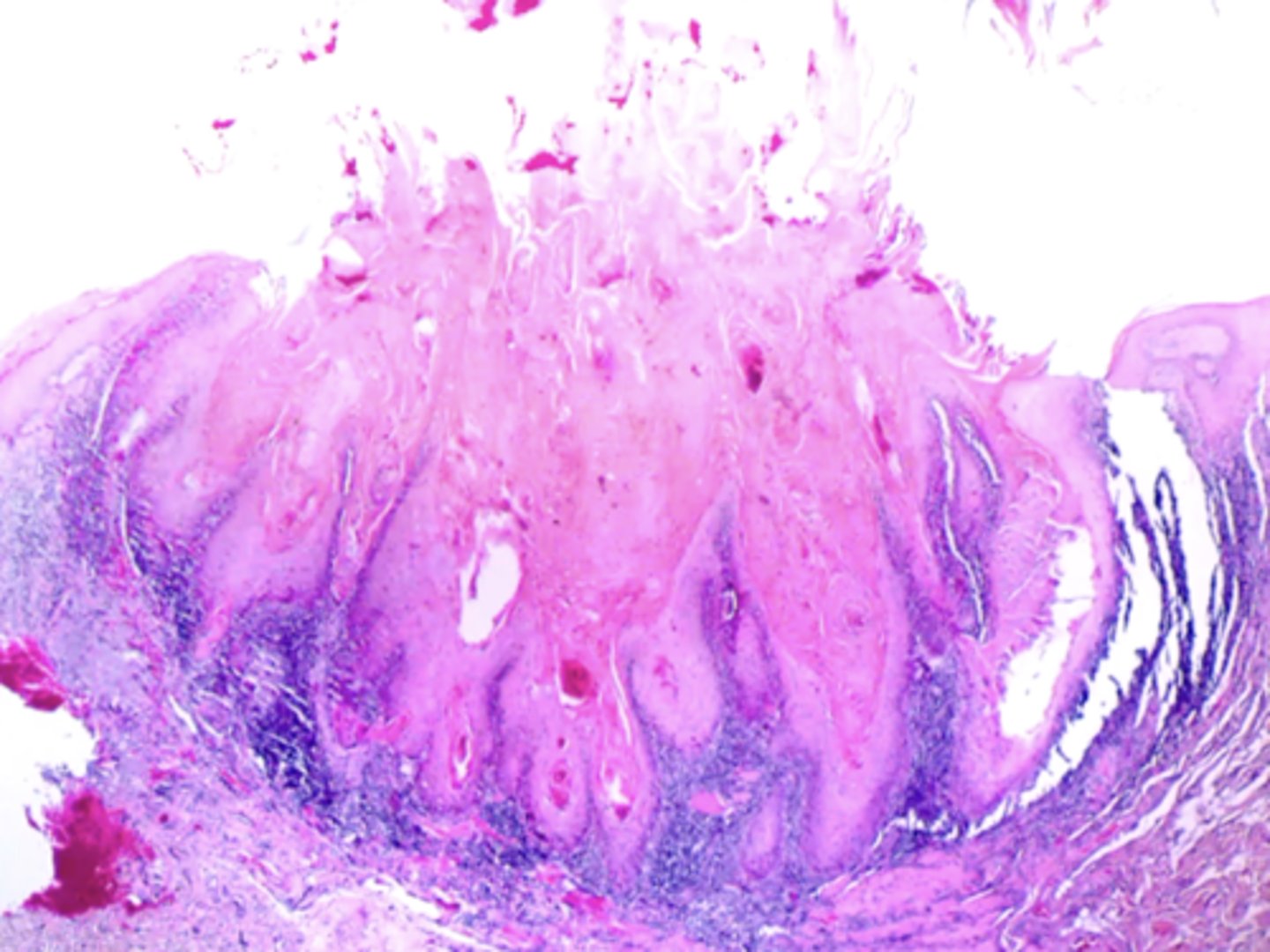
what lesion is characterized by an "ice-tong" or "cupped" look histologically?
