NUR 242 Med/Surg Exam 1 With 100% correct answers 2025-2026 already graded A+
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Four Major subgroups of Late Adulthood
65 - 74 young old
75 - 84 middle old
85 - 99 old old
100 and older elite old
Lifestyle and Practice to Promote Wellness older adults
Yearly flu vaccine
pneumococcal vaccine
Shingles vaccine
tetanus and booster every 10 years
wear seat belts
alcohol in moderation
avoid smoking
smoke detectors
prevent falls - waxed floors and scattered rugs
medications as prescribed
avoid OTC medications unless primary care phyisican directs
Yearly physicial
regular exercise
socialization
reminisce
Common health Issues and Concerns older adults
Decreased nutrition and hydration
Decreased mobility
Stress and loss
Accidents - falls most common/MVA
Drug use and misuse
Mental health/cognition problems (including substance abuse)
Elder neglect and abuse
GFTT ( Geriatric Failure To Thrive) Complex Syndrome
Under nutrition
Impaired mobility
Depression
Cognitive impairment
Depression older adults
Most common mental health/behavioral health problem among older adults.
Use Geriatric Depression Scale form
Mood disorder having cognitive, affective, physical manifestations
Primary (lack of neurotransmitters)
Secondary or situational
Dementia older adults
slowly progresses
generally chronic
intellectual impairment
Most common Alzheimer's
Multi-infarct dementia, the second most common resulting from a vascular disorder
Delirium older adults
Acute and fluctuating onset
results from an unfamiliar place
Symptoms - inattentiveness, disorganized thinking, and altered level of consciousness
Nurse's role in Rehab
Advocate for the patient and family
Create therapeutic rehab milieu
provide whole person patient-centered care
Collaborate with healthcare team for patient outcome and develop care plan
Communicate with effectively with all members of the health care team, patient and family
Evaluate effectiveness of plan of care for the patient and family
Use Braden scale - skin break down risk
Safe Patient Handing and Mobility (SPHM)
-Maintain a wide, stable base with your feet
-Put the bed at the correct height - waist level while providing direct care and hip level when moving patients
- Keep the patient or work directly in front of you to prevent your spine from rotating
- Keep the patient as close to your body as possible to prevent reaching
walker - assisted and cane - assisted procedure
- Apply a transfer belt around patients waist
- guide patient to a standing position
- remind patient to place both hands on the walker
- ensure that the patient's body is well balanced
walker teaching
- lift the walker
- move the walker about 2 feet forward and set it down on all legs
-while resting on the walker, take small steps
- check balance
- repeat sequence
cane teaching
- be sure cane is at the height of the patients wrist when the arm is placed at his or her side
- remind patient to place his or her strong hand on cane
- ensure that the patient's body is well balanced
- move the cane and weaker leg forward at the same time
- move the stronger leg one step forward
- check balance and repeat the sequence
Adaptive equipment
buttonhook
extended shoehorn
plate guard and spork
gel pad
foam buildups
hook and loop fasteners
long-handled reacher
elastic shoelaces or velcro shoe closure
SCIP infection - 1
Prophylactic antibiotic received within one hour prior to surgical incision (to establish bactericidal blood and tissue levels by the time the surgical incision is made)
SCIP infection - 2
Prophylactic antibiotic selection for surgical patients (increased risk for surgical infections)
SCIP infection - 3
Prophylactic Antibiotics discontinued within 24 hours after surgery end time (provides benefit without risk)
SCIP infection - 4
Cardiac surgery patients with controlled 6 am postoperative blood glucose (cardiac patients only) To avoid hyperglycemia
SCIP infection - 6
Surgery patients with appropriate hair removal (removal is performed with electric clippers or chemical depilatories) to avoid skin abrasions and increase risk of surgical site infections
SCIP infection - 9
Urinary catheter removed on postoperative day 1 or postoperative day 2 with day of surgery being day zero ( to avoid urinary tract infections)
SCIP infection - 10
Surgery patients with preoperative temperature management (prevent prolonged hyperthermia, which is associated with wound healing, serious cardiac complications, altered drug metabolism, coagulation problems, and higher surgical infections.
