Depth + Motion Perception
5.0(2)Studied by 4 people
0%Unit 3: Sensation and Perception Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/13
Last updated 11:18 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
1
New cards
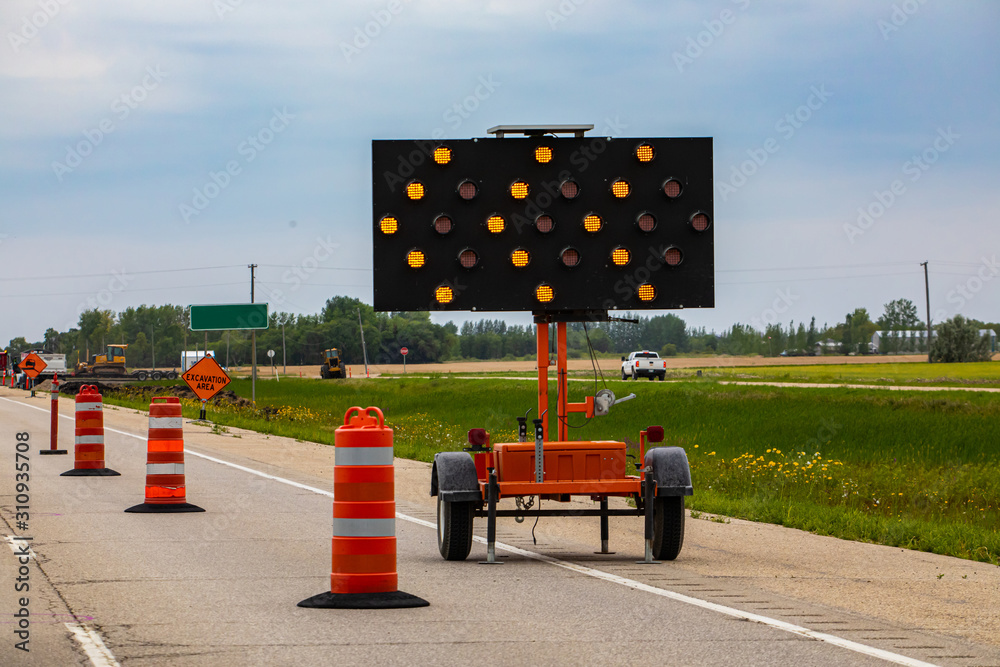
Interposition/Occlusion
= a near object covers/blocks an object farther away
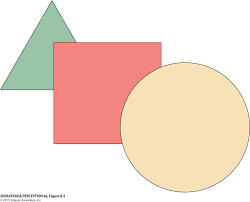
2
New cards
Relative Size
= far-off objects look smaller than close objects do
(when close objects are the same physical/actual size)
(when close objects are the same physical/actual size)

3
New cards
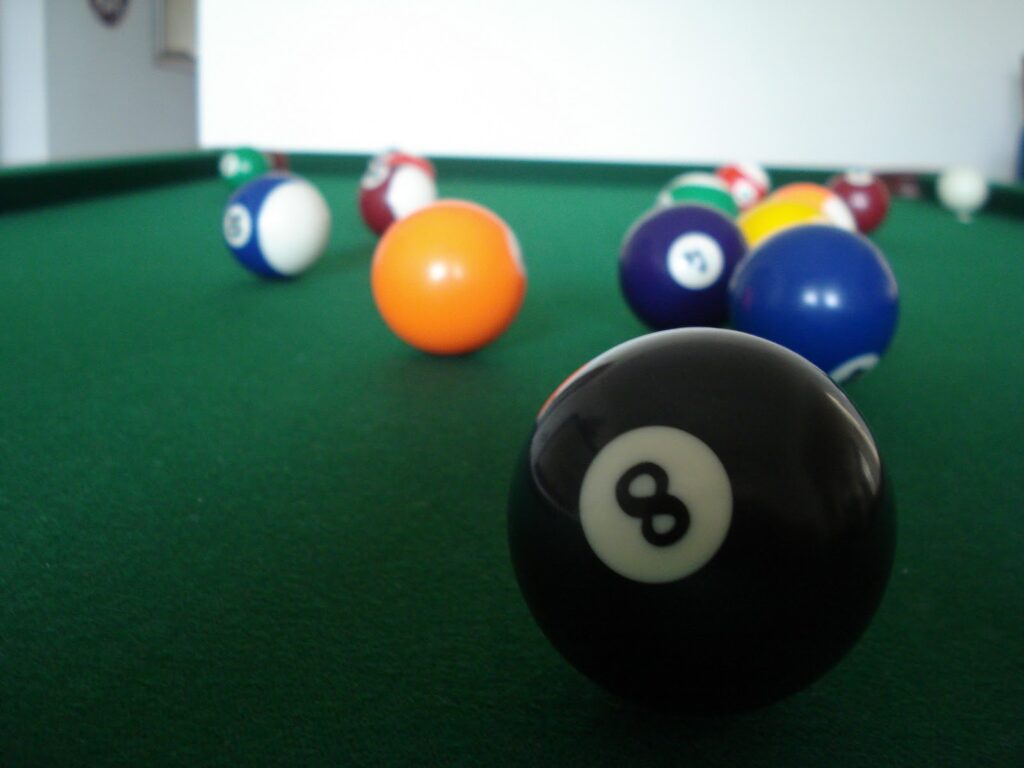
Familiar Size
= we know how large familiar objects are, so we can tell ow far away they are by size of their retinal images
ex. being able to tell how far a person is (gets messed up if it’s like a comically large cardboard cutout\`\`)
