Lecture 2 - Chemistry of Food (Lipids)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Polar molecules are:
Hydrophilic and have a dipole
Why are Lipids hydrophobic?
Even though they contain a polar carboxylic acid group, they have a long carbon chain
A hydrophilic molecule:
Has a dipole, electronegativity difference, and possibly has charges
Why do polar/hydrophilic molecules dissolve in water?
Water is polar, and “like dissolves like”
What is a functional group?
A group on a molecule that is responsible for giving a molecule certain properties
4 Categories of Lipids:
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
Do lipids dissolve in water?
No, because they are hydrophobic
What are the building blocks of lipids?
Fatty acids; they are monomers that form lipids (responsible for lipid properties)
Most fatty acids are insoluble in water except…
Short chain fatty acids
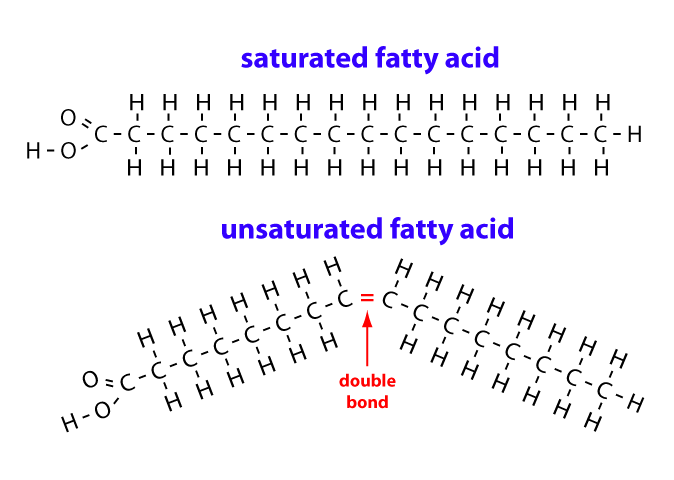
Saturated Fatty Acid Structure
Contain no double bonds; most hydrogens as possible
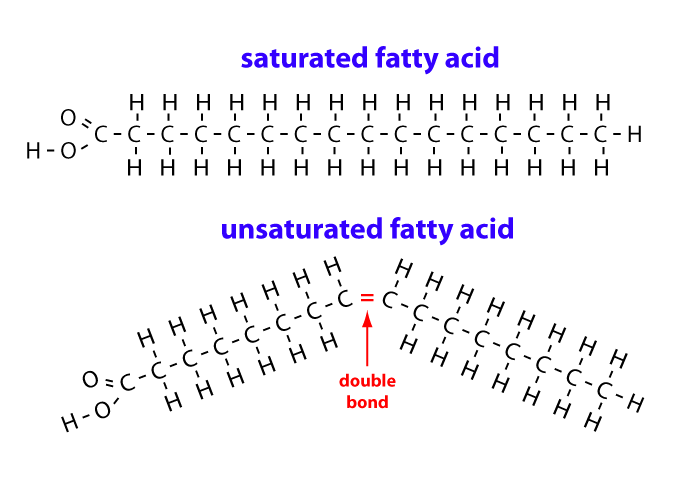
Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structure
Contain at least 1 double bond; can be cis or trans
Which fatty acid is solid at room temp?
Saturated Fatty Acids
Which fatty acid is liquid at room temp?