SCIP CARD - 2
Surgery patients on beta-blocker therapy prior to arrival who received a beta-blocker during the perioperative period ( receive beta-blocker prior and continue immediately after surgery)
SCIP Venous Thromboembolism - 1
Surgical patients with recommended venous thromboembolism prophylaxis ordered (reduce complications from postoperative VTE)
SCIP Venous Thromboembolism - 2
Surgery Patients who received appropriate Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis within 24 hours of prior to surgery to 24 hours after surgery ( reduce complications from postoperative VTE particularly among patients undergoing the types of surgeries in which the risk was highest
Chapter 24 - skin layers
- Epidermis
- dermis
- subcutaneous - hypodermis
Epidermis
- protection
- keratin provides protection from injury by corrosive material
- inhibits proliferation of microorganisms because of dry external surface
-mechanical strength through intercellular bonds
Dermis
-provides cells for wound healing
- provides mechanical strength - collagen fibers - elastic fibers - ground substance
- sensory nerve receptors signal skin injury and inflammation
Subcutaneous tissue
- mechanical shock absorber
-energy reserve
- insulation
Skin assessment - lesions
Primary lesions - direct result of a disease process
Secondary lesions - evolve from primary or develop as a consequence of a patient's activity
Skin assessment - Color
- is affected by blood flow, gas exchange, body temperature, and pigmentation. describe by their appearance. Are changes general or confined to one body region
Skin assessment - ABCDE
A - Asymmetry
B- border irregularity
C- color variation within one lesion
D- Diameter greater than 6 mm
E - Evolving or changing in any feature (shape, size, color, elevation, itching, bleeding, or crusting)
Changes in Dark skin - cyanosis
- examine lips and tongue for gray color
- examine nail beds, palms, and soles for blue tinge
- Examine conjunctiva for pallor
Changes in Dark skin - Inflammation
- Compare effective area with non affected area for increased warmth
-examine skin of affected area to determine whether it is shiny or taut or pits with pressure
- Compare the skin color of affected area with the same area on the opposite side of the body
- palpate the affected area and compare it with unaffected area to determine whether texture is different (affected area may feel hard or "woody"
Changes in Dark skin - Jaundice
- Check for yellow tinge to oral mucous membranes, especially the hard palate
- examine the sclera nearest to the iris rather than the corners of the eye
Changes in Dark skin - Bleeding
- Compare the affected area with the same area on the unaffected body side for swelling or skin darkening
- if the patient has thrombocytopenia, petechiae may be present on the oral mucosa or conjunctiva
Nail assessment - nail color
