Understanding Number Systems and Their Properties
1/528
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
529 Terms
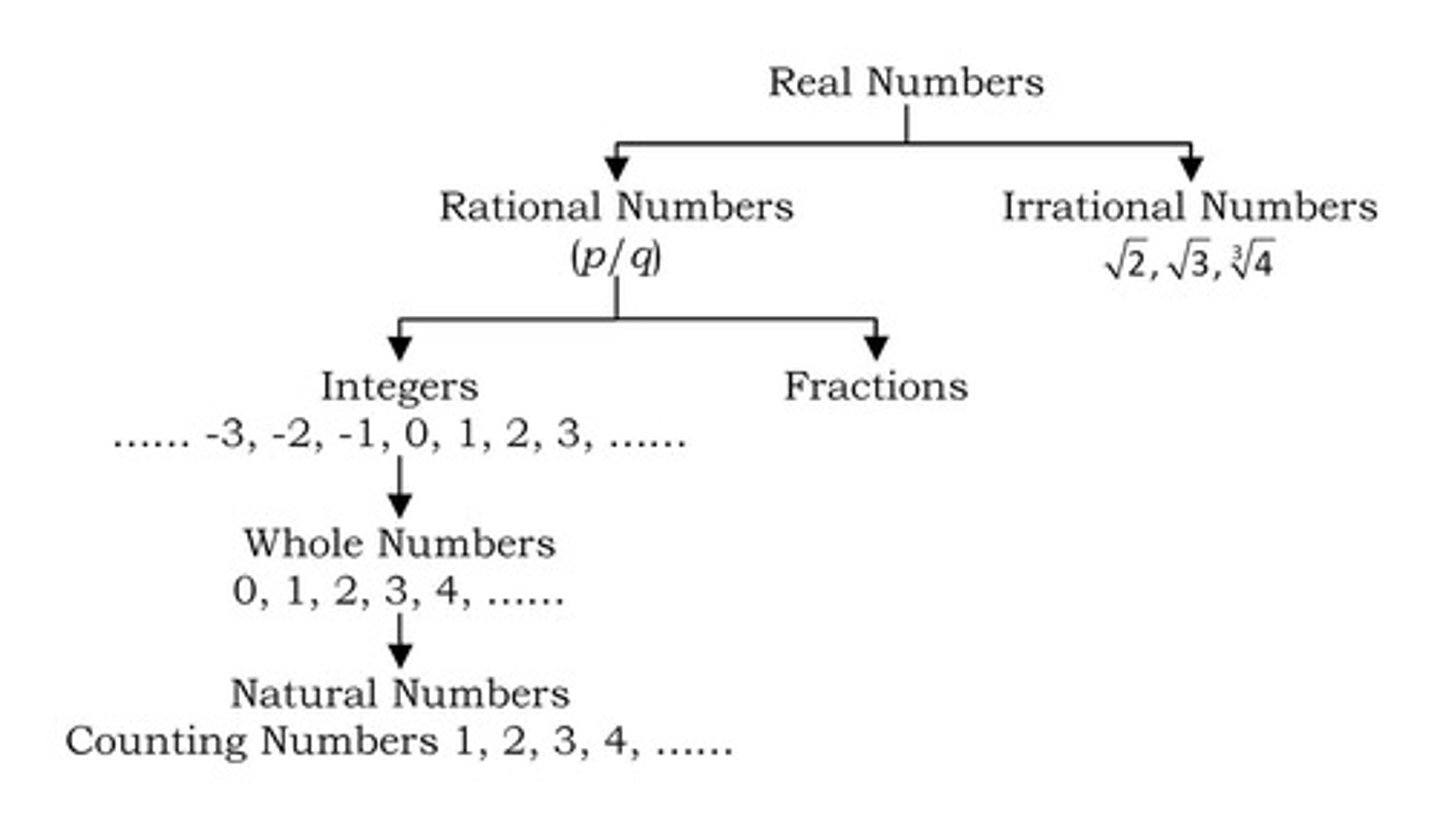
What are Natural Numbers?
Counting numbers, viz. {1, 2, 3, 4, ...} and denoted by N. 0 is NOT a Natural number.
What are Whole Numbers?
Set of Natural numbers and also 0 (Zero), viz. {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ...} and denoted by W.
What are Integers?
