Enzyme regulation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
enzymes
protein catalysts
increase rate of reaction
enzyme function
active site
The part of an enzyme where the chemical reaction occurs.
substrate binding
enzymes have a high affinity or high degree of specificity for a substrate
catalysis
the acceleration of a chemical reaction by a catalyst
Apoenzyme
protein portion of enzyme catalytically inactive by itself
catalytic site/ active site
site where enzyme binds substrate
coenzyme
nonprotein small organic molecule
cofactor
nonprotein metal enzymes
holoenzyme
Enzyme and nonprotein components catalically active
reduce activation energy
what does an enzyme change about a reaction?
substrate, temperature, enzyme concentration, pH
what factors affect kinetic properties of enzymes
maximum rate at which product is created with a given amount of enzyme
Vmax
concentration of substrate required to produce half Vmax
Km
higher Km=lower affinity for substrate
relationship between Km and affinity of substrate
increases when enzyme concentration increases
relationship between Vmax and enzyme concentration
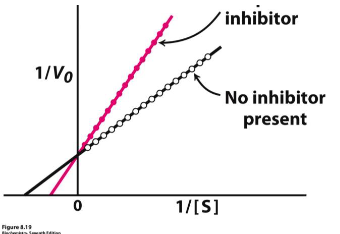
competative inhibitor
affected by concentration, competes with substrate for binding site
non-competative inhibitor
Not affected by concentration, changes shape of active site by binding elsewhere.
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that hydrolyzes bonds in starches into glucose and maltose
parotid gland (salivary gland)
where is salivary amylase mainly produced?
acute pancreatitis
what is indicated when lipase and amylase levels are elevated in serum
alanin/aspartate aminitransfeerase
catalyze transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to a-ketoglutarate
liver damage
what does elevate ALT/ AST indicate
creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
found in heart, brain, and skeletal muscles. leaks into blood when muscle tissue is damaged
stress or injury of heart or other muscles
what does elevated levels of CPK indicate?
Lupus
what disease can be associated with elevated CPK levels
galactose-1-phosphate Uridyltransferase (GALT)
This enzyme is needed for the conversion of galactose.
Galactosemia
inability to metabolize galactose due to non-functional GALT
salivary amylase
which enzyme would be useful to assess radiation damage of salivary glands
ketones in urine and elevated galactose
what is a measurable indicator of galactosemia?
Damage to Salivary Glands
what does elevated levels of amylase but not lipase indicate?
AST/ALT ratio
enzyme valuable for assessing extent of liver damage/injury
in presence of competitive inhibitor
when does Km increase
decreases when non-competative inhibitor is present
with what inhibitor does Vmax change and does it increase or decrease?
non competitive
what kind of inhibitor?
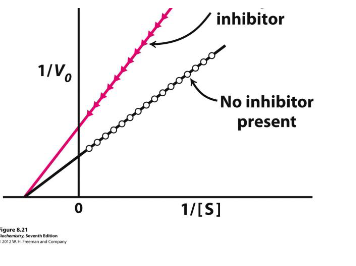
competitive inhibitor