ex. being able to tell how far a person is (gets messed up if it’s like a comically large cardboard cutout\`\`)

4
New cards
Detail/Aerial Perspective
= the further away an object is, the more blurry it is
\
(due to layers of atmosphere)
\
(due to layers of atmosphere)

5
New cards
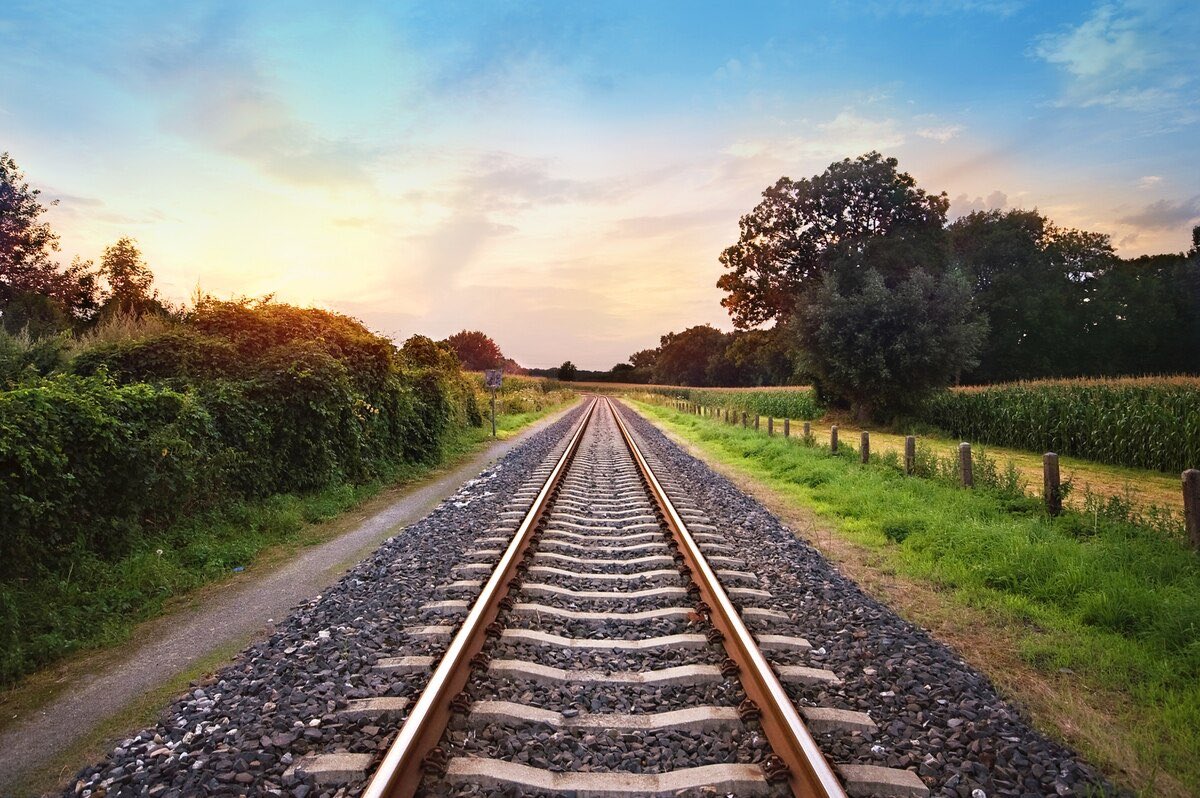
Linear Perspective
= parallel lines appear to converge in the distance

6
New cards
Texture Gradient
= as a uniformly textured surface recedes, its texture continuously becomes denser/smoother-looking

7
New cards
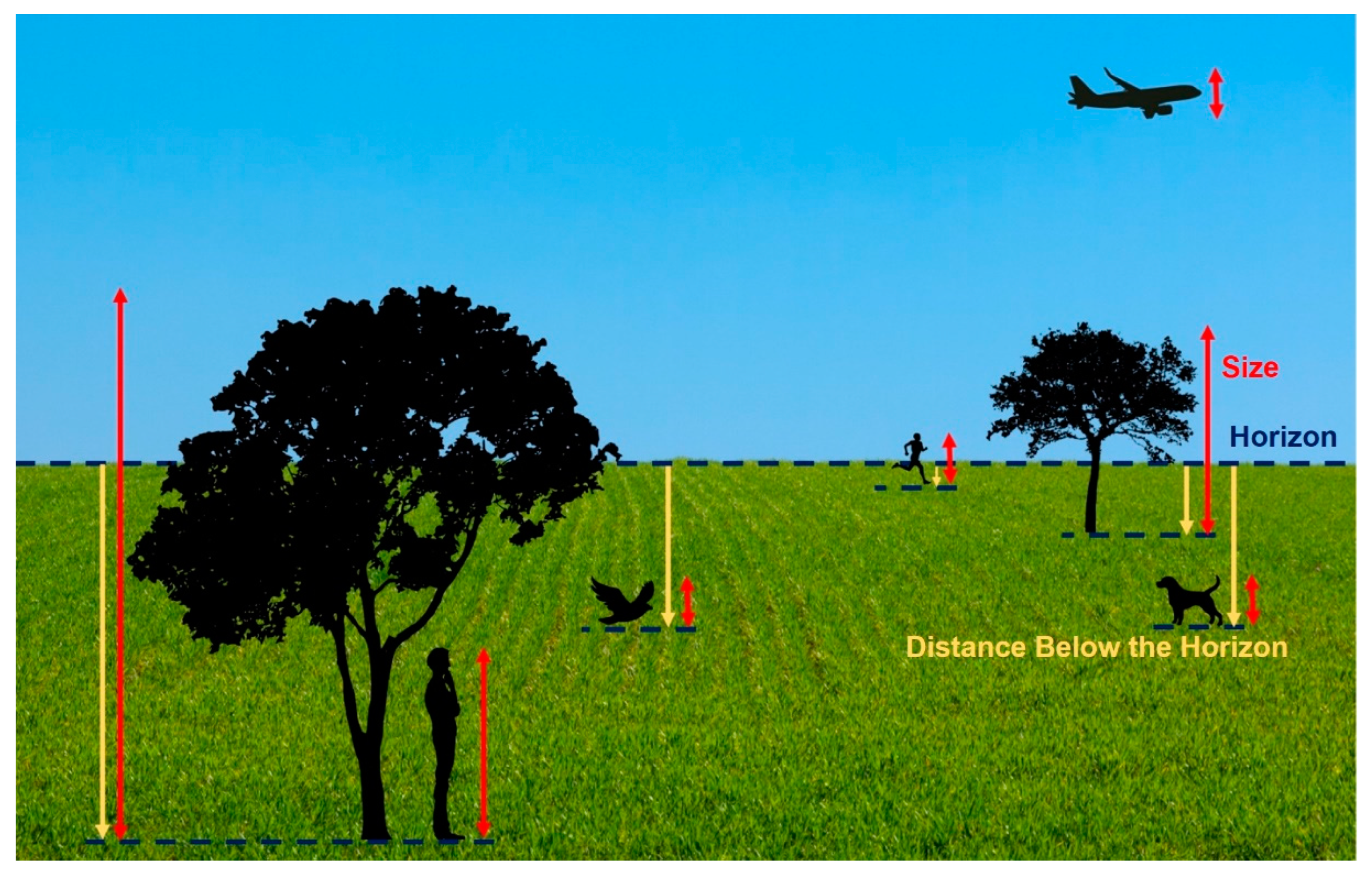
Position Relative to the Horizon
= for equal-size objects below the horizon, the one that appears higher in the vision field is perceived as being farther away

8
New cards
Motion Parallax
