AP Biology Enzymes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Metabolism
the totality of an organisms chemical reactions that result from interactions between molecules within the cell
metabolic pathway
a sequence of chemical reactions undergone by a compound in a living organism, start with substrate end with product
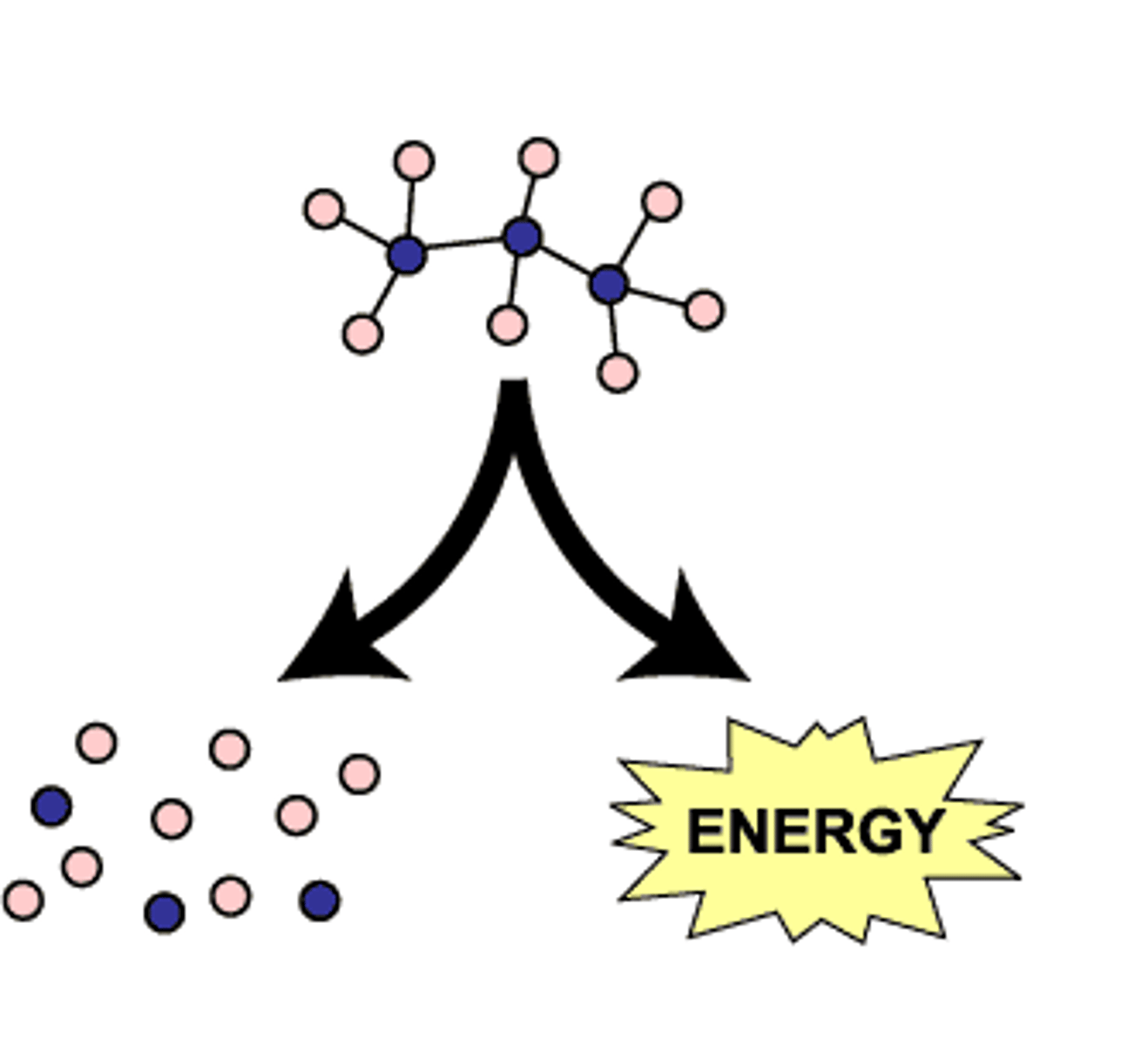
catabolic
breaking a complex molecule down into its simpler parts, releasing energy. ie. cellular respiration
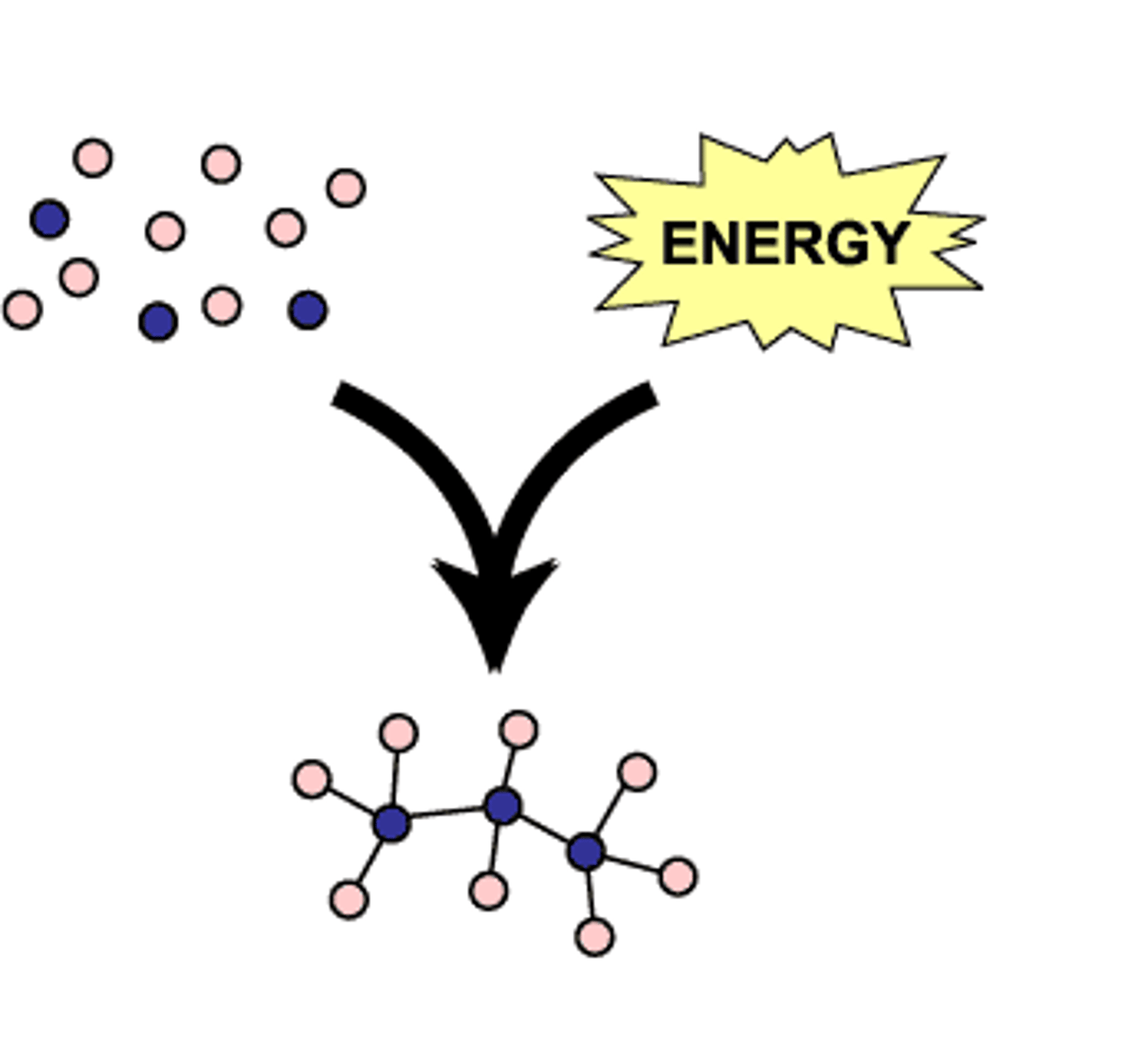
anabolic
using energy to build complex molecules from simpler molecules. ie. protein synthesis
Bioenergetics
the study of how organisms manage their energy resources
energy
capacity to cause change, do work
