cell bio test 3
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
movement, immune defense, membrane transport, hormones/hormone receptors, enzymes, genetic information
genetic information
Describe primary protein structure:
amino acid sequence
Describe secondary protein structure:
alpha helices and beta sheets
Describe tertiary protein structure:
overall three-dimensional shape
Describe quaternary protein structure:
several subunits joined together
Which statement about alpha helices and/or beta sheets is FALSE?
Two or more alpha helices can spiral around each other to form a strong coiled coil structure.
Alpha helices can form membrane-spanning domains in membrane-associated proteins.
Beta sheets can stack together to form rigid amyloid structures.
They’re both always made entirely from nonpolar amino acids.
They both form through multiple hydrogen bonds between different parts of their polypeptide backbones.
They’re always made entirely from nonpolar amino acids
What helps determine, either directly or indirectly, the final 3D conformation of a particular protein?
The sequence of amino acids that make up the protein.
The pH of the organelle (or other environment) in which the protein functions.
The sequence of nucleotides in the gene that codes for the protein.
Hydrogen bonding between different parts of the polypeptide backbone.
Interactions of the amino acids’ side chains.
Why are the side chains of amino acids so important?
They function as a biochemical “tool belt” which determines what the protein can do.
They interact with each other to help the protein fold and remain folded.
What amino acids help to stabilize protein structure by clustering inside of the protein and contributing to its overall shape?
Hydrophobic
What amino acids often participate in the protein’s activities because they’re more likely to be on the outside and interact with other molecules?
Hydrophilic
What are different regions of the same polypeptide which perform distinct functions, and often fold somewhat independently from the rest of the polypeptide?
Protein domains
What are encoded by different genes, transcribed and translated separately, then assembled into a larger functional protein?
Protein subunits
T/F A protein’s preferred conformation is the one with the lowest free energy.
True
What exactly happens when an enzyme becomes denatured?
It unfolds from its normal three-dimensional shape, and therefore no longer fits the reactants on which it used to act
Proteins denatured in the lab will often spontaneously refold into their correct conformation when the denaturing agent is removed. Yet denatured proteins within living things (or in the kitchen) do NOT generally refold correctly. What are some reasons for this?
When large numbers of protein molecules are unfolded, they stick to each other to form tangled aggregates.
The cytoplasm is very crowded with other proteins and molecules. It’s too easy for a denatured polypeptide to stick to these and be prevented from folding correctly.
These laboratory refolding experiments are conducted under simplified ideal conditions which don’t closely match the conditions inside living cells.
What do chaperone proteins do?
They help newly made polypeptides to fold correctly, mostly by shielding then from other cellular components which could potentially interfere with proper folding
At low substrate concentrations:
the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration
At higher substrate concentrations:
the active sites of all the enzyme molecules are constantly occupied, and the reaction rate approaches the maximum rate possible for that enzyme
What are some of the means by which an enzyme can lower activation energy to catalyze a reaction?
Forming temporary bonds with the substrate to redistribute electron density.
Distorting and straining the conformation of the substrate.
Precisely aligning reactants.
What are small molecules which bind as part of an enzyme-substrate complex to enhance catalytic efficiency or function as activated carriers?
cofactors/coenzymes
What is a mechanism for enzyme regulation in which binding of a molecule at one site changes the conformation of the protein, so that the shape of the catalytic site changes?
Allosteric regulation
What is a mechanism for enzyme regulation in which another molecule, similar in shape to the enzyme’s normal substrate, binds in the active site and prevents the substrate from binding?
Competitive inhibition
What is a mechanism for enzyme regulation in which the product of a metabolic pathway binds to and downregulates an enzyme near the beginning of the pathway to prevent wasteful overproduction?
Feedback initiation
What is a long, flexible, largely unstructured polypeptide or noncoding RNS, which binds to various protein components and helps them assemble into a larger multi-protein complex?
Scaffold
What is a dense collection of molecules different enough from their surroundings that they form a distinct phase-separated structure without an enclosing membrane?
Intracellular condensate
What is a membrane-bounded enclosure, whose internal chemical environment may be quite different from the surrounding cytoplasm?
Vesicle
What can antibodies do?
Help fight infections directly and by activating other parts of the immune system.
Be linked to drugs for delivery to specific tissues or tumors, while minimizing systemic side-effects.
Be used as selective filters to bind and purify specific molecules from a mixture.
Be linked to dyes to detect specific molecules on gels or in micrographs.
A centrifuge separates materials by differences in their:
density
How does ion-exchange chromatography separate substances?
electric charge
How does affinity chromatography separate substances?
strong and specific binding to other molecules
How does gel-filtration chromatography separate substances?
size
What research technique measures the mass and charge of vaporized protein fragments deflected through a magnetic field then searches against predicted protein sequence databases?
