UPD and imprinting
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
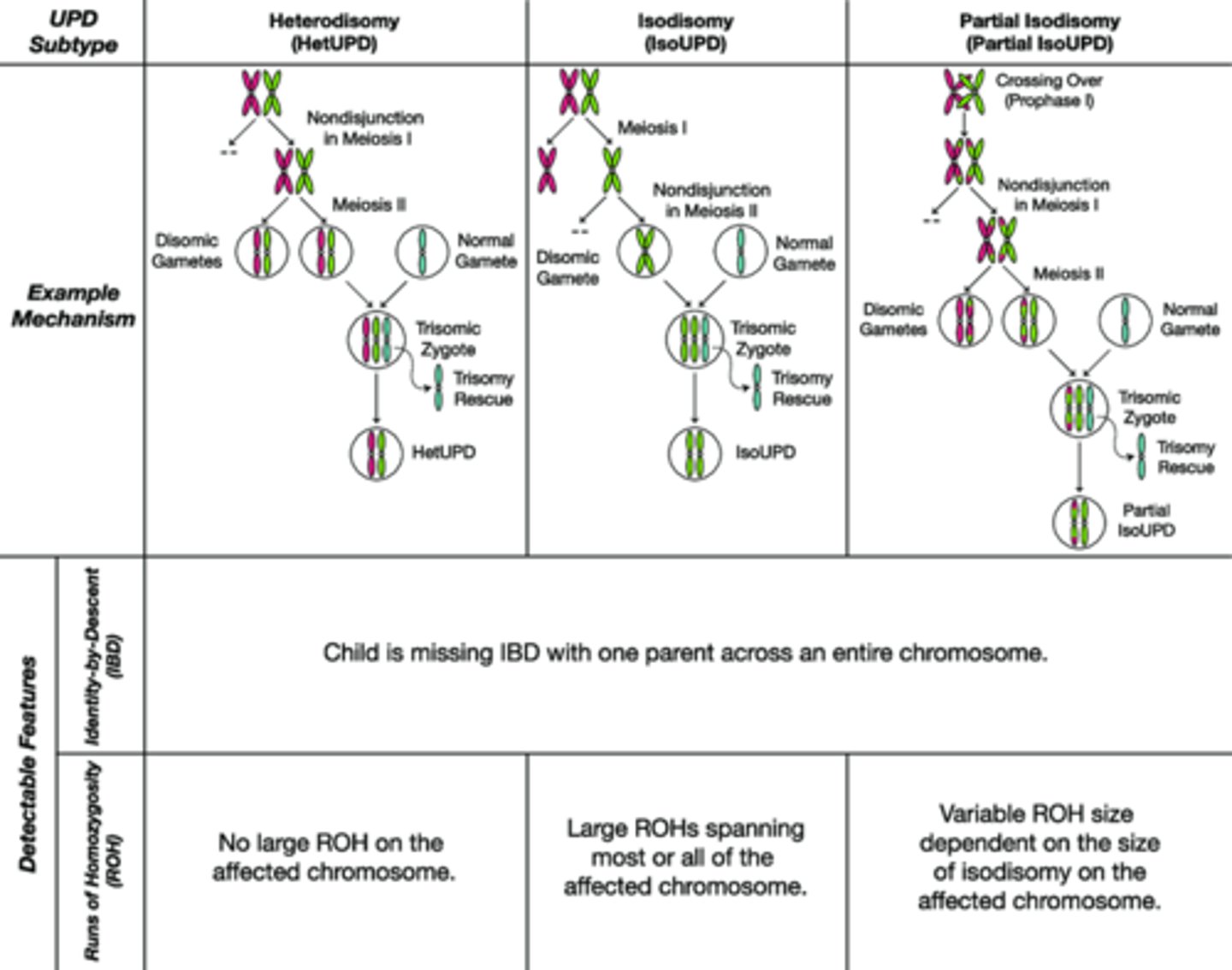
What is UPD isodisomy? and what causes it?
both homologs are identical.