Set of negative and positive Natural numbers and 0, viz. {..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}. Zero is neither positive nor negative.
What is a Proper Fraction?
A fractional number less than 1, where the numerator is less than the denominator.
What is an Improper Fraction?
A fractional number more than 1, where the numerator is greater than the denominator.
How do you compare fractions with the same difference between numerators and denominators?
For proper fractions, the fraction increases as the numerator increases; for improper fractions, the fraction decreases as the numerator increases.
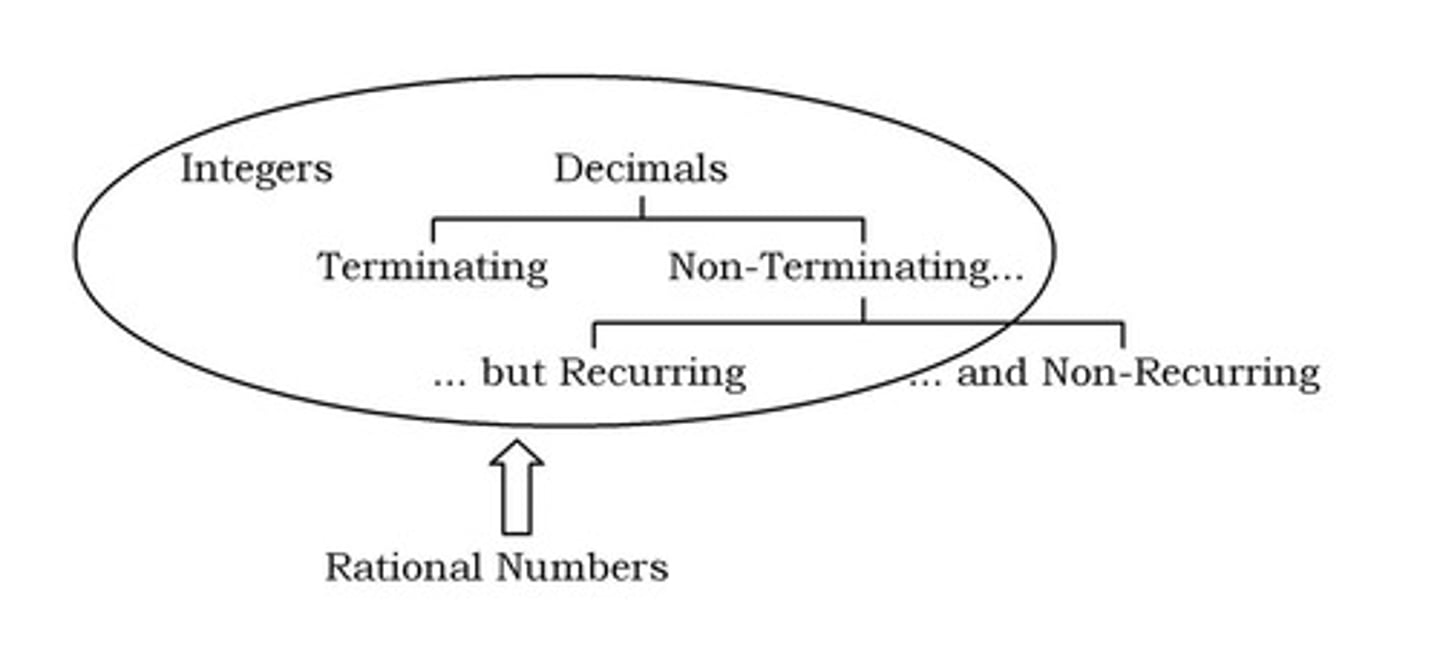
What are Rational Numbers?
The set of all integers and fractions, denoted by Q, which can be expressed in the form p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
How can integers be expressed as Rational Numbers?
All integers can be expressed in the form p/q with q = 1. E.g., 3 can be expressed as 3/1.
What types of decimals are considered Rational Numbers?
All terminating fractions and non-terminating but recurring decimals can be expressed in the form p/q.
What are Irrational Numbers?
Numbers that are non-terminating and non-recurring, such as √2, π, etc.
What is the significance of the invention of 0 in number classification?
The invention of 0 gave rise to the set of Whole Numbers.
What is the set of positive integers?
The set of positive integers is {1, 2, 3, ...} and does not include 0.
What is the set of non-negative integers?