Mass spectrometry
What research technique measures radio waves emitted by atomic nuclei aligned with a perturbed magnetic field and matched with patterns of characteristics of known molecular features?
NMR spectroscopy
SDS-PAGE uses _____ to separate proteins by _____
an electric voltage across a porous gel matrix, size
What modeling technique uses thousands of perfectly aligned proteins to make one image?
X-ray crystallography
What modeling technique images thousands of randomly oriented proteins then assembles those images into an overall 3D model?
Cryo-electron microscopy
Which type of noncovalent interaction can involve either the polypeptide backbone or amino acid side chains?
Hydrogen bonds
A folded protein structure with which free-energy (G) value - 10, 5, 15, 1 - would likely have the most stable conformation?
1
If protein folding is determined by the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain, why are chaperone proteins needed to assist folding in the cell?
Certain proteins easily aggregate with other proteins
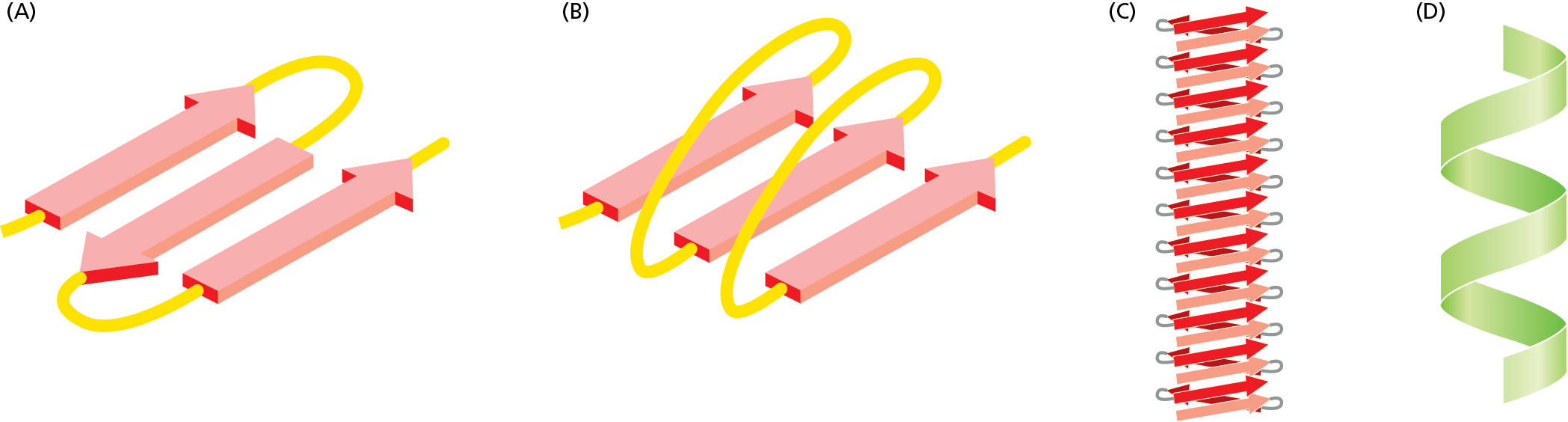
Hydrogen bonding between N-H and C=O groups of every fourth amino acid within a polypeptide chain results in which type of folding pattern?
alpha helix (D)
What is true about amyloid protein structures?
They consist of stacked beta sheets
A stretch of amino acids in a polypeptide chain that is capable of independently folding into a defined structure is called a:
domain
What level of protein structure involves the interaction of more than one polypeptide chain into a three-dimensional structure?