caused by nondisjunction at meiosis II or mitotic error
causes of UP
gamete complementation, trisomic rescue, monosomic rescue, mitotic error
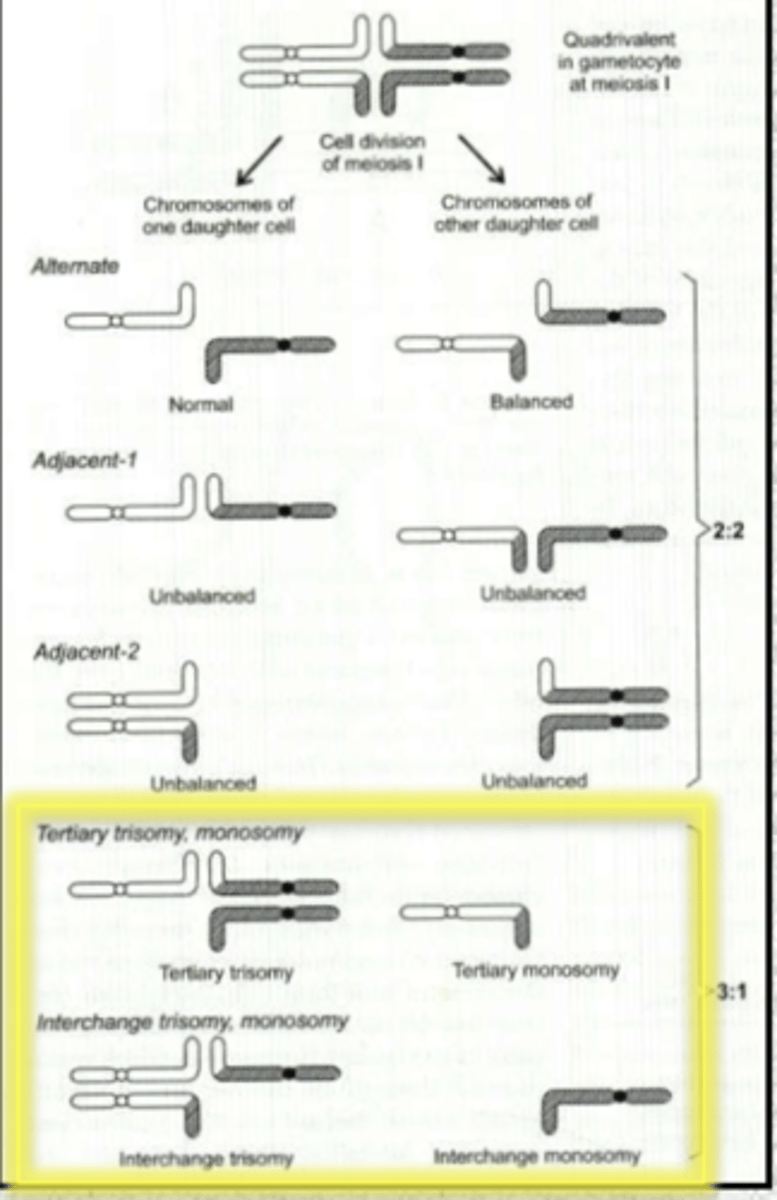
interchange 3:1 segregation
full autosomal trisomy or full monosomy
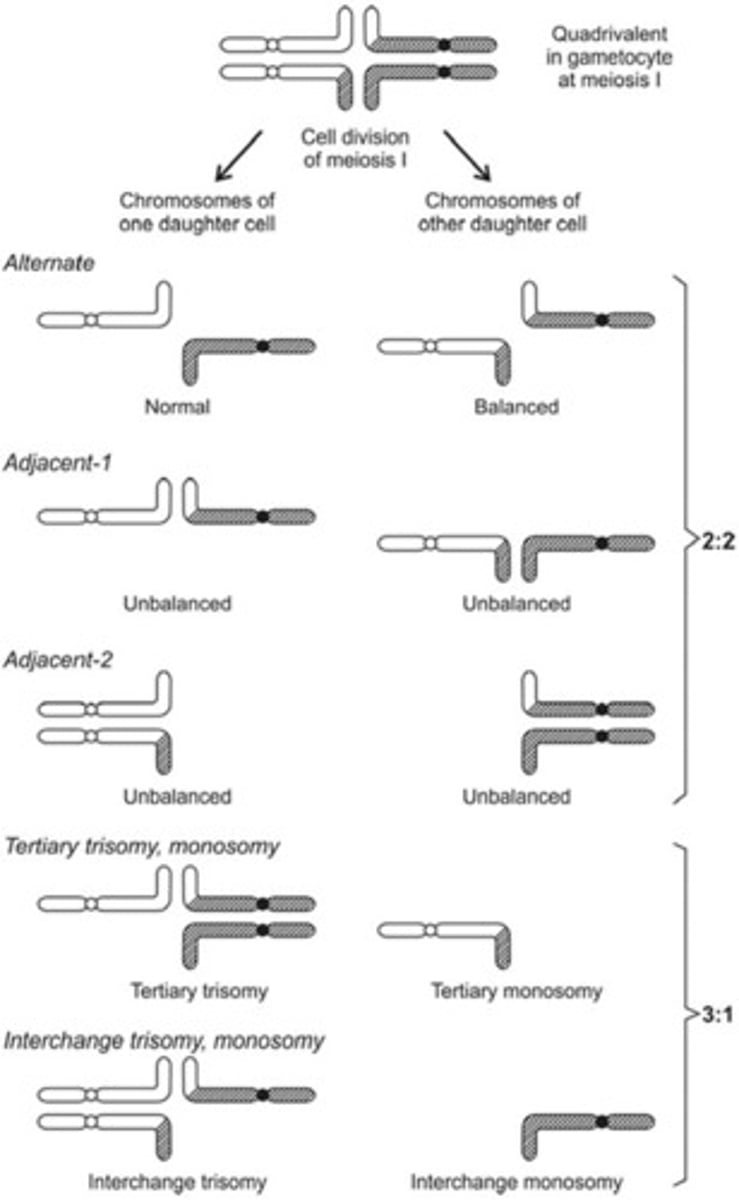
if a parent is a carrier of a balanced or rob translocation, asymmetric segregation of the chromosomes could lead to _________________ ____________. This could result in the __________ chromosome and one of the ___________ homologs being transmitted into the fetus and post-zygotic correction could result in ______
-interchange trisomy
-derivative
-normal
-UPD