heat(thermal energy)
kinetic energy associated with random movement of molecules
chemical energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction, energy within bonds
exergonic reaction
a reaction with a net release of free energy, negative free energy, spontaneous

endergonic reaction
a reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings, non-spontaneous, positive free energy
catalyst
a chemical agent that speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction
enzymes
a catalytic protein, speeds up metabolic reactions by lowering activation energy, very specific, reusable, unchanged by reaction
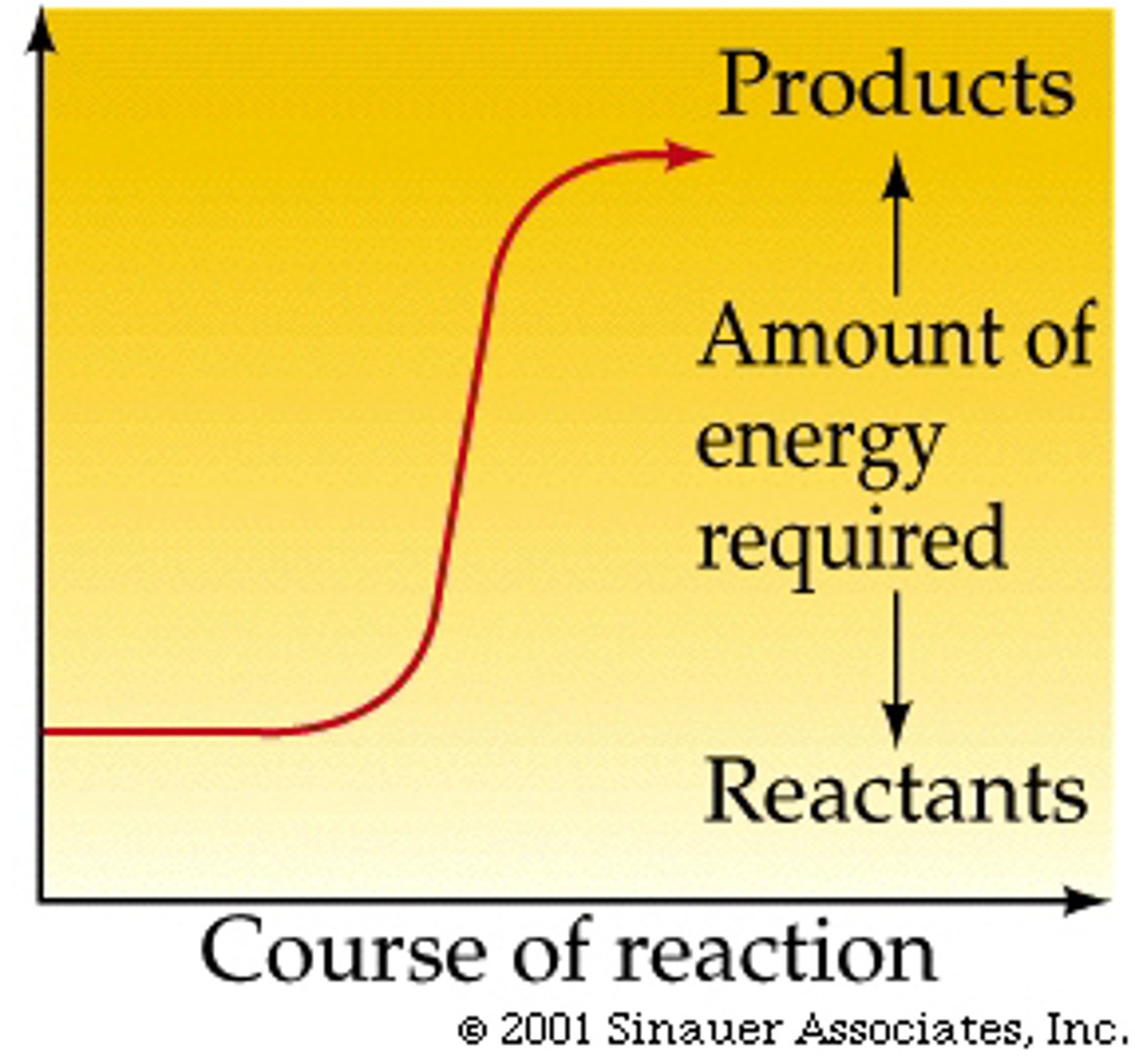
activation energy
initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction, free energy for activating reaction, given off by heat
induced fit
brings the chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the reaction, makes the enzyme more effective
cooperativity
another type of allosteric activation, binds to one active site but locks ALL active sites open, allowing products to be constantly produced
Substrate
the REACTANT that an enzyme acts on
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
enzyme and substrate
Active Site
region on the enzyme where substrate binds
Hydrogen and Ionic Bonds
substrate held in active site by WEAK interactions
Lock and Key
active site on enzyme fits substrate exactly
hydrolysis
The addition of water to a polymer or dimer to split it into monomers.
cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers ex. zinc, iron, copper
coenzymes
organic enzyme helpers ex. vitamens
Denature
above a certain temp activity declines, protein unwinds
Renature
coils it back to normal after temp gets too high and the activity decreased
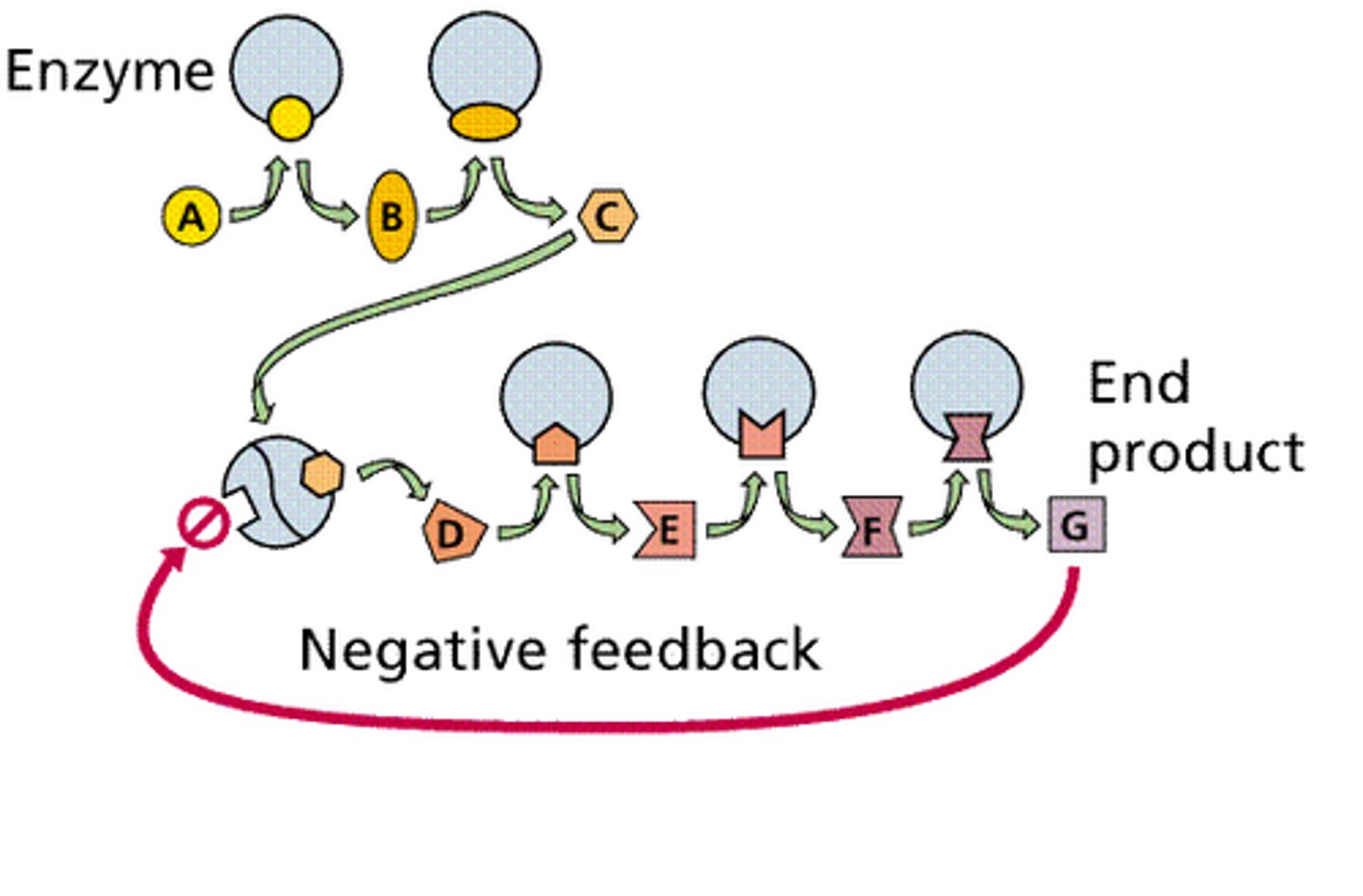
Feedback inhibition
end product of a pathway that continues to produce product (positive) and then turns off (negative)
Allosteric Regulation
can accelerate or inhibit production and enzyme activity by attaching to another part of the protein. this changes the shape of the active site which inhibits substrates from bonding and producing more products
Activator
one of the allosteric regulators, stabilizes and keeps active site open for production, wedges open
Inhibitor
a substance that interferes with the action of a catalyst
Competitive Inhibitor
inhibitor that mimics original substrate by blocking the original substrate
Noncompetetitive Inhibitor
bind to another part of enzyme to change shape and block substrate from producing
Factors that affect enzymatic rate of reaction
environment, pH, temp, salinity, chemicals that infuse enzyme, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration
V-max
Maximum rate of reaction
free energy
energy available to do work