keratoacanthoma
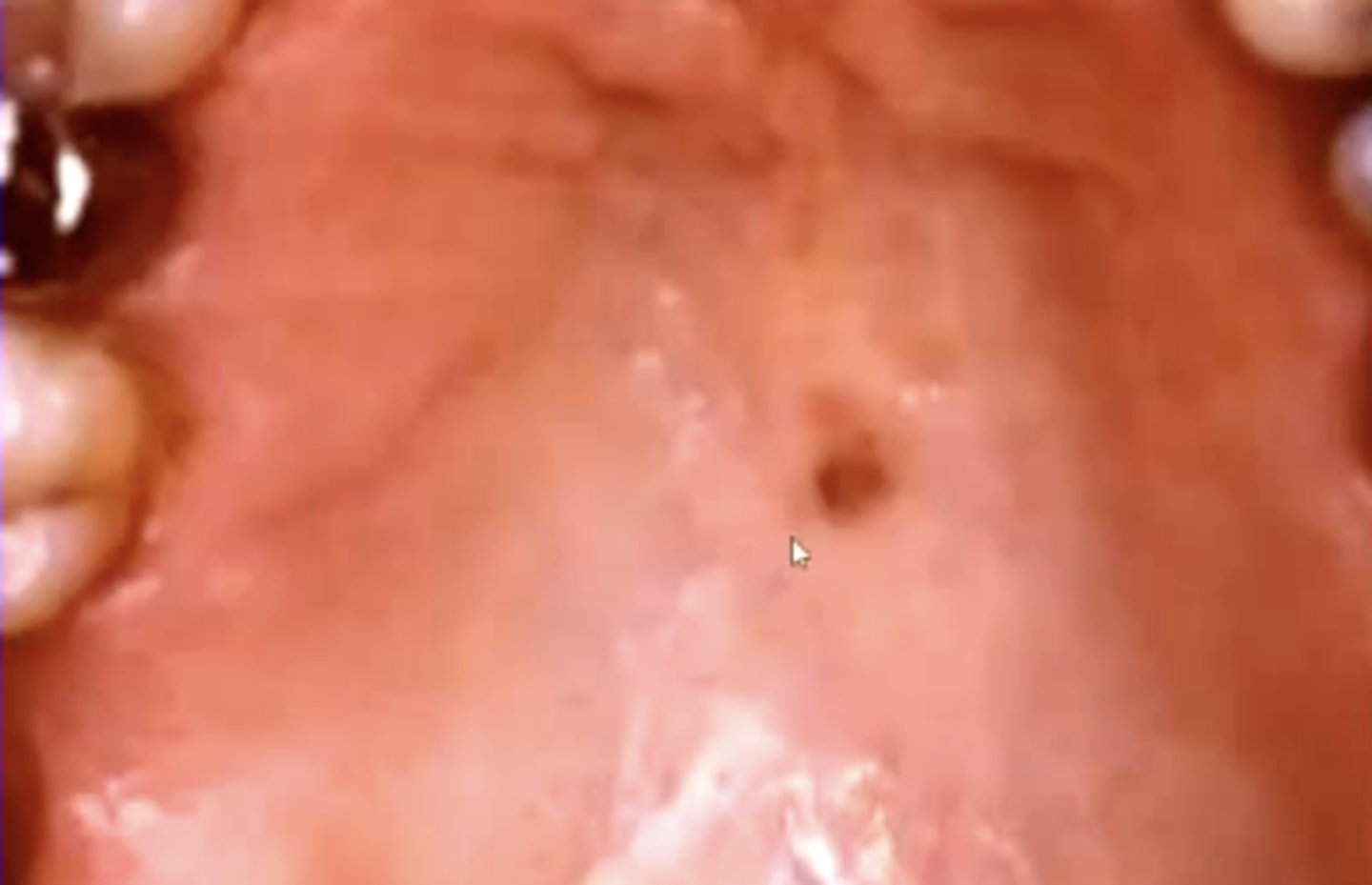
what is an oral melanotic macule?