in the case of an acrocentric chromosome with a parent who has a rob t, the chromosome could replicate as a(n) _______________ and has been reported in UPDs for chromosomes ______, _______, and ______
-isochromosome
-13, 14, and 15
how does segmental UPD arise and where does the segment lay on the chromosome?
caused by post zygotic somatic recombination and the segment lies distally. The rest of the chromosome will have normal biparental inheritance
phenotypes caused by UPD
IUGR/post natal growth retardation, ID, congenital defects, dysmorphia
UPD isodisomy can cause _________ of an AR gene
homozygosity
what does UPD look like on karyotype
normal karyotype
what do polymorphic DNA markers show with UPD isodisomy
markers show both homologs with the same haplotype from one parent.
large runs of homozygosity spanning most or all of the affected chromosome
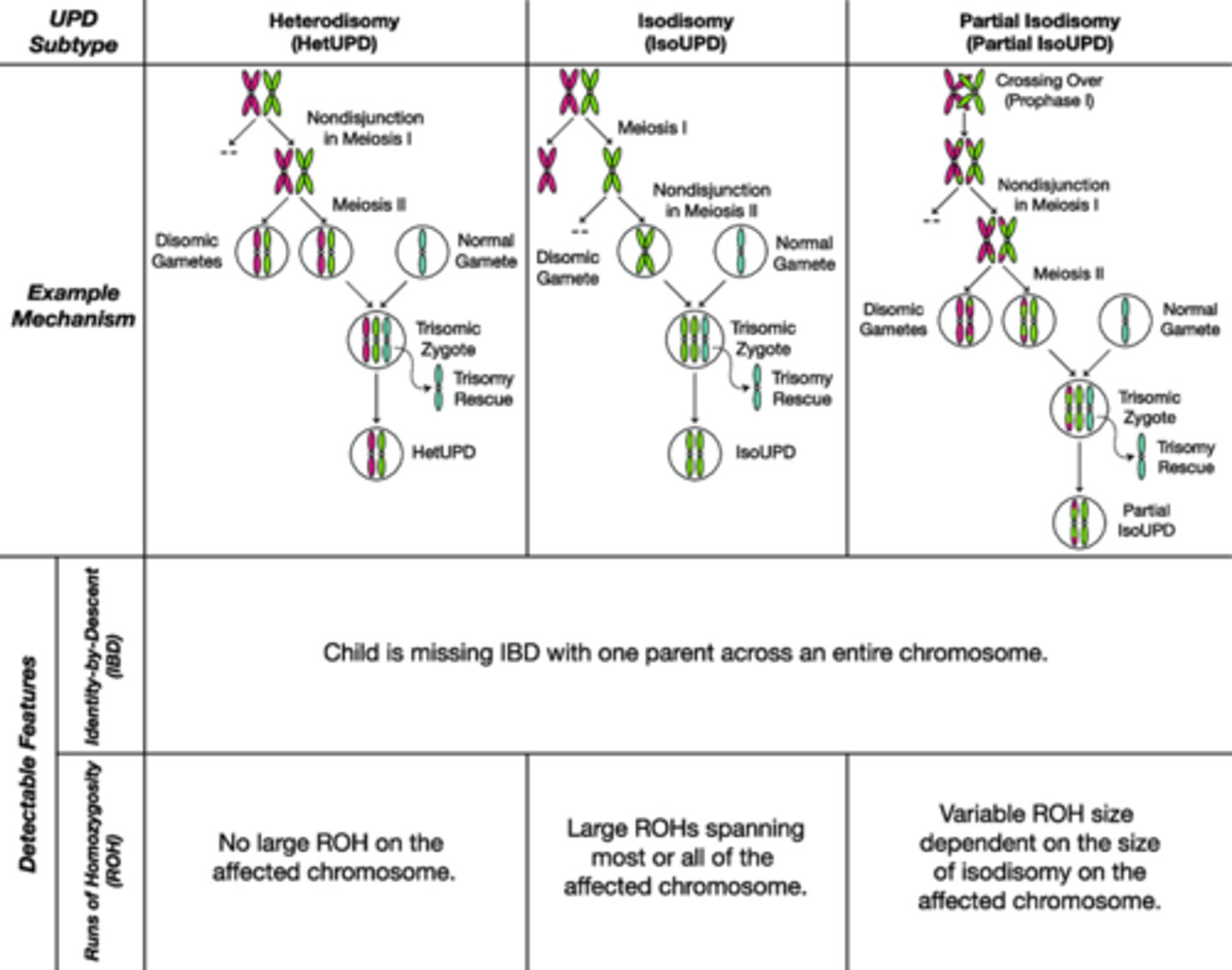
what is UPD heterodisomy
different homologs
what do polymorphic DNA markers show with UPD heterodisomy
2 chromosomes that have the same haplotypes as the chromosome pair form one parent
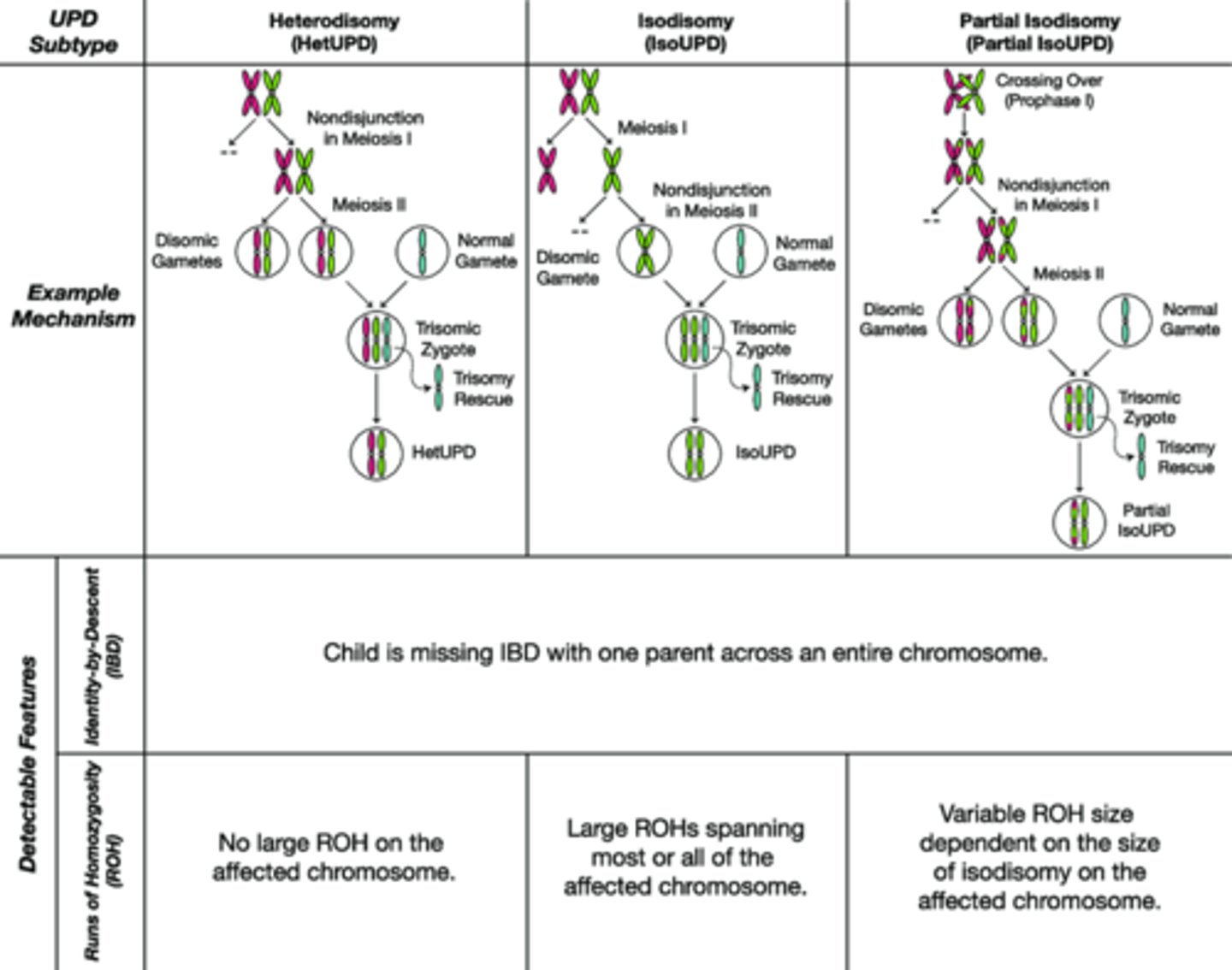
cause of UPD heterodisomy
nondisjunction at meiosis I
define epigenetics/imprinting
same genotype will produce a different phenotype depending on the sex of the transmitting parent due to methylation error
imprinting mechanisms function _____________________
mono-allelically (meaning, when imprinting happens, only the paternal OR maternal segment will be active)
what happens of both imprinted segments originate from one parent
there would be either double the amount of expression or no expression at all, resulting in the phenotypic defects seen in people with UPD
What does paternal UPD of all 46 chromosomes cause
complete hydatidiform mole
what does maternal UPD of all 46 chromosomes cause
benign teratoma (type of ovarian cyst)
what forms from one maternal and two paternal chromosome complements
triploid fetus
what is gamete complementation
This is when you have a gamete with two copies of a chromosome (should have only one), and it gets fertilized with a gamete that happens to have no copies of that chromosome.