= when observer moving in a vehicle and looking out a window, nearer objects in scenery appear to be moving past faster than those farther in the distance
\
\

9
New cards
Visual Cliff
= research paradigm to test development of monocular depth perception in young children
\
ex. children show apprehension crossing glass where the appearance of a cliff exists
\
ex. children show apprehension crossing glass where the appearance of a cliff exists
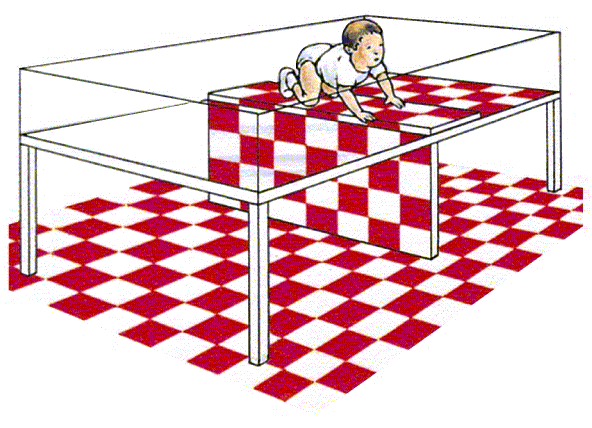
10
New cards
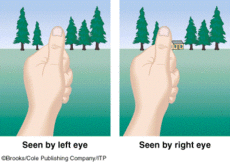
Binocular Disparity
= because 2 eyes are offset, they produce 2 diff images on retina, so brain uses disparity to calculate depth
* far object = not much disparity
* close object = lots of disparity
ex. if bring finger closer to face and close each eye, finger shifts around more the closer it is to eyes
* far object = not much disparity
* close object = lots of disparity
