Core Practical 2: Investigate the Vitamin C Content of Food & Drink
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what is vitamin C
Vitamin C is found in green vegetables, fruits, and potatoes
It is essential for a healthy diet
The chemical name for vitamin C is ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is a good reducing agent and therefore it is easily oxidised
apparatus for investigating vitamin C content of food and drink?
Vitamin C solutions
1% DCPIP solution
Distilled water
Range of fruit juices
Measuring cylinder
Pipette
Stop watch
Test tubes
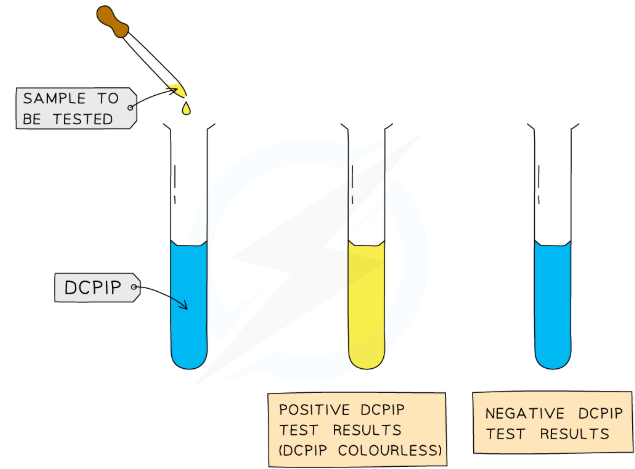
method
Make up a series. e.g. six, of known vitamin C concentrations
This can be done by serial dilution
Use the 5cm3 syringe to draw up 5cm3 of 1% DCPIP. Shake the syringe to expel any air bubbles.
Use a measuring cylinder to measure out 1 cm3 of DCPIP solution into a test tube
Add one of the vitamin C solutions, drop by drop, to the DCPIP solution using a graduated pipette or burette
Shake the tube for a set period of time using a stop watch
It is important to keep the shaking time the same for each concentration; this is a control variable
When the solution turns colourless record the volume, in number of drops, of vitamin C solution added. You can find this from subtractign value of syringe from original 5cm3 in syringe
Repeat steps 2-5 for the same concentration twice more and calculate an average
Repeat steps 2-6 for each of the known concentrations
Results can be plotted as a line of best fit showing the average volume of vitamin C needed to decolourise DCPIP against the concentration of vitamin C
This is a calibration curve and can be used to find the concentration of vitamin C in unknown samples such as fruit juices
safety for DCPIP
DCPIP is an irritant
Avoid contact with the skin
Wear eye protection
analysis
write down the average volume of vitamin C solution needed to decolorise DCPIP (based on your results)
1cm3 of the vitamin C solution contains 10mg of vitain C. You can use this info and yoru calculation of average volume of 1% vitamin C solution requird to decolorize the DCPI to calculate the concentration of vitamin C in fruit juice.use formula:
conc of vitamin c in fruit juice: volume of standard solution/ volume of fruit juice x conc of standard solution
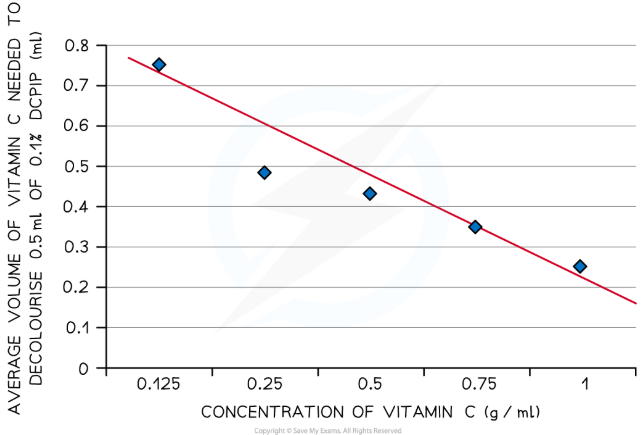
result
The volume of vitamin C solution required to decolourise DCPIP should decrease as the concentration of the vitamin C solution increases
The results of the experiment can be plotted on a graph of volume of vitamin C needed to decolourise DCPIP against the concentration of vitamin C
The line of best fit for such a graph is known as a calibration curve; unknown substances can be compared to it to gain an estimate of their vitamin C concentration
The calibration curve produced from this experiment can be used to estimate the concentration of vitamin C in fruit juices
Why is each titration completed three times to calculate a mean?
Each titration is repeated three times to calculate a mean because:
Improves accuracy – Reduces the impact of random errors and anomalies.
Increases reliability – Ensures that results are consistent and reproducible.
Allows for identification of anomalies – If one value is significantly different, it can be excluded.
Gives a more precise average – A mean value smooths out small measurement variations.
Why are Syringes used instead of burettes?
Syringes are used instead of burettes in this investigation because:
Greater precision at small volumes – Syringes allow for accurate measurement of small liquid volumes, which is useful when only a few cm³ of juice is needed to decolourise DCPIP
Easier handling – They are simpler to use and require less setup compared to a burette, making the experiment more efficient.
Faster titration – Syringes allow quicker addition of the juice, which is beneficial when working with small-scale reactions.
Reduces wastage – Less liquid is needed to fill a syringe compared to a burette, minimizing the amount of juice required for each trial.
Explain why vitamin C is described as an antioxidant
Vitamin C is described as an antioxidant because it prevents oxidation by donating electrons to other molecules. This helps protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals (unstable molecules that can damage DNA, proteins, and cell membranes)
How it works:
Vitamin C donates electrons to free radicals, neutralising them before they can cause harm.
By giving away electrons, Vitamin C itself gets oxidised, but it prevents other important molecules (like DNA and proteins) from being damaged.
This antioxidant property is why Vitamin C is important for maintaining healthy skin, immune function, and preventing cell damage.
Suggest why, when adding ascorbic acid to DCPIP, the tube should be shaken gently and not vigorously with the addition of each drop of DCPIP
When adding ascorbic acid to DCPIP, the tube should be shaken gently rather than vigorously because:
Ensures even mixing – Gentle shaking helps the ascorbic acid react with DCPIP without introducing too much air.
Prevents excess oxygen from interfering – Vigorous shaking could introduce oxygen, which might re-oxidised DCPIP, affecting the accuracy of the results.
Avoids overestimation of vitamin C – If shaken too hard, bubbles may form, making it harder to see when the solution has fully decolourised, leading to inaccurate readings.
This controlled method ensures a fair test and more reliable results.
How can concentration of vitamin C in each fruit juice can be calculated?
Comparing the vitamin C concentration to the standard solution
C1V1 = C2V2
1 = Fruit juice
2 = Standard solution
Explain how increasing the quantity of plant foods that contain vitamin C in the diet may protect against heart disease
because (antioxidants / vitamin C) reduce (the quantity of) free radicals that cause damage to {cells / tissues / blood vessels / endothelium} reducing {plaque / atheroma} formation