The set of non-negative integers includes 0 and is {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}.
What is a mixed number?
A number that includes both an integral part and a fractional part, e.g., 3 3/4.
How can you express a fraction like 15/4 in mixed form?
15/4 can be expressed as 3 3/4.
What is the relationship between the numerator and denominator in a proper fraction?
In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator.
What is the relationship between the numerator and denominator in an improper fraction?
In an improper fraction, the numerator is greater than the denominator.
What is the notation for Rational Numbers?
The set of Rational Numbers is denoted by Q.
What is the condition for a number to be expressed in the form p/q?
The denominator q must be a non-zero integer.
What is an example of a terminating decimal?
0.3 is an example of a terminating decimal.
What is an example of a non-terminating recurring decimal?
0.333... is an example of a non-terminating recurring decimal.
What happens to the value of a proper fraction as the numerator increases?
The value of a proper fraction increases as the numerator increases.
What happens to the value of an improper fraction as the numerator increases?
The value of an improper fraction decreases as the numerator increases.
What is the nature of the constant π?
π is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed in the form p/q.
What is the approximate rational representation of π?
22/7 is a rational approximation of π.
What defines a real number?
Real numbers are the set of rational and irrational numbers that can be plotted on a number line.
Can the number 2 be plotted on the real number line?
Yes, because 2 is a real number.
What is the characteristic of non-terminating non-recurring numbers?
They cannot be expressed in the form p/q.
How can recurring numbers be expressed in p/q form?
Recurring numbers can be converted into p/q form through specific algebraic manipulations.
Convert 0.333... to p/q form.
Let a = 0.333...; then 10a = 3.333...; subtracting gives 9a = 3, thus a = 1/3.
Convert 0.1212... to p/q form.
Let b = 0.1212...; then 100b = 12.1212...; subtracting gives 99b = 12, thus b = 12/99.
What is the general rule for converting purely recurring numbers to p/q form?
The recurring digits are written once over as many 9s as there are digits that recur.
How do you convert numbers with non-recurring and recurring digits, such as 0.1333...?
Let a = 0.1333...; then 10a = 1.333... and 100a = 13.333...; subtracting gives 90a = 13 - 1.
Convert 0.10333... to p/q form.
Let b = 0.10333...; then 100b = 10.333... and 1000b = 103.333...; subtracting gives 900b = 103 - 10.
Convert 0.15757... to p/q form.
Let c = 0.15757...; then 10c = 1.5757... and 1000c = 157.5757...; subtracting gives 990c = 157 - 1.
What is the general formula for a recurring number?
Recurring Number = Non-recurring digits followed by recurring digits over as many 9s as recurring digits, followed by as many 0s as non-recurring digits.
What is the result of evaluating 1/7?
1/7 is a recurring decimal, specifically 0.142857...
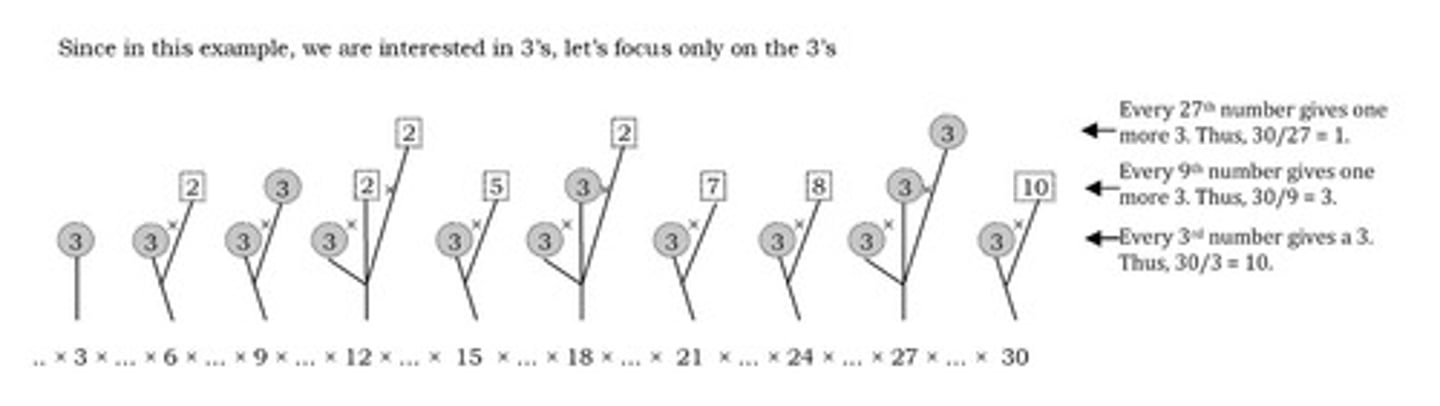
What is the significance of the number tree in relation to rational numbers?