ex. if bring finger closer to face and close each eye, finger shifts around more the closer it is to eyes
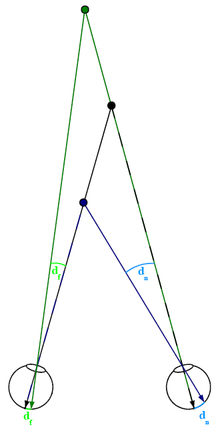
11
New cards
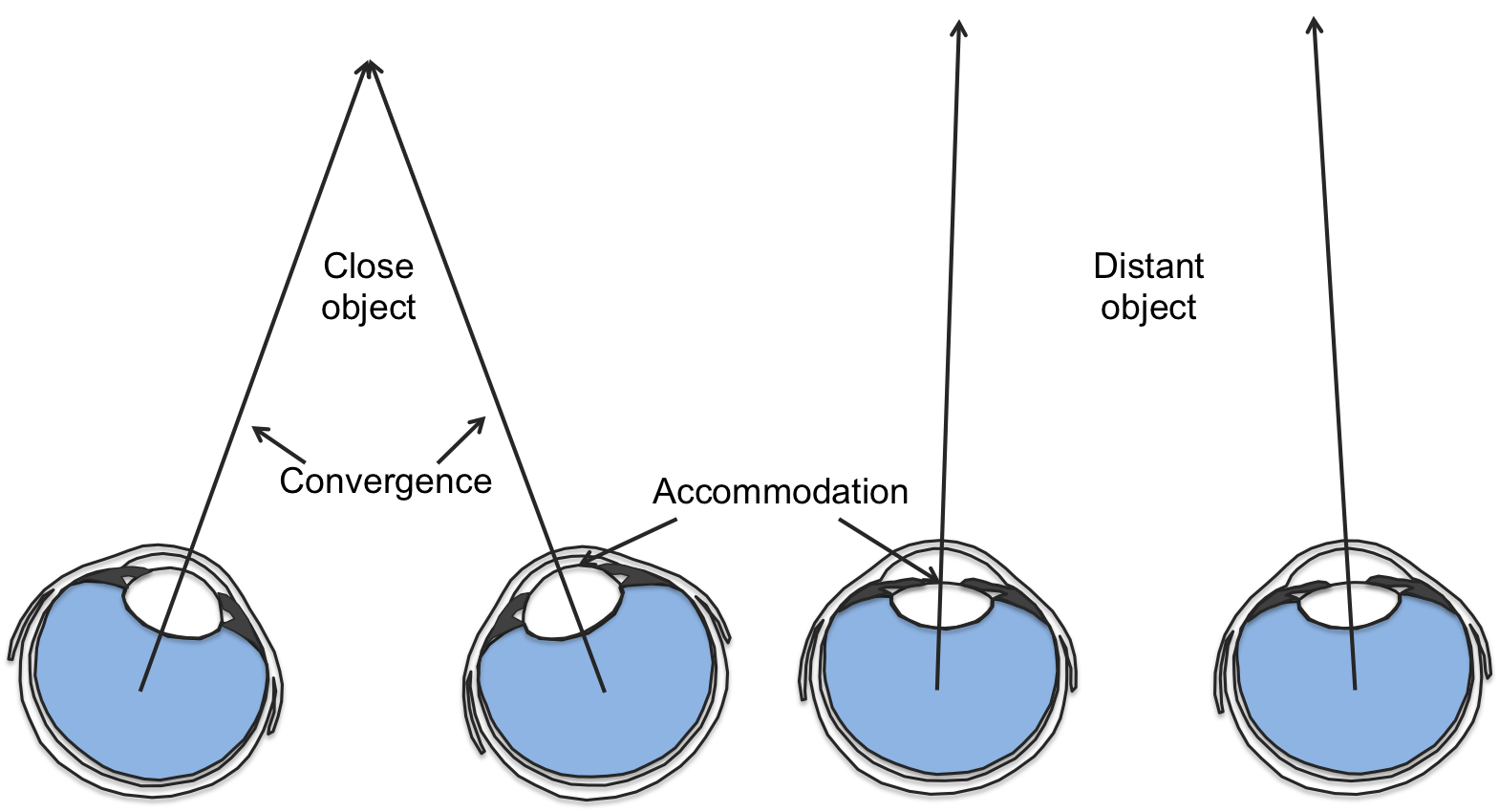
Convergence
= looking at closer objects causes our eyes to converge
* brain uses this info to calculate depth
* when eyes view near object, muscles move eyes toward each other (strain)
* brain uses this info to calculate depth
* when eyes view near object, muscles move eyes toward each other (strain)
12
New cards
Induced Movement
= assumption based on experience that smaller objects must be moving across larger one
\
ex. usually when we see a ball rolling across a table, we think ball is the one moving, not the table moving underneath a stationary ball
\
a misinterpretation of this illusion → the bigger object is moving, but brain assumes otherwise
ex. at traffic light and the big truck next to you starts moving forward and you hit the brakes harder, thinking you are going backward
\
ex. usually when we see a ball rolling across a table, we think ball is the one moving, not the table moving underneath a stationary ball
\
a misinterpretation of this illusion → the bigger object is moving, but brain assumes otherwise
ex. at traffic light and the big truck next to you starts moving forward and you hit the brakes harder, thinking you are going backward
13
New cards
Stroboscopic Movement
= rapidly flashing stationary pictures seem to move continuously

14
New cards
Phi Phenomenon
= set of rapidly flashing lights in slightly different places make it seem like light is moving
* similar to stroboscopic movement but for lights
* similar to stroboscopic movement but for lights
