Protozoans
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANS 389C
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Traditionally, how many Phyla were in Kingdom Protozoa? How many are there now?
traditionally 4 phyla, now 13 phyla
List the phyla of Kingdom Protozoa
- Euglenzoa
- Metamonada
- Apicomplexa
what does it mean when an organism is unicellular?
no matter how complex their bodies may be, all different structures are contained in a single cell
(true/false) protozoa are eukaryotes
true
what does it mean if Protozoa are eukaryotes?
- they’re DNA is compartmentalized within a nucleus
- different from bacteria (which are prokaryotic)
what internal structures do Protozoa have?
- nucleus
- endoplasmic reticulum
- mitochondria
- golgi body
- lysosomes
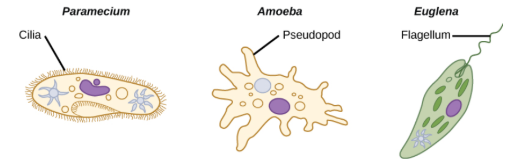
what structures do Protozoans have that allow them to move?
- flagellum (single or multiple)
— whip-like tail for propulsion attached to basal body
— also, may propel and undulating membrane
- cilia
— fine short hairs, each arising from a basal body that beat in unison
- pseudopodia
— prolongation of cytoplasm
endocytosis
the cell membrane gradually enveloping the droplet or object which has become adherent to its outer surface
penocytosis
cell drinking; liquids or dissolved substances
phagocytosis
cell eating; large particles like bacteria or debris
particles are carried into the cell and digested by ________
lysosomes
undigested material is _________ from the cell
extruded
what do some Protozoa have to take in food?
“cell mouth” (Cytosome)
list the two stages of development in protozoa
- sporozoite
- trophozoite
sporozoite
- the infective stage of some protozoa
- this is the stage where it enters the host
trophozoite
- stage of protozoa while in host
- active feeding and growth until protozoal cell division commences
most protozoa go through asexual reproduction. list the different types of asexual reproduction.
- binary fission
- budding
- merogony
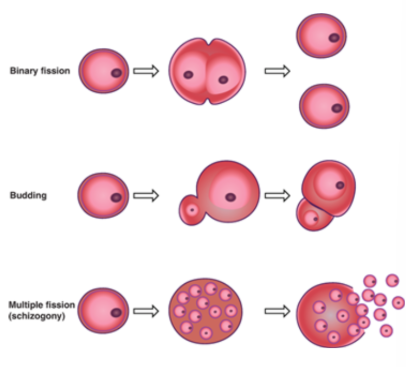
binary fission
one cell splits into 2 identical cells
budding
small new cell beds off parent
Merogony (Schizogony)
- Trophozoite grows to large size while nucleus divides repeatedly resulting in a Meront (Schizont)
- the Meront contains many separate organisms called Merozoites
- the Meront eventually ruptures, liberating individual Merozoites