POL SCI 20 MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
A state that provokes a crisis would most prefer
that the other state capitulate completely
Which of the following examples illustrates realist logic?
The United States invaded Iraq to remove the threat of weapons of mass destruction, which were a security risk.
Which of these countries had global hegemonic influence in the nineteenth century?
Great Britain
Which of the following describes the most important characteristic of the Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union?
The superpowers both possessed nuclear weapons.
Cooperation is a type of
interaction involving two or more actors working together to achieve some outcome that leaves at least one of them better off.
What are two general concepts thought to most strongly drive civil wars?
Greed and grievance
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, some individuals chose not to wear a mask because they felt that they would not personally contract the virus since so many others around them were already wearing masks. However, these unmasked individuals often inadvertently helped to spread the virus and thus exacerbated the pandemic. This dynamic reflects
a collective action problem.
Which type of leader is most likely to lose office after leading their country into war?
A democratic leader whose country loses a war.
Which of the following is an example of linkage?
You agree to drive your little brother to school, and your older brother agrees to do the dishes when it is your turn.
When an actor can get a better deal through an alternative to reaching a bargain, this is sometimes known as:
an outside option.
Which is the following is an explanation for the occurrence of war?
Misperceptions and mistakes by actors can lead to war.
Two individuals are rowing a boat in a river and are trying to get to shore. Each can either
choose to row toward the left or to row toward the right. If they both row in the same
direction, they will easily move in that direction and toward the shore. If they row in different
directions, the boat will spin around but not move toward either shore. Which game best
reflects this situation?
Stag hunt game
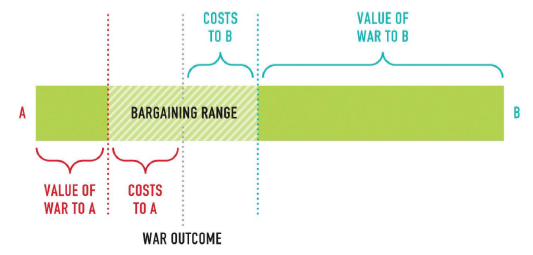
In the figure below, what are the set of potential negotiated deals that State B would accept
but State A would not accept?
Anything inside “Value of War to A”
Why do alliances typically form?
Two or more states have a common security goal and need more military support than one of them has alone.
Which of the following is an example of bargaining?
Two individuals deliberate on how to divide their rock collection.
When we say a good is indivisible, this means that:
the good loses value from being divided.
Which of the following was NOT a consequence of World War I?
The end of colonial empires by many European states
What is the primary risk for a state when it pays for power?
Visible military mobilization may cause the adversary to get anxious and attack.
What is an interest group?
A group of individuals that pushes for policies that benefit members of that group.
What is the essential credible commitment problem for rebel groups to lay down their arms?
Once they disarm, they have no way to be sure that the government will keep the deal.
Which of the following is an example of a diversionary incentive?
The leader of a country starts a war to distract attention from their government’s struggles.
Which of the following is a reason that an alliance commitment might not be reliable?
The lack of an ironclad agreement (to avoid entrapment) could cause a state not to act.
If war is costly, why would domestic actors be willing to risk a conflict?
The costs and benefits are not evenly distributed among domestic actors.
Which of the following is an example of a proxy war?
China giving help to North Korea and the United States giving help to South Korea during the Korean War.
The modern state system is considered to have emerged:
after the Peace of Westphalia.
Which of the following meets the definition of an extremist?
A person whose political views are frequently ignored because no one agrees with them
When constructing a theory of a complex phenomenon, it is necessary to:
make assumptions to simplify the processes being examined.
Theory
Logically consistent set of statements that explains a phenomenon of interest.
Interests
What actors want to achieve through political action
Interactions
The ways in which the choices of two or more actors combine to produce political outcomes.
Bargaining
One actor’s gains hurt the other. (ugly)
Cooperation
At least one actor can gain without hurting anyone else. (nicer, harder to accomplish)
Institutions
Sets of rules that structure interactions in specific ways.
Can be fixed organizations, types of governments, ideas, etc. (UN, types of govs)
Levels of analysis
International
Representatives from states interact
Levels of analysis
Domestic
Actors interacting within the state to make policy (why are the states acting differently)
Levels of analysis
Transnational
Groups with members in multiple states try to influence both domestic and international politics.
Realism
States fear one another, ones capabilities scare another, leading to security dilemma, most involve bargaining + coercion, war is always a possibility and a natural policy
Liberalism
World politics is not just about states. Domestic, internat, and non-gov actors also matter. Each actor has own interests, often not related to fear of living in anarchy, many natural opportunities to cooperate, democracy and wealth help create peace and harmony
Constructivism
Actors interests depend on who they believe they are (identity, culture, beliefs), “Anarchy” is not inevitable; its the view we have taken, The spread of norms is important and often relies on transnational actors to influence states and domestic politics.
Mercantilism
System by which imperial govs use military power to enrich themselves and supporters, then enhance military
The Peace of Westphalia
Stabilized borders, resolved religious conflicts, recognized sovereignty, Start of modern states
Was Napoleon short or average sized?
average sized
Which two countries were fighting for power in 1660s-1815?
France v England
What happened in 1815 between the French Republic and England?
Napoleon defeated in waterloo, ending french republic. England now hegemon
gold standard
Money value depends on how much gold owned in country
What 2 powers did Europe split into in 1870s to 1914?