quaternary
Order the protein organizational units from smallest to largest
domain < subunit < complex
A binding site on the surface of a protein interacts specifically with another protein through:
many weak noncovalent interactions
Disulfide bonds stabilize protein shape outside the cell by:
covalent bonds between cysteines
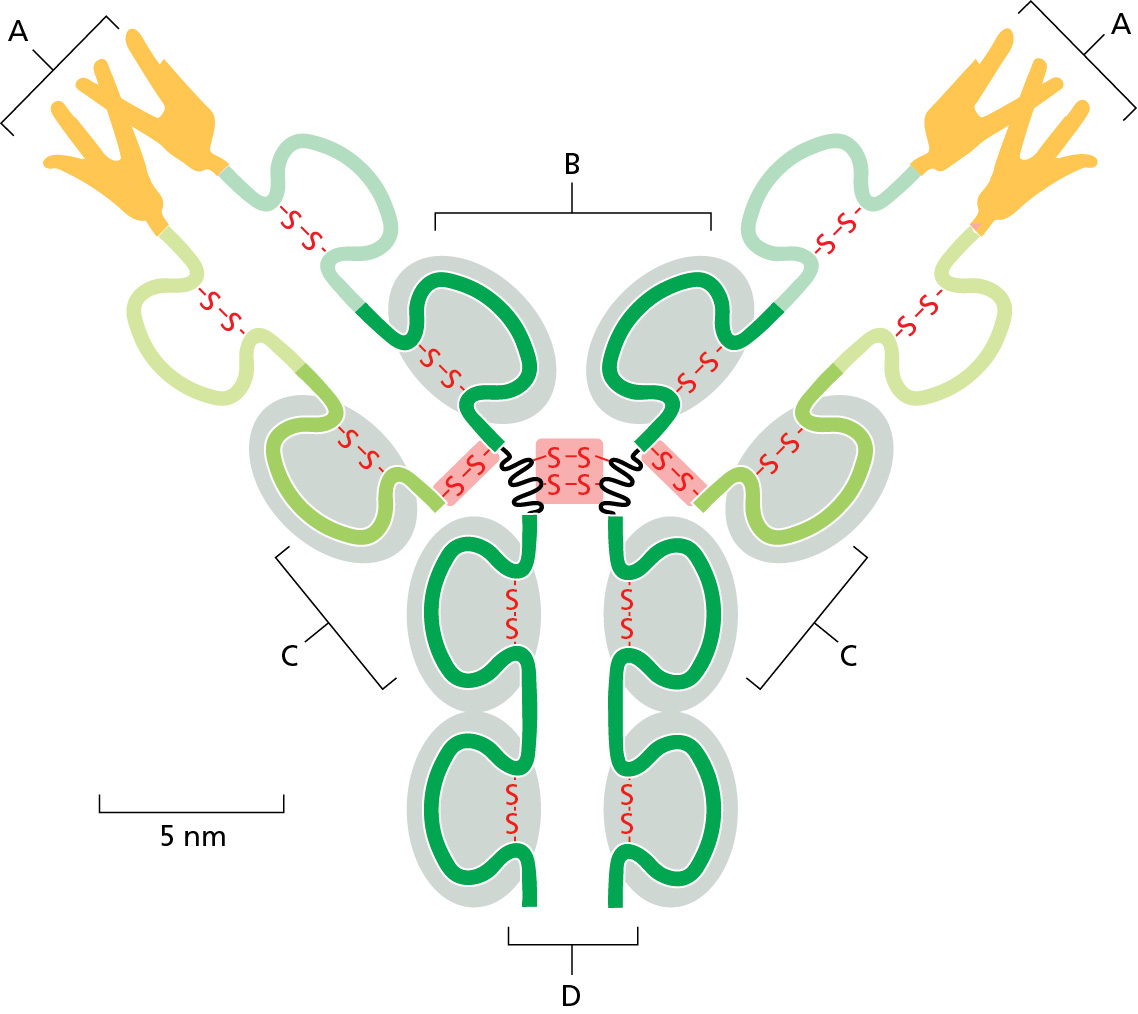
The figure shows a depiction of an antibody. Which label correctly identifies the region(s) of the antibody that contains variable amino acids for binding of a specific antigen?
A
The Michaelis constant (Km) of an enzyme is a measure of:
the binding strength of enzyme to substrate
How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
Encourage the substrates to change shape toward a transition state that favors the reaction.
Align substrates to promote a reaction between them.
Rearrange electrons in the substrates in a way that favors the reaction.
The function of the feedback inhibition of an enzymatic pathway is to:
turn off synthesis of a product when it is in abundance
When a ligand binds to an allosteric enzyme’s regulatory site, it changes the activity of that enzyme by:
inducing a conformational charge
How does phosphorylation of a protein affect its activity?
Could increase or decrease activity
How does binding of GTP to a GTP-binding protein affect its activity?
Always activates the protein
Chemical modifications like phosphorylation and acetylation of proteins occur on ____ of amino acids and can affect interaction of proteins with other cell components or structures.
side chains
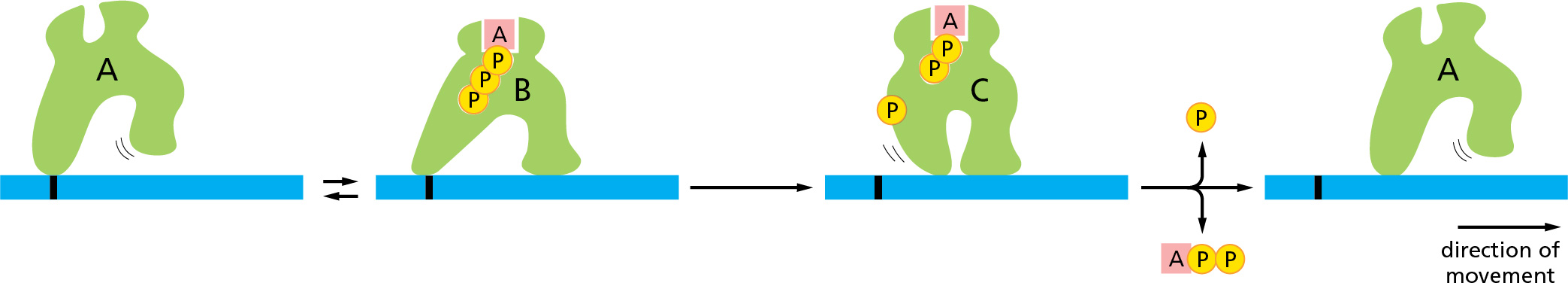
Shown is the ATP hydrolysis cycle of a motor protein. Describe the state of the motor protein in “C”.