The number tree illustrates the classification of numbers, including rational and irrational.
What is the relationship between rational numbers and their decimal representation?
Rational numbers can either terminate or recur in their decimal representation.
What is an example of a non-terminating but recurring number?
0.333... is an example of a non-terminating but recurring number.
What is the value of a + b if 0.ababab... = 8/11?
The value of a + b is 9.
If 0.1010... = x, what is the value of x?
The value of x is 0.444...
What is the decimal representation of x if 0.1010...... = 0.222...... x?
x = 0.444......
What is the least three-digit number n such that 0.abab...... × n is an integer for single digit natural numbers a and b?
n = 990
If 17.abcabc = 37, what is the sum of a + b + c?
a + b + c = 18
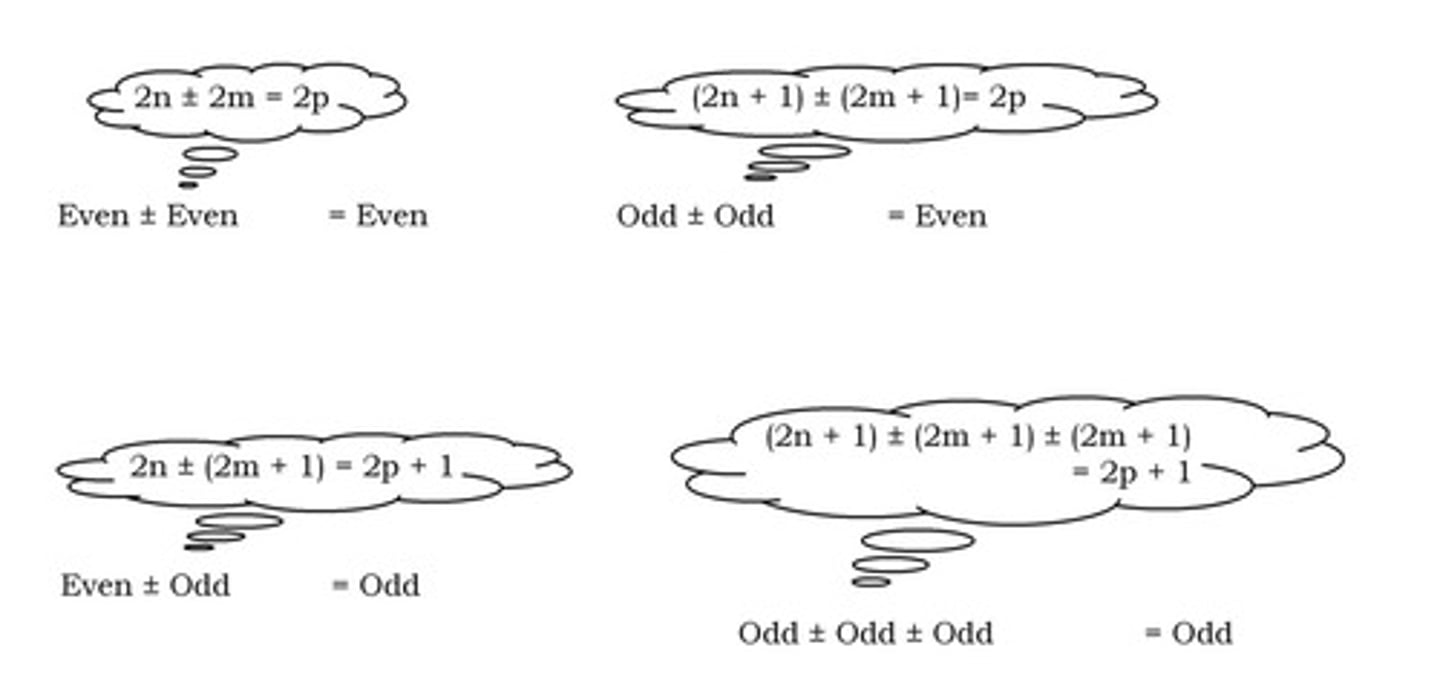
What defines an even number?
