Comprehensive Bowel Elimination: Development, Disorders, and Nursing Care: Lesson 9
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What age do children typically learn to control bowel elimination?
By age 3.
babys learn s/s of need to go age 18m - 2 y
What factors can affect bowel elimination in pregnant women?
Growing fetus can interfere with intestinal peristalsis, leading to constipation.
prenatals can also be high in iron that can also lead to constipation
What are common causes of constipation?
Low fiber intake, inactivity, medications, and dehydration.
What is the nursing care for constipation?
Increase fiber and fluids, use stool softeners, increase mobility, and monitor bowel movements.
What are the symptoms of bowel obstruction?
No stool or gas, abdominal distension, and pain.
What nursing care is required for bowel obstruction?
NPO, NG tube (to decompress) , IV fluids, and monitor for perforation. Possibly surgery.
(from untreated constipation)
What is diarrhea and its potential complication?
Rapid transit of stool that may lead to dehydration.
What nursing care should be provided for diarrhea?
Fluid replacement, identifying the cause, and administering antidiarrheals.
What is fecal incontinence?
Loss of control over bowel elimination.
What nursing interventions are important for fecal incontinence?
Skin care, toileting schedule, barrier creams, and emotional support.
What is the purpose of an occult blood test?
To detect hidden blood in stool, often for colon cancer screening.
What is the typical time frame for bowel movement after surgery?
24-48 hours.
What are ostomy supplies used for?
For patients with colostomies or ileostomies, including wafers and stoma paste.
What is the role of laxatives in bowel care?
To stimulate bowel movements or facilitate easier stool passage.
What should be monitored in patients with altered bowel elimination?
Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and skin integrity.
What are some risk factors for altered bowel elimination?
Excessive medication use, cognitive impairment, and limited access to toilets.
What is a common effect of antidepressants on bowel function?
They can slow down bowel movements.
What is the significance of stoma color in ostomy care?
The stoma should be beefy red/ pink ; other colors may indicate complications.
(if stoma is dusky pink, dull, call provider immediatley and cover with a wet towel)
What are some foods that can affect bowel health?
Spicy foods, cheeses, greasy foods, bread, and spinach.
What is the nursing care for patients with a colostomy?
Clean the stoma, change the appliance, and assess skin condition, apply and barrier creams as needed (such as paste)
What is the proper technique for enema administration?
Lubricate the tip, position the patient in left Sims,' position knee up, and insert carefully.
What are the signs of GI bleeding in stool?
Bright red blood in stool indicates new blood
Black, sticky, tar-like stools indicate older blood in the stool.
What is the nursing process for patients with bowel alterations?
Assess bowel patterns, diagnose issues, plan interventions, implement, and evaluate.
What are the common clinical manifestations of constipation?
Hard, infrequent stools, distension.
What are the clinical manifestations of bowel obstruction?