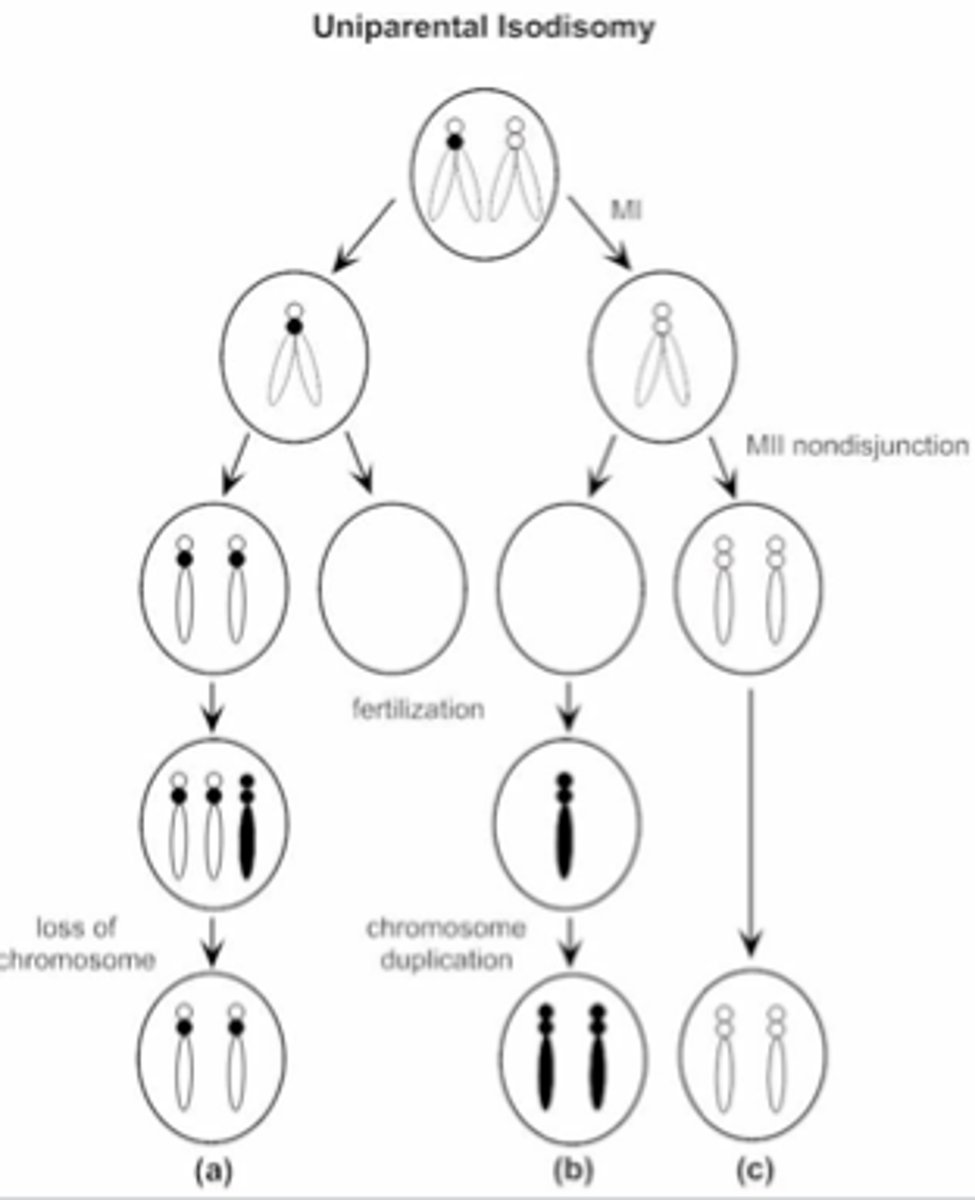
what is the most common mechanism that causes UPD and how does it work
trisomic rescue:
a trisomy that looses the extra chromosome, restoring the zygote to disomy. when the wrong chromosome is lost, this can cause maternal or paternal UPD
what is monosomic rescue and how does it work
monosomic zygote (only one copy of a particular chromosome – the other parent’s dropped out), and that chromosome duplicates itself. replication of the normal homolog can cause UPD isodisomy
what is mitotic error
normal conception that leads to trisomy or monosomy.
trisomy: the wrong chromosome is lost producing either maternal or paternal UPD
monosomy: the chromosome is duplicated
what are some rare mechanisms that cause UPD
- correction of interchange trisomy
- correction of interchange monosomy
- isochromosome formation
- correction of imbalance due to extra structurally abnormal chromosomes.
tertiary 3:1 segregation
trisomy or monosomy dependent on combined content of the der chromosomes
causes tertiary trisomy, tertiary monosomy
what does a karyotype look like when there is a segmental UPD
normal karyotype
examples of conditions that can be caused by segmental UPD
BWS, russell sliver syndrome, transient neonatal diabetes (TNDM)
condition that comes from UPD on chromosome 6
transient neonatal diabetes (TNDM)
condition that comes from UPD of chromosome 7
russell silver syndrome
condition that comes from UPD of chromosome 11
BWS
conditions that comes from UPD/imprinting/deletion on chromosome 15
PWS
AS
majority of PWS and AS cases are caused by _________ on chromosome 15
deletions
PWS is caused by ___ deletion, while AS is caused by a ___ deletion
PWS= paternal deletion
AS= maternal deletion
what gene is usually effected in AS
UBE3A
what gene is usually effected in PWS
SNRPN