MIMM 324 : Fundamental Virology Final
1/264
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Good luck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
265 Terms
Definition of Virus
Infectious, obligate intracellular parasite with genetic material and a protein coat
3 Classes of Viral Capsid
Helical, icosahedral, and complex
Viral Classification Nomenclature
Realm - viria
Kingdom - virea
Phylum - viricota
Class - viricetes
Order - virales
Family - viridae
Genus - virus
2 Virus Phases
Virion - inactive viral particle
Infection - multiplying inside of host
Susceptible Cells
Cells that support viral entry
Permissive Cells
Cells that support entire viral cycle
Early Phase Events
Attachment → Penetration → Uncoating → Early Gene Expression → Genome Replication
Late Phase Events
Late Gene Expression → Assembly → Release
How To Generate New Viral Strains
Reassortment of Segmented Genome in Cell Infected w/ 2+ different strains
Polarity of mRNA Strands
Positive Polarity
Polarity of Anitgenome
Opposite of ssRNA Genome, can be +/-
2 Types of RNA That Are Never Translated
-RNA and dsRNA
Baltimore Class 1
dsDNA virus
Baltimore Class 2
ssDNA virus
Baltimore Class 3
dsRNA virus, carries RDRP
Baltimore Class 4
(+)ssRNA virus, encodes RDRP
Baltimore Class 5
(-)ssRNA virus, carries RDRP
Baltimore Class 6
(+)ssRNA-RT virus, carries reverse transcriptase
Baltimore Class 7
dsDNA-RT virus, carries reverse transcriptase, gapped genome that is first repaired by host mechanisms
Most common baltimore classification in bacteria / archaea viruses
Class 1 - dsDNA
Most common baltimore classification in plants
Class 4 - (+)ssRNA
Most common baltimore classification in humans
Infected equally by Class 1 - dsDNA, Class 4 - (+)ssRNA, and Class 5 - (−)ssRNA viruses.
Chicken Eggs for Vaccine Production
Virus injected into embryonated chicken eggs, used historically for poliovirus vaccine production
Primary Cell Culture
Prepared from animal tissue, only lives 15-20 divisions
Continuous Cell Culture
Tumor tissue or immortalized cell line, replicates indefinitely but may not resemble original cell.
ex. HeLa cells
3 Ways of Making Virus in Cell Culture
Infection by viral particle
Transfection of (Infectious) viral genome, can never be (-)ssRNA
Using an infectious DNA clone, dsDNA plasmid version
Cytopathic Effects
Morphological changes in infected cells.
ex. Lysis, syncytium (fusion), rounding of cells, detachment, and inclusion bodies
How to Find Life Cycle Time
prepare pure viral stock
determine its viral titre
infect cells at appropriate MOI
Perform one step growth cruve
Plaque
Area of lysed cells. Each virion is capable of infecting one cell, lysing it, and releasing new virions to infect neighbouring cells.
Virus Titre
(#plaques / volume plated) * dilution factor
Multiplicity of Infection
Average number of virions added per cell during infection
Cryo Electron Microscopy
Freezing viral particles in water (vitrification), imaging, 3-D and reconstruction of images. Can resolve down to near atomic resolution
Capsid
Protein shell surrounding viral genome
Nucleocapsid
Nucleic acid - protein complex within the virion, normally in enveloped viruses.
Envelope
Host-derived lipid bilayer surrounding the capsid, can contain glycoproteins.
Self Assembly
Most capsid proteins are capable of self-assembly. Each capsid must make identical contacts with its neighbours. Bonding contacts are usually low affinity and non-covalent
Capsid Symmetry
helical - for rod shaped
icosahdral - roughly spherical
platonic polyhedral - spherical or platonic solids (cube, dodecahedral, etc)
Helical Capsids
Usually flexible, rod shaped. Package ssRNA
ex. Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Icosahedral Capsids
Rigid circular shells that package ds/ss DNA/RNA. Made of 60 IAUs.
Icosahedral Asymmetric Unit (IAU)
The smallest repeating unit of an icosahedral capsid from which the complete structure can be built with 5:3:2 symmetry.
Triangulation Number
The number of capsid proteins in the IAU. Smallest capsids have 1 protein per capsomere, so T=1
Quasiequavalent Interactions
head-to-head and tail-to-tail interactions all capsid proteins engage in
Complex Capsids
Capsids that combine different types of symmetry
ex. Bacteriophage: icosahedral head and helical tail
Viral Envelope Glycoproteins
Proteins located on the surface of viral envelopes that facilitate attachment and entry into host cells. Have TM domain, ectodomain, and internal domain.