White - chronic liver disease or kidney disease - shock - anemia - early arteriosclerotic changes (toenails) - myocardial infarction
Yellow - brown - Jaundice - peripheral lymphedema - bacterial or fungal infections of the nail - psoriasis - diabetes - cardiac failure - staining from tobacco, nail polish, or dyes - long term tetracycline therapy - normal aging (yellow - gray color)
Red - normal finding in dark skinned patients - nevus or melanoma of nail matrix in light skinned patients
Thin red vertical lines - bacterial endocarditis - trichinosis - trauma to nail bed - normal finding in some patients
Blue - Cardiac insufficiency - polycythemia vera - respiratory failure - methemoglobinuria - venous stasis disease (toenails)
Deep Tissue Injury (DTI)
-The intact skin appears purple or maroon
- Blood - filled blisters may be present
- Before the previously listed appeared, the tissue in this area may first have been painful
- other changes that may have preceded the discoloration include that area may have felt more firm, boggy, mushy, warmer, or cooler than the surrounding tissue
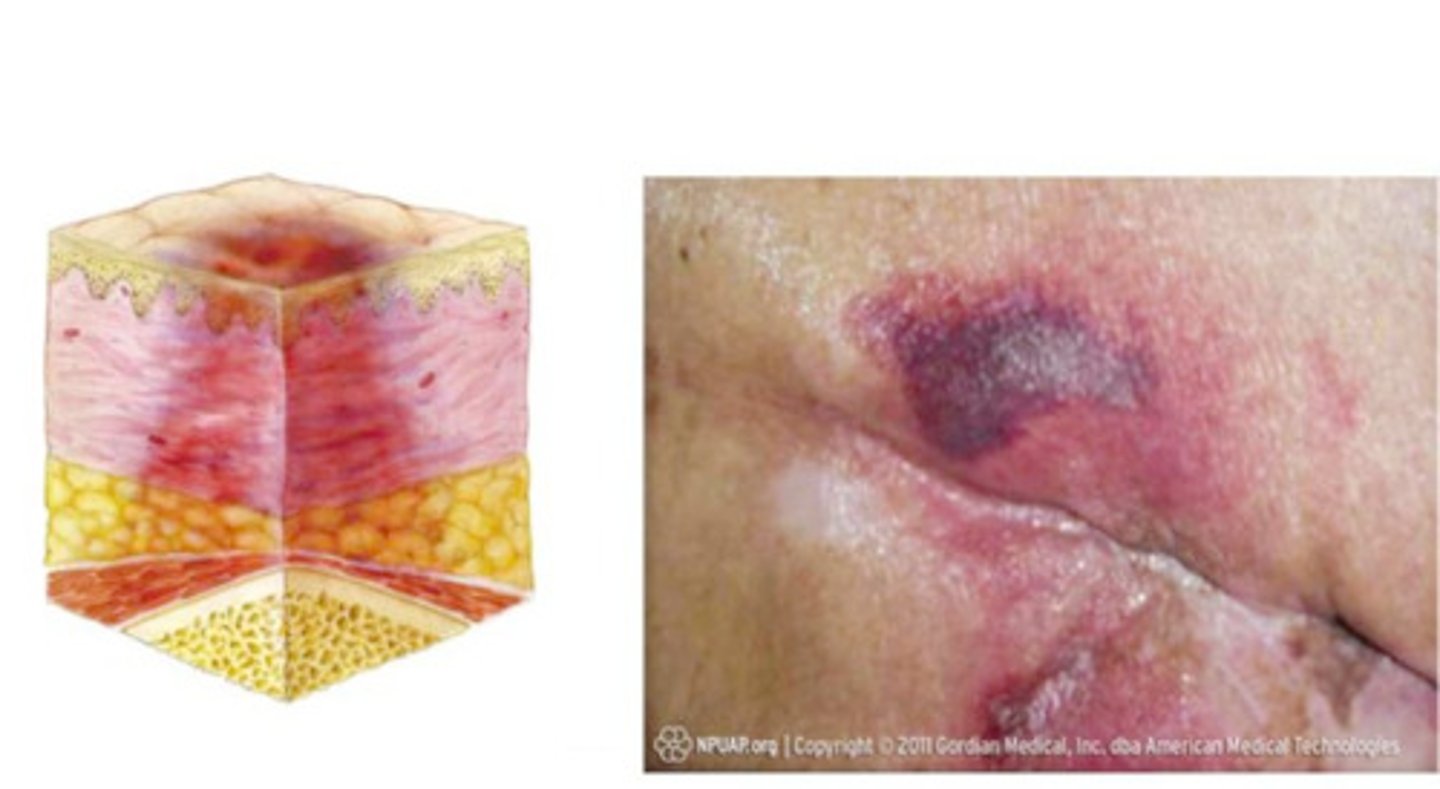
Stage 1 pressure ulcer
- skin is intact
- area, usually over a bony prominence, red and does not blanch with external pressure
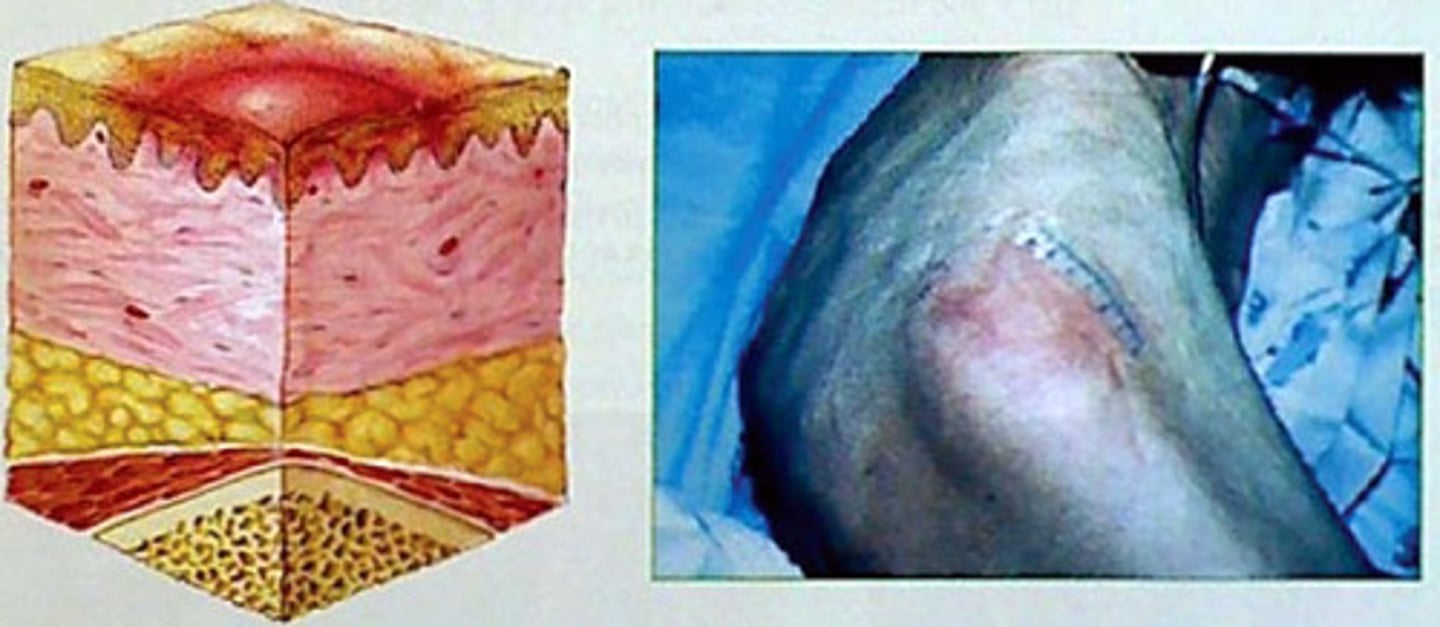
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
- skin is not intact
- there partial -thickness skin loss of the epidermis or dermis
- ulcer is superficial and maybe an abrasion, a blister (open or fluid-filled, or a shallow crater)