An even number is divisible by 2, represented by 2n, where n = 0, 1, 2, ... and includes 0.
What defines an odd number?
An odd number is not divisible by 2, represented by 2n + 1, where n = 0, 1, 2, ...
When adding or subtracting odd numbers, how do you determine the result's parity?
Consider the extra 1s from odd numbers; check if the total number of 1s is odd or even.
What is the result of multiplying an even number by any number?
The result is always even.
What is the result of multiplying an odd number by any number?
The result is always odd.
What is the result of x^3 + x^4 in terms of parity?
Always even.
What is the result of xy^2 + x^2y in terms of parity?
Could be even or odd.
If 3a + 1 is even, what can be inferred about a?
a is odd.
If 5a - 3 is odd, what can be inferred about a?
a is even.
If 4a + 2 is even, what can be inferred about a?
a is odd.
If 7a - 4 is even, what can be inferred about a?
a is even.
If 11a + 10 is odd, what can be inferred about a?
a is odd.
If 10a - 7 is odd, what can be inferred about a?
a is even.
If a × b × c is odd, what can be inferred about ab + bc + ca?
ab + bc + ca is always even.
What can be inferred about (a - b) × (b - c) × (c - a) in terms of parity?
Could be even or odd.
Which statement cannot be true if x, y are odd and positive, and z is even and positive?
(x - z) × y is odd.
Which statement cannot be true if x, y, and z are distinct odd and positive integers?
(x - y)2 × z is even.
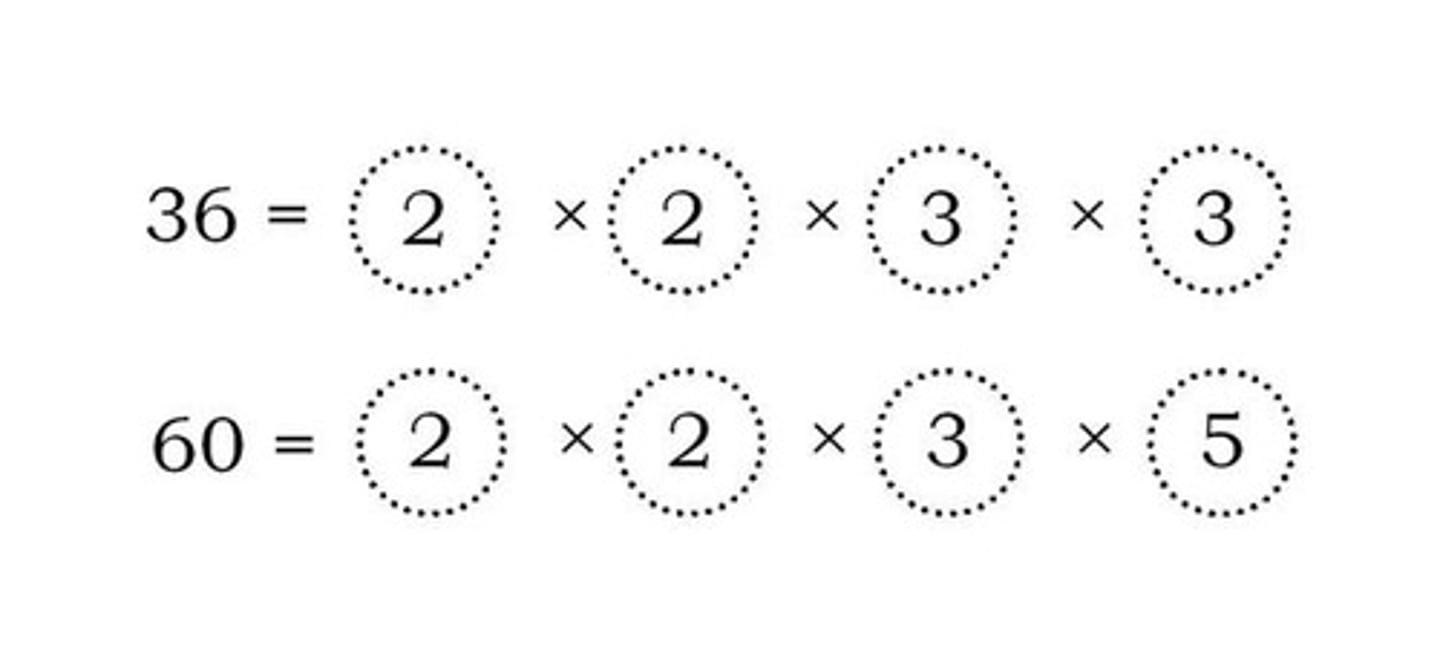
What are prime numbers?