Central powers & Allied powers
Germany was late to the colonizing game, so instead of expanding for new states, they
wanted to colonize existing states in Europe
June 28 1914
Assassination of Franz Ferdinand by Serbian Nationalist
1914-1918
World War I
Political movement between farmers and middle class that desired right-wing ideas in Italy
Fascism
Political movement where works and movements disillusioned with capitalism aimed for rights and equality in the Soviet Union
Socialism
Which President established the League of Nations
Woodrow Wilson
What treaty puts an end to WWI in 1919 and blames Germany for all of it and makes them pay?
Treaty of Versailles
What did Germany do to compensate for their debt after WWI?
Print lots of money, which caused hyperinflation
What happens in 1929 that affects the whole world?
The Great Depression
What convinces Japan to surrender in August 1945, effectively ending WWII?
US bombing on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Who leads Iraq to invade Kuwait?
Saddam Hussein
Why does Pres. Bush push US to invade Iraq?
He suspected they were hiding WMD
Actor
basic unit of analysis. Can be individuals or groups with common interests
Who/What is the key actor and why?
The state: central authority with the ability to make and enforce laws, rules, and decisions within a specified territory. No higher authority exists over states to make them do anything.
Interactions
Multiple actors make choices that combine into pol outcomes
What are the Rational Choice assumptions?
Ass1: Actors know what they want and try to produce what they want
Ass2: Actors choose strats that are best response to anticipated strats of others
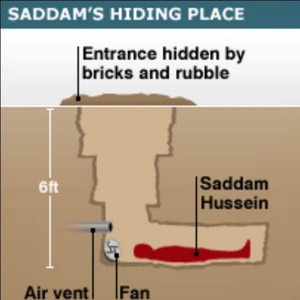
Saddam Hussein hiding spot, found in December of 2003
Even cooperation involves a problem of ______
bargaining
Bargaining
Interactions that make one actor better off at the expense of another.
If A and B already have the entire cake between them; A has 40% and B has 60%.
A and B are on the Pareto frontier. Nothing more left to claim
Any split or deal different from this current position involves redistribution. Someone would lose some cake.
What is this called?
Zero-Sum Interaction
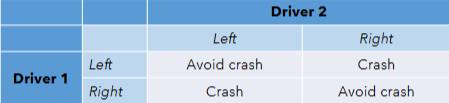
What game does this graph represent?
Stag Hunt
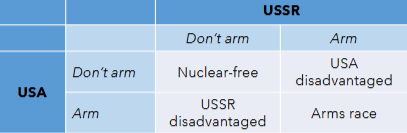
What game does this graph represent?
Prisoner’s Dilemma
What is nash equilibria?
Preferrable outcome for both parties
Collective action problems
actors have incentives to collaborate, but each acts with expectation that others will pay for cost of cooperation
Actors, especially in world politics, tend to stick around and have repeated interactions, or
iterations
Tie together multiple issues through
linkage
Lack of info leads to
uncertainty and misperception
Power
The ability of Actor A to get Actor B to do something that Actor B otherwise wouldn’t do
Coercion
Impose or threaten to impose costs on other actors to induce a change in their behavior
How do you make your threats credible?
Actions taken before or during bargaining that make reversion outcome more favorable for one party
Setting the agenda shapes the choices others can make
War
event involving the organized use of military force by at least two parties that reaches a minimum threshold of severity
interstate war
When main actors are states
civil or intrastate war
When main actors are within states
What issues are wars fought over?
Territory, policies, regime type, relative power
What classical explanations exist for war?
Realism, Misperceptions and mistakes, Domestic policies
bargaining range
a set of deals both prefer over the reversion outcome of war
The bargaining model’s strength is how it highlights the key strategic problems that can lead to war, _____________
even when a peaceful bargain (almost always) exists.
Compellence
Change the squo through threat of force
—start/stop doing this, or else…
Deterrence
Preserve the squo through threat of force
—Don't start doing this, or else…
The world is _______, so no instit can reliably resolve all conflicting interests. States must bargain
anarchic
crisis bargaining
bargaining under the threat of war
The 3 Rationalist explanations for war are….
Incomplete information (they might be lying)
Commitment problems (they might cheat on a deal)
Issue indivisibility (we cant share)
You are more likely to get what you want if the other side thinks……..
you are capable and/or resolved (willing to endure costs)
All credible actors make threats….
costly
Audience costs
negative repercussions for failing to follow through on a threat or honor a commitment
Brinksmanship
Take actions that increase the risk of war, hoping the other side “blinks” first. Make it costly to back away from your threat
It's also hard for states to make credible commitments or promises
not to use force to revise the bargaining results later
Bargaining over future bargaining power:
The disputed good may increase future bargaining power. Giving up the good makes you weaker, and no guarantee…..
other party would not take advantage of you
Factors beyond the bargain impact the
balance of power
preventive war
State A choosing to fight State B hoping to prevent B from getting stronger. No guarantee of victory, but better to try now than later
preemptive wars
State A choosing to fight State B because of the fear of imminent attack by State B
Indivisible good
A good that cannot be divided without diminishing its value, leading to “all or nothing” bargaining
Indivisibility (or a good’s value) is a property that can be shaped………
through politics and rhetoric. It is not necessarily intrinsic
It is theoretically possible to make……
linkages with another issue/good in order to make side payments