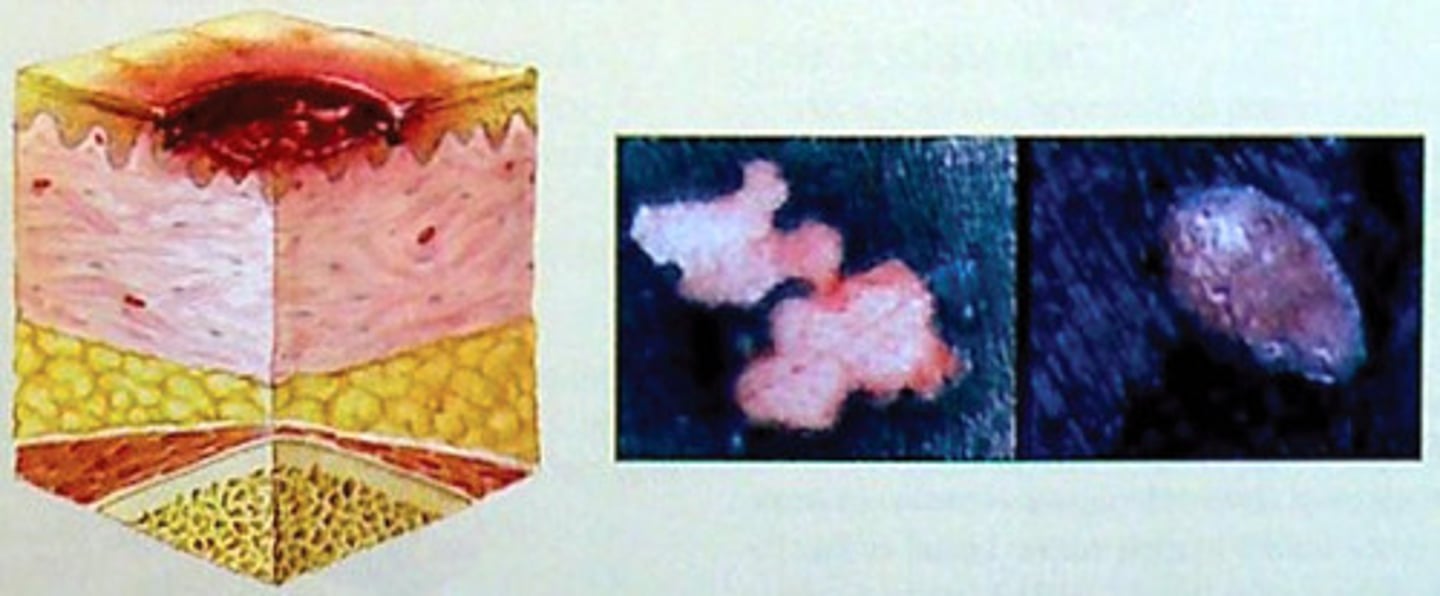
Stage 3 pressure ulcer
- skin loss is full thickness
subcutaneous tissue may be damaged or necrotic
- damage extends to fascia, bone, tendon and muscle
- undermining and tunneling may or may not be present
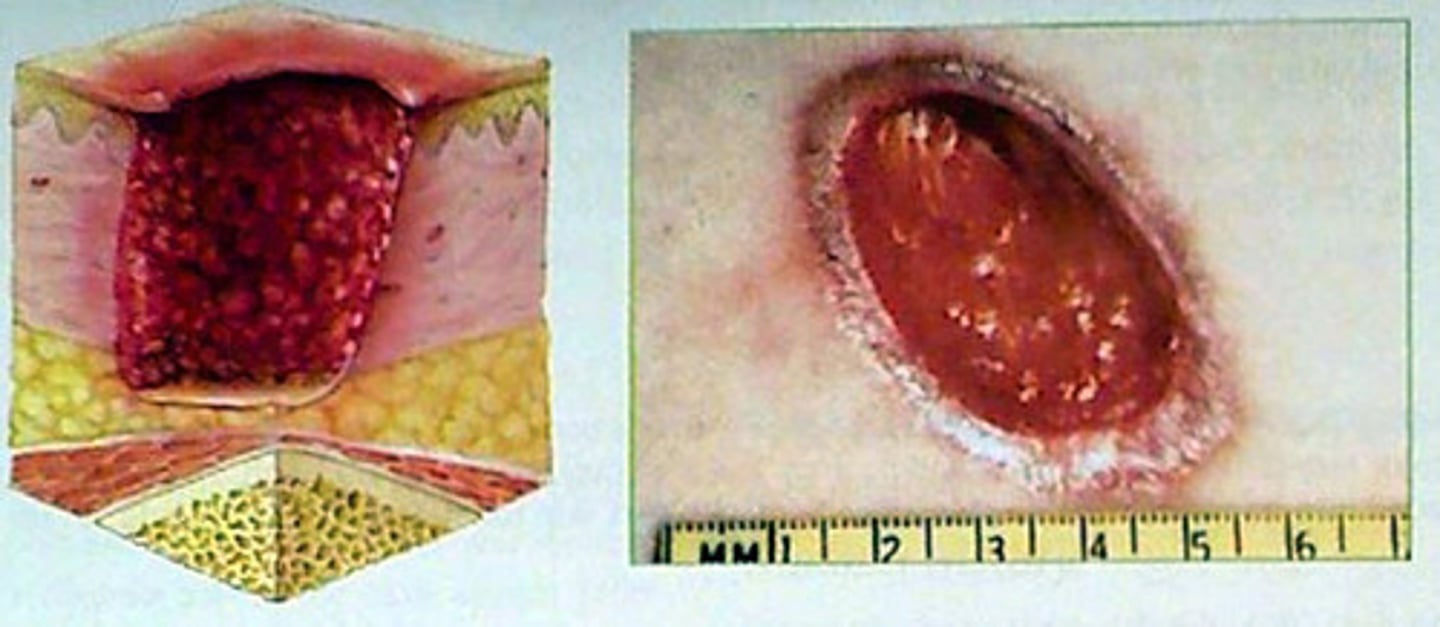
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
-Skin loss is full thickness with exposed or palpable muscle, tendon, or bone
- often excludes undermining and tunneling
- sinus tracts may develop
- slough and eschar are often present or at least part of the wound
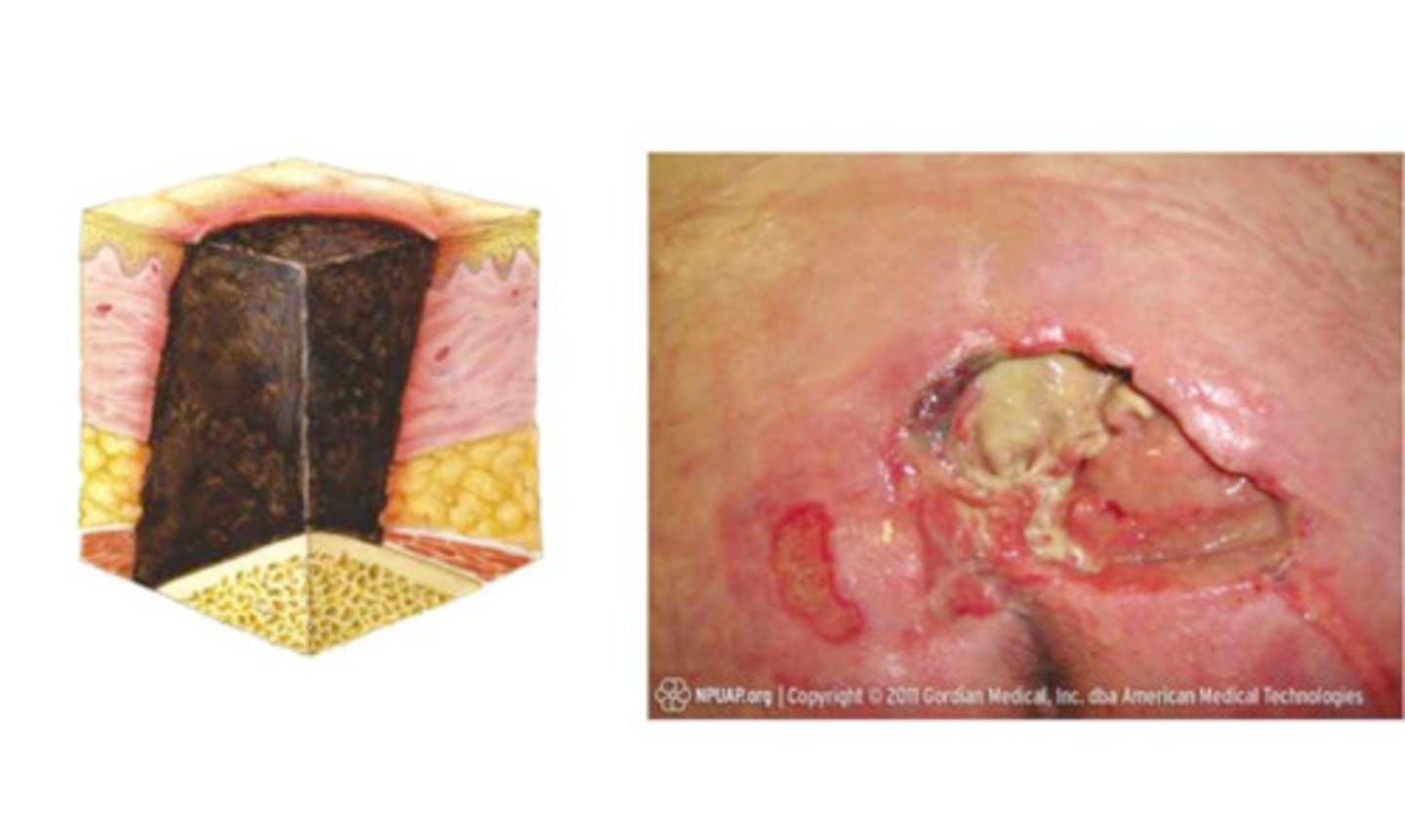
Unstageable
- skin loss is full thickness and the base is completely covered with slough, or eschar, obscurring the true depth of the wound
Wet to damp saline moistened gauze
necrotic debris is mechanically removed but with less trauma to healing tissue
Continuous wet gauze
wound surface continually bathed with wetting agent of choice, promoting dilution of viscous exudate and softening of dry eschar
Topical enzyme preparations
proteolytic action of thick, adherent eschar causes breakdown of denatured protein and more rapid separation of necrotic tissue
Moisture - retentive dressing
Spontaneous separation of necrotic tissue is promoted by autolysis
Wound - vac - negative pressure wound therapy
can reduce and or close chronic injuries by removing fluids or infectious materials, enhancing granulation. Should be changed every 48 to 72 hours.