Natural numbers with exactly two distinct factors: 1 and itself.
What are composite numbers?
Natural numbers with more than two distinct factors.
What is the only even prime number?
2
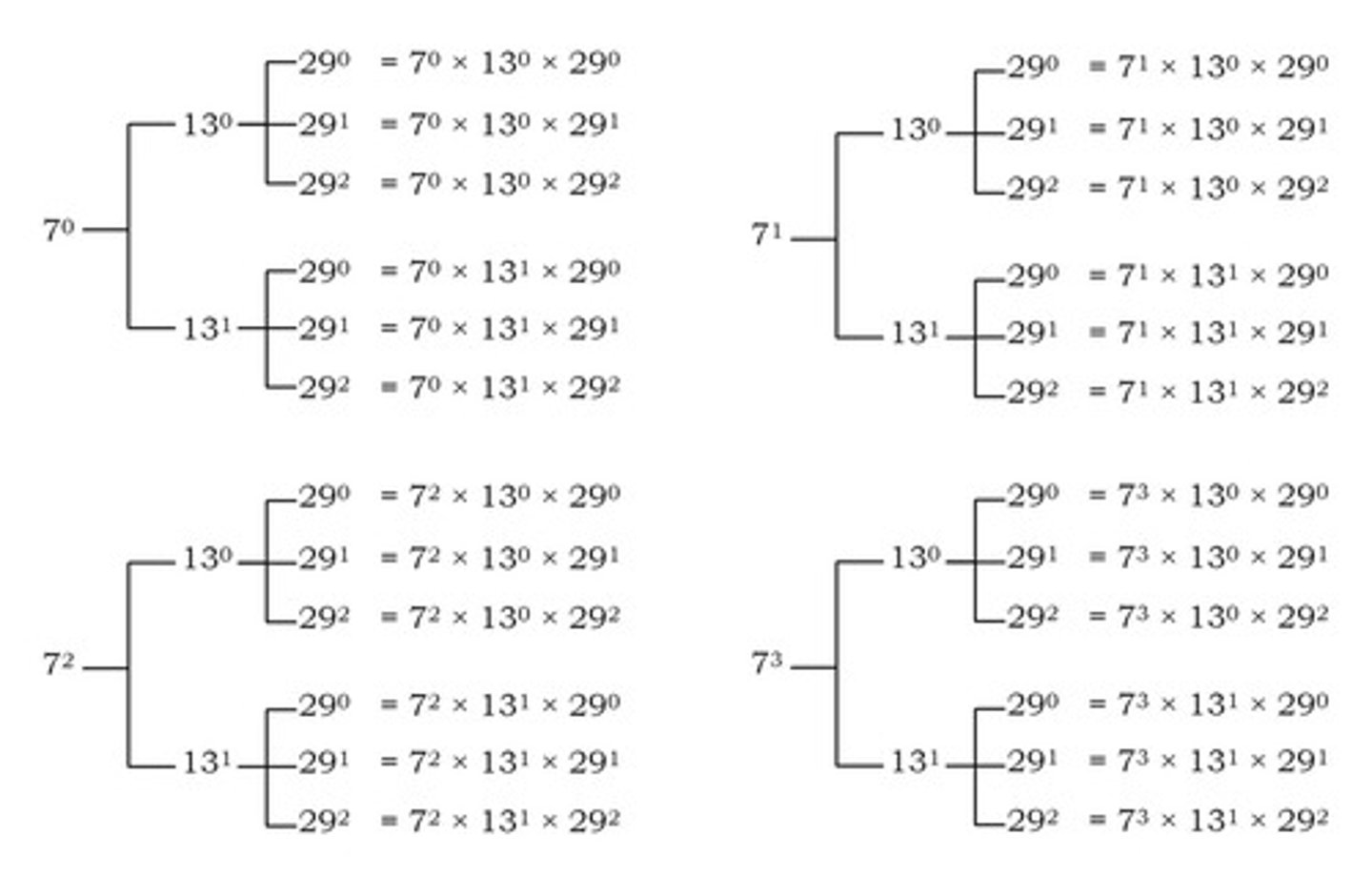
What is the significance of prime numbers in number theory?