Abdominal pain and no stool passage.
What nursing interventions can improve bowel elimination?
Encourage hydration, promote ambulation, and maintain privacy.
What is the purpose of using a lubricant during enema procedures?
To ensure comfort during the procedure.
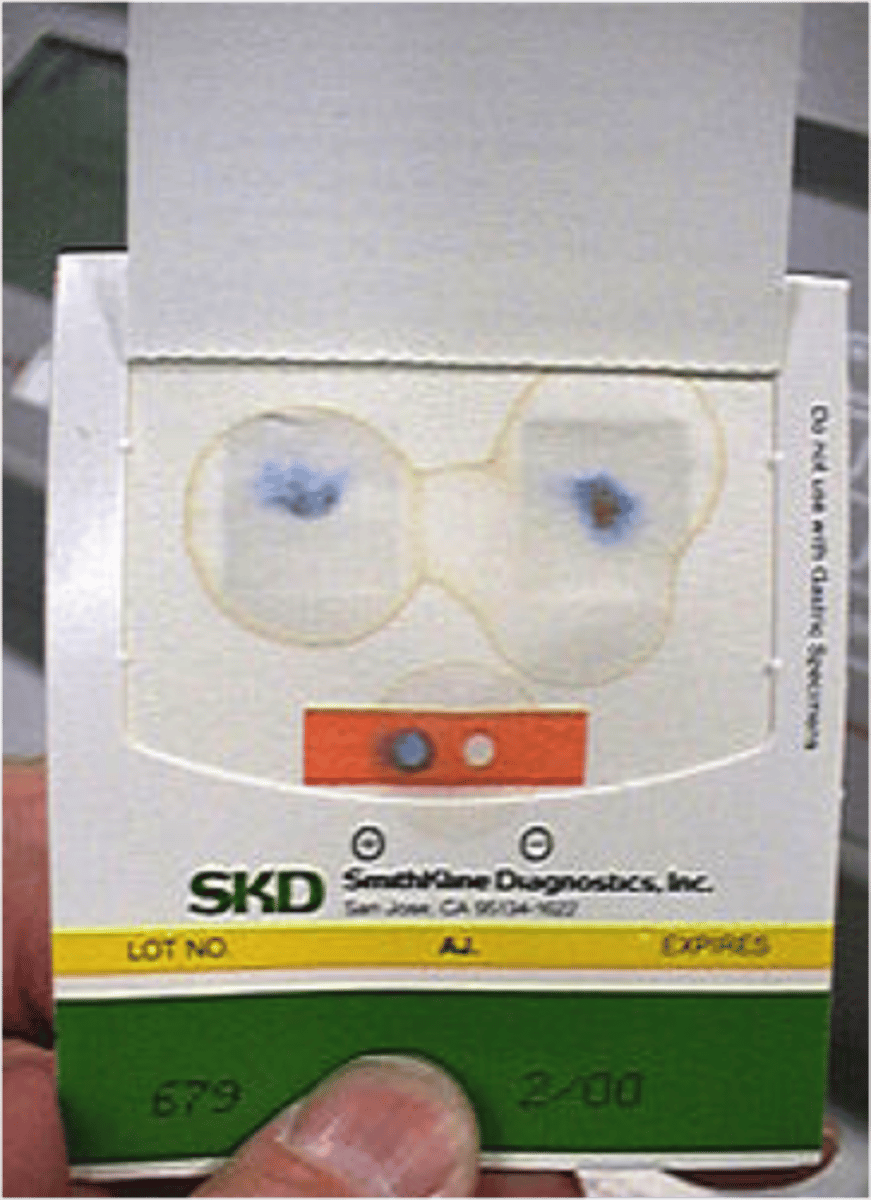
occult blood
need clean stool sample, test for blood in feces
blue means blood is present
ostomy supplies
cutting guide, wafter, stoma adhesive, pouch, clip
colostomy
creation of an artificial opening into the colon
* stool is more formed (colon)
* more formed stool
wafer
cut hole 1/8 inch bigger than stoma
* (too tight can cause strangulation and kill it).
ileostomy
creation of an artificial opening into the ileum
* stool is liquid and watery (small intestine)
* loose/ watery stool
stoma powder/ paste
for extra stick, also acts as a barrier for skin irritation at the base of the stoma
lubricant
use water based lubricant (on enema tip)
older adults - age related differences
experiance peristalsis decline, esophageal emptying slows, muscle tones (like sphincter) weaken, decreased ability to chew
* Comorbidities such as spastic colon affect stool and the ability to go
bowel elimination
excretion of waste products. Breakdown of nutrients from foods ingested and elimination of waste. extends from esophagus to anus.
How many liters of water do adults need per day?
1-2 liters
Not enough liquids can show up as what?
poor skin turgor, hypotension, increased HR
Peristalsis too fast = ?
loose stool
Peristalsis too slow = ?
harder stool
High enema
lift bag 12-18 inches
regular enema
lift bag 12 inches
Low enema
lift bag 3 inches
what contraindicates an enema?
prolapsed rectum (do NOT do)
When should be stop an enema and notfiy the healthcare provider?
severe cramping, bleeding, severe abdominal pain that won't go away
enema liquid amount
750- 1,000 (warm water, cold water will cause cramps) (raise bag slowly)
what are the normal characteristics for an enema?
abdominal cramping is normal, have pt hold in water as long as possible (at least 2-5 mins )
soap suds enema
solution: Castile soap + water (non-medicated)
main purpose: cleansing
action type: irritates bowel
precautions: caution with pregnant women and older adults, mucosal irritation
tap water enema
solution: plain water (non medicated)
main purpose: cleansing
action type: hypotonic, distends colon
precautions: water toxicity risk
normal saline enema
solution: 0.9% NaCl (non-medicated)
main purpose: cleansing
action type: Isotonic, safe
precautions: Safest for all ages
hypertonic solutions (fleets) enema
solution: Sodium phosphate
main purpose: Constipation
action type: Osmotic, draws fluid in
precautions: Dehydration risk (Avoid in renal/elderly)
* contraindicated in dehydrated pts and infants
oil retention enema
solution: Mineral oil
main purpose: Soften stool
action type: Lubricates stool
precautions:Retain 30-60 min
carminative enema
solution: MGW (mag, glycerin, water) Medicated!
main purpose: Relieve gas
action type: Stimulates gas expulsion
precautions: Not for stool removal
colonoscopy prep
Avoid anticoagulants such as aspirin, ibuprofen (NSAIDs), 7 days before as they can give false possitives
avoids citrus or vitamin C 3 days before as they can give false negatives
CT
less detailed
quick look for blockages or constipation problems.
