Classification and Oxidation of Alcohols
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What 3 categories can alcohols be classified into?
Primary alcohols
Secondary alcohols
Tertiary alcohols
What is a primary alcohol?
In primary alcohols, the carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is bonded to one other carbon atom.
Example: ethanol, propan-1-ol.
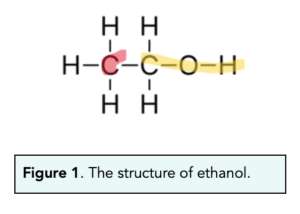
State one alcohol which is considered to be a primary alcohol despite not fitting the definition for one.
Methanol.
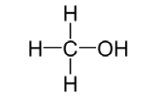
What is a secondary alcohol?
In secondary alcohols, the carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Example: propan-2-ol.
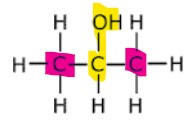
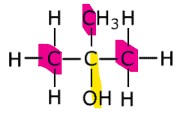
What is a tertiary alcohol?
In tertiary alcohols, the carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
Example: 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
State one reaction that alcohols undergo.
Oxidation.
What does oxidation mean in organic chemistry?
A carbon atom gaining a bond to an oxygen atom.
A carbon atom losing a bond to a hydrogen atom.
How are alcohols oxidised?
Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) is the oxidising agent used and the alcohol is heated.
What is the product formed when an alcohol is oxidised?
The product depends on whether the alcohol is primary, secondary or tertiary.
What product is formed when a primary alcohol is oxidised?
Primary alcohols can be oxidised to an aldehyde, then to a carboxylic acid.
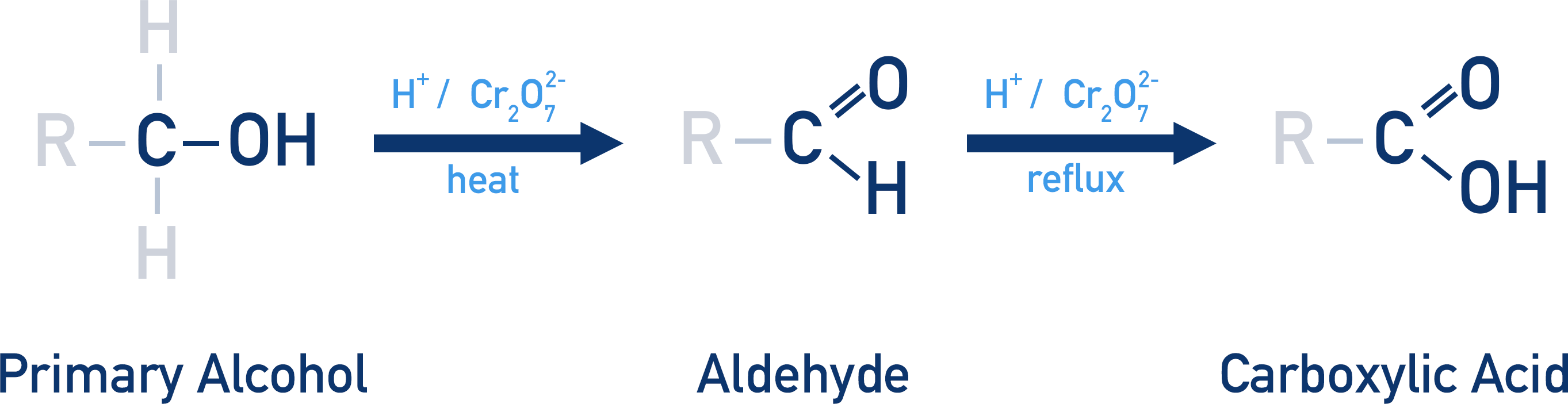
How do you isolate the aldehyde formed when a primary alcohol is oxidised?
To isolate the aldehyde, the products must be distilled from the reaction mixture.
How do you ensure a carboxylic acid is formed when a primary alcohol is oxidised?
If a carboxylic acid is desired, the mixture must be heated under reflux conditions.
Secondary alcohols can be oxidised to form…
Ketones.
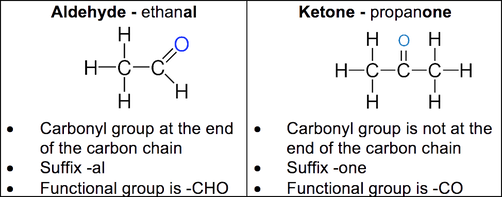
Describe the difference between an aldehyde and a ketone.
Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl functional group, C=O- they are known as carbonyls.
The difference between aldehydes and ketones is the groups bonded to the carbon of the carbonyl group.
The carbonyl group in an aldehyde is always situated at the end of the chain.
The carbonyl group in a ketone is always situated in the middle of the chain.
When a tertiary alcohol is oxidised, what happens?
No reaction occurs- tertiary alcohol CANNOT be oxidised.
What colour change is observed when potassium dichromate (VI) is used as an oxidising agent?
Orange to green.
Name one other oxidising agent that can be used to oxidise alcohols..
Potassium manganate- the colour change observed is purple to colourless.