3 Modes of Interaction Between Envelope and Nucleocapsid
direct
via matrix protein
via multiple proteins
General Viral Life Cycle
Attachment
Penetration
Uncoating
Early Gene Expression
Replication
Late Gene Expression
Assembly
Release
Viral Entry
Steps up to and including transport of viral genome to site of transcription and replication.
Attachment
Virus reversibly binds to attachment factors via non-specific interactions on cell surface then binds irreversibly to specific receptor(s).
Naked vs. Enveloped Virus Receptor Binding
Naked uses capsid surface or protrusions. Enveloped use TM glycoproteins.
Class 1 Glycoproteins
Forms trimeric spikes at the surface of enveloped viruses. Synthesized as precursor that is processed by host proteases into receptor binding subunit and membrane fusion subunit. Largely a-helical.
Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis
Virus-receptor complex is taken up by a clathrin-coated pit that is pinched off the membrane by dynamin, a GTPase. It then fuses with an early endosome
Caveolin-Mediated Endocytosis
A dynamin- and caveolin-dependent pathway is used by some viruses, like polyomaviruses (SV40). Virions reach the ER via the caveosome, a pH-neutral endosomal compartmen
Macropinocytosis
Virus incorporates phosphatidylserine phospholipids to mimic apoptotic bodies. Allows take-up by macrophages. Used by Dengue and Ebola virus.
Furin
Golgi protease used to cleave glycoprotein subunits, priming them.
Class 1 Mediated Membrane Fusion
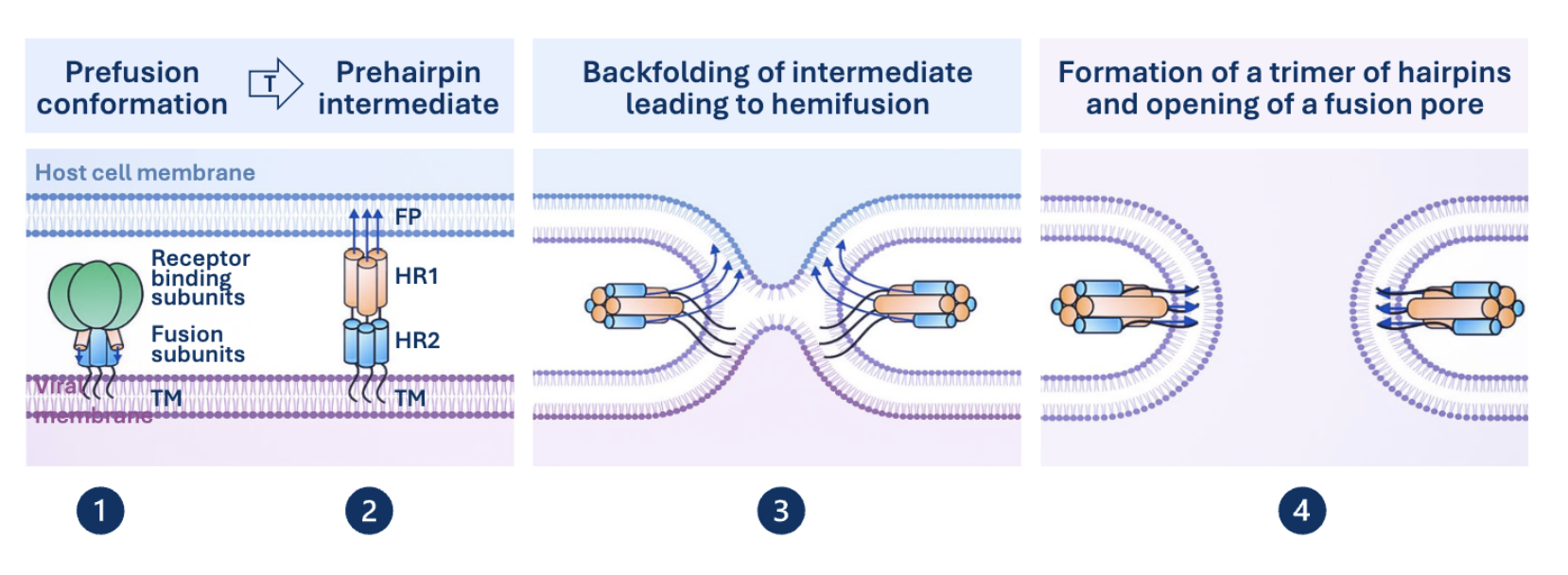
Prehairpin Intermediate
Helical coil that tethers viral membrane and host membrane together via TM anchor domain and fusion peptide respectively. Triggered by receptor binding or low pH.