All natural numbers can be expressed as a product of prime numbers, considered as 'atoms'.
What is factorization?
The process of writing any number as a product of prime numbers.
What are co-prime numbers?
Two numbers that do not share any common factors other than 1.
What is said to be co-prime to all numbers other than 1?
1 is said to be co-prime to all numbers other than 1.
State true or false: All prime numbers are odd.
False.
State true or false: The product of any two prime numbers could be prime.
False.
State true or false: The sum of any two prime numbers is always odd.
False.
State true or false: The difference of any two prime numbers is always even.
False.
If p is a prime number greater than 3, what are the possible remainders when p is divided by 6?
1 or 5.
If p is a prime number greater than 3, what are the possible remainders when p² is divided by 6?
1
In how many ways can 72 be written as a product of two co-prime natural numbers?
6
If a, a + 2, a + 4 are all prime numbers, how many distinct values can a take?
1
If p is a prime number greater than 3, what is the remainder when (p² + 17) is divided by 12?
9
If p and q are prime numbers greater than 3, what is the greatest number by which (p² - q²) is always divisible?
12
How many prime numbers are of the form n³ - 1, where n is any natural number?
1
How many primes cannot be expressed as a difference of squares of two natural numbers?
1
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 3?
The sum of the digits should be divisible by 3.
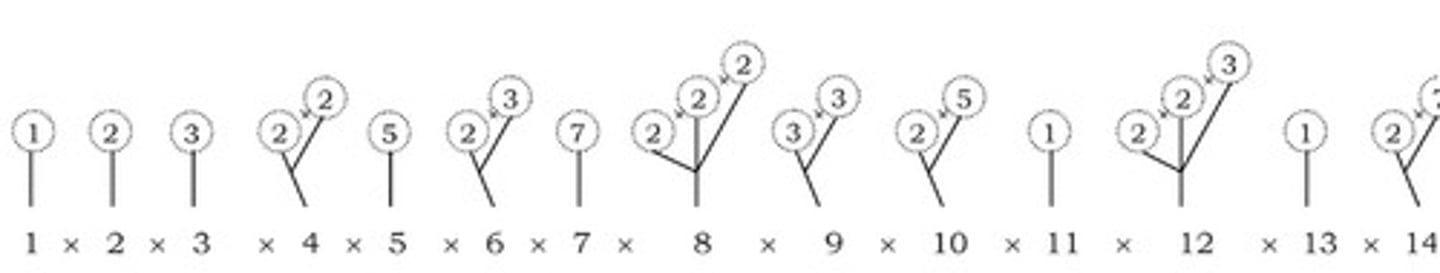
How can you find the remainder when a number is not divisible by 3?
The remainder will be the same as that when the sum of the digits is divided by 3.
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 4?
The two-digit number formed by the last two digits should be divisible by 4.
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 6?
A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 2 and 3.
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 8?
The last three digits should be divisible by 8.
What is the explanation for why the rule for divisibility by 3 works?
Any number can be expressed in a form where the sum of its digits determines its divisibility by 3.
What is the explanation for why the rule for divisibility by 4 works?
For a number to be divisible by 4, the last two digits must be divisible by 4.
What happens if the last two digits of a number are '00'?
The number will be divisible by 4.
