DNA, The Molecule of Heredity (8/23-8/26)
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Robert Brown (Hint: 2)
English scientist
Discovers the nucleus in plant cells
Friedrich Miescher (Hint: 3)
German scientist
Isolates nuclei from white blood cells in pus
Found an acidic substance he called nuclein
Nuclein (Hint: 4)
Found by Friedrich Miescher
Later changed to nucleic acid
High in phosphorus
Now know part of phosphates in DNA
Walther Flemming (Hint: 6)
German scientist
Looked at newt lung cells
Discovers chromatin and chromosomes
Stained cells with aniline dyes (take up by thread like structures in nucleus)
Coined the term chromatin to describe the stained nuclear material
Described the events of mitosis
Chromatin (Hint: 3)
Coined by Walther Flemming
Found in the nucleus
Contains DNA and proteins
Chromosome
Colored Body
Nucleus (Hint: 2)
Discovered by Robert Brown
The structure in a cell that contains the chromosomes
Phoebus Aaron Levene (Hint: 3)
American scientist
Determined that DNA was made up of a large number of linked nucleotides consisting of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of the four nitrogenous bases
Proposed the tetranucleotide hypothesis
Tetranucleotide Hypothesis (Hint: 2)
Nucleotides were proposed to be in a fixed four base sequence consisting of all four bases
DNA does not have enough variation to carry information
Frederick Griffith (Hint: 4)
English microbiologist
Discovers the Transforming Principle
Was working with two strains of Streptococcus pneumonia around WWII
Known for the Griffith Experiment
R Strain (Hint: 3)
Rough colonies
Non-virulent
No capsule so they are vulnerable to the immune system

S Strain (Hint: 3)
Smooth colonies
Virulent
Have a capsule that allows them to evade the immune system
What was the question proposed in the Griffith Experiment?
Can an extract of dead bacterial cells genetically transform living cells?
Describe the 4 Steps of the Griffith Experiment
1.) Control: Living S strain injected into mouse; mouse dies
2.) Control: Living R strain injected into mouse; mouse lives
3.) S strain killed by heating and injected into mouse; mouse lives
4.) Dead S strain cells and Living R strain cells injected into mouse; mouse dies
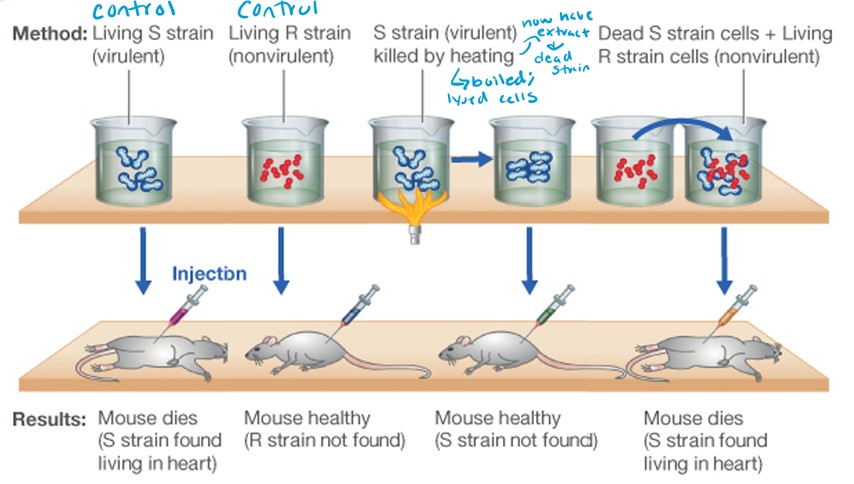
What was the conclusion of the Griffith Experiment
A non-living chemical substance in the heat killed S-strain can genetically transform the non-virulent R strain into live, virulent S strain bacteria!
Transforming Principle (Hint: 2)
Griffith did not know what the substance that caused the R strain to be transformed into S strain, but called it the transforming principle
Hypothesis: Whatever the transforming principle was it was a good candidate for the long sought genetic material
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty Experiment (Hint: 2)
Used the process of elimination to identify the transforming principle
Extract of heat killed S strain cells were treated with enzymes that destroy protein (proteases), DNA (DNase), and RNA (RNase)
Describe the 4 steps of the Avery, MacLeod and McCarty Experiment
Make an extract of heat killed S strain cells
Treat three separate tubes with the following enzymes:
Protease
RNase
DNase
Add each treated extract to R strain cells
Inject mice
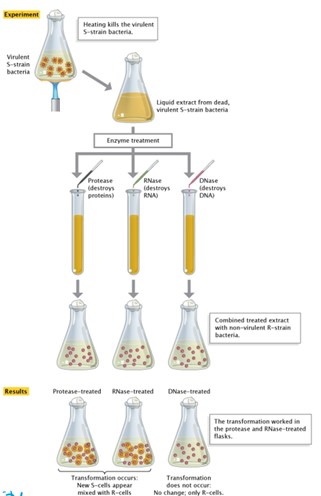
What was the result of the Avery, MacLeod and McCarty Experiment?