flat, brown mucosal lesion possibly due to trauma
basically like a freckle in the mouth
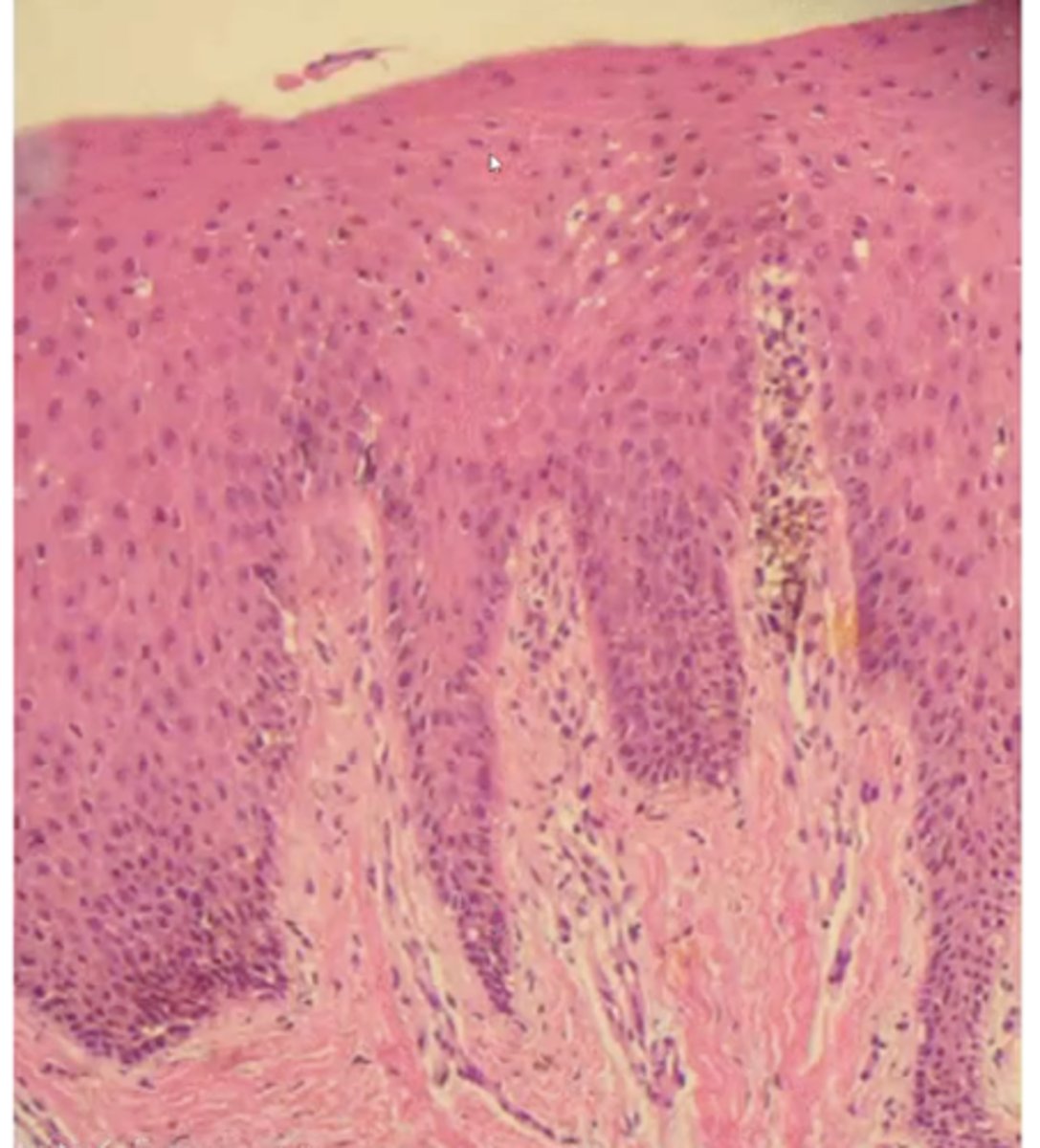
describe the histology of an oral melanotic macule:
increased melanin in the basal layer with melanophages in the connective tissue
epithelium is normal
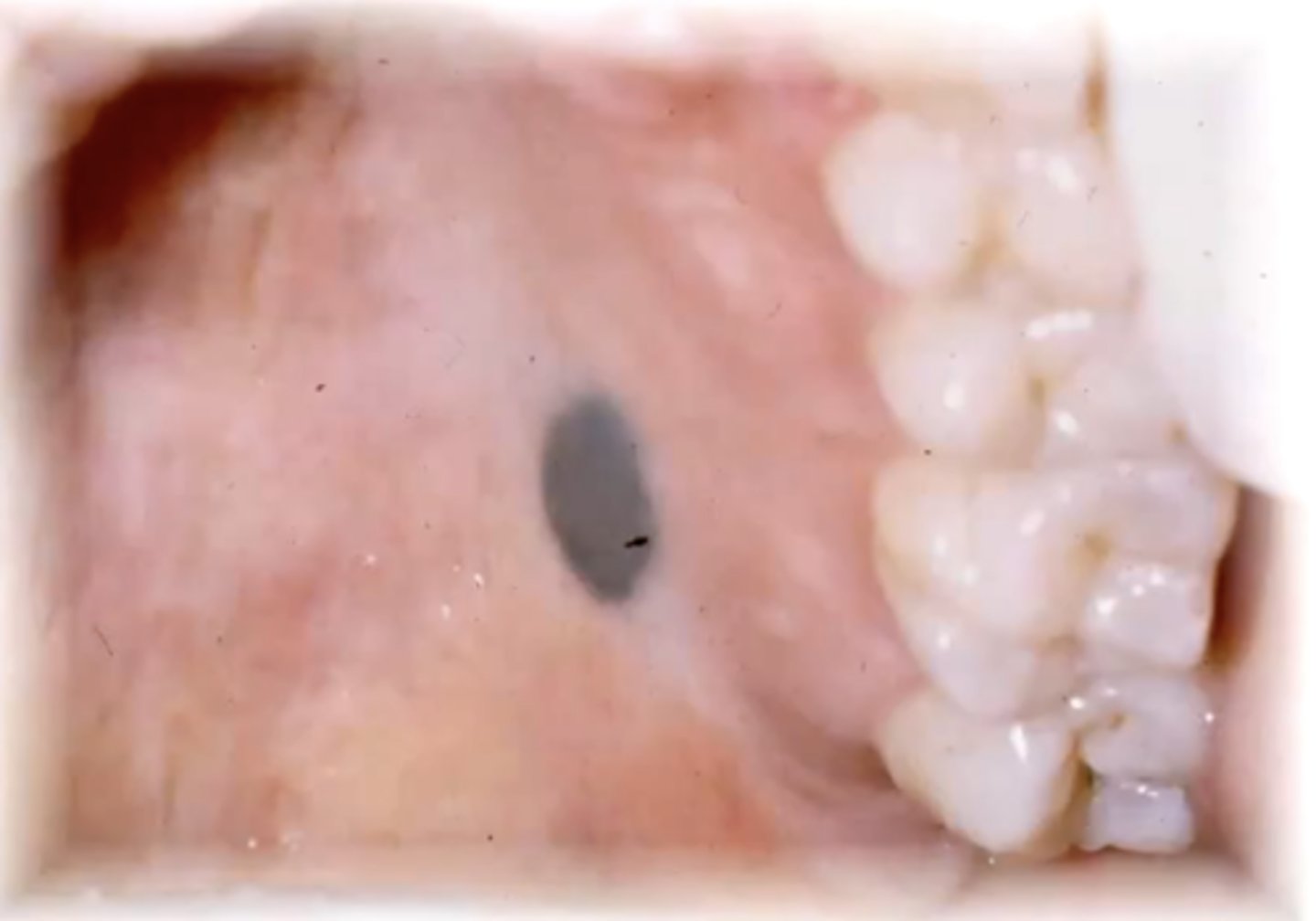
should you excise oral melanotic macules?
yes - you need to rule out that it is not melanoma
you can't tell the difference on clinical appearance alone
what is a melanocytic nevus?
a mole
these are rare to find in the oral cavity
where do nevus cells come from?
the neural crest during embryological development
what are the 4 kinds of melanocytic nevi? which is the worst to have?
1. intramucosal
2. compound
3. junctional
4. blue
junctional - this is the one that can become premalignant
describe the histology of a melanocytic nevus:
small rounded cells that vary in their amount of melanin in the cytoplasm, laying singly or in theques (group)
what is the shape of the nevus cells in a blue nevus?
spindle-shaped/horizontal