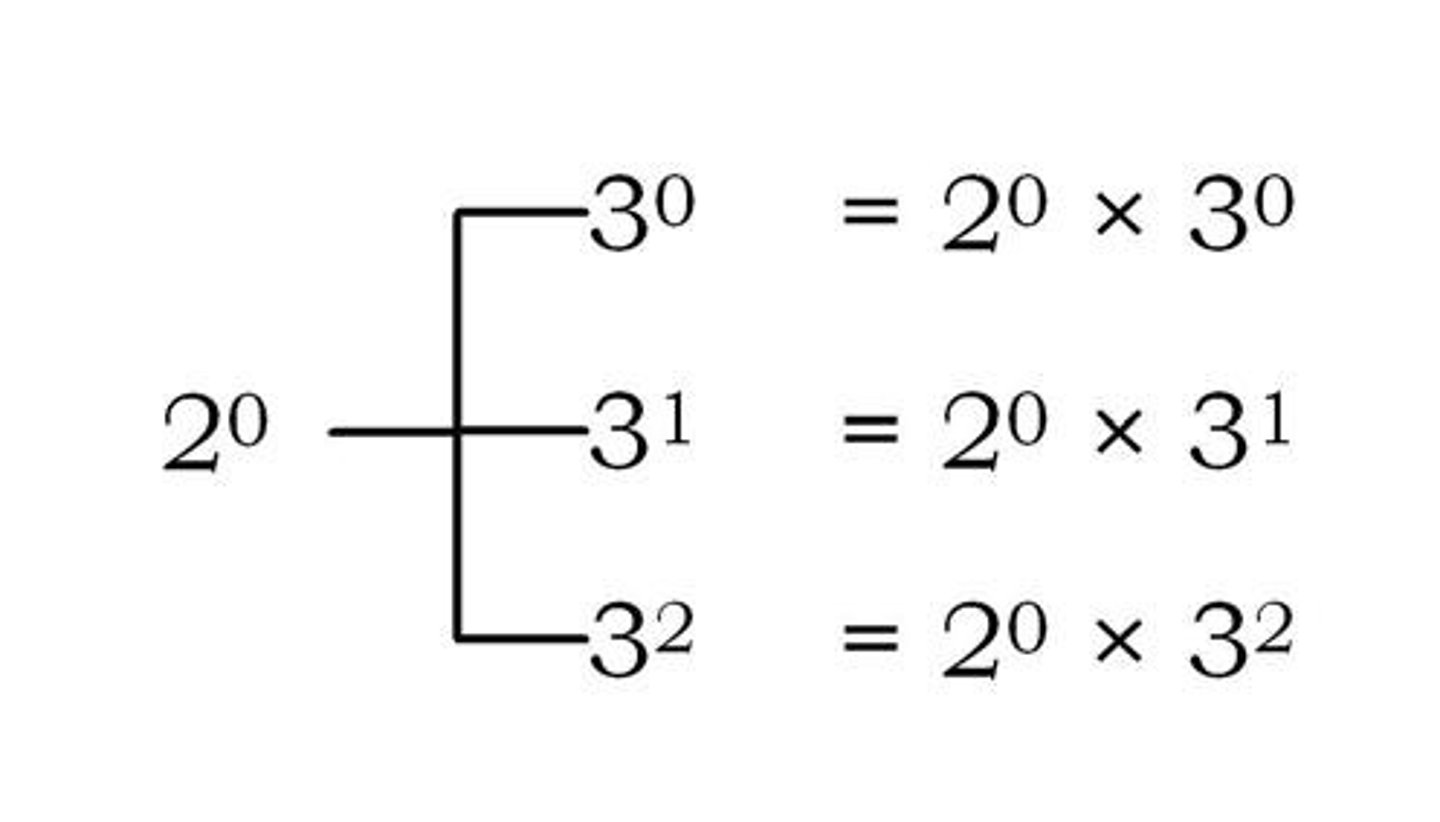
What is the example used to illustrate the rule for divisibility by 3?
The number 34728 is divisible by 3 because the sum of its digits is 24.
What is the example used to illustrate the rule for divisibility by 4?
The number 34728 is divisible by 4 because the last two digits 28 are divisible by 4.
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 8?
A number is divisible by 8 if the last three digits of the number are divisible by 8.
Is the number 1430254 divisible by 8?
No, because 254 is not divisible by 8.
What is the remainder when 1430254 is divided by 8?
The remainder is 6.

What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 9?
A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
Is the number 14043573 divisible by 9?
Yes, because the sum of its digits is 27, which is divisible by 9.
Is the number 24736 divisible by 9?
No, because the sum of its digits is 22, which is not divisible by 9.
What is the remainder when 24736 is divided by 9?
The remainder is 4.
What is the rule for determining if a number is divisible by 11?
Add all the alternate digits starting from the unit place (U) and the remaining alternate digits (T). If the difference U - T is 0 or divisible by 11, the number is divisible by 11.
How do you find the remainder when a number is not divisible by 11?
The remainder is U - T.