The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP caused a conformational change in the protein
Biochemical subcompartments that form inside the nucleus are distinct from their immediate surrounding because of the:
high concentrations of interacting proteins and RNA
What method is used for separating proteins based on specific interactions with other molecules?
Affinity chromatography
What method is most suitable for determining the three-dimensional structure of an extremely large integral membrane protein complex?
Cryo-electron microscopy
What is a protein family?
Structurally related group of proteins
Which parts of amino acids are involved in a peptide bond?
amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of another
What part of an amino acid gives it its unique properties?
side chain
What is the best type of model for visualizing the surface of a protein?
space-filling
What are the two types of beta sheets?
parallel and antiparallel
What does the primary structure of a protein refer to?
the linear amino acid sequence of the protein
What determines the specificity an antibody has for its antigen?
polypeptide loops in its variable domains
For a given protein, hydrogen bonds can form between:
atoms in the polypeptide backbone
atoms of two peptide bonds
atoms in two side chains
a side chain and water
How does an allosteric inhibitor work?
It binds to a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme that makes the active site less accommodating to the substrate
How does phosphorylation control protein acitivity?
the phosphate group induces a change in the protein’s conformation
What kind of enzyme adds a phosphate group to another protein?
kinase
What kind of enzyme removes a phosphate group from a protein?
phosphatase
What is the purpose of active and regulatory sites of an enzyme?
The binding of CTP at a regulatory site on the protein causes decreased production of carbamoyl aspartate
Electrophoresis separates proteins based on:
the proteins net charge and the protein’s size
What are methods for isolating a protein of interest?
chromatography and electrophoresis
What can be used to determine the amino acid sequences of a complex mixture of different proteins?
Mass spectrometry
What is the toughest and most durable of the different types of cytoskeletal filaments?
intermediate filaments
Intermediate filaments are found in what structure?
nuclear lamina
What term describes the structure of intermediate filament monomers?
ropelike
What type of intermediate filaments are found in all animal cells?
nuclear lamins
GTP hydrolysis and whether GTP or GDP is bound to tubulin is an important mechanism to control the dynamic instability of microtubules. Certain aspects of dynamic instability can be viewed using GFP-EB1. What process is it useful for visualizing and why?
growing microtubules; EB1 binds to the GTP-tubulin cap on microtubules
How would microtubule dynamics change after adding a non-hydrolyzable analog of GTP to the cells expressing GFP tubulin?
microtubules would grow longer
What transports cargo to the cell body via backward transport?
dynein
What transports cargo to the axon terminal via outward transport?
kinesin
What does the cellular motility of sperm depend on?
microtubules and dynein
What cytoskeletal structure is the most common for providing tracks for guiding intracellular transport?
microtubles
What do microtubules resemble?
hollow tubes
Dynamic instability in microtubules stems from the intrinsic capacity of tubulin molecules to hydrolyze what?
GTP
Describe the structure of an actin filament.
a twisted chain of actin molecules
What is the name of the thin, sheetlike structures that a fibroblast regularly extends during cell crawling?
lamellipodia
Myosin-1 iis present in what kinds of cells?
all types of cells
What actin-binding proteins would be most involved in the assembly of the contractile ring?
formins
An actin filament undergoing treadmilling at the leading edge of a lamellipodium can do what?
remain the same size
What does not contain both actin and myosin?
the lamellipodium at the leading edge of a crawling cell
In a muscle fiber, what triggers sarcomeres to contract?
a sudden rise in cytosolic Ca2+
What organelle sequesters Ca2+ inside muscle fibers?
sarcoplasmic reticulum
When a muscle is stimulated to contract, what does Ca2+ bind to, and what effect does that have?
troponin, which moves the tropomyosin that otherwise blocks the interaction of actin and myosin
What cytoskeletal structures are made up of protein subunits that are fibrous?
intermediate filaments
What is an important function of intermediate filaments?
providing tensile strength to the cell and the nucleus
How do the intermediate filament proteins keratin, vimentin, and neurofilaments differ from each other?
they are different at the head and tail domains that are exposed at the surface
In terms of structure, if cytoplasmic intermediate filaments are described as ropes, nuclear lamins could be best described as _____
mesh
Microtubules extend from organizing centers in the cell. What is an example of an organizing center?
basal body of a cilium