Hyperbaric - oxygen therapy (HBOT)
administration of oxygen under high pressure, raising tissue oxygen concentration. Usually received under limb life-threatening wounds such as - burns, necrotizing infections, brown recluse spider bites, osteomyelitis, and diabetic ulcers
patient at risk for pressure injury - cardiovascular status
- presence or absence of peripheral edema
-hand-vein filling in the dependent position
-neck-vein filling in the recumbent and sitting position
- weight gain or loss
patient at risk for pressure injury - cognition and mental status
-level of consciousness
- orientation to time, place and person
- can the patient read a seven word sentence containing three syllables or fewer
patient at risk for pressure injury - condition of skin
- assess skin cleanliness
- observe all skin areas, especially bony prominences and areas in contact with the bed or other firm surfaces
- measure and record any redness or loss of integrity
- photograph areas of concern
- note presence of skin tenting over sternum and forehead
- note moistness of skin and mucous membranes
Patient at risk for pressure injury - with wounds
- remove dressing (noting condition of dressing)
- cleanse wound and remove and compare with previous notations of wound condition
- presence, amount and nature of exudate
- use disposable paper tape measurement to measure wound diameter and depth
- amount (%) and type of necrotic tissue
- presence of granulation/epithelium
- presence or absence of cellulitis
presence or absence of odor
take patients temperature to assess for fever
Patient at risk for pressure injury - understanding of illness and compliance with treatment
-s/s to report to primary care doctor
-drug therapy plan (correct time and dosing)
- ambulation or positioning schedule
- dressing changes/skin care
- nutrition modifications (24-hr diet recall)
Patient at risk for pressure injury - nutritional needs
- change in muscle mass
- lackluster nails, sparse hair
- recent weight loss or more than 5% of usual weight
- impaired oral intake
- difficulty swallowing
- generalized edema
Psoriasis
Chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the skin with exacerbations and remissions. Results from overstimulation of the immune system. activates T-lymphocytes. This can not be cured, often patients can control symptoms
Complications of Immobility
Contractors, foot drop, muscle atrophy
DVT
Constipation
Decreased cardiac output
Disorientation
renal calculi, UTI
Pneumonia
pressure ulcers
Prevention of pressure ulcers
Early identification of high risk patients (Braden scale)
Mental status change and decreased sensory perception
impaired physical immobility, requires assistance with turning and positioning or patients who can not verbalize discomfort
nutritional status: serum albumin < 3.5 and prealbumin levels < 19.5 Consult dietitian
Incontinence and excessive moisture
Informed consent
Surgeon is responsible before sedation is given and surgery is performed
nurses role is to CLARIFY facts and CLARIFY the consent has been signed
an "X" is permitted in patients that cannot write but MUST be witnessed
If patient doesn't understand the physician is to be notified
BLIND patients can sign own consent but need 2 witnesses
In an EMERGENCY, obtaining consent is not imperative, however it is preferred
Pain Assessment
Pain is the 5th VS
assess level and location using pain management tools (0-10 or Faces scale)
self-report is the MOST reliable indicator
ALWAYS believe the patient when they report pain and treat it promptly
Consider referral to pain management for chronic pain
Pre-Op medications
DRUGS - sedatives(hydroxyzine) Hypnotics(lorazepam) anxiolytics(midazolam) opioid analgesics (morphine, hydromorphone) or anticholinergics)
Pre-OP medications given "on call" to surgery. The nurse should:
Properly identify the patient using the armband an asking the patient to state their name and date of birth
make sure the operative permit is signed
administer the prescribed preoperative medication in the correct dose(s)
Raise the side rails, place the bed in lowest position, call light within reach
Types of Anesthesia
General
Regional
General Anesthesia
Used most often in head, neck, upper torso and abdomen
Once patient reaches PACU the nurse should immediately assess for patients airway, adequate gas exchange, and LOC
also assess the rate, pattern and depth of breathing to determine adequacy of gas exchange
RR < 10 may indicate respiratory depression due to anesthetic or opioids
Regional Anesthesia
A type of local anesthesia that blocks multiple peripheral nerves in a specific body region.
immediately following surgery the nurse should check the patients VS, skin temperature, circulation, cp refill (should be < 3 seconds)