Protease and RNase treated extracts transform the cultures to S strain, but DNase does not
Protease
Destroys protein
DNase
Destroys DNA
RNase
Destroys RNA
Hershey-Chase Experiment (Hint: 3)
Performed by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Offered further proof of DNA as the genetic material
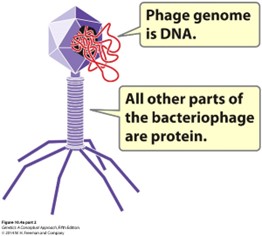
Worked with bacteriophages
Describe the 4 steps of the Hershey-Chase Experiment
1.) Grow phage in either 35S or 32P to radioactively label proteins and DNA
2.) Let phage infect E. coli cells – inject the genetic material into the cells
3.) Use a blender to knock off the viral coat (CRUCIAL STEP)
4.) Centrifuge to spin down the bacterial cells
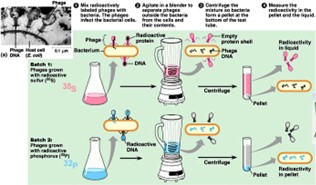
35S (Hint: 2)
Labels proteins
Stays in supernatant
32P (Hint: 2)
Labels DNA
In the pellet with bacterial cells
Bacteriophage
Virus that infect bacteria
Erwin Chargaff
Discovered Chargaff’s Parity Rule
Chargaff’s Parity Rule (Hint: 2)
In DNA, the composition of bases (ATCG) differed between organisms BUT the amount of A=T and C=G
At the time, the reasons for this was unknown, but was one of the fundamental observations that nucleotides form base pairs
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins (Hint: 6)
Pioneer in structural biology
Studied X-ray diffraction pattern of DNA
Conclusion: DNA is a double helical structure with distinctive regularities
0.34 nm between bases
3.4 nm per turn
10 bases per turn of DNA
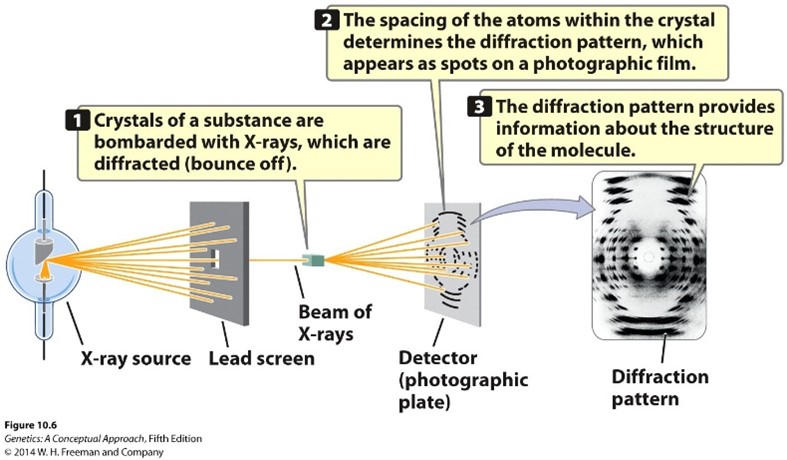
X-Ray Diffraction (Hint: 4)
X-ray crystallography
Crystals of a substance are bombarded with X-rays, which are diffracted (bounce off)
The Spacing of the atoms within the crystal determines the diffraction pattern, which appears as spots on a photographic film
The diffraction pattern provides information about the structure of the molecule
James Watson and Francis Crick (Hint: 3)
Solved the structure of DNA by using the available evidence from biochemistry and the X-ray diffraction images of Franklin
Built models until they got one that matched the available evidence
No experiments, just theory
What are the 3 incorrect theories of inheritance?
Theory of Pangenesis
Theory of Preformation
Blending Theory of Inheritance
Theory of Pangenesis (Hint: 3)
Proposed by the Greek physician Hippocrates
“Seeds” produced by all parts of the body are collected in the reproductive organs then passed to the offspring at the moment of conception
Probably the most ancient theory of inheritance
Theory of Preformation (Hint: 2)
Homunculus simply develops in the womb
Thought women’s role was to “incubate” the men (shows bias of the time)
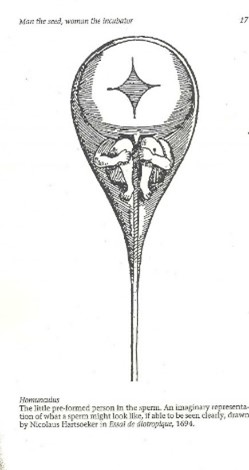
Homunculus
“little man” that early microscopists thought they saw in the sperm
Blending Theory of Inheritance
Factors that control heredity traits are malleable and can blend together from generation to generation
List the 4 characteristics of the genetic material?
Contains complex information: Must contain the information necessary to construct a complete organism
Replication: Must be copied faithfully so the information can be passed on to subsequent generations
Transmission of a trait: Must transmit specific traits to subsequent generations
Variation: Must vary in such a way that accounts for known differences in the appearance of organisms
In humans, 20% of bases in DNA are C. What percentage of the bases are expected to be T?
30%