Unsaturated fatty acids
Melting Points of Fatty Acids
Unsaturated Lower (Liquids at Room Temp)
Saturated Higher (Solids at Room Temp)
Solidification Points of Fatty Acids
Unsaturated higher (Liquids at Room Temp)
Saturated lower (Solids at Room Temp)
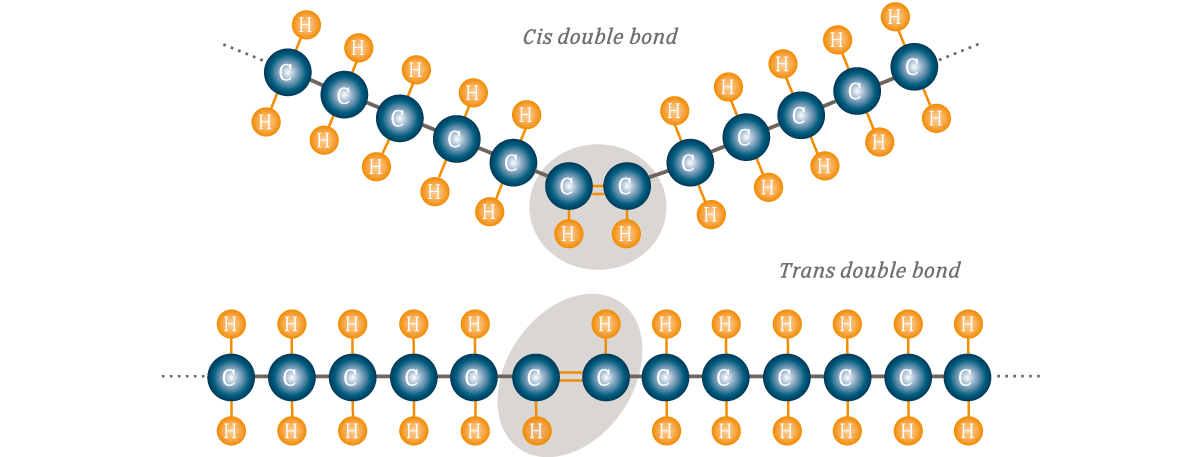
Cis-unsaturated Fatty Acids
Hydrogens on SAME side of double bond; found in nature
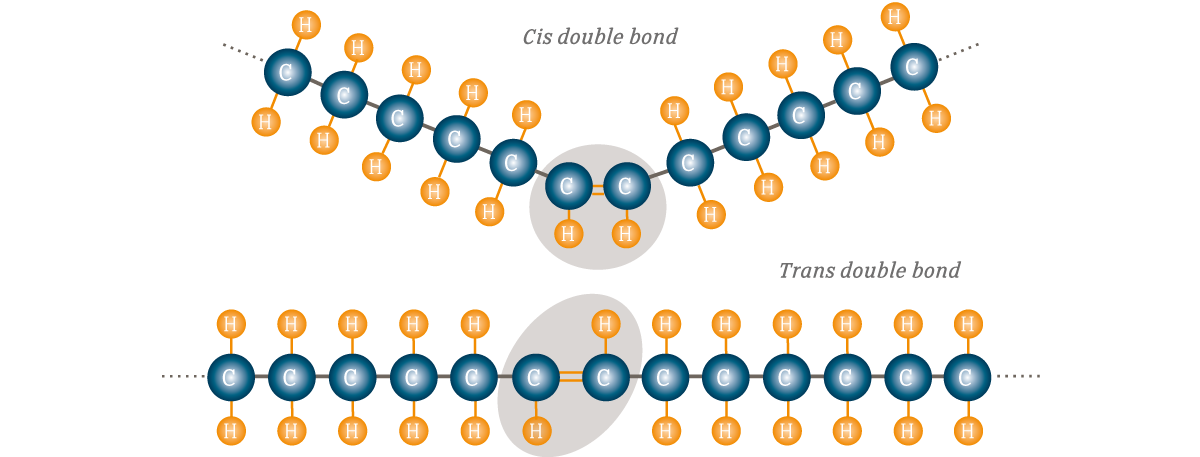
Trans-unsaturated Fatty Acids
Hydrogens on OPPOSITE side of double bond; Synthetic, unhealthy effects on cholesterol metabolism
Esterification
Glycerol (Alcohol) + 3 Fatty Acid → Triglyceride + 3H2O
-OH + 3 -COOH → Triglyceride + 3H2O
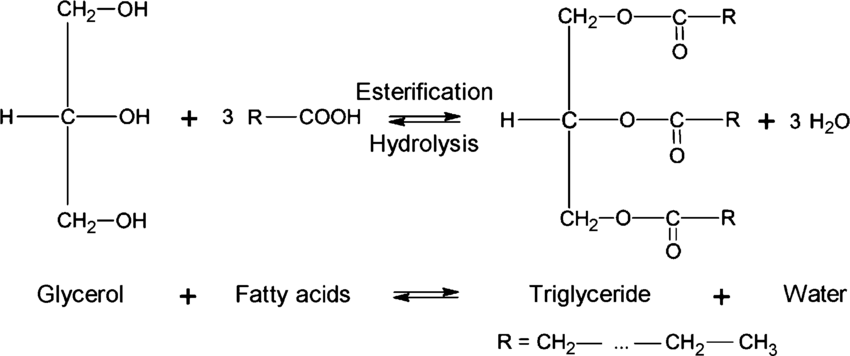
How are esters named?