MRI
more detailed
deeper look at muscles or diseases affecting bowel control.
Endoscopy
checks the top (stomach and throat).
looks at: Esophagus, stomach, small intestine
goes in through: mouth
main purpose: Find ulcers, heartburn, bleeding, tumors
prep: NPO
sedation: yes
fecal characteristics
color: brown
odor: malodorous, may be affected by certain foods
consistency: soft, formed
frequency: twice daily to 3 times a wekk
shape: resembles diameter of rectum
constituents: undigested food, dead bacteria, fat, bile, pigment, cells lining intestinal mucosa, water
What is chyme?
comes into the small intestine as a liquid material and mixes with digestive enzymes
Colonoscopy
checks the bottom (colon)
looks at: colon and rectum
goes in through: anus
main purpose: Find colon cancer, bleeding, polyps
sedation: yes
at what age should you get a colonoscopy?
age 45 then every 10 years after that until you are 75
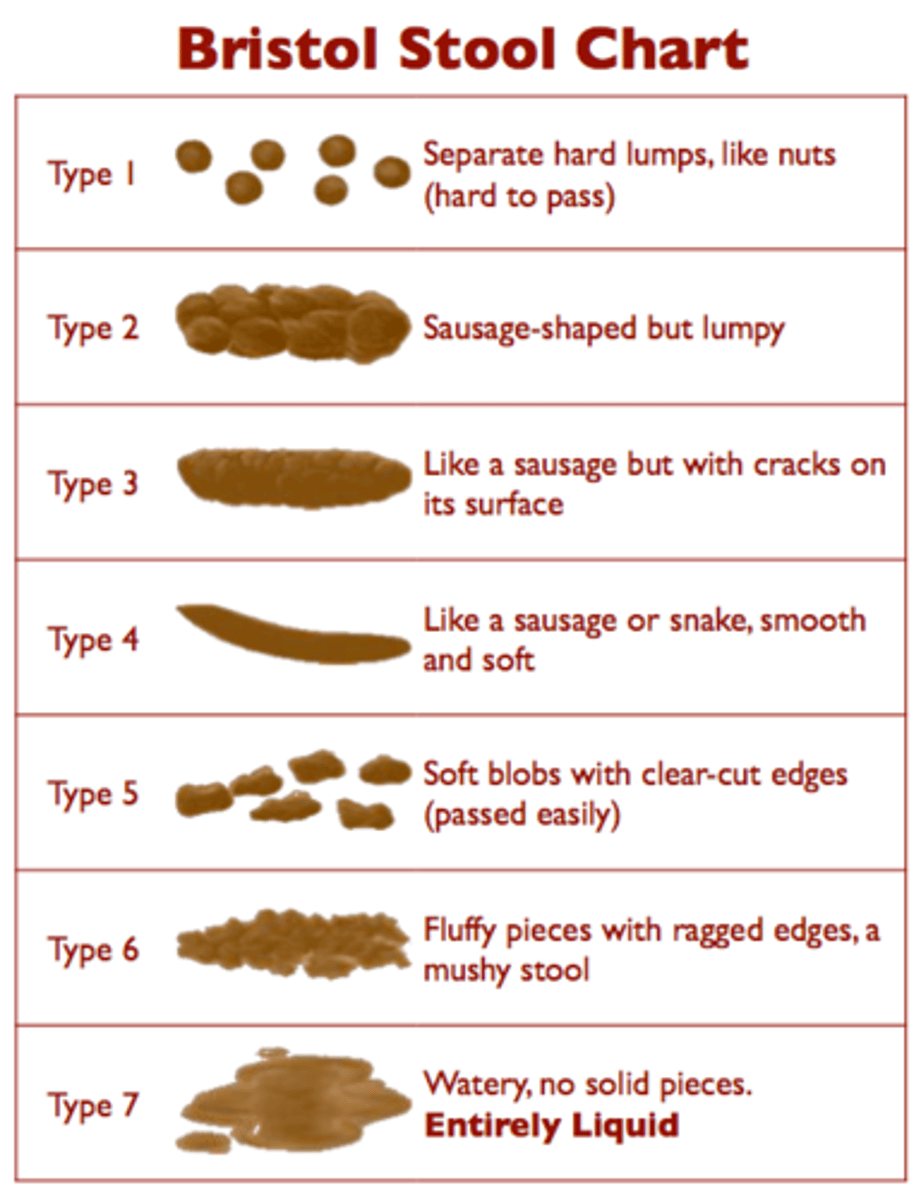
bristool stool chart
3-4 is NORMAL
cleansing enema
non medicated
- high, regular, and low
how often do you change the wafer and colostomy bag?
every 3-7 days
how far do you insert the enema tip?
finger length (3 inches)