Patient controlled analgesia (PCA)
Morphine, fentanyl, and hydromorphone - most common used
the device is programmed to deliver a certain amount of drug (demand dose) within a specific interval (lockout interval) the lockout interval is usually 5-15 minutes
when the patient is cognitively impaired, another method of drug administration should be considered
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) unit
Used as an adjunctive treatment for pain
involves the use of battery-operated device capable of delivering small electrical currents through up to the painful areas
The voltage is regulated by adjusting the dial to the point at which the patient perceived a prickly pins and needles sensation
Post-OP
DVT is the most common type of thrombophlebitis. High risk for pulmonary embolism. Develops most often in the legs but can occur in the upper arms
Interventions: patient education regarding leg exercises, early ambulation, adequate hydration, compression stockings, sequential compression devices (SCD's)
Post-OP
wound healing and prevention of infections
assess the surgical incision at least every 8 hours for redness, increases warmth, swelling, tenderness or pain, and the type/amount of drainage
sanguineous (bloody) to serosanguineous to serous (yellow) drainage is normal during the first few days after surgery. Drainage should gradually decrease
Crusting on the incision line, pink color to the incision line, and slight swelling under the sutures/staples is normal
Post-op Risk for post surgical wound
DEHISCENCE
Obesity
diabetes
corticosteriod use
immune deficiency
malnutrition
Post-op
wound EVISCERATION
Call for help and stay with patient
cover wound with sterile gauze soaked in sterile water
do not attempt to reinsert the protruding organ
place the patient in supine position with hips and knees bent
raise the HOB no more than 15-20 degrees
provide support and reassurance to the patient
Sequence of inflammation
Stage 1 - injured tissue and the leukocytes mast cells in this area secrete histamine, serotonin and kinins that constrict the small veins and dilate the arterioles in the area of injury. These changes cause redness and warmth to the tissues
Stage 2 - An increased number of circulating neutrophils occurs. Exudate in the form of pus occurs, containing dead WBC's, necrotic tissue, and fluids that escape from the damaged cells. Thus, you will see an increase in the neutrophil count
Stage 3 - tissue repair and replacement occur
MIDLINE catheters
peripheral IV access
utilized for short -term therapy (4 weeks or less)
the tip of the midline ends in the axillary vein
should not be used to draw labs
DOES NOT require x-ray for placement
complications of PIV
(peripheral IV) Infiltration
IV becomes dislodged
fluid leaks from the vein to surrounding tissue
discontinue IV and elevate the extremity
apply ice or heat therapy
vesicant medications can cause extravasation if IV infiltrates
Complication of PIV
phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
inflammation of the vein (redness, edema, warmth, pain at site)
discontinue IV
notify physician for treatment
restart IV in the opposite extremity
Central Line Access Devices
All central line access devices terminate in the superior vena cava (PICC line, implantable ports, tunneled and non-tunneled catheters, and central lines)
insertion requires informed consent
need to have a chest x-ray prior to use
PICC line
placed by a PICC certified nurse
used when long-term therapy is needed (up to one year)
always flush with a 10 ml syringe
RN's can remove a PICC line. Have the patient perform the valsalva maneuver, make sure the tip is intact. If discontinuing due to infection, send the tip of the PICC line to the lab for C&S
Implantable ports
surgically implanted in the right or left chest
canoe used for individuals receiving chemotherapy
huber needle is used to access the port at a 90 degree angle
Complications of central Line Access
Central line associated blood stream infection (CLABI)
s/s: localized erythema, tenderness, fever, drainage
can lead to a systemic infection and sepsis
d/c the central line and culture the tip
tx: ABT and antifungals
prevention: meticulous hand washing
Complications of Central Access Device
Air Embolism
Bolus of air enters circulation
potentially fatal
s/s: tachycardia, chest pain, dyspnea, and cyanosis
interventions: trapping the air into the R atrium, turn the client to the left side in trendelenberg position
all lines should be primed prior to use and connections secure when not in use
Complications of central line access
Clotted access