-ate ending (-COOR)
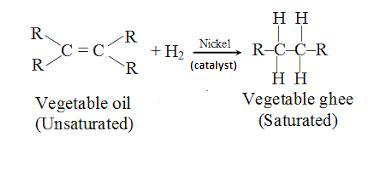
Hydrogenation
Unsaturated Fatty Acid + H2 → Saturated Fatty Acid
Butter to margarine
Interesterification Types
Chemical or Enzymatic
Both replace one ester group with another
Chemical Interesterification
Unspecific, using a chemical catalyst
Enzymatic Interesterification
Use of enzymes to produce specific esters
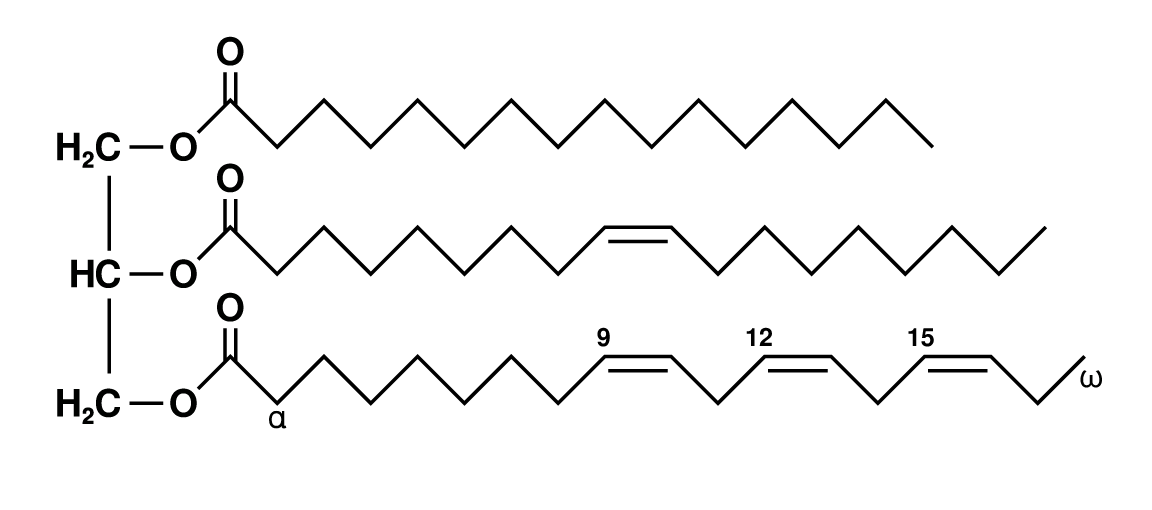
Trigylceride Structure
Glycerol backbone with 3 long-chain fatty acids
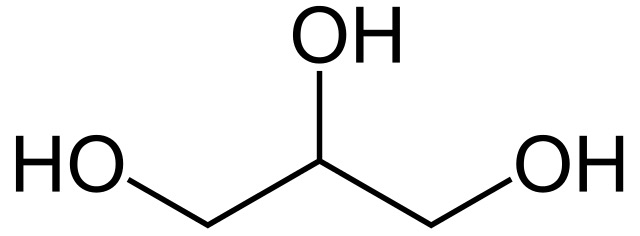
Glycerol Structure
3 carbons, each attached to an -OH group
Delta End of Fatty Acid
Carboxylic Acid end
Delta Naming System
Count number of carbons (including carboxyl), count double bonds, delta symbol, and positions of double bonds
EXAMPLE: 18:3Δ9,12,15
18 carbons, 3 double bonds at positions 9, 12, 15
Omega End of Fatty Acid
Opposite side to carboxylic acid
Omega Naming System
Number of carbons, number of double bonds, only 1 position listed
EXAMPLE: 20:5ω-3 (20:5Δ5,8,11,14,17)
Why are saturated fats and trans-unsaturated fats worse for health?