Class 2 Glycoproteins
Oriented parallel to the surface of the virion, rich in B-strands. Low pH triggers insertion of loops into endosome membrane. Requires priming by cleavage of an associated protein, not the fusion protein itself.
Class 2 Mediated Membrane Fusion
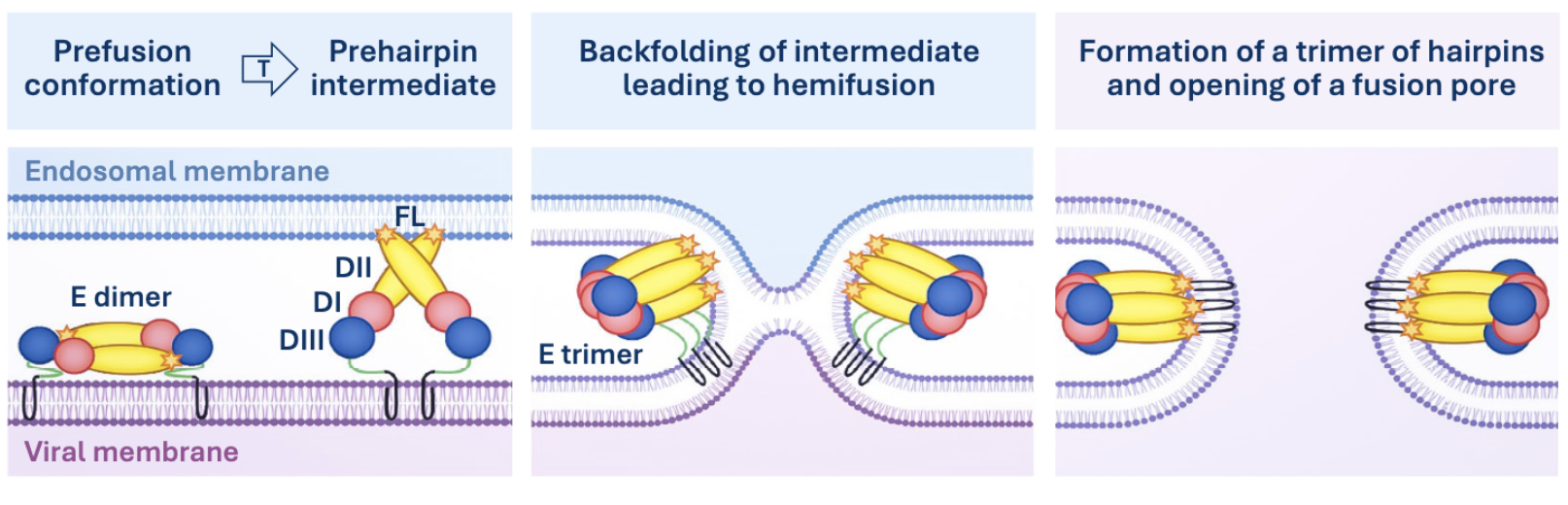
Membrane Perturbation
How naked viruses enter the cell. Either disrupt the membrane, use a membrane penetrating peptide, form a pore, or lipases.
Pore Formation
Ex. poliovirus
release of pocket factor, lipid bound protein that stabilizes the virus
formation of VP4 hexameric pores in endosome membrane
insertion of VP1 N-terminal peptide into membrane as anchor
Uncoating
Occurs concomitantly with membrane crossing, capsid is either degraded or removed to release viral genome. Can occur in cytoplasm, at nuclear membrane, or in nucleus.
Viral Nucleus Entry
Can happen when the nuclear membrane is degraded during division, by entering through the nuclear pore complex, or by disruption of nuclear membrane.
2 Modes of RNA depended RNA Synthesis
De novo initiation - without primer
Primer depended initiation
Viral RdRP
Error prone intentionally to promote genetic diversity. 2 Mg2+ ions catalyze formation of phosphodiester bond. Carried in class 3 and 5, encoded in class 4.
(+)ssRNA Protein Priming
ex. poliovirus
Uses 5’ VPg protein to prime synthesis
(-)ssRNA Protein Priming
Viral nucleoprotein (N) promotes full length synthesis by acting as an anti-termination factor. Coats viral segments to form viral ribonucleoprotein complexes.