The catheter becomes clogged from either the solution being infused or from insufficient flushing
a thrombolytic can be ordered from the physician to dwell and dissolve the clot
needs to be treated promptly to prevent having to remove the central line
prevention: routine flushing
Complications of central line access
Pneumothorax
Occurs following insertion of the central line
fatal if not treated
s/s: tachypnea, absent breath sounds on the affected side, decreased oxygen saturation, and restlessness
ALWAYS verify placement of a central line with a chest x-ray
TPN Total Parenteral Nutrition
Nutritional status is monitored by checking protein levels, such as albumin and pre-albumin levels
TPN care and maintenance of
check each bag of TPN for accuracy by comparing it with the physician's order (2 nurses to check to prevent errors)
if the TPN solution is unavailable, give 10% dextrose/water (or 20% D/W) until the TPN solution can be obtained
if the TPN administration is not on time, do not increase the rate
Change IV tubing every 24 hours when new bag is hung
dressing change around the IV site should be changed every 48-72 hours
Sickle cell Disease
RBC's are sickle shaped, rigid and clump together. the clumps form assess of sickled RBC's that block blood flow, leads to tissue hypoxia. Repeated episodes of ischemia lead to progressive organ damage
Pain is the most common problem
Sickle cell crisis
pain due to tissue injury caused by poor oxygenation from obstructed blood flow. Pain is severe enough to require hospitalization and large doses of opioid analgesic. concerns about substance abuse can lead to inadequate pain treatment
Care of Patient in Sickle Call Crisis
Give prescribed pain medication
hydrate with normal saline IV, encourage oral intake of fluids without caffeine
administer oxygen
remove restrictive clothing, no blood pressure with external cuff
check circulation in extremities every hour
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Results from poor intake of foods containing B12
Vitamin B 12 anemia (pernicious anemia) caused by deficiency of intrinsic factor needed for intestinal absorption of B12. Seen in patients with bowel resections, chronic diarrhea, diverticula, tape worms, or overgrowth of intestinal bacteria
s/s: glossitis (a smooth, beefy red tongue) fatigue, weight loss, and pallor or jaundice
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Avoid close contact with others until infection clears
sleep in separate bed from others
wash all soiled clothing and linens with hot water and laundry detergent
do not share any personal items
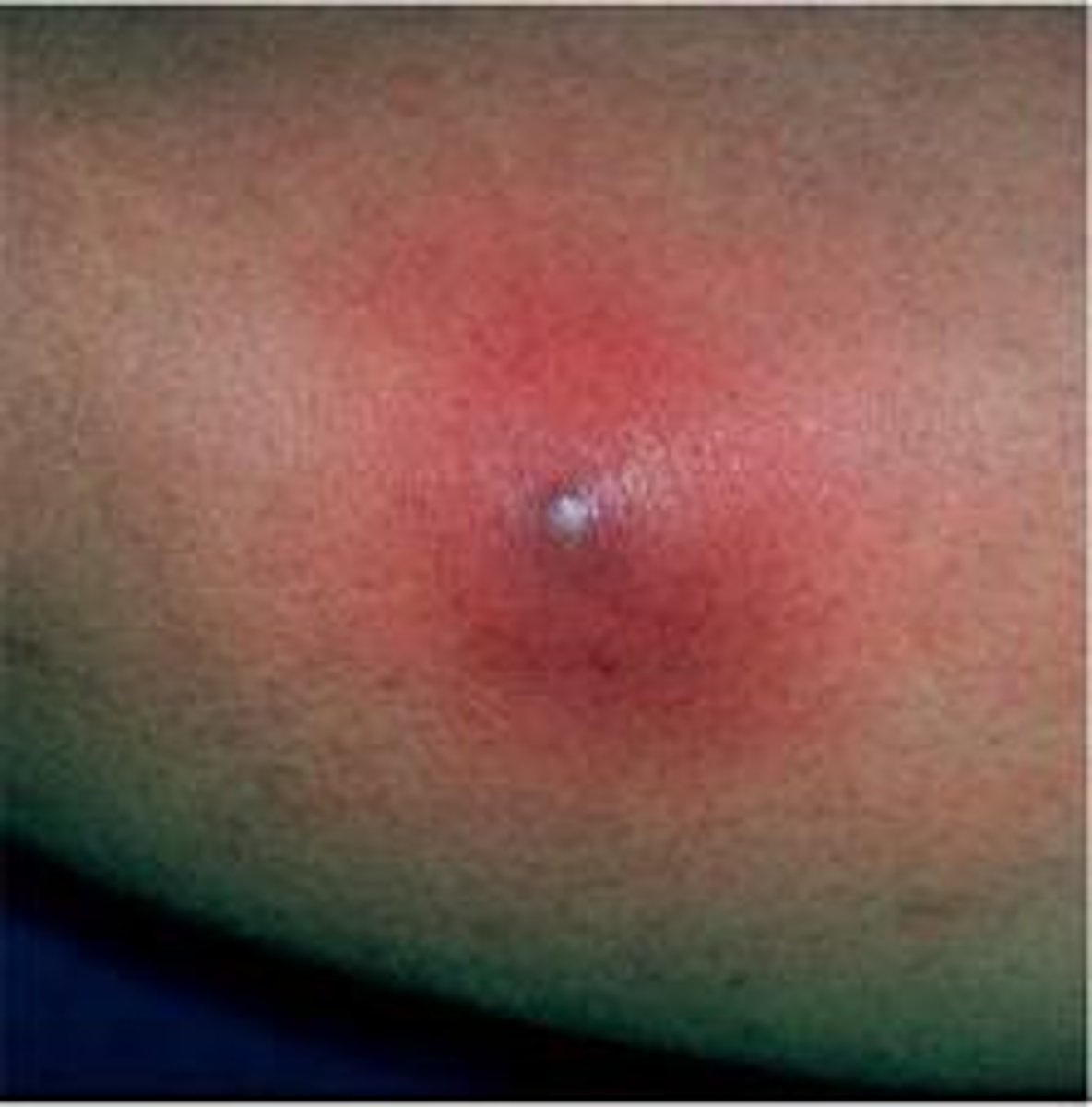
Cellulitis
generalized infection with either staphylococcus or streptococcus and involves deeper connection tissue
infection can spread by scratching or rubbing the skin
can result from a secondary bacterial infection of an open wound or unrelated to skin trauma
localized area of inflammation that may enlarge rapidly if not treated
warm compresses to the area are recommended
treatment with IVABT
Hand Hygiene
wash hands with soap and water when hands are visible soiled or contaminated
not visible soiled may use ABHR
before direct contact with patients wash or use ABHR
Decontaminate hands before putting on sterile gloves, to after contact with patients intact skin (taking a pulse)
Standard precautions
should be used when caring for all patients.
includes: hand hygiene between each patient contact, after removing gloves, after touching bloody, body fluids or secretions, when touching mucous membranes and non-intact skin
Contact precautions
private room, wear gloves when entering the room, wash hands with soap and water when leaving the room, dedicated equipment for patient
C-diff
scabies
impetigo
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants and children
Airborne Precautions
private room with negative pressure airflow, keep door closed, N95 respirator, patient to wear surgical mask when leaving room a clinical reason
M - measles
T - tuberculosis
V - varicella (including disseminated zoster)
Droplet precautions
Private room, if private room not available, may share with patient having the same infectious disease and microorganism, wear mask when working within 3 feet of the patient, patient to wear mask when leaving room for clinical reasons
S - sepsis/streptococcal pharyngitis
P - pneumonia/pertussis
I - influenza
D- Diptheria (pharyngeal)
E - epiglottitis
R - Rubella
M - Mumps/meningitis
AN _ Adenovirus
Skin cancer prevention
avoid sun exposure between 11 - 3pm
use sunscreens with the appropriate skin protection factor
wear a hat, opaque clothing, and sunglasses
keep a body map of skin spots, scars, and lesions to detect when changes have occurred