They stack better, so they have a better chance clogging arteries by building up and interfering with cholesterol metabolism (hardening arteries)
Mono vs. Di vs. Triglycerides
1 vs. 2 vs. 3 fatty acids attached to the glycerol backbone
Fats vs. Oils
Fats are solid; Oils are liquids
Fats are saturated; Oils are unsaturated
Fats in animals/tropical plants; Oils are in plants ONLY
Fats have high melting point; Oils have low melting point
Fats have high solidification point; Oils have low solidification
Fats have cholesterol; Oils have phytosterol
Phospholipid Structure
Polar head with non-polar tails, glycerol and phosphate backbone
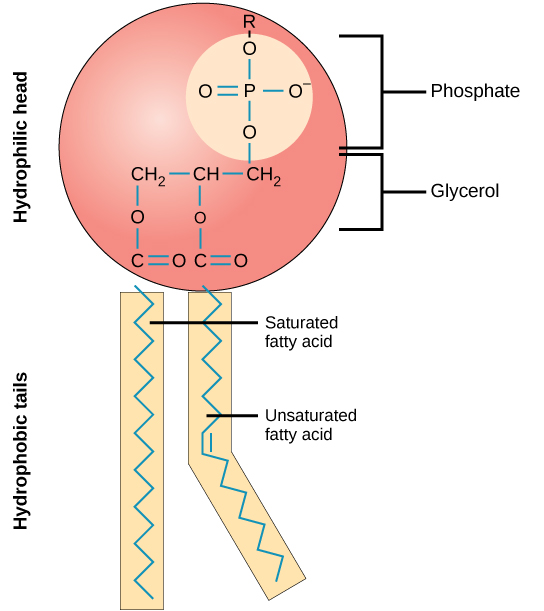
Important Features of Phospholipids
Amphipathic (both nonpolar/polar properties); found in cell membrane
Steroids/Sterols Structure
4 rings, either 6 or 5 carbons, making them all hydrophobic
Types of Sterols
Cholesterol in animals, phytosterols in plants
Importance of Sterols/Steroids
Sex hormones
Signaling molecules acting in another area of body (androgens)
Cholesterol
Determines rigidity/flexibility important to cell membrane structure, but harmful in high amounts (harden artery)
Bile Salts
Vitamin D Synthesis
Waxes
Esters made from long chain fatty acids + alcohol (Esterification)
-COOH + -OH → Wax
Dietary Sources of Lipids
Milkfats
Lauric Acids
Vegetable Butters
Oleic and Linoleic Acids
Linolenic Acid
Animal fats
Marine oils
Milkfats
Short chain fatty acids from cows, sheep, goats
Lauric Acids
Found in oils of tropical plants; saturated fats because tropical
Vegetable Butters
From tropical plant seeds (cocoa butter); saturated due to tropical origin
Oleic and Linoleic Acids
Corn oil, olive oil, cottonseed oil, etc.
Linolenic Acid
Omega-3 acids, soybean oil, flax/linseed oils; from plants
Animal Fats
Saturated fats consumed from meats and poultry products
Marine Oils
Long-chain PUFA (polyunsaturated), omega-3, EPA and DHA
MUST KNOW about tropical plants
Produce saturated fats more often; other plants often produce UFA
Ways Fatty Acids Deteriorate
Auto-oxidation (Oxygen)
Hydrolysis (Add water)
Rancidity
Producing wrong flavor or smell due to deterioration
Auto-oxidation
Oxygen taking electron from double bond, DNA, or cell membrane
(Often double bond, but mutation or instability CAN occur)
Hydrolysis
Release of carboxyl group after addition of water (acting as enzyme)
Optimal Storage for Lipids
Cool, dry, and dark place to decrease rate of reaction
Antioxidants
Give oxygen an electron so it doesn’t take from double bond
Vitamins C and E