Cap Snatching
Viral RdRP has nuclease activity, steals 10-20 nucleotides from host mRNA 5’ caps. Cap primers used to make subgenomic viral mRNAs.
Ambisense RNA Virus
Has both (+) and (-) polarity in its genome.
ex. arenavirus, lassa virus
Lassa Virus Transcription
Transcription termination signal in IGR prevents synthesis of long mRNAs that may bind to each other and trigger host antiviral response
dsRNA Transcription
Transcription and Replication occur in viral subparticle to prevent host antiviral response.
U-Stretches
Template RNA may contain “slippery” stretches of U residues in intergenic region that RdRP to slip and produce long segments of A. Functions as a poly A tail.
IRES
Non-canonical, cap dependent initiation. Uses an Internal Ribosome Entry Site in the 5’ UTR to allow internal initiation based on secondary structure.
Ribosome Shunting
Ribosomes bypass parts of the 5’ UTR to reach start codon or bypass stable secondary elements. Favored by shunting elements such as loops or proteins.
Leaky Scanning
Some, but not all, ribosomes fail to recognize the first start codon and keep going until they find a new one.
Cricket Mosaic Virus Initiation
CrPV IRES mimics met-initiator tRNA. Can recruit 80s ribosome without eIFs and Met-tRNA. Turnip yellow mosaic virus works similarly.
Reinitiation
Fraction of ribosomes that translated an upstream ORF will reinitiate translation at a downstream start codon.
Ribosomal Frameshifting
Ribosome slips by 1 nucleotide, misses stop codon, and continues in a different reading frame.
Readthrough
Ribosome reads through a stop codon but doesn’t stop elongating.
Host Translational Repression
Virus inhibits the host's transcription processes, preventing the expression of host genes.
ex. poliovirus 2A protease cleaves eIF4G, stopping cap dependent initiation.
Factories / Inclusions
Site within infected cells where viral replication and assembly occurs, often containing viral components and host chaperones.
Packaging Signals
Specific DNA sequence or RNA secondary structure needed for selective packaging in sequential assembly
Packaging of Large dsDNA Genomes
Sequential packaging. Capsid formed, and scaffolding proteins bind. Terminases open the cancatimer to pump dsDNA in.
Segmented RNA Packaging
Packaged as a complex of 7 vRNP around central vRNP
Retroviral (+) RNA Packaging
ex. HIV
Psi packaging signals bind GAG precursor which signals to stem loops to interact with kissing loop sequence to form dimer initiation site. Packages in capsid.
Envelope Acquisition
Occurs after assembly of internal structures. Virion takes envelope from nuclear envelope, golgi, ER, or plasma membrane.
Retrovirus Budding
ESCRT recruited to GAG via late domain, used to pinch off bud, releases viral particle. Loss of late domain → failure to release infectious particle.
HIV Maturation
Occurs after budding, involves protease activation to cleave GAG and Gag Pol precursor proteins in individual compartments.
Dengue Virus Maturation
Occurs as virion moves from ER through the TGN, pH induces maturation via pH dependent cleavage
Naked Virus Release
Lysis from apoptosis, necropoptosis, or pyropoptosis. Viral proteins can induce rupture of cell membranes (lytic enzymes, vipoporins)
Non Lytic release from vesicles, exosomes, and autophagic vesicles
Orthomyoxoviridae
(-)ssRNA virus family. Contains influenzavirus.
Influenza Virion
Enveloped, rounded (sometime filamentous) ~100nm particle. Has segmented linear genome encapsulated by nucleoproteins (vRNP)
Influenza Genome
13.5kb linear segmented. Produces 12-14 proteins.
Influenza Receptors
Neuraminic/Sialic Acids (Sugars)
Coronavirus
(+)ssRNA family. Contains Sars-Cov-2
Coronavirus Virion
Roughly spherical, moderately pleomorphic. ~118-136 nm diameter, spike proteins give crown like appearance
Coronavirus Genome
30kb w/ 5’ cap and 3’ polyA tail. 2/3 is nonstructural proteins, other 1/3 is structural and accessory.
Coronavirus Capping
Encodes own RNA capping mechanism, happens in cytoplasm
Coronavirus Entry Pathways
Early - direct membrane fusion, S2’ cuts at cell surface, major
Late - endosomal fusion in late endosome, minor
Coronavirus Replication Organelles
Double Membrane Vesicles (DMVs), prevents host antiviral response. Membrane taken from ER
Coronavirus NSPs
Responsible for DMV formation, capping proteins, and replication/transcription complex core. Derived from polyprotein precursors